Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CT Dimension Ing
Uploaded by
Farhan ShahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CT Dimension Ing
Uploaded by
Farhan ShahCopyright:
Available Formats
s
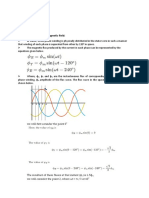
Theory of Protection Co-ordination
in Power Transmission and Distribution Systems
Current Transformer
Dimensioning
Siemens AG, PTD SE NC 5
Postfach 3220, 91050 Erlangen
Paul-Gossen-Straße 100
Tel +49 9131 7- 34324
Fax +49 9131 7- 35017
andrzej.bachry@siemens.com
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Instrument Transformer
Dimensioning, Page 1
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Different Measuring Methods I
Current Voltage
Inductive
Rogowski-Coil Inductive
Ohmic Ohmic
Inductive/Optical Capacitive
Optical
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 2
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Different Measuring Methods II
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 3
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 4
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Principle of Current Measurement Using Farraday Effect
Fibre Input H Fibre Output
linear Rotation of plane of
polarization polarization by angle ρ~N·I
Ey Ey
Ex I Ex
Fibre coil
with N windings
current carrying conductor
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 5
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Optical Current Transducer as a part of circuit-breaker Assembly
Add-On Scheme: Integrated Scheme:
Sensor Head
Sensor Head
Optical Fibre Cable
with Composite Insulator Optical Fibre Cable
with Composite Insulator
Interface Electronics housed in Interface Electronics housed in
breaker control unit breaker control unit
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 6
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Principle of Voltage Measurement Using Pockels Effect
Pockels crystal
E
Electric Field E<0 E=0 E>0
~ Voltage
Ey
Fibre Output
Elliptical Polarization
Ex
Fibre Input
Circular Polarization
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 7
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Electrooptic Potential Transformer for GIS
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 8
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Annealed Fibre Current Transformer
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 9
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Dimensioning Criteria
Requirements of modern relays
Installation points
Relay functions
Relay burden, cable burden and CT burden
Technical criteria Short-circuit current and system time constant
CT-Ratio, Accuracy Limiting Factor, Nominal Burden,
Class, Knee- Point Voltage
Customer criteria Requirements of relays in use
Habits
Tender invitation
National standards
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 10
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
International Standards
Important Standards
IEC 60044-1 1996/12 Current Transformers
IEC 60044-1 2000/07 Current Transformers (amendment 1)
IEC 60044-6 1992/03 Current Transformers (transient performance TP)
IEC 60044-2 1997/02 Voltage Transformers
BS EN 60044-1 Current Transformers
ANSI C57.13/1993 Current Transformers
AS 1675-1986 Current Transformers
IEC 185/1978 obsolete !
BS 7626/1993 obsolete !
BS 3938/1973 obsolete !
VDE 0414 Specifications for Instrument Transformers
Additional
CEI (Italy) SEN (Sweden)
CSA (Canada) SEU (Suisse)
NF (France) ABNT (Brasil)
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 11
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
CT: Equivalent Circuit
CT
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 12
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Saturation Effect
ip
is
0
20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 t/ms
U/V 5 P10 60 VA
L RCT LZ RZ Ritz
iP iM 900
Lb Pfiffner
Lh
Rb
is 90
0,001 0,010 0,100 1,000
IM/A
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 13
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Definitions of Accuracy According to VDE 0414/IEC 60044-1
Isecnn Iprim
Definition of current error: Fi 100
Iprim
Definition of angle error: i angle(Isec ) angle(Iprim )
T
1
T nnisec ( t ) iprim( t ) 2 dt
Definition of composite error:
0
Fi 100
Iprim.rms
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 14
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Qualifying Symbols According to IEC and VDE
10 P 10, 15 VA
Nominal burden
Accuracy Limiting Factor (ALF)
Core Type P = Protection
Accuracy limit in % at ALF * In
Measuring cores are not suitable for protection!
