Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anesthetic Techniques of Mandible
Uploaded by
alireza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views10 pagesuseful ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentuseful ppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views10 pagesAnesthetic Techniques of Mandible
Uploaded by
alirezauseful ppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Anesthetic techniques
of lower jaw
LECTURER: DR. NINO CHICHOA
STUDENT: ALIREZA FARHADIEH
Which nerves innervates mandible?
Totally facial nerves are divided into tree part :
ophthalmic , maxillary and mandibular nerves
Mandibular nerve (third division of trigeminal nerve)
divide mainly into two branch when it
comes out from foramen ovale.
Motor nerves: connect to muscle of
mastication (maseter,temporalis,L&M pterygoid)
Sensory nerves: which include inferior
alveolar nerve, lingual nerve, buccal nerve,
auriclotemporal nerve
Nerve supply for mandibular teeth
Mandibular premolars & molars
(pulp, investing structures) innervated by
inferior alveolar nerve.
Mandibular incisors & canines (pulp,
investing structures) innervated by
incisive nerve.
Type of injection procedures
Nerve block: depositing the local
anesthesia solutions within close
location to a main nerve trunk
Field block: depositing near to the
large nerve branches
Local infiltration: small terminal nerve
ending are insensitive to pain and
anesthetized (it is useful for minor dental
procedures , specially on anterior mandible
because of thin cortical layer of spongy bone
above.)
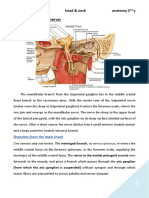
Type of mandibular nerve block
Inferior alveolar nerve block:
enters the mandible throw the mandibular
foramen, goes out throw mental foramen
and gives branches to mental and incisive
nerve so anesthetizes areas will be:
Mandibular teeth to the midline
Anterior two thirds of the tongue and floor
of the oral cavity (lingual nerve)
Mucosa and skin of the lower lip and chin
Gingiva on the labial and lingual surface of
the mandible
Type of mandibular nerve block
Procedure:
For right side IANB we will stay at 8 o’clock position
and for left side at 10 o’clock position
retract the lips then use thump on the anterior
surface of the ramus (coronoid notch)
From the opposite site, cotra lateral premolar region,
6 – 10 mm from the occlusal plane, at the deepest
part of the pterygomandibular raphe
we have to insert about 2/3 of needle until it touch
the bone then release approximately 1.5 ml of
anesthetics over a minimum 60 seconds
Type of mandibular nerve block
Long buccal nerve block:
Mostly we use this type of anesthesia beside IANB
it is the branch of V3 nerve which innervates buccal
soft tissue around the molars, areas which anesthetize
are Soft tissues and periosteum buccal to the
mandibular molar teeth.
Procedure:
Insert about 2 mm of needle at the level of occlusal
plan of second premolar
release 0.3 ml of anesthetics
Type of mandibular nerve block
Mental nerve block:
Its form the last part of the IAN which exit from
mental foramen, area which will be anesthetize
are buccal mucosa of anterior to the mental
foramen and also mucosa of the lower lip and
chin. (provide no anesthesia for teeth)
Procedure:
retract the lip and insert the needle at
mucogingival junction of buccal side of
premolars ( between premolars, between 2nd
premolar and 1st molar )
Type of mandibular nerve block
Incisive nerve block:
Terminal end of IAN, exit from mental foramen anteriorly and anesthetize lower lip/
skin of chin /Incisor, canine premolar
Procedure
Between canine and lateral incisor we will insert 5-6 mm of the needle parallel to long
axis of teeth and release 0.6 ml of anesthetic over 20-30 seconds.
Thank you
Any questions?
