Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MG
Uploaded by
Willie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views22 pagesMyasthenia Gravis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMyasthenia Gravis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views22 pagesMG
Uploaded by
WillieMyasthenia Gravis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
Myasthenia Gravis
• Is an autoimmune disorder affecting the myoneural junction, is
characterized by varying degrees of weakness of the voluntary
muscles
• The thymus may give incorrect instructions to developing
immune cells, ultimately resulting in autoimmunity and the
production of the acetylcholine receptor antibodies.
• The thymus is a specialized organ of the immune system.
The only known function of the thymus is the production
and "education" of T-lymphocytes(T cells), which are critical
cells of the adaptive immune system
• The thymus is composed of two identical lobes and is
located anatomically in the anterior superior mediastinum in
front of the heart and behind the sternum
ETIOLOGY
• Autoimmune disease
• Thymoma
Women suffer at an earlier age (20-40) compared to men (60-70)
and are more affected
Pathophysiology:
• 1. Acetylcholine receptor antibodies interfere with
impulse transmission
• 2. Follows an unpredictable course of periodic
exacerbations and remissions
Clinical Manifestations of Myasthenia
1. Involves the ocular muscles
Gravis
a. diplopia – double vision
b. ptosis – drooping of the eyelids
2. Bulbar symptoms – weakness of the muscles of the eyes , face and
throat
3. Generalized weakness
a. bland facial expression
b. dysphonia
c. decrease vital capacity
• Difficulty in swallowing
• Shortness of breath, Impaired speech, Weakness in the
arms, hands, fingers, legs and neck
• PURELY MOTOR WITH NO EFFECT ON
SENSATION OR COORDINATION
•
• Risk Factors:
• Age 20 to 40
• > Female gender
• Male gender and age over 60 years
• Family history for myasthenia gravis
• Other autoimmune illness: Rheumatoid arthritis, and
Lupus
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
• 1. EMG
• 2. TENSILON TEST (Edrophonium)
• IV injection- provides spontaneous relief of symptoms (
last 5-10 mintutes)- positive
• 3. CT scan
• 4. Serum anti-AchReceptor antibodies
A diagnosis can be confirmed in several ways:
• Acetylcholine Receptor Antibody – A blood test
for the abnormal antibodies can be performed to
see if they are present. Approximately 85% of
MG patients have this antibody and, when detected
with elective of MG concentration the AChR
antibody test is strongly indicative of MG.
• Single Fiber EMG- studies can provide support
for the diagnosis of MG when characteristic
patterns are present. The single Fiber EMG and
AChR antibody test are primary test used to
confirm a clinical diagnosis of MG.
• Anti- Musk Antibody Testing- a blood test for the
remaining for the acetylcholine antibody. These
patients have seronegative(SN) MG. about 40-70% of
patients with SNMG test positive for the anti- Musk
antibody.
• Electromyography-(EMG) studies can provide
support for the diagnosis of MG when characteristic
pattern are present.
MEDICAL THERAPY
• Anticholinesterase drugs-
• PYridostigmine ( mestinon) Neostigmine ( Prostigmin)
• SHOULD BE GIVEN ON TIME
• 30 MINS. BEFORE MEALS W/ MILK AND CRACKERS TO
PREVENT CRISIS
• Corticosteroids- suppress autoimmune response
• Immunosuppresants
• Plasmapheresis- remove circulating acetylcholine receptor antibodies
• Thymectomy- removal of thymus gland
Nursing Diagnosis for Myasthenia Gravis
• Ineffective Breathing Pattern related to respiratory muscle weakness.
• Impaired Physical Mobility related to weakness of voluntary
muscles.
• Risk for Aspiration related to the weakness of bulbar muscles.
• Self-Care Deficit related to muscle weakness, general fatigue.
