Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biomechanical Basis of Traumatic Brain Injury: Mechanisms and Classification
Uploaded by
zixzaxoff0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views21 pagesThis document outlines the clinical classification and mechanisms of traumatic brain injuries. It discusses static versus dynamic loading injuries and how impact, contact forces, and head motion can cause focal injuries like contusions or more diffuse injuries like concussions and diffuse axonal injury. Blast injuries are also addressed, with primary injuries caused by the blast wave and secondary injuries from projectiles or collisions. The various types of head acceleration and their effects on brain strain and injury patterns are also summarized.
Original Description:
Biomechanical
Original Title
Biomechanical
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the clinical classification and mechanisms of traumatic brain injuries. It discusses static versus dynamic loading injuries and how impact, contact forces, and head motion can cause focal injuries like contusions or more diffuse injuries like concussions and diffuse axonal injury. Blast injuries are also addressed, with primary injuries caused by the blast wave and secondary injuries from projectiles or collisions. The various types of head acceleration and their effects on brain strain and injury patterns are also summarized.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views21 pagesBiomechanical Basis of Traumatic Brain Injury: Mechanisms and Classification
Uploaded by
zixzaxoffThis document outlines the clinical classification and mechanisms of traumatic brain injuries. It discusses static versus dynamic loading injuries and how impact, contact forces, and head motion can cause focal injuries like contusions or more diffuse injuries like concussions and diffuse axonal injury. Blast injuries are also addressed, with primary injuries caused by the blast wave and secondary injuries from projectiles or collisions. The various types of head acceleration and their effects on brain strain and injury patterns are also summarized.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 21
Biomechanical Basis of
Traumatic Brain Injury
Outline
Clinical classification of brain injuries
Mechanism of injury
Mechanistic cause of head injuries
Injuries and their mechanisms
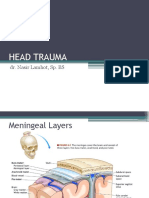
Clinical classification of brain injuries
Skull fracture
May or may not involve damage to the underlying brain
Focal injury
Generally limited to a well-circumscribed region contusions to the
cortex and subdural, epidural, and intracerebral hematomas
Penetrating injury
Blast injury
Clinical classification of brain injuries
Diffuse brain injury
Mildest form : involve only alterations in neural excitability,
neurotransmission, or long-term changes in receptor
dysfunction and associated disabilities : concussion
Prolonged coma without a mass lesion and involves some
degree of structural derangement at the microscopic level
Diffuse axonal injury
Mechanism of injury
Static or quasi-static loading
Dynamic loading
Static or quasi-static loading
Uncommon
Slowly, over times longer than 200 msec
Squeezing or crushing (seen in earthquakes, building collapses, or
machinery accidents)
fractures at the vault or basilar skull region
common that consciousness is preserved
Dynamic loading
More common
Rapidly, duration less than 50 msec
Impulsive
the head is set into motion indirectly by a blow to another body region
inertial force,brain move within the skull
Impact
combination of contact force and inertial (head motion) force
Contact phenomena(head not moving)
> 2 inch localize skull bending
Shockwave localized change in pressure,distortion,injury
small hemorrhage and contusion
More common in children ; flexible, lower calcification
Distortion or strain
Distortion or strain
Compressive strain
Compressive
Book/cylinder/table
Tension strain
elongation
Shear strain
Force applied along surface
Playing card
Dilational strain(volumetric strain)
Pressure applied all exposed face
Mechanistic causes of head injuries
Contact injuries
Head motion(inertial) injuries
Blast induced brain injuries
Contact injuries
Local contact effect
Skull : Linear and depressed skull fracture,Basilar skull fracture,
EDH : associated with skull fracture or without skull fracture
Coup lesion : beneath the side of lesion
Direct injury to the brain,surface vessel
