Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GPRS Basics
Uploaded by
api-3842047Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GPRS Basics
Uploaded by
api-3842047Copyright:
Available Formats
GPRS
GPRS – General Packet
Radio Service
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
Course Objectives
Understand and describe the basic of GPRS
data transmission.
Describe how a GPRS phone works under
GPRS network.
Name the requirements needed for GPRS
services.
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – Content
• GSM-Evolution
• Voice
• Data
• Development
• Data Rates and Speed
• Circuit vs. Packet Switched Network
• Higher Data Transfer Rates through
• New coding schemes
• Timeslot packaging (Multislot Classes)
• Mobile Classes
• Packet switched Data Transfer ( Comparing to HSCSD)
• Using GPRS services
• How GPRS phone works
• How data sent/received over GPRS
• Benefits of GPRS
• GPRS FAQs
• GPRS Q&A
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GSM - Voice Communication
Customers need to verbally communicate ...
Speech
Basic service of GSM network or any telephone
network system.
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GSM - Data Communication
Basic Service
- Short Message Services (SMS)
Popularity of INTERNET and EMAIL Access
- Large amount of data transmission
- Transmission speed critical
Limitation of 9600kbps on GSM
GPRS - General Packet Radio Service
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
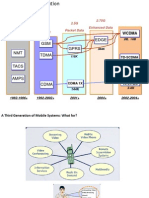
GSM – Development
Content
t i bility
a
Co mp
r d
nwa Phase 2+
Dow
UMTS
• New Services
• High Data Rates
• Closed User Groups
Phase 2 Phase 2
ISDN-Features ISDN-Features
• CLIP • CLIP
• Call Waiting a.s.o. • Call Waiting a.s.o.
Phase 1 Phase 1 Phase 1
Speech + Speech + Speech +
Data Data Data
1991 1995 1997 Year
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
DATA Rates and Speed
Speed EDGE
• Packed switched
• Modified modulation technique: 8 PSK
• Bundling of up to 8 physical channels
• up to 345,6 kbps (ECSD)
• up to 473,6 kbps (EGPRS)
GPRS
• Packed switched
• Bundling of up to 8 physical channels
• Channel coding: up to 21,4kbps >>max. 171,2kbps
HSCSD
• Circuit switched Depends on
• Bundling of up to 8 physical channels coding scheme
• Channel coding: up to 14,4kbps >>max. 115,2kbps
GSM
• Circuit switched Reduced
• one physical channel
• 0,3 to 9.6 kbps error protection Time
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
DATA Rates and Speed
GSM
Traffic channel Information Error protection Time slots Total
>Voice (full rate) 13,0 kbit/ 9,8 kbit/s max. 1 22,8 kbit/s
>Data 2,4 kbit/s 20,4 kbit/s max. 1
4,8 kbit/s 18,0 kbit/s “
9,6 kbit/s 13,2 kbit/s “
HSCSD
Traffic channel Information Error protection Time slots Total
>Voice (full rate) 13,0 kbit/ 9,8 kbit/s max. 1 22,8 kbit/s
>Data 14,4 kbit/s 8,4 kbit/s up to 8
max. Data 115,2 kbit/s
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
DATA Rates and Speed
GPRS
Time slots Time slots Time slots
1 2 8
CS- 1 9,05 kbit/s 18,1 kbit/s 72,4 kbit/s
CS- 2 13,4 kbit/s 26,8 kbit/s 107,2 kbit/s
CS- 3 15,6 kbit/s 31,2 kbit/s 124,8 kbit/s
CS- 4 21,4 kbit/s 42,8 kbit/s 171,2 kbit/s
EDGE (8 PSK modulation)
Time slots Time slots Time slots
1 2 8
ECSD 43,2 kbit/s 86,4 kbit/s 345,6 kbit/s
EGPRS 59,2 kbit/s 118,4 kbit/s 473,6 kbit/s
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – General Packet Radio Service
• New Standard in GSM world allowing high data
transfer rate for data communication
• Achieve by splitting data into small packets size
• “Always online” concept for instant access to data
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – Circuit vs. Packet Switched
Circuit switched vs. Packet switched networks
“Circuit switched Network”
There is a fixed allocation from frequency channel and timeslot during the complete
duration of connection.
