Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MG 11 Desain Lanskap ARL200 2015
Uploaded by
AlfiForbearingStriving's0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views5 pagessasa
Original Title
86032_MG 11 Desain Lanskap ARL200 2015
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsasa
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views5 pagesMG 11 Desain Lanskap ARL200 2015
Uploaded by
AlfiForbearingStriving'ssasa
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Braced Frame
• Braced frames are cantilevered vertical trusses resisting
laterals loads primarily through the axial stiffness of the frame
members.
• The effectiveness of the system, as characterized by a high
ratio of stiffness to material quantity, is recognized for multi-
storey building in the low to mid height range.
• Generally regarded as an exclusively steel system because the
diagonal are inevitably subjected to tension for or to the other
directions of lateral loading.
• Able to produce a laterally very stiff structure for a minimum
of additional material, makes it an economical structural form
for any height of buildings, up to the very tallest.
Advantages Disadvantages
• Girders only participate • Obstruct the internal planning
minimally in the lateral bracing and the locations of the
action-Floor framing design is windows and doors; for this
independent of its level in the reason, braced bent are
structure. usually incorporated internally
• Can be repetitive up the along wall and partition lines,
height of the building with especially around elevator,
obvious economy in design stair, and service shaft.-
and fabrication. Diagonal connections are
expensive to fabricate and
erect.
Rigid Frame Structure
Consist of columns and girders joined by moment resistant
connections. Lateral stiffness of a rigid frame bent depends on
the bending stiffness of the columns, girders, and connection in
the plane of the bents. Ideally suited for reinforced concrete
buildings because of the inherent rigidity of reinforced concrete
joints. Also used for steel frame buildings, but moment-resistant
connections in steel tend to be costly. While rigid frame of a
typical scale that serve alone to resist lateral loading have an
economic height limit of about 25 stories, smaller scale rigid
frames in the for of perimeter tube, or typically rigid frames in
combination with shear walls or braced bents, can be economic
up top much greater heights.
Advantages
• May be place in or around the
core, on the exterior, or
throughout the interior of the
building with minimal
constraint on the planning
module.
• The frame may be
architecturally exposed to
express the grid like nature of
the structure.
• The spacing of the columns in
a moment resisting frame can
match that required for gravity
framing.-Only suitable for
building up to 20 –30
storiesonly; member
proportions and materials cost
become unreasonable for
building higher than that
In-filled Frame Structure
Most usual form of construction for
tall buildings up to 30 stories in
height Column and girder framing of
reinforced concrete, or sometimes
steel, is in-filled by panels of
brickwork, block work, or cast-in-
place concrete. Because of the in-
filled serve also as external walls or
internal partitions, the system is an
economical way of stiffening and
strengthening the structure. The
complex interactive behaviour of the
infill in the frame, and the rather
random quality of masonry, has made
it difficult to predict with accuracy
the stiffness and strength of an in-
filled frame.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Diffusion AssignmentDocument5 pagesDiffusion AssignmentAshley Kyaw100% (1)
- Power System Protective Relaying-Part TwoDocument78 pagesPower System Protective Relaying-Part TwoMohammedSaadaniHassani80% (5)
- AHLSTAR Process PumpsDocument71 pagesAHLSTAR Process PumpsPascal Cote100% (2)
- Allowable Settlement of FoundationsDocument6 pagesAllowable Settlement of Foundationssb1966No ratings yet
- Monorail Design CS 0089 (FINAL)Document8 pagesMonorail Design CS 0089 (FINAL)asvenk309No ratings yet
- Iso 12135 2002 FR en PDFDocument11 pagesIso 12135 2002 FR en PDFPaquita Londdon100% (2)
- 13 03 2019 ChemicalEngineering2014Document12 pages13 03 2019 ChemicalEngineering2014Shereen AminiNo ratings yet
- Pag. 1 / 44 DMAN802000066-SY250 Idro 4/8 Buttons ManualDocument44 pagesPag. 1 / 44 DMAN802000066-SY250 Idro 4/8 Buttons ManualtelenorceNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Research PaperDocument8 pagesPeriodic Table Research Paperafnhlmluuaaymj100% (1)
- Aircraft Structures Pure TorsionDocument60 pagesAircraft Structures Pure TorsionTarik Hassan ElsonniNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Property Relations: Çengel BolesDocument19 pagesThermodynamic Property Relations: Çengel Boleskebaman1986No ratings yet
- WEG Severe Duty Is Standard With W22 Motors USAW22SEVDUTY.7.2017 Brochure English WebDocument16 pagesWEG Severe Duty Is Standard With W22 Motors USAW22SEVDUTY.7.2017 Brochure English WebPAULO SOUZANo ratings yet
- Coordinate Measuring MachineDocument5 pagesCoordinate Measuring MachineMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- The Physics of MusicDocument13 pagesThe Physics of MusicKavithira DevarajanNo ratings yet
- JZBFJZBS Series Semi Hermetic Compressor Condensing Units (Bitzer Compressor)Document9 pagesJZBFJZBS Series Semi Hermetic Compressor Condensing Units (Bitzer Compressor)Coolequipment CeeNo ratings yet
- Stoelting PplygraphDocument3 pagesStoelting PplygraphAriel Cabangunay100% (1)
- Close Coupled Pumps Operating and Maintenance ManualDocument16 pagesClose Coupled Pumps Operating and Maintenance ManualsaifNo ratings yet
- 2 - PhET Simulation - Color VisionDocument3 pages2 - PhET Simulation - Color VisionAva MittoneNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulation of Single Phase TransformerDocument6 pagesVoltage Regulation of Single Phase TransformerMuhammad Ali HaiderNo ratings yet
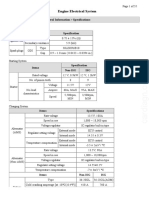
- Engine Electrical System General Information SpecificationsDocument55 pagesEngine Electrical System General Information SpecificationsIsaac Galvez EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Behavior of Aluminum Metal Matrix Composite Reinforcement With Graphene Nano FillersDocument11 pagesMechanical Behavior of Aluminum Metal Matrix Composite Reinforcement With Graphene Nano FillersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- W3Document2 pagesW3Jerlyn AriateNo ratings yet
- Présentation PowerPoint PDFDocument68 pagesPrésentation PowerPoint PDFAssis RochaNo ratings yet
- 2806 01 PDFDocument33 pages2806 01 PDFAmitNo ratings yet
- Textile Softeners On Cotton Dyed With Direct Dyes: Re Ectance and Fastness AssessmentsDocument5 pagesTextile Softeners On Cotton Dyed With Direct Dyes: Re Ectance and Fastness AssessmentsIrfak SaputraNo ratings yet
- WL3 Filled OutDocument8 pagesWL3 Filled OutBraden WellsNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Grade 8 ScienceDocument7 pagesCourse Outline Grade 8 SciencePrincess Mae LumawagNo ratings yet
- Mapua University: Experiment No. 4BDocument9 pagesMapua University: Experiment No. 4BGeojanni PangibitanNo ratings yet
- TYN 0510 - TYN 1010: FeaturesDocument4 pagesTYN 0510 - TYN 1010: FeaturesSofyan AndikaNo ratings yet
- Hindi - Practice Study Material in Hindi For CSS EntranceDocument20 pagesHindi - Practice Study Material in Hindi For CSS Entrancesumit-7No ratings yet