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 15
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
IEC-60044, VDE-0414 Accuracy Classification for Protection CT in Steady State
2 standard accuracy classes: 5P and 10P
Limits of error
At nominal accuracy limit
At nominal primary current
primary current
Accuracy Current error Phase angle Phase angle
class displacement displacement Composite error
% minutes centirad %
5P ±1 ± 60 ± 1.8 5
10P ±3 - - 10
Example: 5 P 10 , 50 VA
nominal burden
accuracy limiting factor (ALF)
accuracy limit in % at I=ALF × In
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 16
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Definition of Protection CT Performance in Steady-State According to VDE/IEC
Isecondary/In burden < 15 VA Definition for type P according to
VDE/IEC 60044-1, only AC component
is taken into account
Only symmetrical saturation is
burden = 15 VA
considered
10
Fi = 10%
burden > 15 VA
However:
5 Short-circuit current consists of AC
and decaying DC components
For CT-dimensioning DC component
should also be considered
0 5 10 15 Iprimary/In
10P10, 15 VA
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 17
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Accuracy Limiting Factor ALF’
The CT’s performance under steady-state conditions is described by
Pn PCT A ccuracy L imiting F actor
ALF` ALFn
P`PCT Betriebsüberstromziffer
ALF’ = Actual Accuracy Limiting Factor
ALFn = Nominal Accuracy Limiting Factor
Pn = Nominal VA Output (Nominal Burden)
PCT = Internal CT Burden
P’ = Actual Connected Burden
IEC: Not high nominal VA or high nominal ALF factor leads to
a better CT performance, but higher actual ALF’ factor
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 18
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Accuracy Limiting Factor ALF - Example
in the same burden
CT1: 1000/1A, 10P10, 30 VA CT2: 1000/1A 10P20, 15 VA
Relay burden: 0.1 VA Relay burden: 0.1 VA
Pi = 6 VA Pi = 6 VA
ALF1’ = 10 x (30 + 6) / (0.1 + 6) = 59 ALF2’ = 20 x (15 + 6) / (0.1 + 6) = 69
Symmetrical saturation at 59 x In Symmetrical saturation at 69 x In
X Better
?
? future: 10P30, 2.5 VA ?
? ?
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 19
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Definition of Knee-Point Voltage According to BS Class X and IEC Class PX
Usecondary/V RCT (internal burden)
U = 10% Uknee
400 R‘
(external burden)
200
I = 50%
Knee-point voltage is the voltage at
which a 10% increase in rms voltage
results in a 50% increase in rms
0 50 100 150 Isecondary/mA magnetizing current
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 20
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
BS Performance Classification for Relaying CTs
Class P: 5P and 10P similar to IEC 60044
Class X: Defined by
Rated primary current
Turns ratio (the error shall not exceed ± 0.25%)
Rated knee-point voltage
Magnetizing current at rated knee-point voltage
Resistance of secondary winding corrected to 75°C
Class X CT will be applied if accuracy limits of class 5P or 10P are not
appropriate
Class X quantities can also be measured and given for class 5P and 10 P
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 21
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Definition der Kniepunktspannung nach Class TPS IEC 60044-6
Usecondary/V RCT (internal burden)
U = 10% Uknee
400 R‘
(external burden)
200
I = 100%
Knee-point voltage is the voltage at
which a 10% increase in rms voltage
results in a 100% increase in peak-
0 50 100 200 Isecondary/mA value of magnetizing current
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 22
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
IEC 60044-6 Transient Performance Classification for Relaying CTs
Class TPS: Defined by
Rated primary current
Turns ratio (the error shall not exceed ± 0.25%
Rated knee-point voltage
Magnetizing current at rated knee-point voltage
Resistance of secondary winding corrected to 75°C
Class TPS will be applied if accuracy limits of class 5P or 10P are not
appropriate
Class TPS quantities can also be measured and given for class 5P and 10P
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 23
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Relation Between Accuracy Limiting Factor ALF and Knee-Point Voltage
Uknee,n
Rn RCT I2n ALFn RCT
1.3 I1N (internal burden) I2N
Pn PCT ALFn
1.3 I2n Rn
Uknee (nominal
external
Example 1: burden)
IEC: 600/1A, 5P10, 15 VA, RCT= 4Ω
15VA 4VA 10 146VA
BS: 600/1A, Uknee,n
1.3 1VA
Example 2: ALFn available
BS: 600/1A, Uknee= 146V, RCT= 4Ω
1.3 Uknee I2n 1.3 146 V 1A 10 15 VA 15 VA
IEC: 600/1A, Pn PCT 4 VA 20 5.5 VA 10 VA
ALFn ALFn 30 2.3 VA 2.5 VA
must be higher than connected burden
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 24
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Conversion of ANSI to IEC CT Data for 1A CTs
RCT Nominal Accuracy Limiting Factor ALFn
Uterm is defined as terminal voltage at 20*In
Uterm and connected external standard burden.
