Professional Documents
Culture Documents
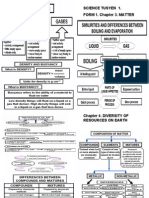
The Variety of Resources On Earth
Uploaded by
Nhs NhsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Variety of Resources On Earth
Uploaded by
Nhs NhsCopyright:
Available Formats
At
the end of the lesson, the students should be able to identify and list down the examples of resources on earth that are needed to sustain life
In pair, list down everything that a human needs in order to sustain life on Earth. (5 minutes) Present and discuss it with other peers and teacher. (10 minutes) Classify each component listed earlier into suitable groups. (10 minutes)
Woods Herbs Cotton Silk Milk Meat Leather Fruits
Vegetables Grain Cooking oil
Water Air Soil Minerals Fossil fuels Metals Non-metals
Make up 70% of the Earths surface Water is needed for transportation of nutrients and oxygen in plants and animals. Water is needed by the green plants to make food during photosynthesis. Water is needed to remove wastes from our body
Contains oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, inert gases and water vapour. Is needed for respiration in all living organisms. Oxygen helps burning. Carbon dioxide helps photosynthesis Nitrogen slows down combustion.
Food comes from plants and animals. Provide nutrients to sustain life.
Soil is the topmost layer of the Earths crust Soil is a mixture of sand particles, clay, humus, minerals, water, air, organisms and microorganisms Humus is formed from the remains of rotten plants and animals. Uses for farming Habitat for organisms such as earthworms, ants, etc.
Minerals are elements or compounds which occur in the Earths crust naturally. Copper : make electrical cables and wires Iron : make steel for construction Aluminium : make kitchen utensil
Petroleum, coal, natural gas. Fossils fuels are formed from partially decayed living things that died millions years ago. Sources of energy power for :
Vehicles Power stations Machinery in factories
Plants and animals Cotton : make cloth Fish : food Wood : furniture Herbs : medicine
The various resources on Earth exists as:
Elements simplest form of matter Compounds chemically combined
elements Mixtures physically mixed elements
All (living and nonliving) of the different kinds of matter in the universe is made from about 100 different substances, called elements.
Elements are called the building blocks of matter because all matter is composed of elements. Each element is made up of the same type of atoms. An atom is the smallest particle in an element. They cannot be broken into anything else by physical or chemicals means.
Carbon atoms Iron atoms Sulphur atoms Oxygen molecules Ozone molecules Hydrogen molecules
Elements can be classified into TWO major groups:
Metals Non-metals
The properties of metals and non-metals:
Surface appearance Malleability Brittleness Heat and electricity conductivity Boiling and melting points
Metals Sodium, copper, iron, aluminium, gold, silver, lead, calcium, mercury, magnesium, platinum and zinc
Non metals Carbon, phosphorus, iodine, sulphur, bromine, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, neon, argon, krypton, fluorine, chlorine, helium and radon Have dull surfaces Brittle and snap easily Poor heat conductors Cannot conduct electricity (except carbon) Have low melting and boiling points
Have shiny surfaces Ductile can be pulled into wires Malleable can be beaten into various shapes Good conductors of heat and electricity High melting and boiling points
compound has properties different than the elements that make it up. The parts of a compound are present in specific ratios. pure substances that are the unions of two or more elements. They can be broken into simpler substances by chemical means only.
Water = Hydrogen + Oxygen Alloy = Iron + Chromium Brass = Copper + Zinc Carbon dioxide = carbon + oxygen Ammonia = Nitrogen + Hydrogen
Most matter in the universe is found in mixtures. A mixture is made up of two or more substances either elements, compounds or both - that are physically combined. It can be by stirring, shaking, mixing or dissolving. We can separate and get the originals back!!
Mixtures Air
Components Oxygen, nitrogen, inert gases, carbon dioxide, microorganisms, dust, water vapour Red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water Water, lemon, sugar, tea Jelly, kidney beans, ice, water, ice-cream, sweet corns, cherry, groundnuts
Blood
Iced lemon tea Ice Kacang
The surface of a copper rod and a piece of sulphur are examined carefully. Both copper plate and the sulphur are rubbed with sandpaper. The surfaces of both objects are observed. Copper shines while sulphur remains dull
Metals have shiny surfaces. Non metals have dull surface
An iron nail is put into a mortar and pounded with a pestle. Then, a piece of sulphur s put into a mortar and pounded with a pestle. The iron nail changes shape when beaten. Sulphur breaks easily when beaten.
