Professional Documents
Culture Documents
US Executive Branch
Uploaded by
Jep Chu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views9 pagesThe US Executive Branch is headed by the President, who has powers as Commander-in-Chief over the military, to make treaties and appointments, and to grant pardons. The President is responsible for faithfully executing laws and informing Congress on the state of the union. The Vice President assumes the presidency if needed and oversees the Senate. The Cabinet consists of heads of executive departments. Congress can impeach the president and restrict executive officials, while courts can review executive actions.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe US Executive Branch is headed by the President, who has powers as Commander-in-Chief over the military, to make treaties and appointments, and to grant pardons. The President is responsible for faithfully executing laws and informing Congress on the state of the union. The Vice President assumes the presidency if needed and oversees the Senate. The Cabinet consists of heads of executive departments. Congress can impeach the president and restrict executive officials, while courts can review executive actions.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views9 pagesUS Executive Branch
Uploaded by
Jep ChuThe US Executive Branch is headed by the President, who has powers as Commander-in-Chief over the military, to make treaties and appointments, and to grant pardons. The President is responsible for faithfully executing laws and informing Congress on the state of the union. The Vice President assumes the presidency if needed and oversees the Senate. The Cabinet consists of heads of executive departments. Congress can impeach the president and restrict executive officials, while courts can review executive actions.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
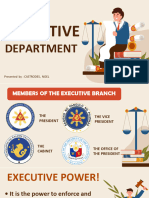
US Executive Branch
^What the title says^
Executive Powers of the
President
• Vested upon the President of the United States.
• Powers over the military, navy and air force by
being the Commander-in-Chief.
• Make treaties and appointments to office.
• Appoints judges and executive heads
• Has power to grant pardons to convicted persons,
except in cases of impeachment.
Responsibilities
• To make sure the faithful execution
of the laws made by Congress
• To execute whatever instructions he
is given by the Congress
• From time to time give to the
Congress Information of the State of
the Union, and recommend to their
Consideration such Measures as he
shall judge necessary and expedient
Vice President
• The primary responsibility of the Vice
President of the United States is to be
ready at a moment's notice to assume
the Presidency if the President is
unable to perform his duties.
• The Vice President also serves as the
President of the United States Senate,
where he or she casts the deciding
vote in the case of a tie
The Cabinet
• Department of Agriculture • Department of Health and
• Department of Commerce Human Services
• Department of Defense • Department of Homeland
• Department of Education Security
• Department of Energy • Department of Housing and
• Department of Justice Urban Development
• Department of Labor • Department of the Interior
• Department of State
• Department of the Treasury
• Department of Transportation
• Department of Veterans
Affairs
Powers of Executive over
Legislative
• Veto a bill
• Requiring every bill passed by the
House and Senate, before becoming
law, to be presented to the
president, and, if he disapproves, to
be re-passed by two-thirds of the
Senate and House
Power of Executive over
Judiciary
• The judges must be appointed by the
president with the advice and
consent of the Senate
Power of Legislative over
Executive
• Terminate appointments by impeachment, and
restrict the president.
• Legislation to restrain executive officials to the
performance of their duties.
• Declare wars.
• Approve appointments to the Vice Presidency and
any treaty that involves foreign trade
• Government Accountability Office
Power of Judiciary over
Executive
• Judicial review - power of a court to
review the constitutionality of a
statute or treaty, or to review an
administrative regulation for
consistency with either a statute, a
treaty, or the constitution itself.