R’
ALFn = 20 for all class C cores
Example C200, 1A Nominal ANSI-Standard burden
Uterm 200 V
R' 10
20 In 20 1A
C100 10P20, 5 VA
C200 10P20, 10 VA
C400 10P20, 20 VA Class P Nominal Burden
C800 10P20, 40 VA
Pn In2 R' (1A )2 10 10 VA
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 25
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Conversion of ANSI to IEC CT Data for 5A CTs
RCT Nominal Accuracy Limiting Factor ALFn
Uterm is defined as terminal voltage at 20*In
Uterm and connected external standard burden.
R’
ALFn = 20 for all class C cores
Example C200 Nominal ANSI-Standard burden
typical 5A
Uterm 200 V
R' 2
20 In 20 5 A
C100 10P20, 25 VA
C200 10P20, 50 VA
C400 10P20, 100 VA Class P Nominal Burden
C800 10P20, 200 VA
Pn In2 R' (5 A )2 2 50 VA
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 26
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
ANSI C57.13 Performance Classification for Relaying CTs
Class C: indicates that the transformer ration can be calculated (bushing type CTs)
Class T: indicates that the transformer ration must be determined by test
wound-type CTs limits of error
s
C800
e 800
c 8Ω
t 700
o Error will not exceed
n e 600
10% for secondary
d r 500 voltage equivalent to
a m 4Ω C400
r
400 or less than value
i described by curve
y 300
n 2Ω C200
a 200
v
o l 100 C100
l 0 1Ω
t
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
s
secondary amperes
Class C: Ration error will not exceed 10% between 1 to 20 times nominal
secondary current.
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 27
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Effective Burden
3 CT Earth-Returns 1 CT Earth-Return
Ri R1 Ri R1
R2 RRelay RRelay
Ri R1 Ri R1
R2 RRelay RRelay
Ri R1 Ri R1
RRelay RRelay
R2
R2
3-phase and 2-phase faults:
RBurden = R1 + RRelay
RBurden = R1 + RRelay + R2 PBurden = In2 *R1 + PRelay
PBurden = In2 (R1 + R2) + PRelay non-symmetrical Earth fault:
RBurden = R1 + RRelays + R2
PBurden = In2 (R1 + R2) + PRelays
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 28
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Effective Secondary Cable Burden with Nominal Current 1A, 5A
60 2,2 2,5 mm2
VA VA 0,70 / 100 m
2,5 mm2 2,0
0,70 / 100 m
50 In = 5 A 1,8 In = 1 A
1,6
40 1,4 4,0 mm2
4,0 mm2 0,44 / 100 m
0,44 / 100 m
1,2
30
1,0
6,0 mm2
6,0 mm2 0,29 / 100 m
0,29 / 100 m 0,8
20
0,6 10,0 mm2
10,0 mm2 0,17 / 100 m
0,17 / 100 m
10 0,4 16,0 mm2
16,0 mm2
0,11 / 100 m 0,11 / 100 m
0,2
0 0,0
0 100 200 300 0 100 200 300
length/m length/m
(In)2 = 25 A2 high burden (In)2 = 1,0 A2 low burden
better
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 29
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Steady State Dimensioning - Transmission Capability
CT-Transmission Capability
RCT RI Relay with nominal burden
2
……Ω 1
……Ω I’’k = ……
10 x In = ……
10 kA
RRelay
RI
0,1
……Ω
Accuracy Limiting Factor
P PCT
n = 1000
…… / 1A 2,1 VA
P’ = …… ALF' ALFn n
P'PCT
10 ...... ...... ......
10 2
...... 29,2
...... ......
2,1 2
Current Transformer CT
CT-Transmission Capability
…… / 1A,
1000 ……
5 P ……,
10 ……
10 VA with actual burden
I’’k = ALF’ x In = ……
29,2 kA
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 30
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Steady State Dimensioning
RCT RI Relay
Necessary Accuracy Limiting Factor
2
……Ω
1
……Ω I' 'k 20
RRelay ALF' ......
RI In
0,1
……Ω
Necessary Nominal Burden
n = 1000
…… / 1A 2,1 VA
P’ = ……
2,1 VA P ......
Pn P' ...... 5 VA
n
Current Transformer CT
? ? Necessary Nominal Accurancy
1000
…… / 1A, 5
…… 15
P ……, 5
…… VA Limiting Factor
P'PCT
ALFn ALF'
Pn PCT
Short-Circuit Current
20 ......2,1 ......
2 11,7
20 x I
20 kA = …… ...... ......
I’’k = …… n 5 ......