“Packed switched Network”
There is no fixed allocation from frequency channel and timeslots within a 52
Multiframe.
Only within a “Radio-Block”
The information transfer is done via packets. Every packet contains the receiver
information.
The frequency channel and the time slots are only engaged if the capacity is required.
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – Circuit vs. Packet Switched
“Circuit switched Network”
Fixed allocation from frequency channel and timeslot during connection.
Downlink
5 6 7 0 1 2 33 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5
Uplink 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – Circuit vs. Packet Switched
“Packed switched Network”
No fixed allocation of frequency channel and timeslots. Only within a “Radio-Block”
Downlink
0-5 6 7 0-5 6 7 0-5 6 7 0-5 6 7 0-4 5 6 7 0-4 5 6 7 0-4 5 6 7
Uplink
0-6 7 0-6 7 0-6 7 0-6 7 0-5 6 7 0-5 6 7 0-5 6 7 0-5 6 7
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – Capacities and Parameters
Capacity on demand: Provides Circuit Switched Channels
and Packet Switched Channels in a dynamic manner
Signalling: BCCH + FCCH + SCH + CCCH
Example: 1 Slot for signalling
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 4 Slots circuit switched
3 Slots packed switched
Circuit switched slots Packet switched channels
PDCH
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – Coding Schemes
Higher Data Transfer through new Coding Scheme
GPRS
(Coding Scheme) 1 2 3 4
Data rate per 9,05 13,4 15,6
21,4 kbps
Timeslot kbps kbps kbps
Data rate with 3 RX 27,15 40,2 46,8
Timeslots 64,2 kbps
kbps kbps kbps
(MS Class 4)
Data rate with 4 RX
36,2 53,6 62,4
Timeslots 85,6 kbps
kbps kbps kbps
(MS Class 8)
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – Multislot Classes
M S M ultislot Classes
Multislot cla ss Ma x imum no. of slots
RX TX SUM
1 1 1 2
2 2 1 3
3 2 2 3
4 3 1 4
5 2 2 4
6 3 2 4
7 3 3 4
8 4 1 5
9 3 2 5
10 4 2 5
11 4 3 5
12 4 4 5
13 3 3 6
14 4 4 8
15 5 5 10
16 6 6 12
17 7 7 14
18 8 8 16
19 6 2 8
20 6 3 9
21 6 4 10
22 6 4 10
23 6 6 12
24 8 2 10
25 8 3 11
Multislot - classes of MS
26 8 4 12 in GPRS network
27 8 4 12
28 8 6 14
29 8 8 16
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – Multislot Classes
Multislot Classes
Multislot Classes RX TX Sum
1 1 1 2
2 2 1 3
3 2 2 4
4 3 1 4 Step1
5 2 2 4
6 3 2 4
7 3 3 4
8 4 1 5 Step2/Step3
9 3 2 5
10 4 2 5
... ... ... ...
... ... ... ...
29 8 8 16
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – Packet Data Transfer
Data transfer of split data packets via Internet server
CSD / HSCD
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – Comparison to HSCSD
Comparing: HSCSD - GPRS
HSCSD GPRS
Transmission Line-oriented Packet-oriented
Speed Up to 38,4 kbps Up to 53,6 kbps
( 05 / 2001 )
Rating Connected time Amount of data
Applications Transmission of Dialogue-
huge data oriented
amount applications
Examples Data transfer, WAP, E-Mail,
transmission of Information
pictures desk /
Information
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – Using GPRS Services
What you need in order to use GPRS Services?
• Mobile phone that supports GPRS e.g. G5200 or G7020
• Subscription to GPRS services
• GPRS services must be enabled. Auto access to GPRS may be
allowed by some network, others will require a specific opt-in
• Destination to send or receive information through GPRS; e.g.
Internet address, since GPRS is designed to make the Internet
fully available to mobile users
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – How GPRS Phone Works?
• The Black Box indicates the upgrade
from the existing GSM networks
• The Black Box consists of the
following components:
GGSN (Gateway GPRS Support Node)
SGSN (Server GPRS Support Node)
PCU (Packet Control Unit)
Source from T3 magazine (June 2001)
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – How GPRS Phone Works?
