Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Non Conventional RAC
Uploaded by
Dhruv Patel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views18 pagesVortex tube refrigeration uses compressed air as a refrigerant. It consists of a nozzle, diaphragm, valve, hot side and cold side. Compressed air passes through the nozzle and acquires high velocity, creating a vortex flow in the chamber. The valve restricts this flow. Some air reverses direction through the core and cools below inlet temperature, while air in the forward direction heats up. It has advantages like simplicity, no moving parts or refrigerants, and low cost. However, its low COP and capacity limit widespread use. Applications include industries requiring simultaneous hot and cold air, spot cooling electronics, body cooling in mines, and cooling cutting tools.
Original Description:
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentVortex tube refrigeration uses compressed air as a refrigerant. It consists of a nozzle, diaphragm, valve, hot side and cold side. Compressed air passes through the nozzle and acquires high velocity, creating a vortex flow in the chamber. The valve restricts this flow. Some air reverses direction through the core and cools below inlet temperature, while air in the forward direction heats up. It has advantages like simplicity, no moving parts or refrigerants, and low cost. However, its low COP and capacity limit widespread use. Applications include industries requiring simultaneous hot and cold air, spot cooling electronics, body cooling in mines, and cooling cutting tools.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views18 pagesNon Conventional RAC
Uploaded by
Dhruv PatelVortex tube refrigeration uses compressed air as a refrigerant. It consists of a nozzle, diaphragm, valve, hot side and cold side. Compressed air passes through the nozzle and acquires high velocity, creating a vortex flow in the chamber. The valve restricts this flow. Some air reverses direction through the core and cools below inlet temperature, while air in the forward direction heats up. It has advantages like simplicity, no moving parts or refrigerants, and low cost. However, its low COP and capacity limit widespread use. Applications include industries requiring simultaneous hot and cold air, spot cooling electronics, body cooling in mines, and cooling cutting tools.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
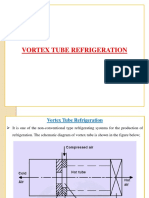
Non conventional Refrigeration: Vortex tube refrigeration
• Vortex Tube Refrigeration:
• It consists of nozzle, diaphragm,
valve, hot-air side, cold-air side.
• The nozzles are of converging or
diverging or converging-diverging
type as per the design.
• An efficient nozzle is designed to
have higher velocity, greater mass
flow and minimum inlet losses.
• Chamber is a portion of nozzle and
facilities the tangential entry of high
velocity air-stream into hot side
• Vortex Tube Refrigeration:
• Generally the chambers are not of
circular form, but they are gradually
converted into spiral form.
• Hot side is cylindrical in cross
section and is of different lengths as
per design.
• Vortex Tube Refrigeration:
• Valve obstructs the flow of air
through hot side and it also controls
the quantity of hot air through vortex
tube.
• Diaphragm is a cylindrical piece of
small thickness and having a small
hole of specific diameter at the center.
• Air stream traveling through the core
of the hot side is emitted through the
diaphragm hole. Cold side is a
cylindrical portion through which
cold air is passed.
• Working:
• Compressed air is passed through the
nozzle. Here, air expands and
acquires high velocity due to
particular shape of the nozzle.
• A vortex flow is created in the
chamber and air travels in spiral like
motion along the periphery of the hot
side.
• This flow is restricted by the valve.
• When the pressure of the air near
valve is made more than outside by
partly closing the valve, a reversed
axial flow through the core of the hot
side starts from high-pressure region
to low-pressure region.
• During this process, heat transfer
takes place between reversed stream
and forward stream.
• Therefore, air stream through the
core gets cooled below the inlet
temperature of the air in the vortex
tube, while air stream in forward
direction gets heated up.
Advantages:
1) It uses air as refrigerant, so there is
no leakage problem.
2) Vortex tube is simple in design and
it avoids control systems.
3) There are no moving parts in vortex
tube.
4) It is light in weight and requires less
space.
Advantages:
5) Initial cost is low and its working
expenses are also less, where
compressed air is readily available.
6) Maintenance is simple and no
skilled labours are required.
Advantages:
5) Initial cost is low and its working
expenses are also less, where compressed
air is readily available.