• Imbalanced Nutrition: Less than Body Requirements related to
dysphagia, intubation, or muscle paralysis.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
• 1. Administer prescribed medication as scheduled
• 2. Prevent problems with chewing and swallowing
• 3. Promote respiratory function
• 4. Encourage adjustments in lifestyle to prevent
fatigue
• 5.maximize functional abilities
• 6. Prepare for complications like myasthenic crisis and cholinergic crisis
• Cholinergic Crisis
• caused by overmedication
• Worsen with tensilon test
• Antidote : atropine sulfate
• Myasthenic crisis
• Abrupt generalized muscle weakness
• Caused by undermedication, physical, emotional stress, infection
• Symptoms improved temporarily with tensilon test
• 7. Prepare for complications like myasthenic crisis and
cholinergic crisis
• 8 . prevent problems associated with impaired vision
resulting from ptosis of eyelids
• 9. provide client teaching
• 10. promote client and family coping
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Nursing WoundDocument20 pagesNursing WoundWillieNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- MedicationadministrationDocument124 pagesMedicationadministrationWillieNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Scoliosis: By: Manilyn B. Lin Bsn-IiiDocument13 pagesScoliosis: By: Manilyn B. Lin Bsn-IiiWillie100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Nursing Board Exam Review Questions in Emergency Part 6/20Document15 pagesNursing Board Exam Review Questions in Emergency Part 6/20Tyron Rigor Silos100% (5)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- ApoplexyDocument40 pagesApoplexyWillieNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- RitisDocument1 pageRitisWillieNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- FundamentalsDocument5 pagesFundamentalsWillieNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Funda 2Document4 pagesFunda 2WillieNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- FundamentalsDocument5 pagesFundamentalsWillieNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Research of Historical Timelines: Jhon Willie S. Ybanez BS Nursing - III Prof. Shiela VeraDocument2 pagesComprehensive Research of Historical Timelines: Jhon Willie S. Ybanez BS Nursing - III Prof. Shiela VeraWillieNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- DiptheriaDocument14 pagesDiptheriaWillieNo ratings yet
- ALSDocument14 pagesALSWillieNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- LolDocument11 pagesLolWillieNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Compart Ment SyndromeDocument17 pagesCompart Ment SyndromeWillieNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Grand Case Presentation SampleDocument23 pagesGrand Case Presentation SampleWillieNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- AmputatingDocument13 pagesAmputatingWillieNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Mood Disorders DEPRESSION (C15Document85 pagesMood Disorders DEPRESSION (C15Denise EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Huntington's ChoreaDocument13 pagesHuntington's ChoreaWillieNo ratings yet
- M SclerosisDocument10 pagesM SclerosisWillieNo ratings yet
- Mers CovvDocument6 pagesMers CovvWillieNo ratings yet
- Spinal FusionDocument23 pagesSpinal FusionWillie100% (1)
- Meniere' S Disease: (Endolymphatic Hydrops)Document9 pagesMeniere' S Disease: (Endolymphatic Hydrops)WillieNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument22 pagesAlzheimer's DiseaseWillieNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument22 pagesAlzheimer's DiseaseWillieNo ratings yet
- Ear ProblemsDocument5 pagesEar ProblemsWillieNo ratings yet
- Ear ProblemsDocument5 pagesEar ProblemsWillieNo ratings yet
- Ear ProblemsDocument5 pagesEar ProblemsWillieNo ratings yet
- How Stem Cell Therapy Benefits Leukemia PatientsDocument4 pagesHow Stem Cell Therapy Benefits Leukemia PatientsWillieNo ratings yet
- EENTDocument5 pagesEENTWillieNo ratings yet
- Science Society Education - Topical Issues and Development Prospects - 5 7.07.20Document341 pagesScience Society Education - Topical Issues and Development Prospects - 5 7.07.20OS IONo ratings yet
- My Early DaysDocument14 pagesMy Early DaysVigneshwar .kNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Cold Calling 26 AugDocument4 pagesCold Calling 26 AugGajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- JNTU-HYD: B.Tech/B.Pharmacy 2,3,4 Years Regular (I & II Semester) Academic Calendar 2010-11Document3 pagesJNTU-HYD: B.Tech/B.Pharmacy 2,3,4 Years Regular (I & II Semester) Academic Calendar 2010-11rocky4bestNo ratings yet
- Boy Scouts Crew MembershipDocument23 pagesBoy Scouts Crew MembershipAldrin M. Obias100% (1)
- Are Women Better Leaders Than MenDocument5 pagesAre Women Better Leaders Than MenArijanaNo ratings yet
