Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Project Proposal
Uploaded by
MuzammalRehman100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
1K views15 pagesmuzammal
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmuzammal
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
1K views15 pagesProject Proposal
Uploaded by
MuzammalRehmanmuzammal
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
STUDY, DESIGN AND FABRICATION
OF A SOLAR POWERED ABSORPTION
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
INTRODUCTION
Air-conditioning is the dominant energy consuming service in buildings in many countries.
The world demand for cooling and dehumidification of indoor air is growing due to
increasing comfort expectations and increasing cooling loads, as well as building
architectural characteristics and trends.
The main type of systems used for air-conditioning of buildings, are vapor compression
systems. These systems have high energy consumption, cause high electricity peak loads
and employ chlorine bearing refrigerants which have negative environmental impacts.
Bearing in mind that in Pakistan there are prevailing electricity shortages and ever
increasing energy prices, there is now a great need for cooling systems that use working
cycles that are reasonably priced and can be driven by renewable energy sources.
The earths surface receives a daily solar
dose of 10E+8 kw-hr, which is equivalent
to 500 000 billion oil barrels that is one
thousand times any oil reserve known to
man.
In hot climates, one energy source abundantly available is solar energy, which could
be used to power solar cooling system based on absorption cycle.
Lithium bromide (LiBr)-water absorption units are more suitable for solar
application since their operating (generator) temperature is lower and thus more
readily obtainable with low-cost solar collectors.
Conventional vapor-compression cooling systems are powered by electricity, which
is expensive and its production is mainly dependent on fossil fuel. Reducing the use
of vapor-compression air conditioning systems will also reduce their effect on
global warming and ozone layer depletion.
Today absorption chillers
deliver 50% of the
commercial space
cooling load worldwide.
AIM & OBJECTIVE
It show the extremely high heat transfer coefficient
in the dropwise condensation regime, occur due to
The aim of project is surface tension instability (one in which the surface
tension ofofthe
Study, design and fabrication mixture
a solar has aabsorption
powered negative gradient with system.
refrigeration
the mass fraction of the volatile component, such as
To See the effect of water
adding- using pinand
ethanol fin tubes
water to the system.mixtures.)
- ammonium
To see the effect of using Marangoni Condensation effect by adding Ethanol.
To make effective refrigerator using solar energy.
To make use in rural areas.
Pollution free system.
Refrigeration system having low maintenance cost
One time investment with minimum running expense to make refrigerator with less
moving parts
LITERATURE REVIEW
Some of the works carried earlier on absorption system usage for cooling purpose
supports the fact.
M. Carmo Elvas et.al: In 1858 a French scientist named Ferdinand Carr invented
an absorption cooling system using water and sulphuric acid.
K. Lingeswaran et.al: He explained the working process of absorption refrigeration
system by giving heat energy using parabolic reflector and he also stated that
working range is 80-150C with 35% concentration ammonia and he used helium to
maintain the constant pressure of 8 bars. He also explained the dimensions of
required parabolic reflectors to achieve effective refrigeration.
Dharamvir Mangal et.al: He suggests evacuated vacuum tube over flat plate solar
collectors. Vacuum tube uses thermo siphon system, it has two tubes separated by
vacuum which reduces the conductive and convective heat loss from tube, as a
result it is more efficient than flat plate collector this paper also gives
specification of evacuated vacuum tube.
Dimitrios A. Kouremenos et.al: He compares H2/NH3 and he2/NH3 gas mixture by
considering all type of boundary conditions like thermodynamic properties
(enthalpy, entropy..Etc.) And transportation properties(density, viscosity.Etc.).
Then he concludes by saying that helium is better substitute to hydrogen for
ammonia absorption system.
O.B Akinbisoye et.al: They used activated carbon & methanol as refrigerant and he
analyzed the amount of heat absorbed in different time intervals during the day
and results are plotted by using graphs. The amount of heat absorbed or rejected
during each process is studied and given formula to calculate. He has used flat
plate solar collector to run the refrigerator.