You might also like
- Cross Sectional Anatomy CT & MRIDocument283 pagesCross Sectional Anatomy CT & MRIneesan100% (2)
- Comprehensive Review in Clinical Neurology - Cheng-Ching Esteban PDFDocument950 pagesComprehensive Review in Clinical Neurology - Cheng-Ching Esteban PDFLidio Neto100% (2)
- Facial Nerve & Trigeminal NerveDocument25 pagesFacial Nerve & Trigeminal NerveRafiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck: Openings in The Base of The Skull and The Structures That Pass Through ThemDocument11 pagesHead and Neck: Openings in The Base of The Skull and The Structures That Pass Through ThemcathdelosoNo ratings yet
- Face BowDocument20 pagesFace BowKhushbu SamaniNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Quiz BeeDocument55 pagesNeuroanatomy Quiz BeeJulienne Sanchez-Salazar100% (3)
- Open Access Atlas of Otolaryngology, Head & Neck Operative SurgeryDocument9 pagesOpen Access Atlas of Otolaryngology, Head & Neck Operative SurgeryvladNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument92 pagesTrigeminal Nervemounika33% (3)
- Illustrations Of Special Effective Acupoints for common DiseasesFrom EverandIllustrations Of Special Effective Acupoints for common DiseasesNo ratings yet
- AnesthesiaDocument62 pagesAnesthesiajarrie abbasNo ratings yet
- Csom (TT)Document24 pagesCsom (TT)SamirNo ratings yet
- Mandibular FracturesDocument67 pagesMandibular FracturesAbel AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Brain and Spinal Cord: W Prasasti Mutiadesi, DR., M. BiomedDocument26 pagesBlood Supply of Brain and Spinal Cord: W Prasasti Mutiadesi, DR., M. Biomedhelda dwianaNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument82 pagesOral Cavitydavid100% (1)
- Mandibular NerveDocument6 pagesMandibular NerveCatalina StoicescuNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Nerve: Dr. Sanjana Mall Department of PedodonticsDocument48 pagesMaxillary Nerve: Dr. Sanjana Mall Department of PedodonticsSanjana MallNo ratings yet
- Concept of PsychobiologyDocument21 pagesConcept of Psychobiologydhivyaram100% (1)
- Fracture of The Mandible (Repaired)Document67 pagesFracture of The Mandible (Repaired)Arafat Masud NiloyNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument76 pagesTrigeminal Nerveanhca4519No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve (Cranial Nerve V) : Presented By: Hamza Yousaf Usaid Yousaf Amna Khalil Maha Aziz Rimsha AkramDocument30 pagesTrigeminal Nerve (Cranial Nerve V) : Presented By: Hamza Yousaf Usaid Yousaf Amna Khalil Maha Aziz Rimsha AkramHamza YousafNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument102 pagesLocal Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgerydr_jamal1983No ratings yet
- Mandibular Injection TechniquesDocument91 pagesMandibular Injection TechniquesRobins Dhakal100% (3)
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCubital Tunnel Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Growth of Maxilla and Cranial Base and Their Clinical ImplicationsDocument196 pagesGrowth of Maxilla and Cranial Base and Their Clinical ImplicationsAnalhaq Shaikh100% (1)
- Trigeminal Nerve: Dr.B.B.GosaiDocument76 pagesTrigeminal Nerve: Dr.B.B.GosaiAlexAlxNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review of Subjects For PG Medical Entrance ExaminationsDocument995 pagesA Systematic Review of Subjects For PG Medical Entrance ExaminationsRonnie Luzuriaga82% (11)
- Maxillary 1Document4 pagesMaxillary 1Farhang Abdułła IsmahiłNo ratings yet
- Blank Book 2Document4 pagesBlank Book 2Rawand Ra'ed D.AlshawabkehNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Nerve, Chorda Tympani Nerve, Otic GanglionDocument33 pagesMandibular Nerve, Chorda Tympani Nerve, Otic Ganglionwaniya irumNo ratings yet
- Technique: Supraperiosteal InfiltrationsDocument11 pagesTechnique: Supraperiosteal Infiltrationsp_npsNo ratings yet
- Q. 4 Anesthesia IiDocument46 pagesQ. 4 Anesthesia IiJoao Zarate JimenezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Trigeminal NerveDocument48 pagesAnatomy of Trigeminal NerveNicky RomeoNo ratings yet
- Injection Technique: Kirana Lina G., DRGDocument45 pagesInjection Technique: Kirana Lina G., DRGFinnyalfNo ratings yet
- Os 3Document11 pagesOs 3مرتضى محمد فاضل جرجوكNo ratings yet
- Trigemina Nerve Sem 2 WordDocument18 pagesTrigemina Nerve Sem 2 WordBharathi GudapatiNo ratings yet
- Intraoral Injections BJVDocument19 pagesIntraoral Injections BJVmavirosemandawe08No ratings yet
- Mandibular NerveDocument3 pagesMandibular Nervervinluan.dentNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document46 pagesPresentation 1anamiqbalNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve AnatomyDocument56 pagesTrigeminal Nerve AnatomyAsfoor gake1No ratings yet
- LA TechDocument46 pagesLA TechLama KhalidNo ratings yet
- 8 Mandibular NerveDocument6 pages8 Mandibular NerveAaaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument28 pagesUntitledAhmed AlrashidNo ratings yet
- ENGanesthesiamanndibleDocument48 pagesENGanesthesiamanndibleRoxanaAnaHociungNo ratings yet
- Pain ControlDocument88 pagesPain ControlShubham KingraNo ratings yet
- Shade Selection: What Is Colour?Document39 pagesShade Selection: What Is Colour?RaiNo ratings yet