6) Maintenance is simple and no skilled
labours are required.
Disadvantages:
1) It‟s low COP, limited capacity and only
small portion of the compressed air
appearing as the cold air limits its wide use
in practice.
Applications:
1) Vortex tubes are extremely small and as
it produce hot as well as cold air. It may be
of use in industries where both are
simultaneously required.
2) Temperature as low as –50°C can be
obtained without any difficulty, so it is very
much useful in industries for spot cooling
of electronic components.
3) It is commonly used for body cooling of
the workers in mines.
4) Used as laboratory sample cooler
5) Spot cooling like cooling of cutting tools.
You might also like
- 3.7 Vortex Tube RefrigerationDocument6 pages3.7 Vortex Tube RefrigerationShaik mahammad ArifNo ratings yet
- Vortex Tube For Cabine CoolingDocument12 pagesVortex Tube For Cabine Coolingamit kumarNo ratings yet
- Vortex Tube For Cabine CoolingDocument12 pagesVortex Tube For Cabine Coolingamit kumarNo ratings yet
- ME 310a Steam Turbines: Cooling TowersDocument33 pagesME 310a Steam Turbines: Cooling Towersshivkumar shindeNo ratings yet
- Air CycleDocument30 pagesAir CycleSalokya KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower: Presented by Anis Abbas ME-1Document36 pagesCooling Tower: Presented by Anis Abbas ME-1muddasirmasoodNo ratings yet
- Condenser Cooling Towers 216Document28 pagesCondenser Cooling Towers 216rajushamla9927No ratings yet
- CondensersDocument25 pagesCondensersARSAL HASHMINo ratings yet
- Vortex Tube Steam Jet RefrigerationDocument14 pagesVortex Tube Steam Jet RefrigerationDInesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Steam CondenserDocument26 pagesSteam CondenserPushkar Pandit100% (1)
- Cooling TowerDocument22 pagesCooling TowerFatin AnisahNo ratings yet
- Vacuum SystemDocument28 pagesVacuum SystemSam100% (1)
- Vacuum SystemDocument28 pagesVacuum SystemDalveer SinghNo ratings yet
- ADV Refrigeration System Using FlashchamberDocument40 pagesADV Refrigeration System Using FlashchamberAwesm RishuNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer EquipmentsDocument24 pagesHeat Transfer EquipmentsCynosure SkyNo ratings yet
- Compressors: - Single Stage - Two Stage CompressorDocument25 pagesCompressors: - Single Stage - Two Stage CompressorsonirocksNo ratings yet
- CT PrsentationDocument47 pagesCT PrsentationArvind ANo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower: Refrigeration and Air Conditioning LabDocument40 pagesCooling Tower: Refrigeration and Air Conditioning LabEngr Saad Bin SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Vacuum SystemDocument49 pagesVacuum Systemssmith2007100% (3)
- Cooling Tower Mto-2017Document28 pagesCooling Tower Mto-2017Priyank kanjariyaNo ratings yet
- RAC 2021-22 Unit 3 CH 1 P 3Document26 pagesRAC 2021-22 Unit 3 CH 1 P 3Aniket BhattaNo ratings yet
- Unit 22 CondensersDocument26 pagesUnit 22 CondensersDebapratim Debnath0% (1)
- Designing Aspects of A Vortex Tube Cooling System: Mahesh Kumar Dhangar, Manujendrasharma, Mangu Singh ChouhanDocument5 pagesDesigning Aspects of A Vortex Tube Cooling System: Mahesh Kumar Dhangar, Manujendrasharma, Mangu Singh Chouhanabcpqr123456No ratings yet
- Vent IllationDocument86 pagesVent Illation73 Tanmay JanawadeNo ratings yet
- EvaporatorsDocument37 pagesEvaporatorsGerald JobNo ratings yet
- Hvac Systems ComponentsDocument28 pagesHvac Systems ComponentsArvind RNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Cooling Towers Etabs StadDocument33 pagesAnalysis and Design of Cooling Towers Etabs StadMohammed MurtuzaNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger ClasificationDocument55 pagesHeat Exchanger ClasificationNikhil Sawant100% (1)