R T Dobson et.al: He describes a natural circulation of closed loop thermosyphon
system that can transfer heat over large distances without any moving parts such
as active control sand pumps. In this paper, a theoretical basis on which to analysis
and predict the flow and heat transfer per the physical layout of the loop to be
theoretically modelled in this paper.
SOLAR ENERGY AND ABSORPTION AIR-CONDITIONING
SYSTEMS
SOLAR ENERGY
Sun is a continuous fusion reactor in which hydrogen is turned into helium. Total
energy output from the sun is 3.8 x 10 20 MW, which is equal to 63 MW/m2 of
sun surface. Earth receives only a tiny fraction of this emitted energy, equal to 1.74
x 1011 MW (or 341 W/ m2 average). However, even with this small fraction, it is
estimated that 84 minutes of solar radiations falling on earth can satisfy world
energy demand for one year (about 900 E joules).
The amount of solar energy available at any specified place depends upon three factors:
Location (latitude and longitude)
Date
Time of the day
SOLAR ENERGY COLLECTION
The major component of a solar thermal air conditioning system is solar collector. These are
heat exchangers that absorb solar radiation energy, convert it into heat and transfer this heat
to heat transfer fluid (air, water or oil).This collected thermal energy either can be used
directly for air-conditioning or can be stored in thermal energy storage tanks for later use at
night times when sun is not available. There are two types of solar collectors: stationary (non-
concentrating) and concentrating.
Solar Collector
Two classifications are stationary collectors and axis tracking collectors. Stationary collectors
are selected for this study since they are relatively cheap and easily available.
Flat plate vs. Evacuated tube collector
Flat plate collector (FPC) type of collector which absorbs the incident solar radiation on a
flat surface whose absorptivity is very high and transmit that energy to fluid running through
different channels. FPC is by far the most used type of collector. They are inefficient for
high temperature applications such as steam generation but are cost effective for low
temperature applications. Well established technology and higher life time are few of the
desirable properties. Disadvantages include increased heat losses at higher temperatures due
to highly exposed surface area and inability to bear intensive weathering conditions.
Evacuated tube collector (ETC) comprises of many evacuated tubes connected in
series that absorb solar radiation and convert them to thermal energy. The outer
tube has small reflectivity and absorptivity but high transmissivity. The space
between outer and inner tube is vacuum (hence the name evacuated) so that no
convective heat loss takes place. The inner plate has high absorptivity and it
performs the function of transferring this energy as heat to the fluid. This
construction ensures its efficient performance at high temperatures.
For a given absorber area, evacuated tubes can maintain their efficiency over a
wide range of ambient temperatures and heating requirements. Another advantage
is easy maintenance of such systems due to modular design of the commercially
available collectors. One disadvantage is that efficiency is strongly dependent on
weather conditions. It drops significantly in cloudy or rainy weather.
SOLAR ABSORPTION SYSTEM MODELLING
Solar absorption system consists of two portions. First one is solar portion
consisting of solar collectors, storage tank and auxiliary heater etc. Second portion
consists of the absorption cycle, cooling tower and refrigerated space.
Absorption cycle thermodynamically, constitutes a heat engine driving a heat pump.
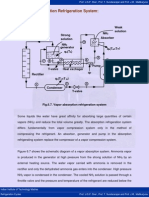
The absorption cooling cycle can be described in three phases:
Evaporation: A liquid refrigerant evaporates in a low partial pressure environment,
thus extracting heat from its surroundings the refrigerator.
Absorption: the gaseous refrigerant is absorbed dissolved into another liquid -
reducing its partial pressure in the evaporator and allowing more liquid to
evaporate.
Regeneration: the refrigerant-laden liquid is heated, causing the refrigerant to
evaporate. It is then condensed in condenser to replenish the supply of liquid
refrigerant in evaporator.
METHODOLOGY
In the experimental setup of vapor absorption refrigeration system, different pin
fin dimension tubes and ethanol will be used. The whole setup will consist of
condenser, expansion valve, evaporator, absorber, pump, generator and pin-fin
tubes.