You might also like
- Executive PowerDocument31 pagesExecutive PowermaricrisandemNo ratings yet
- The Executive Department and Powers of The President: Constitutional Law 1Document30 pagesThe Executive Department and Powers of The President: Constitutional Law 1Noel IV T. BorromeoNo ratings yet
- The Executive Department and Powers of Thepresident: Constitutional Law 1Document30 pagesThe Executive Department and Powers of Thepresident: Constitutional Law 1SulliNo ratings yet
- State LegislatureDocument27 pagesState LegislatureSuryagayathri SNo ratings yet
- Executive BranchDocument29 pagesExecutive BranchTherese Angelie CamacheNo ratings yet
- Pengajian Malaysia: En. Imaduddin Bin AbidinDocument33 pagesPengajian Malaysia: En. Imaduddin Bin AbidinWilliam AnthonyNo ratings yet
- The Powers of Each Branch of GovernmentDocument3 pagesThe Powers of Each Branch of Governmentapi-265300695No ratings yet
- Philippine Government: 3 Major Streanghts 3 Major Weakness 3 Major Influential Persons Exellent SolutionsDocument3 pagesPhilippine Government: 3 Major Streanghts 3 Major Weakness 3 Major Influential Persons Exellent SolutionsNathaniel RectoNo ratings yet
- Becoming The President of The United StatesDocument14 pagesBecoming The President of The United Statesapi-592588138No ratings yet
- Conventions, King, CrownDocument18 pagesConventions, King, CrownAashna JainNo ratings yet
- USC - Role and Functions of Congress - Ed WQS 15-01-2024Document12 pagesUSC - Role and Functions of Congress - Ed WQS 15-01-2024abduljabbarNo ratings yet
- State Executive PlanDocument30 pagesState Executive Plansamy gsNo ratings yet
- Seperation of PowersDocument28 pagesSeperation of PowersDaniel DauodNo ratings yet
- The Legislature: By: Group 3Document35 pagesThe Legislature: By: Group 3Alma CayapNo ratings yet
- Executive DepartmentDocument37 pagesExecutive DepartmentNoel CastrodesNo ratings yet
- Intro To US GovernmentDocument28 pagesIntro To US GovernmentJustinne KaparazNo ratings yet
- 3 Branches of The American GovernmentDocument33 pages3 Branches of The American Governmenthuyen dauNo ratings yet
- Scrutiny OversightDocument29 pagesScrutiny OversightPeped100% (1)
- Chapter 5 NewDocument19 pagesChapter 5 NewRiya IndukuriNo ratings yet
- The Legislative DepartmentDocument37 pagesThe Legislative DepartmentTherese Angelie CamacheNo ratings yet
- International Military Student Preparatory Course P 910: U.S. Constitution/ GovernmentDocument22 pagesInternational Military Student Preparatory Course P 910: U.S. Constitution/ GovernmentwlamillerNo ratings yet
- Our GovernmentDocument5 pagesOur Governmentapi-218680614No ratings yet
- PDF Statutory Construction AgpaloDocument167 pagesPDF Statutory Construction AgpaloCharmaine SaguinNo ratings yet
- Q2: What Is Montesquieu Theory of Separation of Powers? Throw Light On The Veto Power of The President in The Context of Checks and Balances DoctrineDocument5 pagesQ2: What Is Montesquieu Theory of Separation of Powers? Throw Light On The Veto Power of The President in The Context of Checks and Balances DoctrineIbrahim HassanNo ratings yet
- Congress US Politics AQA Unit 4ADocument31 pagesCongress US Politics AQA Unit 4AWilliam StarkNo ratings yet
- Constitution 101Document17 pagesConstitution 101Kouna ChannelNo ratings yet
- The Constitution: Paula ChildsDocument17 pagesThe Constitution: Paula ChildsEdwardtommy TommyNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 2 - Part I Dhonmore ConstDocument11 pagesLecture No 2 - Part I Dhonmore Constchamila2345No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Notesapi-229040920No ratings yet
