Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LEACH
Uploaded by
Mad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
175 views13 pagesOriginal Title
LEACH.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
175 views13 pagesLEACH
Uploaded by
MadCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
By Stephanie Reese
LEACH stands for Low-Energy Adaptive
Clustering Hierarchy
This WSN is considered to be a dynamic
clustering method
LEACH has two phases
The reason we need network protocol such as
LEACH is due to the fact that a node in the
network is no longer useful when its battery
dies
This protocol allows us to space out the
lifespan of the nodes, allowing it to do only
the minimum work it needs to transmit data
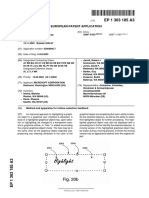
The LEACH Network is made up of nodes,
some of which are called cluster-heads
The job of the cluster-head is to collect data from
their surrounding nodes and pass it on to the base
station
LEACH is dynamic because the job of cluster-head
rotates
The amount of energy
used in figure (a) can
be modeled by this
formula:
eampk(3d1 + d2)2
Whereas the amount of
energy used in figure
(b) uses this formula:
eampk(3d12 + d22)
This is the formula for the amount of energy
depletion by data transfer:
The LEACH network has two phases: the set-
up phase and the steady-state
The Set-Up Phase
Where cluster-heads are chosen
The Steady-State
The cluster-head is maintained
When data is transmitted between nodes
Cluster-heads can be chosen stochastically
(randomly based) on this algorithm:
If n < T(n), then that node becomes a cluster-
head
The algorithm is designed so that each node
becomes a cluster-head at least once
A modified version of this protocol is known
as LEACH-C (or LEACH Centralized)
This version has a deterministic threshold
algorithm, which takes into account the
amount of energy in the node
and/or whether or not the node was
recently a cluster-head
REMEMBER: The goal of these protocol is to
increase the life of the network
The changes between the LEACH stochastic
algorithm and the LEACH-C deterministic
algorithm alone is proven to increase the FND
(First Node Dies) lifetime by 30% and the
HND (Half Node Dies) lifetime by 20%
While neither of these
diagrams is the
optimum scenario, the
second is better
because the cluster-
heads are spaced out
and the network is
more properly
sectioned
Low Energy Adaptive Clustering Hierarchy with
Deterministic Cluster-Head Selection; M.J.
Handy, M. Haas, D. Timmermann; 2002;
http://www.vs.inf.ethz.ch/publ/se/IEEE_MWCN2
002.pdf
Probabilistic Modeling of Leach Protocol and
Computing Sensor Energy Consumption Rate in
Sensor Networks; Song, Dezhen; February 22,
2005;
http://www.cs.tamu.edu/academics/tr/tamu-cs-
tr-2005-2-2
You might also like
- Data Transfer SchemesDocument6 pagesData Transfer Schemesvishwakadarsh100% (11)
- 4-Bit Carry Look Ahead AdderDocument22 pages4-Bit Carry Look Ahead AdderHani MasoumiNo ratings yet
- Final 1Document4 pagesFinal 1Amber BakerNo ratings yet
- CMSC 417 Midterm #2 (Fall 2001)Document2 pagesCMSC 417 Midterm #2 (Fall 2001)NickHenryNo ratings yet
- Difference Between LAN and WANDocument6 pagesDifference Between LAN and WANSyed JaWad HyderNo ratings yet
- EC3023 2015-6 Problemsheet#2Document2 pagesEC3023 2015-6 Problemsheet#2markNo ratings yet
- Infinite Series PDFDocument14 pagesInfinite Series PDFSunny KashyapNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For EmtDocument117 pagesLecture Notes For EmtDibyaranjan Sahu100% (1)
- LOGIC & DISTRIBUTED CONTROL SYSTEM S7 AE B.Tech May 2019Document1 pageLOGIC & DISTRIBUTED CONTROL SYSTEM S7 AE B.Tech May 2019Glan DevadhasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Jayamani KrishnanNo ratings yet
- The Basic Concept NSG2Document17 pagesThe Basic Concept NSG2wise_cee578100% (1)
- P23. Mapping of Course Outcome With Program OutcomesDocument31 pagesP23. Mapping of Course Outcome With Program OutcomesBhaskar MondalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Microwave DevicesDocument18 pagesChapter 10 Microwave DevicesAghna Tiyas MandalNo ratings yet
- LPG Leakage Detector Using Arduino With SMS Alert SystemDocument22 pagesLPG Leakage Detector Using Arduino With SMS Alert Systemsifat islamNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 Electromagnetics 1Document46 pagesLecture3 Electromagnetics 1Esteban Dalas LeonNo ratings yet