...... 2
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 31
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Short Circuit Current
Fault far from generator Fault near to generator
Constant AC component 50/60 Hz Decaying AC component 50/60 Hz
Decaying DC component Decaying DC component
Time constants: Time constants:
Medium voltage 10ms .. 50ms Medium voltage 10ms .. 100ms
High voltage 50ms .. 100ms High voltage 50ms .. 250ms
Extra high voltage 80ms .. 150ms Extra high voltage 80ms .. 250ms
Generator level up to 500ms
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 32
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Meaning of the accuracy limiting factor ALF‘
The multiplication of the accuracy limiting factor and nominal CT-current
specifies the symmetrical short-circuit current which can be transmitted
without saturation.
Relation between magnetic flux density and
secondary nominal CT-current.
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 33
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Overdimensioning factor of CTs
Asymmetrical short circuit current with a superposing DC-component
The DC-component
of an asymmetrical
short circuit is
causing an additional
magnetic
flux.
Transient dimensioning factor
for free
TN : System time constant
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 34
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Overdimensioning factor of CTs
Bsat
Magnetic Flux
secondary current
primary current
The DC-component is producing a steep rising of
tfree
the magnetic flux density
A CT can be saturated by an asymmetrical current
DC-component nevertheless it will not be saturated
by the pure symmetrical current
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 35
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
CT - Dimensioning according to saturation-free transmission time
Overdimensioning factor for saturation-free
transmission time tfree:
Ktd
t free
K td 1 TN (1 e TN
)
(iron-cored CT with TS >> TN)
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 36
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
CT-Dimensioning Instruction for Transformer Differential Protection
A transformer differential protection should be stable on external short-circuit faults.
The CT saturation detection of 7UT612 relays need an unsaturated transmission of
maximum short-circuit current in
For high CT time constants, the maximum transmittable current must not exceed
Ktd Ktd
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 37
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
CT-Dimensioning Instruction for Line Differential Protection
A current differential protection should be stable on external short-circuit faults.
The CT saturation detection of 7SD51 relays need an unsaturated transmission of
maximum short-circuit current in
For high CT time constants, the maximum transmittable current must not exceed
Ktd Ktd
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 38
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
CT-Dimensioning Instruction for Distance Relay
General:
The CT may be saturated, but any short circuit faults in zone 1 must
be cleared undelayed, short circuit faults outside one 1 must be cleared
delayed.
CT may be saturated, but the remaining CT should keep to transmit short circuit
magnitude of fundamental current and currents without saturation in a longer
its phase angle must lead to time than relay operating time.
impedance within zone 1.
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 39
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
CT-Dimensioning Instruction for Overcurrent Relays
General:
The CT my be saturated, but the remaining magnitude of fundamental
current has to be higher than the relay settings I >>.
IS > I> or IS > I>>
I Pn PCT I
ALF ALFn
In P'PCT In
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 40
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Transient Dimensioning - Transmission Capability
RCT RI Relay
Tsys = 0 ms, tfree = ∞, steady state
2 1 Ik = ALF’ * In = ……30 kA
……Ω ……Ω RRelay
RI
0,1
……Ω
n = 1000
…… / 1A 2,1 VA
P’ = ……
Tsys = 50 ms, tfree = ∞, transient
ALF' 30
......
Ik In ......kA
1 1,87
.......kA
K td 16
......
Current Transformer CT
…… / 1A, ……
1000 5 P ……,
10 ……
10 VA
Accuracy Limiting Factor Tsys = 50 ms, tfree = 10 ms, transient
ALF' ......
Pn PCT 30 Ik In 30 ......kA
1 ......kA
7,5
ALF' ALFn ...... K td 4
......
P'PCT
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 41
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Transient Dimensioning
7UT612
RCT RI Relay Necessary Transient Accuracy
Limiting Factor
2
……Ω
1
……Ω RRelay
I' 'k 20 kA
RI
0,1 ALF' K td .......... ...... ......
......... 4 80
……Ω In 1 kA
n = 1000
…… / 1A 2,1 VA
P’ = ……
Necessary Nominal Burden
2,1 VA P ......
Pn P' ...... 5 VA
n
Current Transformer CT
? ?
1000 / 1A, ……
…… 5 P ……,
50 ……
5 VA
Necessary Nominal Accuracy
Limiting Factor
Short-Circuit Current
P'PCT
ALFn ALF'
I’’k = ……
20 kA = ……
20 x In Pn PCT
Tsys = ……50 ms 2,1 2
80 ............ ......
...... 46,85
5 ......
