Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Liver Abscess
Uploaded by
Bheru Lal100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
1K views18 pagesMedical & Surgical nursing
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentYou are on page 1of 18
Liver abscess
• A liver abscess is a collection of pus in the liver
caused by bacteria, fungi, or parasites. You
may have more than one abscess.
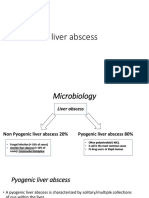
Types Of Liver Abscess
• There are three major forms of liver abscess,
classified by etiology:
– Pyogenic liver abscess, which is most often
polymicrobial, accounts for 80% of hepatic
abscess cases in the United States.
– Amoebic liver abscess due to Entamoeba
histolytica accounts for 10% of cases.
– Fungal abscess, most often due to Candida
species, accounts for less than 10% of cases.
Pyogenic Liver Abscess
Pyogenic Liver Abscess
• A pyogenic liver abscess is a type of liver abscess
caused by bacteria, can be single or multiple.
• The right lobe is affected twice as often as the
left; 5% have bilateral involvement.
• No cause found in 15% cases. Most are secondary
to infection originating in the abdomen. Bacterial
endocarditis and dental infection are other
causes.
• More common in the immunocompromised and
in people with Liver cirrhosis.
Pyogenic Liver Abscess
Amoebic Liver Abscess
• Amoebic liver abscess or amebiasis is a type of
liver abscess caused by Entamoeba Histolytica
(Protozoa).
• E. histolytica causes amoebic colitis and
dysentery but liver abscess is the most common
extra-intestinal manifestation of infection
• Route of entry via oro-fecal roue by ingestion of
contaminated food or water. Amoebae invade
intestinal mucosa and can gain access to the
portal venous system.
Amoebic Liver Abscess
• Causes a large necrotic area which is liquefied
into thick reddish-brown pus (Anchovy sauce
pus) due to liquefied necrosis, thrombosis of
blood vessels, lysis of liver cells
• It affects the right lobe in 80%.
• This type is common in overcrowded areas
with poor sanitation and in alcoholics.
Amoebic Liver Abscess
Fungal Liver Abscess
• Fungal abscesses is a less common type,
primarily due to Candida albicans and occur
in individuals with prolonged exposure to
antimicrobials, hematologic malignancies,
solid-organ transplants, and congenital and
acquired immunodeficiency.
What increases my risk for liver
abscess?
• Traveling to places where infection is common
• Age older than 70 years
• Medical conditions, such as cancer, diabetes,
or a weak immune system
• Medicines, such as steroids or chemotherapy
• Alcohol
• Poor nutrition
signs and symptoms
Pain in the upper right part of the abdomen, just
below the ribs
A cough, or feeling tired and weak
Fever and night sweats
Nausea or vomiting
Loss of appetite
Yellowing of the skin or the whites of the eyes
How is liver abscess diagnosed?
Blood tests will show which germ is causing
your infection.
An x-ray, ultrasound, CT, or MRI may show the
liver abscess.
Laboratory Studies
1. CBC
1. Increased WBC, usually Neutrophilic
Leukocytosis.
2. Raised erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
3. Mild normochromic normocytic anaemia.
2. Liver function studies
1. Hypoalbuminemia
2. Elevation of alkaline phosphatase
3. Elevations of transaminase and bilirubin levels (variable)
Laboratory Studies
3. Blood cultures are positive in roughly 50% of cases.
4. Stool DR: Stools can contain cysts or trophozoites of E.
histolytica.
5. Serology should be carried out if E. histolytica is suspected.
6. Culture of abscess fluid should be the goal in establishing
microbiologic diagnosis. Usually done through Percutaneous
needle aspiration (under CT or Ultrasound Guidance)
Imaging Study
1. Chest X-Ray: May show raised right hemi-diaphragm on.
2. Ultrasonography
a) Can show abscess and also allow guided percutaneous aspiration and
drainage and biliary tree examination. A Doppler ultrasound study
may be done to check for blood flow in your liver.
3. CT scanning
a) Can show the abscess, allow guided aspiration and drainage and
show other intra-abdominal abscesses or a possible cause such as
diverticular disease, appendicitis, etc. It is good for the detection of
small abscesses.