- ECE102 F11 Summary HighlightsDocument24 pagesECE102 F11 Summary HighlightsLolNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Lab: Lab Report: 06 Connecting Local Area Networks (Lans) Using RouterDocument7 pagesComputer Networks Lab: Lab Report: 06 Connecting Local Area Networks (Lans) Using RouterAkira MannahelNo ratings yet
- IT1402 Nov Dec+2009Document20 pagesIT1402 Nov Dec+2009piccoloashNo ratings yet
- G EngcoursesDocument61 pagesG EngcourseskractheworldNo ratings yet
- MOSFET CapacitancesDocument26 pagesMOSFET CapacitancesModyKing99No ratings yet
- ECE321 Lab3Document9 pagesECE321 Lab3Ha Tran KhiemNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Review of Vector AnalysisDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Review of Vector AnalysisDarshit KotadiyaNo ratings yet
- 8257 DMA Controller:: To Fetch The Instruction To Decode The Instruction and To Execute The InstructionDocument25 pages8257 DMA Controller:: To Fetch The Instruction To Decode The Instruction and To Execute The Instructionsatyanarayana12No ratings yet
- Lattice Diagram For ReflectionDocument11 pagesLattice Diagram For ReflectionEarnest ArujNo ratings yet
- Sheet MicorDocument42 pagesSheet MicorFiras TaherNo ratings yet
- 012 - Chapter 2 - L10Document12 pages012 - Chapter 2 - L10nanduslns07No ratings yet
- Barak Shoshany PHY 256 Lecture NotesDocument167 pagesBarak Shoshany PHY 256 Lecture NotesSonali Noronha100% (1)
- DNS Syllabus Rev 5 Final Approved - 2021Document129 pagesDNS Syllabus Rev 5 Final Approved - 2021Aman ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Homework 3 - SolutionsDocument14 pagesHomework 3 - SolutionsYahya Salam SalehNo ratings yet
- Data Link Control FramingDocument79 pagesData Link Control FramingHemanth Yada100% (1)
- TCP in Wireless DomainDocument30 pagesTCP in Wireless DomainMurugan Antham RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Static Performance CharactersticsDocument29 pagesChapter 3 - Static Performance CharactersticsRay DebashishNo ratings yet
- The VESA Local BusDocument15 pagesThe VESA Local Busatorresh090675No ratings yet
- Radio Navigation Systems. (ECE358)Document3 pagesRadio Navigation Systems. (ECE358)scribNo ratings yet
- Solution Gates 2 SamplesDocument9 pagesSolution Gates 2 SamplesluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Chapter4-Loading EffectsDocument41 pagesChapter4-Loading Effectshumervat100% (1)
- Instruction Set Part 1Document3 pagesInstruction Set Part 1Vivek Kumar100% (1)
- Mobility Is The Ability of A Node To Change Its Point-Of-Attachment While Maintaining AllDocument24 pagesMobility Is The Ability of A Node To Change Its Point-Of-Attachment While Maintaining AllDr. Sashi Kanth Reddy ANo ratings yet
- ChronoamperometryDocument7 pagesChronoamperometrybettypaz89100% (1)
- Ee141 HW3Document4 pagesEe141 HW3Vidhya DsNo ratings yet
- Wireshark Lab TCP16171Document5 pagesWireshark Lab TCP16171Emir UkasyahNo ratings yet
- Gnuplot Viva QuestionsDocument5 pagesGnuplot Viva QuestionsLn Amitav BiswasNo ratings yet
- Applied Reactor Technology - Henryk Anglart PDFDocument204 pagesApplied Reactor Technology - Henryk Anglart PDFdogclutchNo ratings yet
- Gummen PoolDocument29 pagesGummen PoolvanithapremkumarNo ratings yet
- Electronics Assignment #2 - Key PDFDocument11 pagesElectronics Assignment #2 - Key PDFKhairi SalehNo ratings yet
- MPLS Basics - PPTDocument31 pagesMPLS Basics - PPTAbhishek SoniNo ratings yet
- RL RC CircuitDocument13 pagesRL RC CircuitMadhav Sameer100% (1)
- VLSI, VLSI System & VLSI System DesignDocument26 pagesVLSI, VLSI System & VLSI System Designrohit_sreerama4040No ratings yet
- Implementation of Ieee 802.15.4 Modified Csma/ca Protocol On NS3Document6 pagesImplementation of Ieee 802.15.4 Modified Csma/ca Protocol On NS3johnNo ratings yet
- CPU Organization Bindu AgarwallaDocument22 pagesCPU Organization Bindu AgarwallaNobodyNo ratings yet
- DAHDI Overview For Asterisk Developers: Presented by Matthew Fredrickson and Shaun RuffellDocument24 pagesDAHDI Overview For Asterisk Developers: Presented by Matthew Fredrickson and Shaun RuffellVergin VaryNo ratings yet
- Classical Optimization Techniques: HapterDocument18 pagesClassical Optimization Techniques: Hapterchirag_693No ratings yet
- Class 1-20Document149 pagesClass 1-20SaurabhBisht100% (1)
- Periodically Loaded Line Phase Shifters Report1Document7 pagesPeriodically Loaded Line Phase Shifters Report1Metehan BulutNo ratings yet
- Intensity ModulationDocument3 pagesIntensity Modulationanon-323096100% (1)
- LEACH HDocument13 pagesLEACH HAman VermaNo ratings yet