Condenser:just like in the traditional condenser of the vapor compression cycle,
the refrigerant enters the condenser at high pressure and temperature and gets
condensed.
Expansion valve or restriction:when the refrigerant passes through the
expansion valve, its pressure and temperature reduces suddenly. This refrigerant
(ammonia in this case) then enters the evaporator.
Evaporator:the refrigerant at very low pressure and temperature enters the
evaporator and produces the cooling effect. This refrigerant flows to the absorber
that acts as the suction part of the refrigeration cycle.
Absorber:the absorber is a sort of vessel consisting of water that acts as the
absorbent, and the previous absorbed refrigerant. Thus the absorber consists of
the weak solution of the refrigerant and absorbent .
Pump:when the absorbent absorbs the refrigerant strong solution
of refrigerant-absorbent (ammonia-water) is formed. This solution is
pumped by the pump at high pressure to the generator. Thus pump
increases the pressure of the solution to about 10bar.
Generator:the refrigerant-ammonia solution in the generator is
heated by solar energy. Due to heating the temperature of the
solution increases. The refrigerant in the solution gets vaporized and
it leaves the solution at high pressure. The high pressure and the
high temperature refrigerant then enters the condenser.
RESULT EXPECTED
As suggested by the previous researchers, it expected that
the COP of absorption refrigeration is between 0.104 to
0.12 an average of 0.11.
We are expected that after our experimental work
methodology we can increase its cop up-to 0.14.
UTILIZATION OF RESEARCH RESULT
The increased surface area result by using pin fin tube with
best geometry like circumferential fin spacing, pin height
and optimum vapor velocity and ethanol can be used in new
designed condensers to increase the heat transfer and
overall COP of the absorption refrigeration system.
You might also like
- Final MorDocument22 pagesFinal MorJeff BugsNo ratings yet
- Salted Egg Cleanser Machine ManuscriptDocument86 pagesSalted Egg Cleanser Machine ManuscriptJoey MalabananNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 and 2Document36 pagesCHAPTER 1 and 2Rexon ChanNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller-Based Matured Coconut Meat and Milk ExtractorDocument151 pagesMicrocontroller-Based Matured Coconut Meat and Milk ExtractorTokki100% (2)
- Ent-Output 21Document1 pageEnt-Output 21Ronna Mae DungogNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument2 pagesActivityKarl Sean UbinaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Solar Traffic LightDocument15 pagesCase Study Solar Traffic Lightசுந்தர மூர்த்தி சேப்பிளையார்No ratings yet
- SOLAR DRYER v1Document43 pagesSOLAR DRYER v1Maria Angelica Borillo100% (1)
- Improvised Transmission JackDocument27 pagesImprovised Transmission Jackgrazur philips100% (1)
- Development of Manual Multipurpose Coconut Cutting MachineDocument1 pageDevelopment of Manual Multipurpose Coconut Cutting MachineNeil John LayagueNo ratings yet
- Final ErDocument27 pagesFinal ErEvol LahamNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Peanut Peeler MachineDocument7 pagesDesign and Development of Peanut Peeler MachineKristoffer SamsonNo ratings yet
- CHE183F plant visit Central Azucarera Don PedroDocument3 pagesCHE183F plant visit Central Azucarera Don PedroEdrian A. MañalongNo ratings yet
- Precision Wood Cutting Machine DesignDocument82 pagesPrecision Wood Cutting Machine DesignSergiero DadoleNo ratings yet
- Design, Fabrication and Performance Evaluation of A Small Capacity Mungbean ShellerDocument42 pagesDesign, Fabrication and Performance Evaluation of A Small Capacity Mungbean Shellerprincejhumer0% (1)
- The Feasibility of Jackfruit Peeling As Binder To Whiteware Plastic Mass (Revised Chapter 1,2,3)Document26 pagesThe Feasibility of Jackfruit Peeling As Binder To Whiteware Plastic Mass (Revised Chapter 1,2,3)Joshua PicartNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Bases of ResearchDocument49 pagesPhilosophical Bases of Researchapi-222431624No ratings yet