High negative pressure from skull rapid snaps back to place
Contact injuries
Remote contact effects
Vault fracture away from the impact site, basilar skull fracture, contrecoup
Thick portion of the skull, relatively broad object
Stress wave radiate in 3D
Formation of intermediate coup contusion
Scatterd ICH, traumatic intracerbral hematoma
Global change in skull shape(infant and developing children) :
localized change in pressure small petechiae
fluctuation in intracranial volume brain herniation
Head motion(inertial injuries)
Acceleration-deceleration injuries
Brain tissue strain
Differential movement of the skull and
brain localized strain of surface
Strain within the brain parenchyma
widespread disturbances in brain function
and structure cerebral concussion and
DAI
Type of head acceleration
Type of head acceleration
Translational acceleration
Uncommon
Center gravity of brain move in straight line
Focal injuries(contrecoup, intracerebral, subdural hematoma )
Rotational acceleration
Brain rotation without center gravity of brain moving
Highly injuries
High surface strain,deep surface strain
Angular acceleration
Most common,compound translational and rotational
Neck anatomy
Most damaging (except : skull fracture and EDH)
Determinants of Acceleration injury
Not only on the type of acceleration
The magnitude of acceleration propagational to the
amount of strain delivered to the brain
First : Brief acceleration c extremely high acceleration
Second : Slightly longer
Strain restricted to periphery
skull, dura surface, brain periphery and vessel
Third : Increase even more
Strain propagate to deeper
DAI
Blast-induced brain injuries
Temporary altermental status or confusion immediately
after blast
Primary bTBI
Rapidly expanding wave,rapid rise and fall
Secondary bTBI
Penetrating and non-penetrating injuries that occur when high
velocity projectile/fragment impact the head
Tertiary bTBI
Primary bTBI cause the victim to collide with fixed or mobile
object
Injuries and their mechanisms
Skull fracture
Linear fracture
Contact effect secondary to impact
Depressed fracture
Small(< 2 inch), hard, impact
Basilar fracture
Impact or propagation of stress wave
Injuries and their mechanisms
Focal injury
Epidural hematoma
More complex case of linear skull fracture
Head motion and inertial do not cause
Coup contusion
Under impact point
Skull rebounding
Contrecoup contusion
Cavitation effect : negative pressure at opposite loading
point cause damage + small bubble turn to normal
pressure,
small bubble rupture
Injuries and their mechanisms
Intermediate coup contusion
Impact generate shock wave
Intracerebral hematoma
Impact
acceleration
Tissue tear hemorrhage(microhemorrhage)
Inertial or head motion
Superior frontoparietal white matter, corpus callosum,
centrum semiovale, periventricular white and gray matter,
internal capsule, basal ganglia
Injuries and their mechanisms
Diffuse brain injury
Cerebral concussion
Inertial loading,not form contact phenomena effect
Angular rotation
Diffuse axonal injury
Angular rotation
You might also like
- Twisted Neck, (Torticollis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandTwisted Neck, (Torticollis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Head Injury OkeDocument42 pagesHead Injury OkeAnonymous p9msXAEwNo ratings yet
- Neck Trauma, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandNeck Trauma, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Head N Spinal InjuryDocument34 pagesHead N Spinal InjuryGG WPNo ratings yet
- Neck Disorders, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Improvised TreatmentFrom EverandNeck Disorders, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Improvised TreatmentNo ratings yet
- How to Care for Head InjuriesDocument31 pagesHow to Care for Head InjuriesZawawi Ibnu Rosyid0% (1)
- Concussion Rescue: A Comprehensive Program to Heal Traumatic Brain InjuryFrom EverandConcussion Rescue: A Comprehensive Program to Heal Traumatic Brain InjuryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Head and Spinal Cord Injuries OverviewDocument68 pagesHead and Spinal Cord Injuries Overviewiam jessNo ratings yet
- 19 - Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument62 pages19 - Traumatic Brain InjurymichelleNo ratings yet
- Head TraumaDocument32 pagesHead TraumacokarisaNo ratings yet
- Biomechanical Basis of Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument32 pagesBiomechanical Basis of Traumatic Brain InjuryPutu AnantaNo ratings yet