- A2085788030 17433 24 2017 L26-LeachDocument11 pagesA2085788030 17433 24 2017 L26-LeachThupakula Gowri Shankar CWuqAbmqqk ll 80 6316No ratings yet
- LeachDocument13 pagesLeachkumaarrNo ratings yet
- LEACH Protocol: For Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument13 pagesLEACH Protocol: For Wireless Sensor NetworksAkshay ShindeNo ratings yet
- Energy Based Routing Protocol For Wireless Sensor Networks: Paramveer Singh Bali, Srinivas B KDocument4 pagesEnergy Based Routing Protocol For Wireless Sensor Networks: Paramveer Singh Bali, Srinivas B KInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- Forti AP For Advetisment Targeting DraftDocument5 pagesForti AP For Advetisment Targeting DraftMadNo ratings yet
- IPR Actuarial Science Food: Cultural IdentityDocument1 pageIPR Actuarial Science Food: Cultural IdentityMadNo ratings yet
- IPR Actuarial Science Food: Cultural IdentityDocument1 pageIPR Actuarial Science Food: Cultural IdentityMadNo ratings yet
- European Patent Application: Method and Apparatus For Hollow Selection FeedbackDocument4 pagesEuropean Patent Application: Method and Apparatus For Hollow Selection FeedbackMadNo ratings yet
- Learning French EbookDocument36 pagesLearning French EbookDonnette Davis100% (20)
- 3GPP TS 33.108Document198 pages3GPP TS 33.108Sunny Girija SapruNo ratings yet
- M&E DelayDocument3 pagesM&E DelayAssem ElhajjNo ratings yet
- Hadoop SessionDocument65 pagesHadoop SessionSuresh ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- LockedDocument8 pagesLockedapi-647061770No ratings yet
- ICC - AC38 - Acceptance Criteria For Water-Resistive BarriersDocument9 pagesICC - AC38 - Acceptance Criteria For Water-Resistive BarriersbatteekhNo ratings yet
- The X Window SystemDocument27 pagesThe X Window SystemDheeraj SoniNo ratings yet
- First Floor PlanDocument1 pageFirst Floor PlanHEET MEWADANo ratings yet
- Sap 2Document35 pagesSap 2Michael Vincent B. Nierva88% (8)
- SCL (NATM) TunnellingDocument74 pagesSCL (NATM) Tunnellingthauwui86100% (1)
- BENZZDocument26 pagesBENZZManimegalai PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Incr Yanbu All DetailDocument3 pagesIncr Yanbu All DetailUsman RanaNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS LoggingDocument3 pagesCisco IOS LoggingAnsari FaisalNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document11 pagesActivity 2Lebron Bryant100% (1)
- Revised 2 Storey House W Elelc PlumbingDocument2 pagesRevised 2 Storey House W Elelc PlumbingLucio AdaNo ratings yet
- 4.6. Nonlinear Analysis of A 16-Storey RC Building Designed According To EC2 & EC8Document8 pages4.6. Nonlinear Analysis of A 16-Storey RC Building Designed According To EC2 & EC8Dipak BorsaikiaNo ratings yet
- BK QuickStart HDPWin-20151221Document11 pagesBK QuickStart HDPWin-20151221Wallace AmorimNo ratings yet
- These Interview Questions Test The Knowledge of x86 Intel Architecture and 8086 Microprocessor SpecificallyDocument4 pagesThese Interview Questions Test The Knowledge of x86 Intel Architecture and 8086 Microprocessor Specificallyswathikomati7870No ratings yet
- NewsoutlDocument103 pagesNewsoutlpepito_perez_hellNo ratings yet
- Parasoft Soatest 9.x TutorialDocument9 pagesParasoft Soatest 9.x Tutorialblunt2vitreNo ratings yet
- Sample Offered Anirban SinhaDocument4 pagesSample Offered Anirban SinhaSourabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Recon 2010 Skochinsky PDFDocument57 pagesRecon 2010 Skochinsky PDFntcaseNo ratings yet
- Types of Stairs PDFDocument12 pagesTypes of Stairs PDFAkshay Kumar100% (1)
- Mapeh 9 ModuleDocument10 pagesMapeh 9 ModuleJohnReyBarnachea80% (5)
- GRCA SpecificationDocument15 pagesGRCA SpecificationfaisaltmNo ratings yet
- Mayur Engineer AmbalaDocument26 pagesMayur Engineer Ambalaamritesh pandeyNo ratings yet
- Quantum With Unity Pro: 141 MMS 425 01, 141 MMS 535 02 SERCOS Multi-Axis Motion Controller User ManualDocument36 pagesQuantum With Unity Pro: 141 MMS 425 01, 141 MMS 535 02 SERCOS Multi-Axis Motion Controller User Manualrmorenodx4587No ratings yet
- Al-Andalus Exhibition: Workbook (2º ESO)Document26 pagesAl-Andalus Exhibition: Workbook (2º ESO)lumaromartinNo ratings yet
- Virtual MemoryDocument2 pagesVirtual MemoryJohn Cliff BautistaNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment - Preliminary DesignDocument2 pagesGroup Assignment - Preliminary Designlost968No ratings yet
- VLAN Routing: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDocument14 pagesVLAN Routing: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDmangla\No ratings yet