...... 2
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 42
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
CT - Demagnetizing
circuit breaker switched-off at current
zero crossing
Maximum of induction
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 43
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
TP - current transformer classes acc. IEC 60044 - 6
- Iron - cored CT without limited remanence
TPX - Mechanical construction corresponds to class P (IEC 60044 - 1)
- transient behavior is specified additionally
- same as TPX
TPY - remanence limited to <10% (anti - remanence air gap)
- remanence neglectable
TPZ - error limit are only formulated for AC component
- DC - component will be shortened considerably
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 44
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
CT - Induction curve during AR
A – Iron cored CT TPX
A
B – Iron cored CT with BR
anti - remanence B
air gap TPY
BR
tF1 tSp tF2 t
Bmax ωTN TS tTF1N TF1
t t t
SpT F2 ω T1 TS tTF2N TF2
t
K td 1 (e e ) e
S S
1 (e e S )
Bˆ TN TS TN TS
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 45
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
CT - Induction curve during AR
Ip
Linear core CT
Is
TPZ
B
• Advantages by AR
• Cost intensive partitioned core Im
• very short sec. Time constant
(<100ms): sec. DC component is no longer
Bmax TN TS tTF2N TF2
t
transformed correctly K td 1 (e e S )
• high demagnetizing current Bˆ TN TS
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 46
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Error limits of TP - current transformer classes acc. to IEC 60044 - 6
Error at anted current Peak error at rated
class
ratio angle overcurrent
TPX ± 0,5% ± 30 min ε ≤ 10%
TPY ± 1,0% ± 60 min ε ≤ 10%
TPZ ± 1,0% ± 180 ± 18 min ε ≤ 10% (only I~)
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 47
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
CTDim 3.2 - Current Transformer Dimensioning Program
Technical Optimization
Dynamic Check of Requirements
Automatic Report Generation
Standard Conversion
Dynamic Simulation
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 48
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
weitere Folien nicht gepflegt
09.08.2005/ab
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 49
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Saturation-Free Transmission Time - Example
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 50
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Transient CT- Behavior
Equivalent Circuit:
Magnetic induction curve:
leakage inductance << main inductance B TN TS TtN Tt
i2 1 i1 1 (e e S )
N Ri i1 B̂ TN TS
Maximum value:
LM U2 RB
Bmax
1 TN TS >> TN
B
TN Time constant of power system
U (t) dt (R R ) i (t) dt
TS Time constant of CT secondary
B 2 i B 2 circuit
δ angle error
LM I
TS
Ri RB tan
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 51
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
CT - Dimensioning acc. to saturation - free transmission time
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 52
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Maximum Transmittable Current and Transient Dimensioning Factor (1)
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 53
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Maximum Transmittable Current and Transient Dimensioning Factor (2)
Short-circuit current: Tt
iSC ( t ) 2 ISC ( cos t e )
Transient dimensioning factor (high CT time constant): Y' 1 Tsy s
I ALF'
Maximum transmittable current without saturation: ISC n
Y'
80
f = 60 Hz
Y’∞
f = 50 Hz
60
Estimated transient di-
mensioning factor for 40
different iron cores and
system frequencies 20 f = 16 2/3 Hz
0
0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20
Tsys
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 54
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Maximum Transmittable Current and Transient Dimensioning Factor (3)
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 55
s
Instrument Transformer Dimensioning
Magnetizing characteristics of TP - CTs:
Copyright SIEMENS AG. PTD SE PT 2005. All rights reserved.