Metals are malleable. Non metals are brittle.
A circuit is connected as shown in the following figure. Connect the circuit with a copper plate. Then, connect the circuit with a piece of sulphur. The bulb lights up when the copper plate is connected but does not when the sulphur is connected
Metals are good electrical conductors. Non metals are poor electrical conductors.
Metals
are good heat conductors. Non metal are poor heat conductors. Can you give 3 examples of good and poor heat conductors, each?
Compound Through chemical reactions Heat is absorbed or released New substance is formed New properties are formed Ratio of components is fixed
Differences Formation Energy change Formation of new substance Properties of components Composition
Mixture Through physical methods No heat change No new substance Properties of components remain Ratio of components is not fixed Physical processes
Chemical processes Separation methods
Element Oxygen Carbon Hydrogen Sulphur Aluminium Copper Gold Mercury
Compound Water Ammonia Acid Limestone Salt Starch Carbon dioxide Fat
Mixture Seawater Bronze Steel Petroleum Pewter Brass Soil Air
Using magnet Filtration Distillation Using a strainer Evaporation Using separating funnel
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Cladding & Overlay - Ni InstituteDocument24 pagesCladding & Overlay - Ni Institutesajid aslamNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Form 1 Science: Form 1 Chapter 6 Sources of EnergyDocument9 pagesForm 1 Science: Form 1 Chapter 6 Sources of Energynaza9775100% (2)
- Gold Making Process PDFDocument3 pagesGold Making Process PDFMichelle50% (2)
- Astm B805Document7 pagesAstm B805Jonicus-DextoreNo ratings yet
- COE 107.01 Cathodic Protection PrinciplesDocument56 pagesCOE 107.01 Cathodic Protection PrinciplesMo'tasem Serdaneh100% (1)
- WG's Process Engineers' Codes StandardsDocument18 pagesWG's Process Engineers' Codes StandardskurtbkNo ratings yet
- Astm E1019-2011Document24 pagesAstm E1019-2011Юрий КостенкоNo ratings yet
- Failure - Mechanisms - of - C-Steels - API - 571 - .Xls - Filename UTF-8''Failure Mechanisms of C-Steels (API 571)Document100 pagesFailure - Mechanisms - of - C-Steels - API - 571 - .Xls - Filename UTF-8''Failure Mechanisms of C-Steels (API 571)أحمد صبحى100% (2)
- Themal Spray To Protect SteelDocument169 pagesThemal Spray To Protect Steel123vigenNo ratings yet
- Baby Registry ChecklistDocument3 pagesBaby Registry ChecklistNhs Nhs100% (3)
- Understanding Cell Structure and FunctionDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Cell Structure and FunctionNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- Devcon Catalog PDFDocument24 pagesDevcon Catalog PDFSergio MarchettiNo ratings yet
- Missing AlphabetDocument5 pagesMissing AlphabetNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 HouseDocument2 pagesCovid 19 HouseNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 5 TopengDocument8 pagesCovid 19 5 TopengNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- FingersDocument1 pageFingersNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- Label - IyyadDocument1 pageLabel - IyyadNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 MTDocument2 pagesCovid 19 MTNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 2 English Body PartDocument3 pagesCovid 19 2 English Body PartNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- Jubin Algebra MT TG 2Document3 pagesJubin Algebra MT TG 2Nhs NhsNo ratings yet
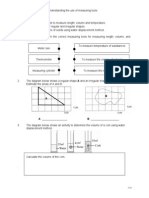
- Learning Objective: 1.4 Understanding The Use of Measuring ToolsDocument2 pagesLearning Objective: 1.4 Understanding The Use of Measuring Toolsapit9No ratings yet
- Alphabet Tracing 1Document26 pagesAlphabet Tracing 1noorhafizaNo ratings yet
- Fruit Zahra DianaDocument6 pagesFruit Zahra DianaNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- b2 Sel Haiwan Dan TumbuhanDocument2 pagesb2 Sel Haiwan Dan TumbuhanNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- 2Document3 pages2Nhs NhsNo ratings yet