- Grou5 AirConditioner Assignment5Document17 pagesGrou5 AirConditioner Assignment5AnkurMahantyNo ratings yet
- Fabrication and Performance Analysis of A Vortex Tube Refrigeration SystemDocument5 pagesFabrication and Performance Analysis of A Vortex Tube Refrigeration SystemMaheshNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration: "Refrigeration Is The Process of Removing Heat From An Enclosed Space, orDocument16 pagesRefrigeration: "Refrigeration Is The Process of Removing Heat From An Enclosed Space, ordjgondalNo ratings yet
- Unit 22 CondensersDocument42 pagesUnit 22 CondenserssprotkarNo ratings yet
- EME PPT (For 32 To 35) by DivyeshDocument24 pagesEME PPT (For 32 To 35) by DivyeshDivyesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Thermo CycleDocument15 pagesThermo CycleMohamad Afiq Amiruddin ParnonNo ratings yet
- EvaporatorDocument17 pagesEvaporatorJudith EspenidoNo ratings yet
- Air CompressorsDocument23 pagesAir CompressorssubscruNo ratings yet
- 1 - Blow-Thru Vs Draw-ThruxDocument2 pages1 - Blow-Thru Vs Draw-ThruxtehtehtehNo ratings yet
- Heating Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Document12 pagesHeating Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Atia Khursheed50% (2)
- Vortex Tube RefrigerationDocument3 pagesVortex Tube RefrigerationSUMITNo ratings yet
- Condenser: By: Ragragio, Millaine Joy EDocument11 pagesCondenser: By: Ragragio, Millaine Joy ELaine RagragioNo ratings yet
- Vortex Tube NewDocument14 pagesVortex Tube NewneerajNo ratings yet
- Vortex Tube ManufacturingDocument3 pagesVortex Tube ManufacturingSameer JainNo ratings yet
- Fans and Blowers: Jade B. Cortes Bsme - 4Document20 pagesFans and Blowers: Jade B. Cortes Bsme - 4Tricia Kate TungalaNo ratings yet
- Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers: LectureDocument39 pagesAir-Cooled Heat Exchangers: LectureBaraa Shurbaji No 111No ratings yet
- Basic Air Conditioning System.2022 NotesDocument25 pagesBasic Air Conditioning System.2022 NotesKITSAO SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning SystemannNo ratings yet
- PHT Open Ended Laboratory Report: SUBMITTED BY: 2018-CH-58Document9 pagesPHT Open Ended Laboratory Report: SUBMITTED BY: 2018-CH-58Muhammad Suleman AttariNo ratings yet
- Air Cooler PresentationDocument9 pagesAir Cooler Presentationarcduke100% (3)
- Lecture 5Document23 pagesLecture 5Shubham SinghNo ratings yet
- EvaporatorDocument24 pagesEvaporatorS R Akhil Krishnan100% (1)
- CondensorDocument20 pagesCondensorLaka 98No ratings yet
- Unit 45Document53 pagesUnit 45Irfan KhanNo ratings yet
- FMM PBLDocument8 pagesFMM PBLsarveshkulkarni1810No ratings yet
- Research 1 - Mechanical System BU2Document17 pagesResearch 1 - Mechanical System BU2Zachary Yassir GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Vacuum SystemDocument28 pagesVacuum SystemManinder Cheema100% (1)
- Fin Tube Heat ExchangerDocument8 pagesFin Tube Heat ExchangerPrabhavJainNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Condensers and EvaporatorsDocument32 pagesPresentation On Condensers and Evaporatorsvipul sharma100% (1)
- Module 5-Multi-Stage Air CompressorDocument26 pagesModule 5-Multi-Stage Air Compressoramit3184No ratings yet
- Condenser S and Cooling Towers: By, Prof. M.B. GohilDocument55 pagesCondenser S and Cooling Towers: By, Prof. M.B. Gohilanilm130484meNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&AFrom EverandAir Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&ANo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronic Measurements Model Curriculum 2020-21Document1 pageElectrical & Electronic Measurements Model Curriculum 2020-21devi ji0% (1)
