Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Proposal Template
Uploaded by
mimiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Proposal Template
Uploaded by
mimiCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3 Method Analysis
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Introduction
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Chapter 3 Content
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Review
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis
500W 500W
I1 V 1kW 500W I2
500W
–
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
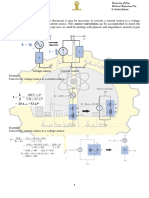
Steps of Nodal Analysis
1. Choose a reference node.
2. Assign node voltages to the other nodes.
3. Apply KCL to each node other than the
reference node; express currents in terms
of node voltages.
4. Solve the resulting system of linear
equations.
Important key idea resistance is a passive element, by
the passive sign convention, current must always flow
from a higher potential to a lower potential
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis with voltage source
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis with Voltage source
Case 1:
If a voltage source is connected between
the reference node and a nonreference
node, we simply set the voltage at the
nonreference node equal to the voltage of
the voltage source.
Case 2:
If the voltage source (dependent or
independent) is connected between two
nonreference nodes, the two nonreference
nodes
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis with Voltage source
(Supernode)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Properties of Supernode
1. The voltage source inside the supernode
provides a constraint equation needed to
solve for the node voltages.
2. A supernode has no voltage of its own.
3. A supernode requires the application of
both KCL and KVL.
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Steps to Solve Supernode
1. Identify supernode in the circuit
2. Identify Current flow direction on
supernode
3. Apply KCL on the supernode
4. Apply Ohms Law on KCL
5. Apply KVL to the supernode loop
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis (Supernode) (Eg 3.3)
Find the node voltages
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis (Supernode) (Eg 3.3)
Applied KCL
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis (Supernode) (Eg 3.3)
Applied KVL
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis (Supernode) (Eg 3.3)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis (Supernode) (Eg 3.3)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis (Supernode) (PP 3.3)
Find the v and i in the circuit
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis (Supernode) (PP 3.3)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis (Supernode) (PP 3.3)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis (Supernode) (PP 3.4)
Find the v1, v2, v3 in the circuit
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis (Supernode) (PP 3.4)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis (Supernode) (Example)
Find the v1 in the circuit
7V
2A 4W 2W V1 4W
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Nodal Analysis (Supernode) (Example)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis
1. Mesh analysis provides another general
procedure for analyzing circuits.
2. Recall that a loop is a closed path with
no node passed more than once.
3. A mesh is a loop that does not contain
any other loop within it.
4. Mesh analysis apply KVL to find
unknown currents
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis
1. Nodal analysis applies KCL to find
unknown voltages in a given circuit,
while mesh analysis applies KVL to find
unknown currents.
2. Mesh analysis is not quite as general as
nodal analysis because it is only
applicable to a circuit that is planar.
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis (Planar Circuit)
1. A planar circuit is one that can be drawn
in a plane with no branches crossing one
another; otherwise it is nonplanar
2. A circuit may have crossing branches and
still be planar if it can be redrawn such
that it has no crossing branches.
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis (Non Planar Circuit)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis (Non Planar Circuit)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis (Non Planar Circuit
Redraw)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis Steps
1. Assign mesh currents to the n meshes
2. Apply KVL to each of the n meshes. Use
Ohm’s law to express the voltages in
terms of the mesh currents.
3. Solve the resulting n simultaneous
equations to get the mesh currents.
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis (Eg 3.5)
Find branch current I1, I2, I3 in the circuit
using mesh analysis
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis (Eg 3.5)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis (Eg 3.5)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis (PP 3.5)
Find branch current I1, I2 in the circuit
using mesh analysis
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis (PP 3.5)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
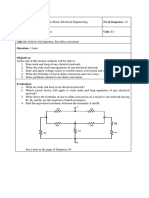
Mesh Analysis (Example extra 1)
Write the mesh equation for the following
circuit.
R1 R3 R5
VB1 R2 R4 VB2
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis (Example extra 1)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis (Example extra 2)
Find Vo for the following circuit.
4A
41V
2W 3W
2A Vo 6W 4W
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis (Example extra 2)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis (Example extra 3)
Find io for the following circuit.
Io
10Ω 24Ω
4Ω
24V
4I
12Ω o
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Mesh Analysis (Example extra 3)
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Quiz 1
Find Io for the following circuit.