- 2013 Ecpe Class Final Test Grammar Structure Units 19 25 KeyDocument12 pages2013 Ecpe Class Final Test Grammar Structure Units 19 25 KeyLet Banis FloresNo ratings yet
- Ameribar: Action Plans and Sample SchedulesDocument1 pageAmeribar: Action Plans and Sample SchedulesBrianna Bar PrepNo ratings yet
- Individual Reflection 4Document4 pagesIndividual Reflection 4Urvashi PuraniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Reading Comprehension: Vocabulary Task: Match Words in The First List To Their Meaning in The SecondDocument8 pagesChapter 2: Reading Comprehension: Vocabulary Task: Match Words in The First List To Their Meaning in The SecondPape Serigne DiopNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson PlanHazel Paguio-Lastrollo0% (3)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Civil Service ExamDocument3 pagesCivil Service ExamKaren Gina Dupra100% (1)
- Support Vector ClassificationDocument8 pagesSupport Vector Classificationapi-285777244No ratings yet
- Basic Consideration in Assessing WritingDocument4 pagesBasic Consideration in Assessing WritingIsabela TrejoNo ratings yet
- Standard Form of Quadratic EquationDocument2 pagesStandard Form of Quadratic EquationTheKnow04No ratings yet
- Rubric Lab Report Fundamental ProgrammingDocument2 pagesRubric Lab Report Fundamental ProgrammingMuhd HasbulNo ratings yet
- Script - Ueh Economic Events Commentary Series 2023Document5 pagesScript - Ueh Economic Events Commentary Series 2023Minh HươngNo ratings yet
- Intimate RelationshipDocument3 pagesIntimate RelationshipMelody LiuNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ SỐ 2Document3 pagesĐỀ SỐ 2Nguyễn Kiều OanhNo ratings yet
- Minit Mesyuarat Kokurikulum KALI Ke-2 - 2020Document6 pagesMinit Mesyuarat Kokurikulum KALI Ke-2 - 2020ruzilawatiNo ratings yet
- Cycloid Psychosis Phenomenology, Course and Outcome - A Naturalistic StudyDocument123 pagesCycloid Psychosis Phenomenology, Course and Outcome - A Naturalistic StudyAngela EnacheNo ratings yet
- Resume of Arindam PalDocument8 pagesResume of Arindam PalKrishna Moorthy GanesanNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Introduction, Project Environment & Role of Project Manager (1) - Read-Only (53) - Read-OnlyDocument33 pagesDay 1 Introduction, Project Environment & Role of Project Manager (1) - Read-Only (53) - Read-OnlySuraj ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Estimated Time The Activity Is To Be Accomplished) : E.G. 56 HoursDocument9 pagesEstimated Time The Activity Is To Be Accomplished) : E.G. 56 HoursEarl Jeofrey LagarasNo ratings yet
- Left-Handed: Handwriting PagesDocument11 pagesLeft-Handed: Handwriting PagesejoghenetaNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional de Cuyo Facultad de Educación: Lengua Extranjera: EnglishDocument8 pagesUniversidad Nacional de Cuyo Facultad de Educación: Lengua Extranjera: EnglishLiliana AlisaresNo ratings yet
- 1890 Pgmedicalcqsecondphaseallotments201920Document60 pages1890 Pgmedicalcqsecondphaseallotments201920krishnaNo ratings yet
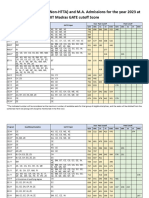
- M.Tech 2023 CutoffDocument6 pagesM.Tech 2023 Cutoffmshail30No ratings yet
- Models Show Nature's RealityDocument7 pagesModels Show Nature's RealityanaNo ratings yet
- Anuja Anil Vichare Resume 5-19-14Document3 pagesAnuja Anil Vichare Resume 5-19-14api-310188038No ratings yet
- Breaking the Habit of Being YourselfFrom EverandBreaking the Habit of Being YourselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1454)
- How to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipFrom EverandHow to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1135)
- Bedtime Stories for Adults: Tales to Soothe the Tired SoulsFrom EverandBedtime Stories for Adults: Tales to Soothe the Tired SoulsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Ikigai Journey: A Practical Guide to Finding Happiness and Purpose the Japanese WayFrom EverandThe Ikigai Journey: A Practical Guide to Finding Happiness and Purpose the Japanese WayRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (27)
- Deep Sleep Meditation: Fall Asleep Instantly with Powerful Guided Meditations, Hypnosis, and Affirmations. Overcome Anxiety, Depression, Insomnia, Stress, and Relax Your Mind!From EverandDeep Sleep Meditation: Fall Asleep Instantly with Powerful Guided Meditations, Hypnosis, and Affirmations. Overcome Anxiety, Depression, Insomnia, Stress, and Relax Your Mind!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Deep Sleep Hypnosis: Guided Meditation For Sleep & HealingFrom EverandDeep Sleep Hypnosis: Guided Meditation For Sleep & HealingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (103)
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellFrom EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellNo ratings yet