4. Liver Scan
5. MRI
How is liver abscess treated?
• Medicine can help treat an infection caused by bacteria, a fungus,
or a parasite.
• Needle aspiration is a procedure to drain fluid with a needle.
• Catheter drainage is a procedure to drain fluid through a catheter
inserted into an incision.
• Surgery may be needed if your abscess is large or if you have more
than one. Surgery may also be needed if your abscess bursts.
How can I manage my symptoms?
Eat a variety of healthy foods. Healthy foods
include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain breads,
low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats, and
fish.
Do not drink alcohol. Alcohol can damage your
liver and increase your risk for another abscess.
Liver Abscess (cont.)
Medical Mgt.
surgical drainage of abscess and antibiotics
Metronidazole (Flagyl), Chloroquine, Emetine for amoebic abscesses
Nursing Mgt.
provide adequate fluids and nutrition
provide comfort measures for fever, pruritus
- coal sponge baths - prevention of dry skin
- use of soft linens - provide cool environment
frequent oral hygiene
pt. education
complete dose of medications (several weeks to months) to prevent
recurrence
monitor for signs of recurrence or worsening hepatic function
cirrhosis
proper hygiene, drink clean water and avoid uncooked foods
You might also like
- AppendicitisDocument17 pagesAppendicitisAhmed Halaby100% (1)
- HerniasDocument64 pagesHerniasKalpana SubediNo ratings yet
- Esophageal ObstructionDocument18 pagesEsophageal ObstructionArun Murali50% (2)
- Clinical Presentation on TonsillectomyDocument46 pagesClinical Presentation on TonsillectomySREEDEVI T SURESH100% (1)
- Gastric Cancer: Calag, Prescilla Tavas, Charme FayeDocument20 pagesGastric Cancer: Calag, Prescilla Tavas, Charme FayeDareRaymond0% (1)
- Bladder TraumaDocument13 pagesBladder TraumaBernardNo ratings yet
- Pyloric StenosisDocument18 pagesPyloric StenosisAnkita Samanta0% (1)
- Appendectomy Procedure GuideDocument36 pagesAppendectomy Procedure GuidedeathwishesNo ratings yet
- Food Poisoning Classification: Bacterial TypesDocument19 pagesFood Poisoning Classification: Bacterial TypesJohnykutty Joseph100% (2)
- HerniaDocument41 pagesHerniashobharamkrishna67% (3)
- Esophageal CADocument25 pagesEsophageal CADan Kenneth83% (6)
- MastitisDocument12 pagesMastitismanal at100% (1)
- The Major Differences Between Diarrhea and DysenteryDocument2 pagesThe Major Differences Between Diarrhea and DysenteryZee Yong100% (1)
- CholelithiasisDocument65 pagesCholelithiasisGAURAV0% (1)
- Intestinal Obstruction: MSU Medical Students. Batch 2. Group 2Document31 pagesIntestinal Obstruction: MSU Medical Students. Batch 2. Group 2Qp Nizam100% (2)
- JaundiceDocument29 pagesJaundiceMurali TiarasanNo ratings yet
- Case Study FistulectomyDocument94 pagesCase Study FistulectomyQuolette Constante80% (5)
- Blindness 191024143246 PDFDocument8 pagesBlindness 191024143246 PDFMamta KumariNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis PPT 1Document30 pagesAppendicitis PPT 1Prashant Mishra100% (1)
- Surgical CP ParotidDocument43 pagesSurgical CP ParotidValarmathiNo ratings yet
- Sigmoid Volvulus: Rashid Swed S. (Md4) Mwanyingili John A. (Md3)Document46 pagesSigmoid Volvulus: Rashid Swed S. (Md4) Mwanyingili John A. (Md3)Amani Twaha MsemakweliNo ratings yet
- Vulvitis, Vaginitis, Bartholin's Cyst and CervicitisDocument56 pagesVulvitis, Vaginitis, Bartholin's Cyst and CervicitisSushma Thakuri100% (1)
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument120 pagesIntestinal ObstructionHussam Abdur RabNo ratings yet
- 3 - Diagnosis of PregnancyDocument5 pages3 - Diagnosis of PregnancyM7 AlfatihNo ratings yet
- Case Management of Ari at PHC LevelDocument29 pagesCase Management of Ari at PHC Levelapi-3823785No ratings yet