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Quiz 1
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
Quiz 1
Electrical Principles I:BNR10203) © FTK UTHM 2018
By Dr.Lam Hong Yin All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Anna University Notes - 1Rk5Hv4ueYENIxdqJYc 4G8NXvJG33nPqDocument17 pagesAnna University Notes - 1Rk5Hv4ueYENIxdqJYc 4G8NXvJG33nPqbharathiv053No ratings yet
- Lab Manual (CSE133)Document18 pagesLab Manual (CSE133)Shreya Das 203-15-14489No ratings yet
- 19EEE181 ManualDocument39 pages19EEE181 ManualabcdNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument25 pagesLab ManualchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Prepared byDocument17 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Prepared bykrishnandrkNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcome 6: Know The Principles of Electricity As They Relate To The Mechanical Services IndustryDocument13 pagesLearning Outcome 6: Know The Principles of Electricity As They Relate To The Mechanical Services IndustrybendeniNo ratings yet
- PHY547 - LAb Manual-2019Document26 pagesPHY547 - LAb Manual-2019zulhaimirasheedNo ratings yet
- ES Unit-1Document48 pagesES Unit-1Mazin VoraNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor As A Switch: Ali Habeb Aseeri, Fouzeyah Rajab AliDocument6 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor As A Switch: Ali Habeb Aseeri, Fouzeyah Rajab AlishahzaibNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 4 Es NotesDocument233 pagesUnit 1 - 4 Es NotesAshish OraonNo ratings yet
- Electrical ScienceDocument2 pagesElectrical ScienceUjjwal KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Testing of M52A3B1 PrimersDocument29 pagesElectrostatic Testing of M52A3B1 Primersorpheus1972No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Engg. Lab ManualDocument54 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Engg. Lab Manualtanay jaiswal100% (2)
- Electrical Circuit Lab ReportDocument9 pagesElectrical Circuit Lab Reportapi-297082885100% (1)
- Short-Circuit Analysis of Industrial plant-IJAERDVO5IO346787 PDFDocument9 pagesShort-Circuit Analysis of Industrial plant-IJAERDVO5IO346787 PDFpriyanka236No ratings yet
- BH CurveDocument12 pagesBH CurvemohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 0 IntroductionDocument19 pagesChapter 0 IntroductionDƯƠNG NGUYỄN THÁI BÌNHNo ratings yet
- VL2020210106034 Ast03Document6 pagesVL2020210106034 Ast03M S MIHIR BHARADWAJNo ratings yet
- 10methods of Analysis ACDocument8 pages10methods of Analysis ACHusam A. Al-HaidriNo ratings yet
- Lecture Plan 3Document1 pageLecture Plan 3Sandeep SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- BH Khan Introduction To Sustainable EnergyDocument40 pagesBH Khan Introduction To Sustainable EnergyTushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- 21ELE13 - Module 5 P&D - BEEDocument13 pages21ELE13 - Module 5 P&D - BEEAffan KhanNo ratings yet
- The Device Parameters Simulation of Electrical Fast Transient GeneratorDocument6 pagesThe Device Parameters Simulation of Electrical Fast Transient GeneratorKen OhNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Training NewDocument273 pagesElectrical Safety Training NewagumsyahNo ratings yet
- AC II CDT3 Summary Unit1 4ECE3 MRDocument8 pagesAC II CDT3 Summary Unit1 4ECE3 MRShaik Mudassir NawazNo ratings yet
- Practical Applicationof Eddy Current Generated by WindDocument6 pagesPractical Applicationof Eddy Current Generated by WindMuhammad Heikal HasanNo ratings yet
- 6412 FundamentalsShort BK 20120716 Web PDFDocument14 pages6412 FundamentalsShort BK 20120716 Web PDFEduardo SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Transducer AssignmentDocument5 pagesTransducer AssignmentdagemNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Analysis of EMP Transient Electromagnetic Effect of AircraftDocument4 pagesSimulation and Analysis of EMP Transient Electromagnetic Effect of Aircraftreza mirzakhaniNo ratings yet
- Surge Current Protection Using Super Conductors: Chandupatla Sai Teja (160115734302)Document23 pagesSurge Current Protection Using Super Conductors: Chandupatla Sai Teja (160115734302)Mahendhar AnugulaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Noise Analysis of LiiionDocument9 pagesElectrochemical Noise Analysis of LiiionShubham RaizadaNo ratings yet
- EasyChair Preprint 8082 PDFDocument6 pagesEasyChair Preprint 8082 PDFLejandro CobarrubiasNo ratings yet