Network Architecture and differences
ERI VLR HLR
PSTN
BTS MSC GMSC ISDN
BSC PCU
Internet
SGSN GGSN IP/X25
Additional GPRS Network-Components
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – How GPRS Phone Works?
Packet Control Unit
PCU
> Channel access control
> Access request management
> Control and management of TCH, PCL
> Structuring of the PDCH
Serving GPRS Support Node
SGSN
> Control of MS position
> Coding of data and authentification
> Diverting of Data packets
> Mobility management
Gateway GPRS Support Node
GGSN
> Interface between PLMN and Packet Data Network (e.g. Internet)
> Providing “Screening Filters” (not wanted information)
> Can act as a firewall
> Data / Packet counting (for charging purpose)
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – How GPRS Phone Works?
Network and Cell Selection
M
GS
2.
d
Rea
St
ep:
ep
t
1. S
:R
ea
GSM
d
G
PR
System
S
Information
Pointer to GPRS GPRS
System
New Information
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – How GPRS Phone Works?
Operation Modes of a MS in GSM/GPRS-Service
Initialisation
GPRS Cell found
Cell Selection
GPRS IDLE State
GSM attach GPRS attach GPRS detach
GSM IDLE Mode GPRS READY State
READY Timer expiry PDU transmission
GSM DEDICATED Mode GPRS STANDBY State
GSM States GPRS States
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – How GPRS Phone Works?
Mobility Management States
• MS not GPRS attached
MS in IDLE State • Cell Selection
GPRS GPRS
attach detach
• MS is GPRS attached
MS in STANDBY State • Perform Routing area Update
• Listen to Paging Channels
PDU Ready timer
Transmit Expires
• MS transmit/receives data
• Perform Cell area update
MS in READY State • read signalling to keep communication established
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – How GPRS Phone Works?
GPRS Attachment Procedure
An attach is performed, when a mobile indicates its presence to the network for the purpose
of using the services provided by that network.
Depending on the class of mobile, this may be an IMSI attach for GSM circuit switched (CS)
services, a GPRS attach, or a combined IMSI/GPRS attach.
A GPRS attach is made to the SGSN and includes information like:
• The mobile‘s identification (IMSI or Packet -TMSI)
• the mobile‘s position - indicated by the Routing Area Identification (RAI)
The opposite of an attach is the so called detach.
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – How GPRS Phone Works?
Routing Area
LAI = Location Area Identity
Mobile has to do a location update,
if the mobile station leaves the location area
RAI = Routing Area Identity
Mobile has to do a routing area update,
if the mobile station leaves the routing area
!!Important for paging!!!
CI = Cell Identity
If mobile station is in ready mode (receiving
or transmitting data), the MS has to report a
change to an other cell to the network.
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – Data Sent / Received
• Illustrated under Class 4 conditions
• Each timeslot is highly dependent
on the coding scheme(CS) used
e.g. CS-4 (21.4kbps)
• After each download, connection
to network will become virtual
(always on-line, data can be
downloaded anytime)
Source from T3 magazine (June 2001)
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – Benefits
• Improves the Utilisation of Radio Resources
• Higher Data capacity
• Data rates from 21.4kbps using one Timeslot
and up to 171.2kbps (8 Timeslot)
• Transmit and Receive allocated separately
• Shorter access time ( below 1 second )
• Consumption/Volume based billing
Digital Dream Service
GPRS
GPRS – Frequently Asked Questions
Do I have to apply for GPRS at my network provider?
Yes, you always have to apply for a SIM card with GPRS enabled.
I do not get the highest data rate capacity !
The data transfer rates depend on the radio cell and
the network workload.
Please contact your network provider.
Will the GPRS mobile be an integration in an existing
mobile or a new mobile phone?
It will be a new mobile phone. The current mobile phones cannot
support this new technology.