- Cari Kata 1: Kosa Kata KaranganDocument1 pageCari Kata 1: Kosa Kata KaranganNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- Soalan Ujian 2Document10 pagesSoalan Ujian 2Nhs NhsNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan Introduction To Kepada Sainsscience: IstilahDocument8 pagesPengenalan Introduction To Kepada Sainsscience: IstilahNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- b5 Udara Sedutan Dan HembusanDocument2 pagesb5 Udara Sedutan Dan HembusanNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- b7 Pengembangan JirimDocument3 pagesb7 Pengembangan JirimNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- b7 Penyerapan Dan Pembebasan HabaDocument2 pagesb7 Penyerapan Dan Pembebasan HabaNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- Koleksi Word SearchDocument14 pagesKoleksi Word SearchNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Exercises Air Pollution Part 2Document1 page5.4 Exercises Air Pollution Part 2Nhs NhsNo ratings yet
- Student Handout Science F1Document20 pagesStudent Handout Science F1rarmaa70% (10)
- What Air Is Made OfDocument2 pagesWhat Air Is Made OfNhs NhsNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Exercises Air Pollution Part 2Document1 page5.4 Exercises Air Pollution Part 2Nhs NhsNo ratings yet
- Improving Cylindrical Inconel 718 Ingots Produced at PAO RuspolimetDocument5 pagesImproving Cylindrical Inconel 718 Ingots Produced at PAO RuspolimetJH ShinNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of Bend Tube Preheater On Heat Recovery Steam GeneratorDocument6 pagesFailure Analysis of Bend Tube Preheater On Heat Recovery Steam GeneratorarifbogNo ratings yet
- Nama Kelompok dan Taks Page 23Document4 pagesNama Kelompok dan Taks Page 23Soly Deo Glorya HutagalungNo ratings yet
- Mma Electrodes For Mo & Crmo Alloyed Heat & Creep Resisting SteelsDocument1 pageMma Electrodes For Mo & Crmo Alloyed Heat & Creep Resisting SteelsstkmNo ratings yet
- GS118 7Document48 pagesGS118 7JoseEZerpaNo ratings yet
- Hastelloy alloys corrosion resistant metal trademarkDocument3 pagesHastelloy alloys corrosion resistant metal trademarktalparadipakNo ratings yet
- Environment Law AssignmentDocument49 pagesEnvironment Law AssignmentGouri SureshNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument14 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2023 Answershithesh365No ratings yet
- Sustainability - The Role of Mineral Processing and Extractive MetallurgyDocument9 pagesSustainability - The Role of Mineral Processing and Extractive MetallurgyakshukNo ratings yet
- Visio - Lign - 000294GB (1623396) PDFDocument12 pagesVisio - Lign - 000294GB (1623396) PDFAna AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- AMIE Coaching Material Science Engineering Exam QuestionsDocument0 pagesAMIE Coaching Material Science Engineering Exam QuestionsN Dhanunjaya Rao BorraNo ratings yet
- Order among ElementsDocument3 pagesOrder among ElementsCris CorsinoNo ratings yet
- Not The Latest Sample: Mobile EquipmentDocument8 pagesNot The Latest Sample: Mobile EquipmentBOANERGES IRUNGNo ratings yet
- CP601s & CF116-45Document4 pagesCP601s & CF116-45Syed AsadullahNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Aluminum Foam Production MethodsDocument8 pagesAn Overview of Aluminum Foam Production Methodsgouhua yuanNo ratings yet
- Autoclaving PDFDocument101 pagesAutoclaving PDFUdochukwu MarkNo ratings yet
- January 2017 AMSOIL Dealer EditionDocument24 pagesJanuary 2017 AMSOIL Dealer EditionamsoildealerNo ratings yet
- Science 1 and 2 Question Bank Objectives SolutionDocument60 pagesScience 1 and 2 Question Bank Objectives SolutionWanderer Supreme96% (46)
- DR Krishna Kanth - DSTDocument19 pagesDR Krishna Kanth - DSTIncubator AIMNo ratings yet
- All Punjab Boards Chemistry XII Chapterwise important MCQsDocument150 pagesAll Punjab Boards Chemistry XII Chapterwise important MCQsRaheem Ullah KakarNo ratings yet
- Annual Foreign Trade Statistics (2074-75)Document1,545 pagesAnnual Foreign Trade Statistics (2074-75)Ajay GauroNo ratings yet