- A Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Planned Teaching Programme On Knowledge Regarding Eating Disorders Among Adolescent Girls in The Selected Schools of Jabalpur City, MPDocument8 pagesA Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Planned Teaching Programme On Knowledge Regarding Eating Disorders Among Adolescent Girls in The Selected Schools of Jabalpur City, MPEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyBandana RajpootNo ratings yet
- Swine FluDocument4 pagesSwine FluNader Smadi100% (2)
- ASTHMADocument16 pagesASTHMAAyesigwa Gerald96100% (1)
- Everything You Need to Know About AnemiaDocument45 pagesEverything You Need to Know About AnemiaZeeshan Ahmed67% (3)
- ICD Insertion and ManagementDocument44 pagesICD Insertion and Managementvamshidh100% (1)
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument21 pagesIntestinal ObstructionBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Urinary RetentionDocument24 pagesUrinary RetentionMuhammad Amri Kautsar100% (1)
- Cancer Colon and Rectum (Wardah)Document23 pagesCancer Colon and Rectum (Wardah)WardahAliNo ratings yet
- Examination of Inguinal HerniaDocument3 pagesExamination of Inguinal HerniaNoor Ul AinNo ratings yet
- Drug Presentation On AminophyllineDocument10 pagesDrug Presentation On Aminophyllineelisha immanuelNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of LabourDocument28 pagesMechanism of LabourVanitha NNo ratings yet
- Liver AbscessDocument15 pagesLiver AbscessAli Aborges Jr.No ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction: Yohannes TDocument34 pagesIntestinal Obstruction: Yohannes TVincent Ser100% (1)
- Appendicitis Nursing NotesDocument2 pagesAppendicitis Nursing NotesFreeNursingNotes33% (3)
- Cholelithiasis SneDocument12 pagesCholelithiasis SneSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Case Study of HypospadiaDocument19 pagesCase Study of Hypospadiagaylenice100% (10)
- Pregnancy Diagnosis StagesDocument25 pagesPregnancy Diagnosis StagesA suhasiniNo ratings yet
- Inguinal Hernia by Dr. TalabiDocument16 pagesInguinal Hernia by Dr. TalabidayomanNo ratings yet
- Malabsorption Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument5 pagesMalabsorption Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentPriyaNo ratings yet
- Case Study TBDocument9 pagesCase Study TBCheche_Guinto_8235100% (2)
- Urethritis PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesUrethritis PathophysiologyMonica Melo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument9 pagesIntestinal ObstructionHamss AhmedNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease FDocument51 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease FSharmila Laxman Dake100% (2)
- CVADocument22 pagesCVAPankaj Shahi100% (1)
- Types of Shock: Ms. Saheli Chakraborty 2 Year MSC Nursing Riner, BangaloreDocument36 pagesTypes of Shock: Ms. Saheli Chakraborty 2 Year MSC Nursing Riner, Bangaloremalathi100% (6)
- Seminar 6 Approach To Neonatal JaundiceDocument50 pagesSeminar 6 Approach To Neonatal JaundiceKelvin Su100% (1)
- Ascariasis: Roundworm Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument18 pagesAscariasis: Roundworm Ascaris LumbricoidesSuneel Kumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Morning SessionDocument20 pagesWelcome To The Morning SessionGENERAL sharpNo ratings yet
- Phimosis and Paraphimosis: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument14 pagesPhimosis and Paraphimosis: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDhella 'gungeyha' RangkutyNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Gastric Outlet ObstructionDocument37 pagesCase Study On Gastric Outlet ObstructionJunayed Safar Mahmud100% (4)
- Heart Block: BY DR - AriyalakshmiDocument26 pagesHeart Block: BY DR - AriyalakshmiDiksha chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy &physiology JaundiceDocument2 pagesAnatomy &physiology JaundiceHCX dghhqNo ratings yet