- Guide to Head Injury: Signs, Symptoms, Diagnosis and ManagementDocument76 pagesGuide to Head Injury: Signs, Symptoms, Diagnosis and ManagementWafa Nabilah KamalNo ratings yet
- Head Injury 2Document47 pagesHead Injury 2drvishal bhattNo ratings yet
- Brain Swelling Hemorrhaging of The Brain Overlooked or Misdiagnosed Rollover AccidentsDocument6 pagesBrain Swelling Hemorrhaging of The Brain Overlooked or Misdiagnosed Rollover AccidentsNICOLE RAFAEL TACDERASNo ratings yet
- Head Injury 8Document48 pagesHead Injury 8drvishal bhattNo ratings yet
- Craniocerebral Trauma Skull Fractures Concussion, Contusion Extradural and Subdural HaematomaDocument43 pagesCraniocerebral Trauma Skull Fractures Concussion, Contusion Extradural and Subdural HaematomaHoney PrasadNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain Injury N Europsychol P TestsDocument20 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury N Europsychol P TestsrobouNo ratings yet
- Pathomechanics of Brain Injury: Types, Signs & SymptomsDocument27 pagesPathomechanics of Brain Injury: Types, Signs & Symptomsamber tariq100% (1)
- Diffuse Injury FIxDocument22 pagesDiffuse Injury FIxoomculunNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument45 pagesTraumatic Brain InjuryShitaljit IromNo ratings yet
- Head Injuries Injuries To The ScalpDocument6 pagesHead Injuries Injuries To The Scalpashythegreat93No ratings yet
- Biomechanical Factors in NeuroemergenciesDocument20 pagesBiomechanical Factors in NeuroemergenciesJunus EufrataNo ratings yet
- Head InjuriesDocument26 pagesHead InjuriesCHARLOTTE DU PREEZNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain Injury: Avy RamosDocument31 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury: Avy Ramosedeliza22No ratings yet
- Functional Neuroanatomy and Traumatic Brain Injury The Frontal Lobes (Presentation) Author Jessica MatthesDocument17 pagesFunctional Neuroanatomy and Traumatic Brain Injury The Frontal Lobes (Presentation) Author Jessica Matthessari dianitaNo ratings yet
- Craniocerebral TraumaDocument52 pagesCraniocerebral TraumachjmbnqyzvNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma & Management: Dr. Utham Murali. M.S M.B.A. Asso - Prof of Surgery IMS / MSU / MalaysiaDocument48 pagesHead Trauma & Management: Dr. Utham Murali. M.S M.B.A. Asso - Prof of Surgery IMS / MSU / MalaysiaNinaNo ratings yet
- Spinalinjuries 180518121456Document40 pagesSpinalinjuries 180518121456Akash KoulNo ratings yet
- Regional InjuriesDocument5 pagesRegional InjuriessivaniNo ratings yet
- Head TraumaDocument32 pagesHead Traumajeevan kumar reddyNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgery Case 1Document111 pagesNeurosurgery Case 1api-3704562No ratings yet
- Trauma Brain InjuryDocument66 pagesTrauma Brain Injurymulyanto nurNo ratings yet
- 3 - Head Injured PatientDocument94 pages3 - Head Injured PatientAmmarNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument66 pagesHead Injurynur muizzah afifah hussinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 017Document60 pagesChapter 017Jackson VonkNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine InjuryDocument95 pagesCervical Spine InjuryJhing Rodriguez Borjal100% (1)
- Head Injury Outline of Management CDocument89 pagesHead Injury Outline of Management CPanna SahaNo ratings yet
- Regional Injuries ForensicsDocument4 pagesRegional Injuries ForensicsMaryam Syed100% (1)
- Traumatic Brain Injury Cause Non-Traumatic Brain Injury CausesDocument10 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury Cause Non-Traumatic Brain Injury CausesBaoz PingNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument55 pagesHead InjuryDakaNo ratings yet
- Injury During TraumaDocument20 pagesInjury During TraumaWanda RendraswaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24Document4 pagesChapter 24monster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Head Injury Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentsDocument12 pagesHead Injury Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentsFerdyNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument49 pagesTraumatic Brain InjuryCHANGEZ KHAN SARDARNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument39 pagesTraumatic Brain InjuryDung Nguyễn Thị MỹNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma: Dr. Nasir Lamhot, Sp. BSDocument31 pagesHead Trauma: Dr. Nasir Lamhot, Sp. BSYohannes KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Opiana Christian Joseph - ReseachassignmenttraumaDocument42 pagesOpiana Christian Joseph - ReseachassignmenttraumaChristian Joseph OpianaNo ratings yet