- EE103 Lecture10 BGF 06 Dec 2022Document21 pagesEE103 Lecture10 BGF 06 Dec 2022Raunak MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Science: Lecture-5: Topic-Nodal and Mesh AnalysisDocument13 pagesElectrical Science: Lecture-5: Topic-Nodal and Mesh Analysisi_khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Network TheoremsDocument5 pagesNetwork TheoremsSandeep SarmahNo ratings yet
- L-08-unit-1-Super Position TheoremDocument18 pagesL-08-unit-1-Super Position TheoremSumit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics Lab JournalDocument50 pagesApplied Physics Lab JournalSahendraNo ratings yet
- Physics Experiment Report (I) Basic Physics "Kirchoff's Law"Document8 pagesPhysics Experiment Report (I) Basic Physics "Kirchoff's Law"Ananda Natalia TuranganNo ratings yet
- Micro Electret Power GeneratorDocument5 pagesMicro Electret Power GeneratorOmkar DashNo ratings yet
- BEEE Module 3 TransformersDocument89 pagesBEEE Module 3 Transformersmanohar kintaliNo ratings yet
- An Investigation Into The Failure Mechanisms of Schottky Barrier Diodes, As Commonly Implemented As Bypass Diodes in Photovoltaic ModulesDocument9 pagesAn Investigation Into The Failure Mechanisms of Schottky Barrier Diodes, As Commonly Implemented As Bypass Diodes in Photovoltaic ModulesbitudayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Electromagnetic Induction Cutnell11eDocument45 pagesChapter 22 - Electromagnetic Induction Cutnell11ebob robNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Distribution & Utilization: Lab ManualDocument40 pagesElectrical Power Distribution & Utilization: Lab ManualUzair HussainNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Technical Loss in Distribution Line SyDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Technical Loss in Distribution Line SychimiwangmoNo ratings yet
- Latest Basic Electrical and Electronics Lab ManualsDocument96 pagesLatest Basic Electrical and Electronics Lab Manualspinev96397No ratings yet
- Short Circuit Current Algorithm and Software DesigDocument9 pagesShort Circuit Current Algorithm and Software Desigpran14nykNo ratings yet
- Van de Graaff Generator: By: CH - Anvesh Ad - No:160711734006Document18 pagesVan de Graaff Generator: By: CH - Anvesh Ad - No:160711734006Lalit AshokNo ratings yet
- Ferroresonance Dist TXDocument6 pagesFerroresonance Dist TXsno-koneNo ratings yet
- Wireless Ac Power Detector 1Document27 pagesWireless Ac Power Detector 1belacheweshetu222No ratings yet
- AER204Electrics and Electronics-Chapter 3Document22 pagesAER204Electrics and Electronics-Chapter 3tyoudalpenaNo ratings yet
- Applying Low Voltage CB To Limit Arc FlashDocument6 pagesApplying Low Voltage CB To Limit Arc FlashtechtricNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam JopiaDocument2 pagesMidterm Exam JopiaGABRIEL ABRAM JOPIANo ratings yet
- Lecture On:energy Storage Systems: Ontrol and Ntegration of Renewable Energy ResourcesDocument21 pagesLecture On:energy Storage Systems: Ontrol and Ntegration of Renewable Energy ResourcesSONU KUMARNo ratings yet
- Leiter2001 RIT15SDocument7 pagesLeiter2001 RIT15SРуслан РахимовNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Transformer Health Index Using Condition Situation Monitoring (CSM)Document10 pagesPrediction of Transformer Health Index Using Condition Situation Monitoring (CSM)IntekhabNo ratings yet
- 4-RTD - Dr.A.GangulyDocument12 pages4-RTD - Dr.A.GangulyAbhigyan GangulyNo ratings yet
- Fault Diaonosis Reerence 1Document9 pagesFault Diaonosis Reerence 1m.v.naidu.No ratings yet
- Eee BEE BEEE LAB MANUAL 10122019Document36 pagesEee BEE BEEE LAB MANUAL 10122019ale aleNo ratings yet
- Piezoelectric Actuators: Vector Control Method: Basic, Modeling and Mechatronic Design of Ultrasonic DevicesFrom EverandPiezoelectric Actuators: Vector Control Method: Basic, Modeling and Mechatronic Design of Ultrasonic DevicesNo ratings yet
- Assignment Math VectorDocument2 pagesAssignment Math VectormimiNo ratings yet
- Soalan KTDocument1 pageSoalan KTmimiNo ratings yet
- Proposal TemplateDocument7 pagesProposal TemplateIlham AdEeNo ratings yet
- Bengkel Aplikasi AMOS IPG 12 Mac 2019 PDFDocument9 pagesBengkel Aplikasi AMOS IPG 12 Mac 2019 PDFmimiNo ratings yet
- Nota MultimediaDocument84 pagesNota MultimediamimiNo ratings yet
- ListeningDocument4 pagesListeningmimiNo ratings yet
- ToolsDocument3 pagesToolsmimiNo ratings yet
- Ee Ah MengDocument1 pageEe Ah MengmimiNo ratings yet
- Hide Reveal AnimationDocument6 pagesHide Reveal AnimationmimiNo ratings yet