- Liver InfectionsDocument53 pagesLiver Infectionsdemiana shawkyNo ratings yet
- AMEBIASIS GUIDEDocument31 pagesAMEBIASIS GUIDELino ShpNo ratings yet
- Post RN BSN 29.10.2019Document121 pagesPost RN BSN 29.10.2019moin udddinNo ratings yet
- A2 Biology Homeostasis Assignment: by Samir BabaldinDocument13 pagesA2 Biology Homeostasis Assignment: by Samir BabaldinNahla TammamNo ratings yet
- 10 Biology 1-16-07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDocument34 pages10 Biology 1-16-07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsErivieNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Proudly Presents byDocument23 pagesHomeostasis: Proudly Presents byBheru LalNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument45 pagesEndocrineKatrina JornadalNo ratings yet
- CNA LPN Curriculum 11 March 2013Document72 pagesCNA LPN Curriculum 11 March 2013Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- PMDC Curriculum 2011 PDFDocument170 pagesPMDC Curriculum 2011 PDFRao Rizwan ShakoorNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument2 pagesHomeostasisImelda Verawaty Lumban GaolNo ratings yet
- Policy Guidelines For Nursing Education in Pakista - 220418 - 132804Document3 pagesPolicy Guidelines For Nursing Education in Pakista - 220418 - 132804Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- Anak JurnalDocument10 pagesAnak JurnallolytaindahNo ratings yet
- HEC BSN 4 YearDocument254 pagesHEC BSN 4 Yearkhizar hayatNo ratings yet
- BSCSyllabus 2019-20 PDFDocument251 pagesBSCSyllabus 2019-20 PDFAmrita Charlotte KapoorNo ratings yet
- Outpatient Treatment of Severe Acute MalnutritionDocument7 pagesOutpatient Treatment of Severe Acute MalnutritionBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Status of Children Admitted For DiarrhoealDocument4 pagesNutritional Status of Children Admitted For DiarrhoealBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Assessment of Children AdmittedDocument8 pagesNutritional Assessment of Children AdmittedBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Practices Among Ethnic Minorities and ChildDocument8 pagesNutritional Practices Among Ethnic Minorities and ChildBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Joosten2009 Nationa Malnutrition Screening Days in Hospitalised Children in The NetherlandsDocument6 pagesJoosten2009 Nationa Malnutrition Screening Days in Hospitalised Children in The NetherlandsHaggai Daniel SaudaleNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Midupper Arm Circumference and Weight-For-height ZDocument6 pagesComparison of Midupper Arm Circumference and Weight-For-height ZBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Malnutrition in Children Admitted To HospitalDocument7 pagesMalnutrition in Children Admitted To HospitalBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Nutritional Status in Children AdmittedDocument7 pagesEvaluation of The Nutritional Status in Children AdmittedBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Outpatient TherapeuticDocument9 pagesEvaluation of Outpatient TherapeuticBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Malnutrition Among Children Under 5 Does NotDocument16 pagesMalnutrition Among Children Under 5 Does NotBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Diagnostik Criteria Severe Acute Malnutrition Aged 0-6 BulanDocument9 pagesDiagnostik Criteria Severe Acute Malnutrition Aged 0-6 BulanirenaNo ratings yet