- Positive Comments From Student EvaluationsDocument5 pagesPositive Comments From Student Evaluationsapi-329560184100% (1)
- Experimental Study: Extracted Resin Oil of Pili (Canarium Ovatum) Tree As An Alternative For FuelDocument9 pagesExperimental Study: Extracted Resin Oil of Pili (Canarium Ovatum) Tree As An Alternative For Fuelchristan yapNo ratings yet
- Solar & Wind Powered Water Dispenser for Sustainable UseDocument2 pagesSolar & Wind Powered Water Dispenser for Sustainable UseDoms100% (2)
- Antique Wind PowerDocument94 pagesAntique Wind PowerBorly GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Coffee Plant Uprooting MachineDocument35 pagesDesign and Development of Coffee Plant Uprooting MachinePrathapNo ratings yet
- Plastic PulverizerDocument23 pagesPlastic PulverizerMarck DiegoNo ratings yet
- Hand Crank Mobile Charger: A DIY Power Bank for Mobile DevicesDocument18 pagesHand Crank Mobile Charger: A DIY Power Bank for Mobile DevicesAnonymous jzs1Wv100% (1)
- BSU IE Students Request Company ObservationDocument11 pagesBSU IE Students Request Company ObservationMalvin Roix OrenseNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Autonomated Chicken Slicing MachineDocument51 pagesDesign and Development of Autonomated Chicken Slicing MachineSheena Bejasa100% (1)
- Final ProposalDocument13 pagesFinal ProposalHermela100% (1)
- Ice Plant RRLDocument17 pagesIce Plant RRLJohn Paul Panganiban SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Cage ConstructionDocument21 pagesCage ConstructionNehaNo ratings yet
- Portable Cacao Bean SorterDocument4 pagesPortable Cacao Bean SorterDeteu Cabadonga100% (1)
- Pili Nut Cracking MachineDocument5 pagesPili Nut Cracking MachineJefferNo ratings yet
- Improvised Vacuum Cleaner Using A 9 Liter GallonDocument15 pagesImprovised Vacuum Cleaner Using A 9 Liter GallonEhrin AgustinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document23 pagesChapter 1Alessandra Abrau100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Lecture 3 Energy EquationDocument1 pageThermodynamics Lecture 3 Energy EquationGot7100% (1)
- Rice Milling FeasibilityDocument20 pagesRice Milling FeasibilityMharJhun Virtudazo100% (1)
- How soil erosion affects fertility and costs of productionDocument1 pageHow soil erosion affects fertility and costs of productionGriever RenzNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal-Group 4Document5 pagesProject Proposal-Group 4meenachiNo ratings yet
- Iot Finals Clap Switch Group 5Document15 pagesIot Finals Clap Switch Group 5RICHYBOY SALACNo ratings yet
- GDB3023 Assignment Analyzes Costs, Benefits of Gas Station TripDocument3 pagesGDB3023 Assignment Analyzes Costs, Benefits of Gas Station TripDanish ZabidiNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument3 pagesRRLelCrisNo ratings yet
- Crispy Kangkong: Easy Filipino AppetizerDocument4 pagesCrispy Kangkong: Easy Filipino AppetizerMigs YuNo ratings yet
- Badiang Chapter 2 (Latest)Document10 pagesBadiang Chapter 2 (Latest)Alna Jae100% (2)
- Scope and LimitationDocument1 pageScope and Limitationmgoldiieeee67% (3)
- Biomass-Fueled Grain Dryer With Recirculation of Heated Air - Chapter 1-6 With AppendicesDocument100 pagesBiomass-Fueled Grain Dryer With Recirculation of Heated Air - Chapter 1-6 With AppendicesJam PamaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Power BankDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic Power BankSaravanan SukumaranNo ratings yet
- Manual On Aqua EngDocument102 pagesManual On Aqua EngGIMRIL ATESNo ratings yet
- Coconut DryerDocument11 pagesCoconut DryerJohn Joseph MoralNo ratings yet
- Solid WasteDocument67 pagesSolid WasteSing KhoNo ratings yet
- Binungey Ice CreamDocument6 pagesBinungey Ice CreamCassandra BorbonNo ratings yet