Power Transmission and Distribution Power Technology
Page 56
You might also like
- Fast-Front OvervoltagesDocument49 pagesFast-Front Overvoltagessorry2qazNo ratings yet
- The Technology of Instrument Transformers: Current and Voltage Measurement and Insulation SystemsFrom EverandThe Technology of Instrument Transformers: Current and Voltage Measurement and Insulation SystemsNo ratings yet
- CT Sizing For MalawiDocument2 pagesCT Sizing For MalawiDharmenderSinghChoudharyNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- IEC Standards and Nonconventional Instrument TransformersDocument9 pagesIEC Standards and Nonconventional Instrument TransformersgilbertomjcNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Capacitor Bank Switching Transients: Dharshana Muthumuni Manitoba HVDC Research CenterDocument62 pagesCase Study - Capacitor Bank Switching Transients: Dharshana Muthumuni Manitoba HVDC Research Centersandeep kumar mishraNo ratings yet
- ShortCircuit - Table of ContentDocument8 pagesShortCircuit - Table of ContentFasil Paruvanath0% (1)
- High Impedance Restricted Earth Fault Protection: Answers For EnergyDocument40 pagesHigh Impedance Restricted Earth Fault Protection: Answers For EnergyWildan erik77No ratings yet
- New Approaches to the Design and Economics of EHV Transmission Plant: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringFrom EverandNew Approaches to the Design and Economics of EHV Transmission Plant: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Short-Circuit Current CalculationsDocument10 pagesShort-Circuit Current CalculationsBash MatNo ratings yet
- Protection 2Document50 pagesProtection 2Mouhemed MouhaNo ratings yet
- Current Interruption Transients CalculationFrom EverandCurrent Interruption Transients CalculationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Testing Directional Overcurrent ProtectionDocument2 pagesTesting Directional Overcurrent ProtectionZokiNo ratings yet
- Instrument Transformers PDFDocument39 pagesInstrument Transformers PDFJuan Sebastián GómezNo ratings yet
- Magnetizing Inrush Phenomena in Transformer BanksDocument9 pagesMagnetizing Inrush Phenomena in Transformer BanksAlejandro Gil RestrepoNo ratings yet
- X R RatioDocument2 pagesX R RatioSaber AbdelaalNo ratings yet
- Transformers For Renewable Energy ApplicationsDocument13 pagesTransformers For Renewable Energy Applicationskrmurali2000No ratings yet
- Protection Challenges Under Bulk Penetration of Renewable Energy Resources in Power Systems: A ReviewDocument15 pagesProtection Challenges Under Bulk Penetration of Renewable Energy Resources in Power Systems: A ReviewAnonymous vLerKYANo ratings yet
- System Details for Nara-Matore LineDocument35 pagesSystem Details for Nara-Matore LinemichyimNo ratings yet
- Overexcitation ProtectionDocument7 pagesOverexcitation Protectionravi shankarNo ratings yet
- Current Transformer Sizing & Saturation Calculation With Transient Performance Analysis of CT Using ATP SoftwareDocument8 pagesCurrent Transformer Sizing & Saturation Calculation With Transient Performance Analysis of CT Using ATP SoftwareInvyteNo ratings yet
- Invited Speaker - Vitor Sokolov PDFDocument21 pagesInvited Speaker - Vitor Sokolov PDFAndar ApriadiNo ratings yet
- ABB REM 543 Relay Energy Meter CalibratiDocument10 pagesABB REM 543 Relay Energy Meter CalibratiPrashant GaurNo ratings yet
- Transformers: Sector Energy Dseptinc Steffen SchmidtDocument34 pagesTransformers: Sector Energy Dseptinc Steffen SchmidtJitamitra BehuraNo ratings yet
- Shunt Reactor Switching Transients at High Compensation LevelsDocument14 pagesShunt Reactor Switching Transients at High Compensation LevelsJames Ernes Llacza Carmelo100% (1)
- Reference IEC FaultDocument37 pagesReference IEC FaultVictor Luiz MerlinNo ratings yet
- CT SizingDocument3 pagesCT SizingadauNo ratings yet
- 16 - Prevost IT - Technology & DesignDocument39 pages16 - Prevost IT - Technology & DesignbcqbaoNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection - Part 08Document16 pagesPower System Protection - Part 08Rahul MandalNo ratings yet
- TechRef CableSystemDocument25 pagesTechRef CableSystemROYNo ratings yet
- Current TransformersDocument24 pagesCurrent TransformersArif KhanNo ratings yet
- Neutral Reactors On Shunt Compensated Ehv LinesDocument8 pagesNeutral Reactors On Shunt Compensated Ehv Linessubbu2051No ratings yet
- Overcurrent Grading TutorialDocument28 pagesOvercurrent Grading Tutorialmubarakkirko100% (1)
- Current TransformerDocument21 pagesCurrent Transformerbalaeee123No ratings yet
- Restricted Earth FaultDocument26 pagesRestricted Earth FaultAfsar AliNo ratings yet
- CT Saturation PDFDocument16 pagesCT Saturation PDFsureshNo ratings yet