Digital Dream Service
You might also like
- Introduction To GprsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To GprsANUPAM_HOLLOWNo ratings yet
- Week 7 GSM Enhancements: - HSCSD - GprsDocument21 pagesWeek 7 GSM Enhancements: - HSCSD - GprsConor O 'ReganNo ratings yet
- GPRS & EDGEDocument37 pagesGPRS & EDGEEr AyushNo ratings yet
- GenerationsDocument22 pagesGenerationstahura.nabi07No ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document30 pagesLecture 9TalalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument40 pagesLecture 1 IntroductionSadia AltafNo ratings yet
- Protocol Support ManagementDocument1 pageProtocol Support ManagementPedroEspañaNo ratings yet
- General Packet Oriented Radio ServiceDocument29 pagesGeneral Packet Oriented Radio ServiceHusnainNo ratings yet
- Broad BandDocument16 pagesBroad BandTasmeen HussainNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Subhash Chandra IV Year (B.tech, VIII Sem), CSEDocument24 pagesPresented By: Subhash Chandra IV Year (B.tech, VIII Sem), CSEvaibhavgupta160No ratings yet
- GSM Gprs Edge: 2G Digital 2.5G Packet Data 2.75G Enhanced DataDocument17 pagesGSM Gprs Edge: 2G Digital 2.5G Packet Data 2.75G Enhanced Datashikhar15No ratings yet
- 2G-3G Overview: Technologies and EvolutionDocument19 pages2G-3G Overview: Technologies and EvolutionVepin VydulaNo ratings yet
- Copy (2) of GPRS2Document14 pagesCopy (2) of GPRS2saha_debajyoti0No ratings yet
- 21 Final 3GDocument41 pages21 Final 3GSubhi RosdianNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Wireless Data Communications TechnologiesDocument63 pagesAn Overview of Wireless Data Communications TechnologiesnahuNo ratings yet
- 04 Air Interface Perspective TSG-CDocument18 pages04 Air Interface Perspective TSG-CBuchi ReddyNo ratings yet
- 3G PresentationDocument38 pages3G Presentationmalhan2010No ratings yet
- GPRS: General Packet Radio System: - A Packet Data Overlay Onto Existing GSM Networks - 2 GDocument20 pagesGPRS: General Packet Radio System: - A Packet Data Overlay Onto Existing GSM Networks - 2 GGourav NagNo ratings yet
- 3G Wcdma: Aditya K. Jagannatham Indian Institute of Technology KanpurDocument30 pages3G Wcdma: Aditya K. Jagannatham Indian Institute of Technology KanpurFaisal MalikNo ratings yet
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Document32 pagesGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Ojas_Bhatia_2380No ratings yet
- 3G TrainingDocument12 pages3G Trainingmonty1709No ratings yet
- 8x4 /16x4 / 24x8 WiFi Cable Modem with 4 Port ETH & Dual-Band Concurrent AccessDocument2 pages8x4 /16x4 / 24x8 WiFi Cable Modem with 4 Port ETH & Dual-Band Concurrent AccessAlejandro MalagáNo ratings yet
- Edge Technology: An Evolution in Mobile TechnologyDocument36 pagesEdge Technology: An Evolution in Mobile TechnologyVarsha G NairNo ratings yet
- GSM: The Global System for Mobiles ExplainedDocument185 pagesGSM: The Global System for Mobiles ExplainedSam Sunny34100% (1)
- Overview of 3G Technologies and ApplicationsDocument41 pagesOverview of 3G Technologies and ApplicationsMosab MohammadNo ratings yet
- DS-RTCD905 H6W4Document2 pagesDS-RTCD905 H6W4david fonsecaNo ratings yet
- BSNL's history and telecom services overviewDocument20 pagesBSNL's history and telecom services overviewAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- EDGEDocument24 pagesEDGEKishan RaoNo ratings yet
- Ac RE56 41 GSM Data SecondDocument7 pagesAc RE56 41 GSM Data SecondCedrik PendjiNo ratings yet