- Topic 10 - Commonwealth Parliament - Summer 2019Document82 pagesTopic 10 - Commonwealth Parliament - Summer 2019masterpharmusaNo ratings yet
- Adnan 2278 4080 1 Introduction To Law 1Document46 pagesAdnan 2278 4080 1 Introduction To Law 1Shahzad C7No ratings yet
- Art VII. Executive DepartmentDocument27 pagesArt VII. Executive Departmentkristine319No ratings yet
- PowersofpresidentDocument28 pagesPowersofpresidentapi-353522727No ratings yet
- Comm Law Revision NotesDocument39 pagesComm Law Revision NotesedNo ratings yet
- USA President Election, Powers and FunctionsDocument26 pagesUSA President Election, Powers and FunctionsKasvi MalhotraNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Powers of The PresidentDocument27 pages4.2 Powers of The PresidentPriyanshu PandeyNo ratings yet
- Philippine Executive BranchDocument10 pagesPhilippine Executive BranchElton John Santos CapiliNo ratings yet
- The Sacred Policy of The British Armed ForcesDocument5 pagesThe Sacred Policy of The British Armed ForcesRaw MountbattenNo ratings yet
- PPG LegislativeDocument55 pagesPPG LegislativeJulie Bee TolinNo ratings yet
- Unit+I +lecture+9Document11 pagesUnit+I +lecture+9Natasha KapoorNo ratings yet
- Topic - 2.5 - NOTES JHDocument6 pagesTopic - 2.5 - NOTES JHJonathan HerreraNo ratings yet
- What Do They Do - 3 Branches of U.S. GovtDocument2 pagesWhat Do They Do - 3 Branches of U.S. Govtjadeerin99100% (1)
- Civics LessonDocument5 pagesCivics Lessonapi-273344635No ratings yet
- Branches of The GovernmentDocument9 pagesBranches of The Governmentpatrick castilloNo ratings yet
- Colegio Bilingüe Richmond: BY:Sebastian Guerra Mr:Diego VillamizarDocument20 pagesColegio Bilingüe Richmond: BY:Sebastian Guerra Mr:Diego VillamizarJhonabie Suligan CadeliñaNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of The American ConstitutionDocument17 pagesSalient Features of The American Constitutiontaha_shakir5286% (7)
- Comparing The Legislative Branches in The UK USADocument14 pagesComparing The Legislative Branches in The UK USASimo MijmijNo ratings yet
- CivicsDocument22 pagesCivicsjackbabe41No ratings yet
- Our Legal FrameworkDocument7 pagesOur Legal FrameworkvngoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Notes (9.1-9.4)Document20 pagesChapter 9 Notes (9.1-9.4)buddylembeckNo ratings yet
- Our GovernmentDocument5 pagesOur Governmentapi-302707797No ratings yet
- Skills Builder - Civics LessonDocument5 pagesSkills Builder - Civics Lessonapi-354682843No ratings yet
- WK 2Document26 pagesWK 2yexiahongmu999No ratings yet
- FCHS 22-23 Executive BranchDocument28 pagesFCHS 22-23 Executive BranchKarla GomezNo ratings yet
- Branches of Us GovernmentDocument21 pagesBranches of Us Governmenthuyen dauNo ratings yet
- Our Government: A System of Checks and BalancesDocument5 pagesOur Government: A System of Checks and BalancesAshley Renee JordanNo ratings yet
- Constitution of Pakistan: Relations Between Federation and ProvincesDocument11 pagesConstitution of Pakistan: Relations Between Federation and ProvincesSuhrab Khan JamaliNo ratings yet
- Our GovernmentDocument5 pagesOur Governmentapi-308138734No ratings yet
- Checks and BalancesDocument33 pagesChecks and BalancesNina ENo ratings yet
- Selection Letter Abhishek TodkarDocument1 pageSelection Letter Abhishek TodkarDipak GiteNo ratings yet
- ,وثيقة تعارفDocument3 pages,وثيقة تعارفAyman DarwishNo ratings yet
- Henry IV Part 1 Study GuideDocument21 pagesHenry IV Part 1 Study GuideawtshfhdNo ratings yet
