Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH05
Uploaded by
Ankit Rajput0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views12 pagesChapter 5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChapter 5
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views12 pagesCH05
Uploaded by
Ankit RajputChapter 5
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
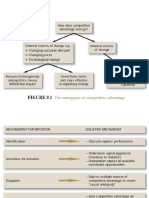
FIGURE 5.1 Analyzing resources and capabilities: the interface between strategy
and the firm
Honda First gasoline-
‘Technical Competes in 4-cylinder powered car Civic Hybrid
Research Isle of Man TT 750cc ‘to meet U.S. (dual gasoline)
Institute motorcycle motorcycle Low Emission lectrie)
founded races Vehicle Standard
Portable
generator Power products: Honda wins
ground tillers, marine Indy
‘engines, generators,
40sec lumps, ehansaws, “nese
motor snowblowers
cycle
a
1946 1950 1955 1960 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2006
The I U mini ‘Acura Car == co-
Supercub ar divson | generation
system
=)
Begins
production of
diesel engines
crore |
Honda Enters Indy
Cwie ‘arracing
First product: SaParns | Formula 1 1000cc
Model A Grand Perec Prix racing Gold Wing
clip-on engine touring
for bicycles
motorgycle
FIGURE 5.2 Honda Motor Company: product development milestones
INDUSTRY KEY,
COMPETITIVE SUCCESS FACTORS
ADVANTAGE J STRATEGY SHER |
ORGANIZATIONAL
CAPABILITIES
RESOURCES,
TANGIBLE INTANGIBLE HUMAN
© Financial (cash, © Technology © Skills/know-how
securities, borrowing (patents, copyrights, © Capacity for
capacity) ‘ade secrets) communication
© Physical (plant, © Reputation (brands, and collaboration
equipment, land, felationships) © Motivation
mineral reserves) ees
FIGURE 5.3 The links among resources, capabilities and competitive advantage
TABLE 5.1 Major companies with the highest market-to-book ratios, December 2006
Valuation Valuation
Company Ratio Country Company Ratio Country
Yahoo! Japan 72.0 Japan Coca-Cola 78 US.
Colgate-Palmolive 208 Us Diageo 74 UK.
GlaxoSmithKline 13.4 U. 3M 73 US.
Anheuser-Busch 12.6 US. Nokia 67 Finland
eBay 2 US. Sanofi-Aventis 63 France
SAP 108 Germany AstraZeneca 59 UK.
Yahoo! 10.7 US. Johnson & Johnson 57 US.
Dell Computer 10.0 Boeing 57 US.
Sumitomo Mitsui Financial 88 Eli Lily 5.6 US.
Procter & Gamble 84 US. Cisco Systems 55 US.
Qualcomm 83 Us. Roche Holding 55 Switz.
Schlumberger 8.2 US. UOréal 53 France
Unilever 8.1 Neth/UK. Altria 52 US.
Pepsico 8.0 US. Novartis 51 switz.
Note: The table includes companies with the highest market capitalization as a proportion of balance sheet net asset value
among the top 200 companies of the world with the largest market capitalization at the end of 2006
TABLE 5.2 The world’s most valuable brands, 2008
Brand value Change Country
Rank Brand in 2008, $ billion from 2007 _— off origin
1 Coca-Cola 66.7 -1% US.
2 18M 59.0 +11% US.
3 Microsoft 59.0 -2% US.
4 GE 53.1 +14% US.
5 Nokia 35.9 +35% Finland
6 Toyota 34.1 +37% Japan
7 Intel 31.3 6% US.
8 McDonald's 31.0 0% US.
9 Disney 29.3 +11% US.
10 Google 25.6 +96% US.
1" Mercedes Benz 25.6 +28% Germany
12 Hewlett-Packard 23.9 +26% US.
13 BMW 23.3 +36% Germany
14 Gillette 22.1 +5% us.
15 American Express 21.9 +18% US.
16 Louis Vuitton 21.6 +34% France
7 Cisco 21.3 +22% US.
18 Marlboro 213 0% US.
19 ith 20.2 41% US.