- Rice and Corn MillingDocument24 pagesRice and Corn MillingJessa San PedroNo ratings yet
- De-Husking Mechanism For Mini Rice Milling MachineDocument32 pagesDe-Husking Mechanism For Mini Rice Milling MachineSanjay Kang Chul100% (1)
- Practice Task DPD - AnswersDocument2 pagesPractice Task DPD - AnswersMK KMNo ratings yet
- How Do You See Yourself 10 Years From NowDocument1 pageHow Do You See Yourself 10 Years From NowEjay MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-Unrevised and Chapter2Document9 pagesChapter1-Unrevised and Chapter2Sophia IsabelNo ratings yet
- Ojt RequirementsDocument28 pagesOjt RequirementsALPAY Keilah ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Boosting Pili Nut Farming in Albay ProvinceDocument40 pagesBoosting Pili Nut Farming in Albay ProvinceAngelo TabbayNo ratings yet
- Biogas and Natural GasDocument53 pagesBiogas and Natural GasSamuel OsifesoNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument5 pagesReportabdulNo ratings yet
- Adsorption Refrigeration Systems ExplainedDocument23 pagesAdsorption Refrigeration Systems ExplainedSoujanya PuhanNo ratings yet
- Study of The Performance of A Solar Adsorption Cooling SystemDocument15 pagesStudy of The Performance of A Solar Adsorption Cooling SystemwidhisaputrawijayaNo ratings yet
- AbcdDocument2 pagesAbcdMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- 8CBFDocument1 page8CBFMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1: Directorate of Distance Learning Education G.C University, FaisalabadDocument1 pageAssignment No.1: Directorate of Distance Learning Education G.C University, FaisalabadMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- CV FinalDocument2 pagesCV FinalMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument3 pagesCase StudyMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Miller Cycle PresentationDocument27 pagesSeminar On Miller Cycle PresentationMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Head of DepartmentDocument1 pageHead of DepartmentMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1: Directorate of Distance Learning Education G.C University, FaisalabadDocument1 pageAssignment No.1: Directorate of Distance Learning Education G.C University, FaisalabadMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- 1276Document24 pages1276MuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- CVDocument2 pagesCVMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Iftikhar Amjad CVDocument3 pagesIftikhar Amjad CVMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Quiz#3 Cad/Cam: Sir SaeedDocument5 pagesQuiz#3 Cad/Cam: Sir SaeedMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Deflection and Average Stresses: Assignment No. 2Document4 pagesDeflection and Average Stresses: Assignment No. 2MuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Comsats Institute of Information Technology SahiwalDocument2 pagesComsats Institute of Information Technology SahiwalMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- 001 v2 2 PDFDocument6 pages001 v2 2 PDFMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- C0409 03-1318 PDFDocument6 pagesC0409 03-1318 PDFMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Presentation Format BSMEB7Document10 pagesPresentation Format BSMEB7MuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Why Solar Absorption Refrigeration SystemDocument5 pagesWhy Solar Absorption Refrigeration SystemMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument19 pagesProposalMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Vapor Absorption Vs CompressionDocument3 pagesVapor Absorption Vs Compression78kbalajiNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument19 pagesFinalMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- PPPPPPPDocument2 pagesPPPPPPPMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations Lab ReportDocument1 pageMechanical Vibrations Lab ReportMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- 