- RAN16.0 Optional Feature DescriptionDocument520 pagesRAN16.0 Optional Feature DescriptionNargiz JolNo ratings yet
- Ulta Beauty Hiring AgeDocument3 pagesUlta Beauty Hiring AgeShweta RachaelNo ratings yet
- 13th Format SEX Format-1-1: Share This DocumentDocument1 page13th Format SEX Format-1-1: Share This DocumentDove LogahNo ratings yet
- Environmental Management Plan GuidelinesDocument23 pagesEnvironmental Management Plan GuidelinesMianNo ratings yet
- Chapter (2) Industry and Competitive AnalysisDocument16 pagesChapter (2) Industry and Competitive Analysisfsherif423No ratings yet
- Martin, BrianDocument3 pagesMartin, Brianapi-3727889No ratings yet
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocument7 pagesBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledYanna ManuelNo ratings yet
- Deed OfAdjudication Cresencio Abuluyan BasilioDocument4 pagesDeed OfAdjudication Cresencio Abuluyan BasilioJose BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Prayer For World Teachers Day: Author: Dr. Anthony CuschieriDocument1 pagePrayer For World Teachers Day: Author: Dr. Anthony CuschieriJulian ChackoNo ratings yet
- Scott Kugle-Framed, BlamedDocument58 pagesScott Kugle-Framed, BlamedSridutta dasNo ratings yet
- Assignment MS-28 Course Code: MS - 28 Course Title: Labour Laws Assignment Code: MS-28/TMA/SEM - II /2012 Coverage: All BlocksDocument27 pagesAssignment MS-28 Course Code: MS - 28 Course Title: Labour Laws Assignment Code: MS-28/TMA/SEM - II /2012 Coverage: All BlocksAnjnaKandariNo ratings yet
- Digest Pre TrialDocument2 pagesDigest Pre TrialJei Essa AlmiasNo ratings yet
- International Law Detailed Notes For Css 2018Document95 pagesInternational Law Detailed Notes For Css 2018Tooba Hassan Zaidi100% (1)
- Achieving Rapid Internationalization of Sub Saharan Africa - 2020 - Journal of BDocument11 pagesAchieving Rapid Internationalization of Sub Saharan Africa - 2020 - Journal of BErnaNo ratings yet
- 240 Marilag v. MartinezDocument21 pages240 Marilag v. Martinezdos2reqjNo ratings yet
- UNIDO EIP Achievements Publication FinalDocument52 pagesUNIDO EIP Achievements Publication FinalPercy JacksonNo ratings yet
- Profil AVANCER FM SERVICES SDN BHDDocument23 pagesProfil AVANCER FM SERVICES SDN BHDmazhar74No ratings yet
- Authors & Abstract Guideline V-ASMIUA 2020Document8 pagesAuthors & Abstract Guideline V-ASMIUA 2020tiopanNo ratings yet
- The Holy Rosary 2Document14 pagesThe Holy Rosary 2Carmilita Mi AmoreNo ratings yet
- Microplastic Occurrence Along The Beach Coast Sediments of Tubajon Laguindingan, Misamis Oriental, PhilippinesDocument13 pagesMicroplastic Occurrence Along The Beach Coast Sediments of Tubajon Laguindingan, Misamis Oriental, PhilippinesRowena LupacNo ratings yet
- Timeline of American OccupationDocument3 pagesTimeline of American OccupationHannibal F. Carado100% (3)
- Adidas Case StudyDocument5 pagesAdidas Case StudyToSeeTobeSeenNo ratings yet
- Full Download Health Psychology Theory Research and Practice 4th Edition Marks Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Health Psychology Theory Research and Practice 4th Edition Marks Test Bankquininemagdalen.np8y3100% (39)
- Lectio Decima Septima: de Ablativo AbsoluteDocument10 pagesLectio Decima Septima: de Ablativo AbsoluteDomina Nostra FatimaNo ratings yet
- Marking SchemeDocument8 pagesMarking Schememohamed sajithNo ratings yet
- Actividad N°11 Ingles 4° Ii Bim.Document4 pagesActividad N°11 Ingles 4° Ii Bim.jamesNo ratings yet
- Louis I Kahn Trophy 2021-22 BriefDocument7 pagesLouis I Kahn Trophy 2021-22 BriefMadhav D NairNo ratings yet