- Regional Anesthesia of The Face: Jeffrey S. Eaton, MD and Roy C. Grekin, MDDocument4 pagesRegional Anesthesia of The Face: Jeffrey S. Eaton, MD and Roy C. Grekin, MDPrajna PNo ratings yet
- Mandibular AnatomyDocument61 pagesMandibular AnatomyDeb SNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Nerve BlockDocument20 pagesMaxillary Nerve BlockMaitreyi LimayeNo ratings yet
- Mandibular NerveDocument19 pagesMandibular Nervenadaelhamy03No ratings yet
- NervesDocument16 pagesNervesDerahNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Mandibular NerveDocument23 pagesHuman Anatomy Mandibular Nerveمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- BuccalDocument2 pagesBuccalFarhang Abdułła IsmahiłNo ratings yet
- LADocument93 pagesLAkaedeamira_113974100% (2)
- Bones of The Skull 2Document31 pagesBones of The Skull 2anaNo ratings yet
- Lecture of Temporal & InfratemporalDocument60 pagesLecture of Temporal & InfratemporalShahd YehiaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document206 pagesPresentation 1Mohamed NagibNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions Pediatric OMF Surgery V Eng 2021-2022 (Repaired)Document53 pagesExam Questions Pediatric OMF Surgery V Eng 2021-2022 (Repaired)Beni KelnerNo ratings yet
- Nervio MaxilarrDocument85 pagesNervio MaxilarrGermanLoopezzNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve: D.Nimer D.Rania Gabr D.Safaa D.ElsherbinyDocument24 pagesTrigeminal Nerve: D.Nimer D.Rania Gabr D.Safaa D.ElsherbinyRakesh Kumar RanjanNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Facial ExpressionDocument63 pagesMuscles of Facial Expressionraphaelyohana140No ratings yet
- 7.local Anaesthesia IIDocument104 pages7.local Anaesthesia IIsailajanekkanti03No ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia Technique - Oral SurgeryDocument97 pagesLocal Anesthesia Technique - Oral SurgeryfaniaNo ratings yet
- Applied Surgical AnatomyDocument52 pagesApplied Surgical AnatomyEmad AdelNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Anesthesia: Dr. Deepak K GuptaDocument63 pagesMandibular Anesthesia: Dr. Deepak K GuptaArindom ChangmaiNo ratings yet
- Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block: D. Abdullah Al NasserDocument23 pagesInferior Alveolar Nerve Block: D. Abdullah Al NasserMira AnggrianiNo ratings yet
- 11-N Mandibular Techniques 2Document27 pages11-N Mandibular Techniques 2Shahenda El-falkyNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of Mandible: Department of Oral and Maxilofacial SurgeryDocument92 pagesSurgical Anatomy of Mandible: Department of Oral and Maxilofacial SurgerySAMEENANo ratings yet
- 15-Facial NerveDocument22 pages15-Facial NerveLucy LimNo ratings yet
- Neuromodulation in Headache and Facial Pain Management: Principles, Rationale and Clinical DataFrom EverandNeuromodulation in Headache and Facial Pain Management: Principles, Rationale and Clinical DataGiorgio LambruNo ratings yet
- Study of The Effect of Mobile Phones On HearingDocument5 pagesStudy of The Effect of Mobile Phones On HearingPranay DasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Thyroid GlandDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Thyroid GlandShienna Marie SalvioNo ratings yet
- Muscles of MasticationDocument12 pagesMuscles of MasticationGokul VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Temporal Bone Dissection Dr. Stelian LUPESCUDocument29 pagesTemporal Bone Dissection Dr. Stelian LUPESCUEdy MorarNo ratings yet
- NOE FractureDocument71 pagesNOE FractureAlex HaileyesusNo ratings yet
- 4b. Bimbingan Neuroimaging CT Scan Kepala 2 - ResidenDocument60 pages4b. Bimbingan Neuroimaging CT Scan Kepala 2 - ResidenDebby SejahteraNo ratings yet
- Neurobiological Theories of ConsciousnessDocument14 pagesNeurobiological Theories of ConsciousnessRodrigo Aguirre BáezNo ratings yet
- Colocación de Los ElectrodosDocument8 pagesColocación de Los ElectrodosTahysse Andrea Varela SilvaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka ReferatDocument4 pagesDaftar Pustaka ReferatRizandiny0% (1)
- Chapter 10 Neuropsychological Assessment and ScreeningDocument26 pagesChapter 10 Neuropsychological Assessment and ScreeningKadir Say'sNo ratings yet
- Vision: - Carlene S. Solidum, MD, DPPSDocument98 pagesVision: - Carlene S. Solidum, MD, DPPSJimell ObradorNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Cranium PDFDocument24 pagesAnatomi Cranium PDFVelrones TampubolonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 4 PDFDocument1 pageAnatomy 4 PDFJihan SalsabillaNo ratings yet
- Unit II: Endocrine Nursing: Muhammad Yaqoob Instructor Ion-DuhsDocument51 pagesUnit II: Endocrine Nursing: Muhammad Yaqoob Instructor Ion-DuhsyaqoobmdNo ratings yet
- The Head Anatomy Tutorial: Name Date ScoreDocument10 pagesThe Head Anatomy Tutorial: Name Date ScoreNoralina IshakNo ratings yet
- Brain Infographics-1Document8 pagesBrain Infographics-1PivvkyNo ratings yet
- Feeding Plate Fabrication For A 15 Day Old Neonate Using RTV Silicone A Case ReportDocument4 pagesFeeding Plate Fabrication For A 15 Day Old Neonate Using RTV Silicone A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Tympanic Membrane Retraction PocketDocument94 pagesTympanic Membrane Retraction Pocketthegeekysquirrel23No ratings yet