- InrushDocument226 pagesInrushDinesh SelvakumarNo ratings yet
- Application and principles of directional overcurrent and earthfault protectionDocument72 pagesApplication and principles of directional overcurrent and earthfault protectionNeelakandan MasilamaniNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit StudyDocument45 pagesShort Circuit Studymohamad arifinNo ratings yet
- Zero Sequence Impedance of Overhead Transmission LinesDocument11 pagesZero Sequence Impedance of Overhead Transmission LinesMohammed JavithNo ratings yet
- Instrument TransformersDocument95 pagesInstrument TransformersEngr Fahimuddin QureshiNo ratings yet
- ABB Surge Arresters Buyers GuideDocument84 pagesABB Surge Arresters Buyers GuideJoel PalomaresNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric Cahier Technique 151Document24 pagesSchneider Electric Cahier Technique 151Anonymous BwLfvuNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Fault Analysis at Q-ORE DistributionDocument1 page3 Phase Fault Analysis at Q-ORE DistributionkumarNo ratings yet
- CT Calculation MFAC14Document10 pagesCT Calculation MFAC14Jay WinNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual Directional Overcurrent Protection Relay Grd140 - XXXDDocument438 pagesInstruction Manual Directional Overcurrent Protection Relay Grd140 - XXXDEpsp MedNo ratings yet
- Gapped Core Current Transformer Characteristics and PerformanceDocument9 pagesGapped Core Current Transformer Characteristics and PerformanceBalajiNo ratings yet
- CT and VT SizingDocument21 pagesCT and VT SizingMaheswariNo ratings yet
- Capacitive Voltage Transformer - SpecificationDocument6 pagesCapacitive Voltage Transformer - Specificationbalaeee123No ratings yet
- 04 TransformerDocument98 pages04 TransformerahmedNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Transient in Power System and Insulation Coordination Studies PDFDocument210 pagesElectromagnetic Transient in Power System and Insulation Coordination Studies PDFOrcun CalayNo ratings yet
- Broken Conductor ProtectionDocument2 pagesBroken Conductor ProtectionThirumalNo ratings yet
- Over Fluxing in Transformer - Electrical EngineeringDocument5 pagesOver Fluxing in Transformer - Electrical Engineeringsriramv93No ratings yet
- PSCON01-02 (HPCL Nagaon) PDFDocument120 pagesPSCON01-02 (HPCL Nagaon) PDFgopi100% (1)
- 07a - Instrument - Transformers - Tech - r8 401Document77 pages07a - Instrument - Transformers - Tech - r8 401tajudeen100% (1)
- Ep 3Document18 pagesEp 3MancamiaicuruNo ratings yet
- Services PDFDocument4 pagesServices PDFFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Valve Selection and Sizing: Section of Engineering Manual of Automatic Control 77-1100Document20 pagesValve Selection and Sizing: Section of Engineering Manual of Automatic Control 77-1100intequabNo ratings yet
- Ml30e100 PDFDocument2 pagesMl30e100 PDFFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Specifications For: 11Kv Pad Mounted SwitchDocument8 pagesSpecifications For: 11Kv Pad Mounted SwitchFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Busbar Selection TabelDocument1 pageBusbar Selection TabelFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Lightning and HV Electrical Installations PDFDocument24 pagesLightning and HV Electrical Installations PDFRiazAhmedNo ratings yet
- ECT191 Fuzzy LogicDocument32 pagesECT191 Fuzzy LogicBernardMightNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Networks Using Symmetrical ComponentsDocument33 pagesAnalysis of Networks Using Symmetrical ComponentsashawishNo ratings yet
- E&DPlanDocument8 pagesE&DPlanFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Cable Capacity Table for PVC Insulated WiresDocument1 pageCable Capacity Table for PVC Insulated WiresFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Insideiec04 eDocument36 pagesInsideiec04 eFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Cti PDFDocument5 pagesCti PDFFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- New Cable ChartDocument1 pageNew Cable ChartFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Power capacitor bank componentsDocument1 pagePower capacitor bank componentsFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Power capacitor bank componentsDocument1 pagePower capacitor bank componentsFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- IEC 62271-200 SwitchgearDocument22 pagesIEC 62271-200 SwitchgearFarhan Shah100% (7)
- Pirelli PDFDocument24 pagesPirelli PDFFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Latest Iec Vs Siemens SGDocument36 pagesLatest Iec Vs Siemens SGFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- 8PT112 WiresDocument4 pages8PT112 WiresFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- IEC61850 Message StatusDocument6 pagesIEC61850 Message StatustonytomsonNo ratings yet