2193Document6 pages2193MuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Cu 4201638643Document6 pagesCu 4201638643MuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Experiments List and GuideDocument1 pageMechanical Experiments List and GuideMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- CAD/CAM Assignment #4 Submitted to Sir Muhammad SaeedDocument1 pageCAD/CAM Assignment #4 Submitted to Sir Muhammad SaeedMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document1 pageAssignment 4MuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration NumericalsDocument5 pagesRefrigeration NumericalsMuzammalRehmanNo ratings yet
- Equiptmet Capital Budget JustificationDocument3 pagesEquiptmet Capital Budget Justificationapi-249687869No ratings yet
- Electrical Power SystemsDocument14 pagesElectrical Power SystemsEternalOOOSunshine100% (1)
- Final 4X06 ReportDocument151 pagesFinal 4X06 Reportyliu8877No ratings yet
- Hydro Power GenerationDocument112 pagesHydro Power Generationnaveed1986sirfNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Sundaya - Ulitium - KitDocument1 pageMicrosoft Word - Sundaya - Ulitium - KitFerdi RukmantoNo ratings yet
- CE 4188 Senior Design IDocument13 pagesCE 4188 Senior Design ImrstewardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 High Tech Slow TechDocument4 pagesChapter 5 High Tech Slow TechThư AnhNo ratings yet
- Iraq Power Sector Conference SpeechDocument15 pagesIraq Power Sector Conference Speechnaniee1707No ratings yet
- Catalog Chinese 201205 PDFDocument36 pagesCatalog Chinese 201205 PDFtitusaffectionativeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ME-GI Engines (Dual Fuel)Document23 pagesIntroduction To ME-GI Engines (Dual Fuel)Lucinio PittiNo ratings yet
- Gayatri Projects LTD - Sembcorp Launches 2640 MW Power Complex (Company Update)Document4 pagesGayatri Projects LTD - Sembcorp Launches 2640 MW Power Complex (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Westco PumpDocument8 pagesWestco PumpWorapat PuttakasemNo ratings yet
- Electrical Q&ADocument388 pagesElectrical Q&AOkore Philip Nwankwo100% (2)
- Biodiesel-Water Emulsions: An Alternative Approach For Conventional FuelsDocument5 pagesBiodiesel-Water Emulsions: An Alternative Approach For Conventional FuelsAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rNo ratings yet
- Transformer DesignDocument9 pagesTransformer DesignHansraj AkilNo ratings yet
- Energy 05 00077Document20 pagesEnergy 05 00077Efstathios MaliakisNo ratings yet
- Earth 2050 & BeyondDocument17 pagesEarth 2050 & BeyondSumit RamNo ratings yet
- Quenching of Flame Anaylsis by ManasDocument17 pagesQuenching of Flame Anaylsis by ManasManas Srivastav100% (1)
- MIS-M-DS-04052 50m3 Treated Water Tank Data Sheet (T-04320) - CDocument2 pagesMIS-M-DS-04052 50m3 Treated Water Tank Data Sheet (T-04320) - Chappale2002No ratings yet
- ME2403-Power Plant EngineeringDocument5 pagesME2403-Power Plant EngineeringkrishnabrNo ratings yet
- The Future of Energy Use - Nicola Pearsall PDFDocument297 pagesThe Future of Energy Use - Nicola Pearsall PDFPaul Frederick MitchellNo ratings yet
- Water Pumping Windmill: A Historical Application of Wind EnergyDocument11 pagesWater Pumping Windmill: A Historical Application of Wind EnergySaravanapriya Karthik100% (1)
- OeEB Study Energy Efficiency Finance SerbiaDocument58 pagesOeEB Study Energy Efficiency Finance SerbiaIvanRomanovićNo ratings yet
- Learning Area Grade Level Quarter DateDocument5 pagesLearning Area Grade Level Quarter DateCheska Mary BarceloNo ratings yet
- Candu PosterDocument1 pageCandu PosterJohn BaynerNo ratings yet
- Project Interim ReportDocument33 pagesProject Interim ReportAnonymous L7XrxpeI1zNo ratings yet
- ZU BombaDocument105 pagesZU BombaErwin CastroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document14 pagesChapter 5Ben AhmedNo ratings yet
- Awardedhydro2015 04 30Document24 pagesAwardedhydro2015 04 30Mark Daryl MayandocNo ratings yet