- Aromatic Waters - Liniments Lab NotesDocument9 pagesAromatic Waters - Liniments Lab NotesElaine Sombrano100% (7)
- Lab Session 13: Generics in JavaDocument11 pagesLab Session 13: Generics in JavaParsa ShereenNo ratings yet
- Ece Scheme-2017 IIIIV Sem SyllabusDocument42 pagesEce Scheme-2017 IIIIV Sem Syllabusapi-279049687No ratings yet
- Soal Soal Bahasa InggrisDocument14 pagesSoal Soal Bahasa Inggrisnur hidayahNo ratings yet
- Applied Business Tools and Technologies: A. Activation of Prior KnowledgeDocument12 pagesApplied Business Tools and Technologies: A. Activation of Prior KnowledgeClaire CarpioNo ratings yet
- Wauu (MKW) - RendaniDocument3 pagesWauu (MKW) - RendaniAbang FayyadNo ratings yet
- Standard Chartered PLC Is A British Multinational BankingDocument8 pagesStandard Chartered PLC Is A British Multinational Bankingaditya saiNo ratings yet
- FA2 Syllabus and Study Guide 2021-22Document11 pagesFA2 Syllabus and Study Guide 2021-22Aleena MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Department of Labor: cm-915Document2 pagesDepartment of Labor: cm-915USA_DepartmentOfLaborNo ratings yet
- Termination of Employment in The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesTermination of Employment in The PhilippinesGerry MalgapoNo ratings yet
- Sectoral AnalysisDocument416 pagesSectoral AnalysisNICOLE EDRALINNo ratings yet
- ICDS Practical IssuesDocument43 pagesICDS Practical IssuesSushil KumarNo ratings yet
- Acs JPCC 5b06515Document20 pagesAcs JPCC 5b06515hemedi kitilaNo ratings yet
- Le Et Al v. ArciTerra Group, LLC - Document No. 7Document2 pagesLe Et Al v. ArciTerra Group, LLC - Document No. 7Justia.comNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Types of Objectivs - Learning ObjectivesDocument20 pages1.3 Types of Objectivs - Learning ObjectivesGustavoCuellarNo ratings yet
- FortiWiFi and FortiAP-6.4-CookbookDocument113 pagesFortiWiFi and FortiAP-6.4-CookbookЖастлек ТолешевNo ratings yet
- Fee Schedule For The 2021-2022 School Year: Rate OptionsDocument1 pageFee Schedule For The 2021-2022 School Year: Rate OptionsABC News 4No ratings yet
- ITCC in Riyadh Residential Complex J10-13300 01300-1 SubmittalsDocument4 pagesITCC in Riyadh Residential Complex J10-13300 01300-1 SubmittalsuddinnadeemNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research ProposalDocument42 pagesMarketing Research ProposalFahmida HaqueNo ratings yet
- BME-02 Initial Testing and EvaluationDocument2 pagesBME-02 Initial Testing and EvaluationPAPPU RANJITH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Navigating The Landscape of Higher Engineering EducationDocument120 pagesNavigating The Landscape of Higher Engineering EducationWatchara KhoviNo ratings yet
- Geography SyllabusDocument4 pagesGeography SyllabusmvrthedocNo ratings yet
- Install Bootloader and Extra To EFI PartitionDocument4 pagesInstall Bootloader and Extra To EFI PartitionAionesei VasileNo ratings yet
- The Return of "Patrimonial Capitalism": in The Twenty-First CenturyDocument16 pagesThe Return of "Patrimonial Capitalism": in The Twenty-First CenturyjlgallardoNo ratings yet
- Panera Bread Holiday MenuDocument8 pagesPanera Bread Holiday MenuAbby VanbrimmerNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project "Addressing Marketing and Growth Issues of Chattha's Pakistani Street Food" BBA-8Document143 pagesFinal Year Project "Addressing Marketing and Growth Issues of Chattha's Pakistani Street Food" BBA-8Muhammad Humayun KhanNo ratings yet
- Data BaseDocument8 pagesData BaseoolalaiNo ratings yet
- Uk Earthing Systems and RF EarthingDocument5 pagesUk Earthing Systems and RF Earthingapi-267600826No ratings yet