- Helu NeuroDocument80 pagesHelu NeuroHussenNo ratings yet
- Spinal Traumas: Fisseha G (MD)Document63 pagesSpinal Traumas: Fisseha G (MD)mubarek nesiroNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord InjuryDocument44 pagesSpinal Cord InjuryMohd Farid Bin RosliNo ratings yet
- Head Injury-1Document74 pagesHead Injury-1Aviral BishtNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument81 pagesTraumatic Brain InjuryShine JyothNo ratings yet
- Brain TumorDocument43 pagesBrain TumorjeremiahNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma Guide: Concussions, Hematomas & CT InterpretationDocument193 pagesHead Trauma Guide: Concussions, Hematomas & CT InterpretationhanimozaghiNo ratings yet
- Depressed Skull FractureDocument4 pagesDepressed Skull FractureAngel Mae Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Brain Injury: Closed (Blunt) Brain Injury Occurs When The Head Accelerates and ThenDocument7 pagesBrain Injury: Closed (Blunt) Brain Injury Occurs When The Head Accelerates and Thencute_tineeNo ratings yet
- Head Injury... Jackie 1Document54 pagesHead Injury... Jackie 1Fatius KagenziNo ratings yet
- DR Mohamed Al Tamiami:5 Class Lecture 1 OnDocument6 pagesDR Mohamed Al Tamiami:5 Class Lecture 1 OnAmmarNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument88 pagesHead InjuryPrisca Angelina100% (2)
- Head and Spine InjuriesDocument5 pagesHead and Spine InjuriesKIMBERLY MARGARETTE REDNo ratings yet
- Vasospasm After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: NeurologyDocument9 pagesVasospasm After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: NeurologyzixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Vasospasm As Its Complication: A ReviewDocument6 pagesSubarachnoid Hemorrhage and Vasospasm As Its Complication: A ReviewzixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Turan 2014Document17 pagesTuran 2014zixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Treatment of DCIDocument11 pagesTreatment of DCIbilly2107No ratings yet
- A Review of Cerebral Vasospasm in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid HaemorrhageDocument8 pagesA Review of Cerebral Vasospasm in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid HaemorrhagezixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Kramer 2013Document8 pagesKramer 2013zixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Lin 2014Document4 pagesLin 2014zixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Le Fournier 2010Document8 pagesLe Fournier 2010zixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Cossu 2014Document14 pagesCossu 2014zixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Clinical Review: Prevention and Therapy of Vasospasm in Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument10 pagesClinical Review: Prevention and Therapy of Vasospasm in Subarachnoid HemorrhagezixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Chamberlain - 2002 - Etoposide For Recurrent Spinal Cord EpendymomaDocument3 pagesChamberlain - 2002 - Etoposide For Recurrent Spinal Cord EpendymomazixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Kale 2013Document6 pagesKale 2013zixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Cerebral Vasospasm - Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesSubarachnoid Hemorrhage and Cerebral Vasospasm - Literature ReviewzixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Bauer 2014Document8 pagesBauer 2014zixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Tao 2017Document34 pagesTao 2017zixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Sala Et Al. - 2006 - Motor Evoked Potential Monitoring Improves Outcome After Surgery For Intramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors A HistoricalDocument15 pagesSala Et Al. - 2006 - Motor Evoked Potential Monitoring Improves Outcome After Surgery For Intramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors A HistoricalzixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- S 0034 1395780Document5 pagesS 0034 1395780zixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Intramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors: Part II - Management Options and OutcomesDocument10 pagesIntramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors: Part II - Management Options and OutcomeszixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- 