- Economic Cost of Community-BasedDocument14 pagesEconomic Cost of Community-BasedBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Community-Based Management of Acute MalnutritionDocument9 pagesCommunity-Based Management of Acute MalnutritionBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Community-Based Management of Severe Acute Malnutrition in IndiaDocument13 pagesCommunity-Based Management of Severe Acute Malnutrition in IndiaBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Early Childhood Undernutrition Increases Risk of Hearing Loss in YoungDocument10 pagesEarly Childhood Undernutrition Increases Risk of Hearing Loss in YoungBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Intervention of MalnutritionDocument11 pagesAnalysis and Intervention of MalnutritionBheru LalNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Digestive System: StructuresDocument18 pagesCH 8 Digestive System: StructuresBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Health Assessment: Akram Mohammad Abusalah BNS, MSN, Ph. D. Islamic University of Gaza StripDocument262 pagesNursing Health Assessment: Akram Mohammad Abusalah BNS, MSN, Ph. D. Islamic University of Gaza StripBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Practice 8A - Sofía Sendín PDFDocument1 pageVocabulary Practice 8A - Sofía Sendín PDFSofia SendinNo ratings yet
- The LoversDocument4 pagesThe LoversabnerdormiendoNo ratings yet
- Salem RPGDocument16 pagesSalem RPGabstockingNo ratings yet
- Silk Road Journal 6-2Document69 pagesSilk Road Journal 6-2Ciro Lo MuzioNo ratings yet
- Eucoelomates Lab ReportDocument13 pagesEucoelomates Lab Reportsatvindar singhNo ratings yet
- Noun Practice PagesDocument6 pagesNoun Practice PagesMaggie Plby100% (1)
- Card ListDocument32 pagesCard ListAntonio DelgadoNo ratings yet
- S9.1 Laboratory Work TextDocument4 pagesS9.1 Laboratory Work TextJennie Jane LobricoNo ratings yet
- Michael Chinery-Insects of Britain and Western Europe-Revised 2007 EditionDocument324 pagesMichael Chinery-Insects of Britain and Western Europe-Revised 2007 EditionDIPOLMEDIA100% (6)
- Charting A Path Forward: Reaching California's Policy To Save All Adoptable and Treatable AnimalsDocument57 pagesCharting A Path Forward: Reaching California's Policy To Save All Adoptable and Treatable AnimalscashelteringreportNo ratings yet
- A2.student. Parts of The BodyDocument4 pagesA2.student. Parts of The BodyLaia MartíNo ratings yet
- GOMERA BSBA FM-1 Gods of EgyptDocument3 pagesGOMERA BSBA FM-1 Gods of EgyptGOMERA, ENGELONo ratings yet
- Shadowdark RPG - Welcome Pack - BWDocument17 pagesShadowdark RPG - Welcome Pack - BWVal89% (9)
- CH 12 Word ListDocument3 pagesCH 12 Word ListtigertiaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map - Abby !Document2 pagesConcept Map - Abby !Abegail Abaygar100% (3)
- MeerkatDocument4 pagesMeerkatCont JocNo ratings yet
- Rapid Assessment SheetDocument5 pagesRapid Assessment SheetElise HowardNo ratings yet
- Gamefowl Fighting Styles!Document27 pagesGamefowl Fighting Styles!Lawrence TumaponNo ratings yet
- Clinical MicrosDocument54 pagesClinical MicrosLois DanielleNo ratings yet
- Animal Farm / Chapter 8 Reading Organizer Sample AnswersDocument7 pagesAnimal Farm / Chapter 8 Reading Organizer Sample AnswersJacques SnicketNo ratings yet
- Retrogressive Metamorphosis in Herdmania-1Document2 pagesRetrogressive Metamorphosis in Herdmania-1G. ShilpaNo ratings yet
- The Porn Circuit - Covenant Eye - DesconocidoDocument47 pagesThe Porn Circuit - Covenant Eye - DesconocidoirvmacNo ratings yet
- One Thousand Magical Herbs and FungiDocument16 pagesOne Thousand Magical Herbs and FungiSayanSanyal100% (1)
- IZZ - PiodermaDocument51 pagesIZZ - PiodermavivilmNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greek Myths and Their OriginsDocument28 pagesAncient Greek Myths and Their OriginsJenny WoychukNo ratings yet
- VSDDocument4 pagesVSDtikabdullahNo ratings yet
- OZ 02 The Marvelous Land of OzDocument62 pagesOZ 02 The Marvelous Land of Ozbunnycat666No ratings yet
- Getting The Main Idea Answer KeyDocument2 pagesGetting The Main Idea Answer KeyMuh Azan100% (1)
- GanapathyDocument5 pagesGanapathybravindranath5768No ratings yet
- Story-Telling Competition Title: The Milkmaid and Her PailDocument6 pagesStory-Telling Competition Title: The Milkmaid and Her PailCoffee&LoveNo ratings yet