- Gprs CodingDocument4 pagesGprs CodingPuneet GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1 - 2 Evolution - 2 - 5G - GPRSDocument14 pages1 - 2 Evolution - 2 - 5G - GPRSKOMBOLCHA DRYPORTTERMINALNo ratings yet
- 4 2G EvolutionDocument21 pages4 2G EvolutionTechy GuyNo ratings yet
- Mobile Handset Cellular NetworkDocument45 pagesMobile Handset Cellular NetworkChung HuynhNo ratings yet
- 06 Lte3 PDFDocument105 pages06 Lte3 PDFnikolar85No ratings yet
- NSW GSM GPRS EdgeDocument72 pagesNSW GSM GPRS EdgeNILESH WANKHEDENo ratings yet
- SatLink 2900 Mobile VSAT - Rev K - 0Document2 pagesSatLink 2900 Mobile VSAT - Rev K - 0Christian Starchy Mimeck'sNo ratings yet
- EDGE Technology: Prepared byDocument17 pagesEDGE Technology: Prepared bySantosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Mobile GenerationDocument24 pagesMobile GenerationPhantom FireNo ratings yet
- VUHF HandheldDocument2 pagesVUHF Handheldriyanto_fisika5535No ratings yet
- G3-PLC Alliance Technical PresentationDocument28 pagesG3-PLC Alliance Technical PresentationHector Bandoni100% (1)
- Sim900 SpecDocument1 pageSim900 SpecAnonymous 1Wb6JCkNo ratings yet
- Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) BY M C KoladiyaDocument48 pagesPublic Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) BY M C KoladiyaTim KabiNo ratings yet
- 3G Apps for MobileDocument8 pages3G Apps for MobilejayveernetNo ratings yet
- Sted Adaptive Slide Collection - NewDocument80 pagesSted Adaptive Slide Collection - NewMuhammadAleemAsghar100% (1)
- Rcadcm 425Document2 pagesRcadcm 425spylakeNo ratings yet
- IDirect Evolution X3 BrochureDocument2 pagesIDirect Evolution X3 BrochureAsim Penkar PenkarNo ratings yet
- HSPA/HSDPA: Beyond 3G Mobile TechnologyDocument16 pagesHSPA/HSDPA: Beyond 3G Mobile TechnologyhusseinelatarNo ratings yet
- Presentation ON 4G-Technology: Presented By: Ajay Kanwal 2K8/COE/108Document22 pagesPresentation ON 4G-Technology: Presented By: Ajay Kanwal 2K8/COE/108Ajay KanwalNo ratings yet
- Week 8 2.5G/3G/CDMA: - 2.5G - HSCSD, Gprs - EdgeDocument50 pagesWeek 8 2.5G/3G/CDMA: - 2.5G - HSCSD, Gprs - EdgeConor O 'ReganNo ratings yet
- Mobile Wireless Communication Systems: Part 1Document49 pagesMobile Wireless Communication Systems: Part 1muralitejasNo ratings yet
- GSM To 3G: A Journey of Wireless CommunicationDocument45 pagesGSM To 3G: A Journey of Wireless Communicationsrshelke100% (1)
- Enhanced Data-Rates For Global Evolution (EDGE) : An OverviewDocument72 pagesEnhanced Data-Rates For Global Evolution (EDGE) : An OverviewPrashant SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Manual switching directly connected local loopsDocument90 pagesManual switching directly connected local loopsRiya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument17 pagesReportRushit D. BrahmbhattNo ratings yet
- Q-Flex™: Dual IF/L-Band Satellite ModemDocument6 pagesQ-Flex™: Dual IF/L-Band Satellite ModemARIFNo ratings yet
- Soft Handover For 3G WCMDA NetworksDocument53 pagesSoft Handover For 3G WCMDA NetworksNoilalam100% (2)
- GSM, GPRS and EDGE Performance: Evolution Towards 3G/UMTSFrom EverandGSM, GPRS and EDGE Performance: Evolution Towards 3G/UMTSTimo HalonenNo ratings yet
- 1: Ipv6 Addresses Are 128-Bit Hexadecimal Numbers: Private Ipv6 Network Id:-Fd30:5A40:A5Bc:206E::/64Document3 pages1: Ipv6 Addresses Are 128-Bit Hexadecimal Numbers: Private Ipv6 Network Id:-Fd30:5A40:A5Bc:206E::/64ajsurkhiNo ratings yet
- 10 2 10 118 IjbkmaDocument8 pages10 2 10 118 IjbkmaJohnn UrdinNo ratings yet
- CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure Practical Exam TopicsDocument8 pagesCCIE Enterprise Infrastructure Practical Exam Topicsdeltakio@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Extending A Wifi Network With Cascaded Routers PDFDocument2 pagesExtending A Wifi Network With Cascaded Routers PDFMartiNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent Omniswitch 6350: Gigabit Ethernet Lan Switch FamilyDocument8 pagesAlcatel-Lucent Omniswitch 6350: Gigabit Ethernet Lan Switch Familycnrk777No ratings yet
- Notes For CiscoDocument1 pageNotes For CiscoJan JansenNo ratings yet
- WSC2019 - TP39 - Final 30% ChangesDocument13 pagesWSC2019 - TP39 - Final 30% ChangesIT Comp0% (1)
- Lulzsec Private LogDocument121 pagesLulzsec Private LogcephursNo ratings yet
- Huawei Prepaway H12-224 v2020-01-12 by Paul 432qDocument181 pagesHuawei Prepaway H12-224 v2020-01-12 by Paul 432qSan BautistaNo ratings yet
- Paradox Ip100Document2 pagesParadox Ip100flagadaNo ratings yet
- Kodedkloud Instalation HardwayDocument153 pagesKodedkloud Instalation HardwayJuca LocoNo ratings yet
- Data & Computer Communications Data & Computer Communications Data & Computer Communications Data & Computer CommunicationsDocument35 pagesData & Computer Communications Data & Computer Communications Data & Computer Communications Data & Computer CommunicationsshimeNo ratings yet
- Understanding TCP - IP Network Stack & Writing Network Appsderstanding TCP - IP Network Stack & Writing Network Apps - CUBRID BlogDocument26 pagesUnderstanding TCP - IP Network Stack & Writing Network Appsderstanding TCP - IP Network Stack & Writing Network Apps - CUBRID BlogdaynisNo ratings yet
- Carrier VoIP Networks Quick ReferenceDocument354 pagesCarrier VoIP Networks Quick Referencerio1603100% (1)
- Assala Ip SubnetsDocument167 pagesAssala Ip SubnetsTito kombilaNo ratings yet
- Bài tập Static RoutingDocument2 pagesBài tập Static RoutingBảo BìnhNo ratings yet
- 200 355UpadatedJan2016 PDFDocument179 pages200 355UpadatedJan2016 PDFFemi Branch DadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: MAC Protocols For Ad-Hoc Wireless NetworksDocument28 pagesChapter 6: MAC Protocols For Ad-Hoc Wireless NetworksAakash AdhikariNo ratings yet
- 135-RIPE71 GoBGPDocument26 pages135-RIPE71 GoBGPhotsync101No ratings yet
- Huawei Product and Knowledge Enterprise Customer Training ManualV2.1Document1,056 pagesHuawei Product and Knowledge Enterprise Customer Training ManualV2.1John Cristouv CortezNo ratings yet
- CS610 Final Term Past Papers Mega FileDocument35 pagesCS610 Final Term Past Papers Mega Filehowtoplaygames38No ratings yet
- Firmware 7.1 Release NotesDocument7 pagesFirmware 7.1 Release Notesmiguel angel jaramilloNo ratings yet
- The Webmin Configuration ModuleDocument28 pagesThe Webmin Configuration ModulemohammadNo ratings yet
- 802.1X Configuration GuideDocument28 pages802.1X Configuration Guidepero27No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1nazir143No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NetworkingDocument22 pagesFundamentals of NetworkingManeth PathiranaNo ratings yet
- ZTE NR8120 ConfigurationDocument14 pagesZTE NR8120 ConfigurationAnonymous DKZem3lA100% (2)
- Aci 3545Document110 pagesAci 3545Phuwanart PhiNo ratings yet
- أفضل 20 أداة اختراق والقرصنة ألاخلاقية مفتوحة المصدر في 2020 - GNU-Linux RevolutionDocument1,033 pagesأفضل 20 أداة اختراق والقرصنة ألاخلاقية مفتوحة المصدر في 2020 - GNU-Linux RevolutionMohamed TahaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae - AmitDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae - AmitAmit RaoNo ratings yet