- HttpsDocument1 pageHttpsmimiNo ratings yet
- Ee Ah MengDocument1 pageEe Ah MengmimiNo ratings yet
- Excell NorazilaDocument2 pagesExcell NorazilamimiNo ratings yet
- Expository Essay English MPUDocument5 pagesExpository Essay English MPUmimiNo ratings yet
- BiDocument1 pageBimimiNo ratings yet
- Bi BlographyDocument4 pagesBi BlographymimiNo ratings yet
- Family + Student + School + Policymakers/Voters Student SuccessDocument13 pagesFamily + Student + School + Policymakers/Voters Student SuccessmimiNo ratings yet
- BiDocument1 pageBimimiNo ratings yet
- Bi BlographyDocument4 pagesBi BlographymimiNo ratings yet
- Laser Light Cable (LLK-B) Spare Parts CatalogDocument6 pagesLaser Light Cable (LLK-B) Spare Parts CatalogBuentello B GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Accelerometer MPU6050 Z-Axis 0-90-Degrees PWMDocument3 pagesAccelerometer MPU6050 Z-Axis 0-90-Degrees PWMDariusz BartniakNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER VII Direct Current CircuitsDocument28 pagesCHAPTER VII Direct Current CircuitsNandya GuvitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-17: Identifying Ports: IC Training - Module One: Computing FundamentalsDocument2 pagesLesson 1-17: Identifying Ports: IC Training - Module One: Computing FundamentalsVinMarNo ratings yet
- HV857 High Voltage EL Lamp Driver For Low Noise ApplicationsDocument14 pagesHV857 High Voltage EL Lamp Driver For Low Noise ApplicationsMaxim FalchenkoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 17 - Electrical Safety of Medical EquipmentDocument4 pagesLecture Notes 17 - Electrical Safety of Medical Equipmentnramanathan1No ratings yet
- Parameters of A Transmission LinesDocument26 pagesParameters of A Transmission LinesFrancis IlardeNo ratings yet
- Manual Party Light & Sound Party 15 PackDocument24 pagesManual Party Light & Sound Party 15 PackARTURO PEREZREVERTENo ratings yet
- XFX 750W Black Edition PSU Modular True Power Power SupplyDocument5 pagesXFX 750W Black Edition PSU Modular True Power Power SupplyPenyelongkar KonspirasiNo ratings yet
- Infineon CYW43455 DataSheet v16 00 enDocument121 pagesInfineon CYW43455 DataSheet v16 00 enOlivier AgbenonwossiNo ratings yet
- Implementation of AES Algorithm in UART Module For Secured Data TransferDocument1 pageImplementation of AES Algorithm in UART Module For Secured Data Transferblesson123No ratings yet
- DX20VC: High-Efficiency, Communicating, Variable-Speed, Inverter Drive Split System Air Conditioner Up To 24.5 SEERDocument20 pagesDX20VC: High-Efficiency, Communicating, Variable-Speed, Inverter Drive Split System Air Conditioner Up To 24.5 SEERJohn AristaNo ratings yet
- P 3 U 30Document120 pagesP 3 U 30ArcoolNo ratings yet
- Checking Data, I-CANDocument3 pagesChecking Data, I-CANWaldek KozlowskiNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Serving The Physician Since 1937Document72 pagesService Manual: Serving The Physician Since 1937JiThiN vPNo ratings yet
- Wollo UniversityDocument13 pagesWollo UniversitySISAy AyalewNo ratings yet
- Contract0r AgreementDocument13 pagesContract0r AgreementramadhanNo ratings yet
- DigiLink Technical Catalogue 2011Document44 pagesDigiLink Technical Catalogue 2011Anonymous gMgeQl1SndNo ratings yet
- DS - SG10KTL-MT Datasheet - V10 - EN PDFDocument1 pageDS - SG10KTL-MT Datasheet - V10 - EN PDFalbertusngNo ratings yet
- Tomasi Book PDFDocument191 pagesTomasi Book PDFJeremy JavierNo ratings yet
- STM 32 L 073 RZDocument157 pagesSTM 32 L 073 RZJuanal PulidoNo ratings yet
- Wallis SubmittalDocument87 pagesWallis Submittalsubmittal cetcNo ratings yet
- Miniature FusesDocument88 pagesMiniature FusesEliasNo ratings yet
- Chowdhury 2017Document11 pagesChowdhury 2017bhatttanmayhNo ratings yet
- HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen11 QuickspecsDocument103 pagesHPE ProLiant DL360 Gen11 QuickspecsJules ExNo ratings yet
- Harman Kardon AVR4000 110 210 310 510 2000 3000 5000Document78 pagesHarman Kardon AVR4000 110 210 310 510 2000 3000 5000Ivan MojsaNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: General-Purpose InverterDocument74 pagesInstruction Manual: General-Purpose Inverteranhthong3k100% (2)
- Ts 590sg Idm OkDocument76 pagesTs 590sg Idm OkLoco Soy Loco SoyNo ratings yet
- The Long and Short of Wires: Background KnowledgeDocument2 pagesThe Long and Short of Wires: Background KnowledgeNilar SanNo ratings yet
- E7125v1 0Document135 pagesE7125v1 0uti12345No ratings yet