20 Honda 19.1 +21% Japan
Note: Brand values are calculated as the net present value of future earnings generated by the brand,
Source:Interbrand
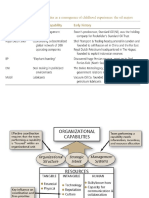
TABLE 5.3 A functional classification of organizational capabilities
Functional area
Capability
Exemplars
CORPORATE FUNCTIONS
MANAGEMENT INFORMATION
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT
OPERATIONS
PRODUCT DESIGN
MARKETING
SALES AND DISTRIBUTION
Financial control
Management development
Strategic innovation
Multidivisional coordination
Acquisition management
International management
Comprehensive, integrated MIS
network linked to managerial
decision making
Research
Innovative new product development
Fast-cycle new product development
Efficiency in volume manufacturing
Continuous improvements in operations
Flexibility and speed of response
Design capability
Brand management
Building reputation for quality
Responsiveness to market trends
Effective sales promotion and execution
Efficiency and speed of order processing
Speed of distribution
Customer service
ExxonMobil, PepsiCo
General Electric, Shell
Google, Haier
Unilever, Shell
Gisco Systems, Luxottica
Shell, Banco Santander
Wal-Mart, Capital One, Dell
Computer
IBM, Merck,
3M, Apple
Canon, Inditex (Zara)
Briggs & Stratton, YKK
Toyota, Harley-Davidson
Four Seasons Hotels
Nokia, Apple
Procter & Gamble, Altria
Johnson & Johnson
MTV, LOréal
PepsiCo, Pfizer
LL. Bean, Dell Computer
Amazon.com
Singapore Airlines, Caterpillar
FIRM INFRASTRUCTURE SUPPORT
ACTIVITIES:
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT
PROCUREMENT
INBOUND
LOGISTICS
OPERATIONS OUTBOUND
LOGISTICS
MARKETING
AND SALES
SERVICE
PRIMARY ACTIVITIES
FIGURE 5.4 Porter’s value chain
cROss-
FUNCTIONAL
CAPABILITIES,
BROAD,
FUNCTIONAL
CAPABILITIES
activity-
RELATED
CAPABILITIES
(Operations
related only)
‘SPECIALIZED.
CAPABILITIES.
(Manufacturing
related only)
SINGLE-TASK
CAPABILITIES,
(Only those
related to PCB
assembly)
New product
development
‘capability
Customer Quality
Support management
capability ‘capability,
——
Operations
‘capability
R&D and
desi
capability
Marketing
‘and sales.
capability
Human
management
‘capability
eo
Manufacturing
capability
Materials Process
management engineering
capability capability
Product
engineering
capability
Test
‘engineering
‘capability
-——_
Printed
circuit-board
assombly
Telset
assembly
System
assembly
-———_—_,
Automated
through-hole
‘component
insertion
aH
Manual
Wave
insertion of
components ae
= =
INDIVIDUALS’ SPECIALIZED KNOWLEDGE
J
FIGURE 5.5 The hierarchical nature of capabilities: a manufacturer of PBXs
THE EXTENT OF Scarcity |
THE COMPETITIVE ———
ADVANTAGE
ESTABLISHED Relevance |
Durability |
THE PROFIT-EARNING
POTENTIAL
OF A RESOURCE OR
CAPABILITY
SUSTAINABILITY OF
THE COMPETITIVE
Transferability |
ADVANTAGE
Replicability |
Property rights |
APPROPRIABILITY Relative
bargaining power
Embeddedness |
FIGURE 5.6 Appraising the strategic importance of resources and capabilities
TABLE 5A Appraising VW's resources and capabilities
Importance’ VWs relative strength? Comments
RESOURCES
Ri. Finance 6 6 Credit rating is above average for the industy but free cash flow
remains negative
2. Technology 7 5 Despite technical strengths, WY is not a leader in automotive technology
R3. Pant and equipment 8 8 Has invested heavily in upgrading plants
A, Location 4 4 Plants in key low-cost, growth markets (China, Mexico, Brazil) but
German manufacturing base is very expensive
RS. Distribution 8 5 Geographically extensive distribution with special strength in emerging
(Gealership netweark) ‘markets, Historically weak position within the U.S.