- 7SJ80xx Manual A1 V040005 Us PDFDocument514 pages7SJ80xx Manual A1 V040005 Us PDFFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- IEC 62271 - EN - 2003-10-27 - HandoutDocument18 pagesIEC 62271 - EN - 2003-10-27 - HandoutFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- The New IECDocument10 pagesThe New IECFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Portable Device For PD MeasurementDocument52 pagesPortable Device For PD MeasurementFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- E&DPlan0708 1Document80 pagesE&DPlan0708 1Farhan ShahNo ratings yet
- TF Testing RecommendationDocument4 pagesTF Testing RecommendationFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Vortrag - WandlerJun 04Document13 pagesVortrag - WandlerJun 04Farhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Transients On Secondary Equipment in MV Switchgear InstallationsDocument6 pagesTransients On Secondary Equipment in MV Switchgear InstallationsFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Damping ResistorDocument8 pagesDamping ResistorFarhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Review A 2014 ANSWERSDocument5 pagesMagnetism Review A 2014 ANSWERSSharath MysoreNo ratings yet
- Especificacion SHY73MC4 UDocument3 pagesEspecificacion SHY73MC4 UYgor Salgado100% (3)
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 1: Effects of Force On ObjectsDocument26 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 1: Effects of Force On ObjectsJobelle Canlas100% (1)
- Various Methods of Speed Control of Induction MotorDocument11 pagesVarious Methods of Speed Control of Induction MotorSufail ANo ratings yet
- Eee 205-W2Document9 pagesEee 205-W2mahamudul hasanNo ratings yet
- InterferenceDocument15 pagesInterferenceShamim khanNo ratings yet
- AnalysisMethods SSR SSCI SSTIDocument27 pagesAnalysisMethods SSR SSCI SSTIRaturi DeepankarNo ratings yet
- Richard J. Blakely-Potential Theory in Gravity and Magnetic Applications (Stanford-Cambridge Program) (1995) PDFDocument461 pagesRichard J. Blakely-Potential Theory in Gravity and Magnetic Applications (Stanford-Cambridge Program) (1995) PDFDwi AgustiyaniNo ratings yet
- Mock Test - 1: (Physics)Document29 pagesMock Test - 1: (Physics)kalloliNo ratings yet
- IEEE9 Buses System Simulation and Modeling in PSCADDocument4 pagesIEEE9 Buses System Simulation and Modeling in PSCAD_Alastair_No ratings yet
- Cbse-Viii Chapter-11 Force and Pressure: 1. Match The ColumnDocument3 pagesCbse-Viii Chapter-11 Force and Pressure: 1. Match The ColumnVipul Vaibhav MahajanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Source transformation-SVDocument29 pagesCHAPTER 4 Source transformation-SVnurul najwaNo ratings yet
- Circuit ReductionDocument13 pagesCircuit Reductionaathavan1991No ratings yet
- Tutorials in Power ElectronicsDocument66 pagesTutorials in Power ElectronicsAbdullah Al AsikNo ratings yet
- Generation of Rotating Magnetic FieldDocument3 pagesGeneration of Rotating Magnetic FieldSUNIL MAURYANo ratings yet
- g482 Mod 2 2 2 3 and 2 2 4 Resistance and ResistivityDocument10 pagesg482 Mod 2 2 2 3 and 2 2 4 Resistance and Resistivityapi-236179294No ratings yet
- Important Questions - APS - IDocument3 pagesImportant Questions - APS - IAakash MehtaNo ratings yet
- Jecrc University: Submitted By: Lokesh Choudhary Neetu ChoudharyDocument31 pagesJecrc University: Submitted By: Lokesh Choudhary Neetu ChoudharyshubhamNo ratings yet
- Control Ratio CalculationDocument15 pagesControl Ratio CalculationJayanth KolliNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction Motor ExplainedDocument13 pagesThree Phase Induction Motor ExplainedB ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Bus ReactorDocument6 pagesBus Reactorbibhoo100% (1)
- Mini RomagDocument13 pagesMini Romagranjan1491100% (1)
- (BLACK DOG) Change Is The Only ConstantDocument379 pages(BLACK DOG) Change Is The Only Constantradu ciureaNo ratings yet
- Utility Application of Power ElectronicsDocument21 pagesUtility Application of Power ElectronicsTanishqa SahaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Question BankDocument19 pagesCircuit Theory Question BankVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Notes Switchgear and Protection Unit 2Document32 pagesNotes Switchgear and Protection Unit 2Pratik SinghNo ratings yet
- Astm E4-03Document9 pagesAstm E4-03柏斯材料科學檢驗有限公司公司No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Nature of LightDocument45 pagesChapter 8 Nature of LightjellNo ratings yet
- Physics DefinitionsDocument2 pagesPhysics DefinitionsElaine Neo Kai WenNo ratings yet