2049936115624630Document16 pages2049936115624630zixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Jkns 47 102Document5 pagesJkns 47 102zixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Intramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors: Part I - Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and DiagnosisDocument11 pagesIntramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors: Part I - Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and DiagnosiszixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Eroes Et Al. - 2010 - Intramedullary Low Grade Astrocytoma and Ependymoma. Surgical Results and Predicting Factors For Clinical OutcomeDocument8 pagesEroes Et Al. - 2010 - Intramedullary Low Grade Astrocytoma and Ependymoma. Surgical Results and Predicting Factors For Clinical OutcomezixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- FrontoetDocument3 pagesFrontoetzixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgical Management of AnteriorDocument14 pagesNeurosurgical Management of AnteriorzixzaxoffNo ratings yet
- Critical Perspectives - Dissertation OgrDocument15 pagesCritical Perspectives - Dissertation OgrPipNo ratings yet
- Radial Club Hand TreatmentDocument4 pagesRadial Club Hand TreatmentAshu AshNo ratings yet
- F.A.S.T.H.U.G: I W. AryabiantaraDocument35 pagesF.A.S.T.H.U.G: I W. Aryabiantaraarnawaiputu60No ratings yet
- Sefcik Ashley Resume 2018Document1 pageSefcik Ashley Resume 2018api-394215168No ratings yet
- Reading ComprehensionDocument42 pagesReading Comprehension14markianneNo ratings yet
- Influence of Anthropometric Parameters On Aerobic Capacity Among DancersDocument7 pagesInfluence of Anthropometric Parameters On Aerobic Capacity Among DancersAnonymous izrFWiQNo ratings yet
- Abdominal UltrasoundDocument6 pagesAbdominal Ultrasounds0800841739100% (1)
- Care Study CAESARIAN SECTIONDocument29 pagesCare Study CAESARIAN SECTIONNoreen EndinoNo ratings yet
- Mel Tappans Personal Survival Letter Issue 11 (Tappan)Document24 pagesMel Tappans Personal Survival Letter Issue 11 (Tappan)buckonbeach100% (1)
- Select All That Apply SATADocument58 pagesSelect All That Apply SATANicholas TagleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - MidazolamDocument2 pagesDrug Study - MidazolamKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Bradford Assay To Detect Melamine ConcentrationsDocument3 pagesBradford Assay To Detect Melamine ConcentrationsVibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Depressive Disorders: PathophysiologyDocument19 pagesDepressive Disorders: Pathophysiology21613284No ratings yet
- APVS 2005 Proceedings More On PigsDocument258 pagesAPVS 2005 Proceedings More On PigsDulce AmorNo ratings yet
- ActivatorDocument69 pagesActivatorParijat Chakraborty PJNo ratings yet
- Free Gingival Graft Procedure OverviewDocument1 pageFree Gingival Graft Procedure OverviewTenzin WangyalNo ratings yet
- HPLC - 4Document24 pagesHPLC - 4Melisa Soledad Barco Jara100% (1)
- PR Menarini PDX Ab RBCDocument2 pagesPR Menarini PDX Ab RBCvyasakandarpNo ratings yet
- BarryKuebler Lesson1 AssignmentDocument4 pagesBarryKuebler Lesson1 AssignmentBarry KueblerNo ratings yet
- ProspectusDocument52 pagesProspectusRabinder BakhshiNo ratings yet
- Genetic Counseling: A Study and SuggestionsDocument10 pagesGenetic Counseling: A Study and SuggestionsraphynjNo ratings yet
- Audit Program Ppi (Mariani, SKM, Mha)Document23 pagesAudit Program Ppi (Mariani, SKM, Mha)Dedy HartantyoNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity AlgorithmDocument1 pageLocal Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity AlgorithmSydney JenningsNo ratings yet
- Aghamohammadi Et Al 2016 WEB OF SCIENCE Integrative Cancer TherapiesDocument9 pagesAghamohammadi Et Al 2016 WEB OF SCIENCE Integrative Cancer Therapiesemmanuelle leal capelliniNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman by Yulia VionitaDocument21 pagesRangkuman by Yulia VionitaRizqi AkbarNo ratings yet
- A Novel Visual Clue For The Diagnosis of Hypertrophic Lichen PlanusDocument1 pageA Novel Visual Clue For The Diagnosis of Hypertrophic Lichen Planus600WPMPONo ratings yet
- AIDS - The Mycoplasma EXPOSE Document PDFDocument13 pagesAIDS - The Mycoplasma EXPOSE Document PDFPierre Le GrandeNo ratings yet
- 1413272524world10 15 14 PDFDocument38 pages1413272524world10 15 14 PDFCoolerAdsNo ratings yet
- DylasisDocument3 pagesDylasisyuvi087No ratings yet
- Askin TumorDocument6 pagesAskin TumorGaluh Kresna BayuNo ratings yet