6. Brands 6 5 \Wwy, Au, Bentley and Bugatti are strong brands but, together with
Skoda and Seat, VW's brand portfolio lacks coherence and clear
market positioning
CAPABILITIES
CC, Product development 9 4 Tragitionally weak at VW. Despite a few big hits: Beetle (introduced
1938), Golf (1974, Passat (1974), Vanagon (1979), VW still not an
industry leader in new product development
2, Purchasing 7 5 Tacitionally weak—strengthened by senior hires from Opel and elsewhere
3, Engineering 7 8 The core technical strength of VW
C&, Manufacturing 8 4 Wis a high-cost producer, but struggles to attain above average quality
CS, Financial management 6 4a Has traditionally lacked a strong financial orientation
5. RED 5 4 Despite several technical strengths, VW is not a leader in automotive
innovation
C7. Matketing and sales 9 4 Despite traditional weakness in recognizing and meeting customer
‘needs in different national markets, VW has increased its sensitivity to
‘the market, improved brand management, and managed its
advertising and promotion with increasing dexterity
B, Government relations 4 8 Important in emerging markets
9, Strategic management 7 4 Effective restructuring and cost cutting, But lack of consistency and
‘consensus at top management level
Beth scales range from 1 to 10(1 = vary low, 10 = very high
Vokswagen's rescurces and capabilities are compared with those of GM, Ford, Toyota, DaimlerChrysler, Nissan, Honda, iat, and PSA, where S represents parity. The
ratings are based on the authors subjective judgment.
Superfluous Strengths Key Strengths
-— @
Os
mrep a.
mays) yal
Relative Strength
wu
1 Zone of irrelevance Key Weaknesses
1 5
Strategic Importance
Note: Figure 5.7 is based on the ratings of resources and capabilities in Table 5.4.
FIGURE 5.7 Appraising VW’s resources and capabilities (hypothetical)
4, Develop strategy implications.
(a) In relation to strengths
— How can these be exploited more
effectively and fully?
(b) In relation to weaknesses
— Identify opportunities to outsource STRATEGY
activities that can be better performed by
other organizations
— How can weaknesses be corrected
through acquiring and developing
resources and capabilities?
3. Appraise the firm's resources and capabilities POTENTIAL FOR
in terms of: SUSTAINABLE
(a) strategic importance COMPETITIVE
ADVANTAGE
(b) relative strength
2. Explore the linkages between resources
and capabilities
CAPABILITIES
RESOURCES
FIGURE 5.8 Summary: a framework for analyzing resources and capabilities
1.
Identify the firm’s resources and capabilities
You might also like
- ShouldiceHospital Group 2Document11 pagesShouldiceHospital Group 2Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- CH14Document5 pagesCH14Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- CH13Document2 pagesCH13Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- CH08Document6 pagesCH08Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- CH06Document5 pagesCH06Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- CH11Document7 pagesCH11Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- CH11Document7 pagesCH11Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- CH09Document6 pagesCH09Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- CH10Document6 pagesCH10Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- CH07Document7 pagesCH07Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- CH06Document5 pagesCH06Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- CH05Document12 pagesCH05Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- Cypress Semiconductors - Interim ReportDocument9 pagesCypress Semiconductors - Interim ReportAnkit RajputNo ratings yet
- CH02Document6 pagesCH02harleydavidson6915No ratings yet
- CH04Document9 pagesCH04Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- BPCL IndividualDocument12 pagesBPCL IndividualAnkit RajputNo ratings yet
- CH03Document11 pagesCH03Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- Shouldice Group Report FinalDocument12 pagesShouldice Group Report FinalAnkit RajputNo ratings yet
- Nandi Chat BhandarDocument13 pagesNandi Chat BhandarAnkit RajputNo ratings yet
- Fairness Cream Presentation: Factors Influencing Consumer BehaviorDocument42 pagesFairness Cream Presentation: Factors Influencing Consumer BehaviorAnkit RajputNo ratings yet
- CH01Document7 pagesCH01Ankit RajputNo ratings yet
- Jyotirao PhuleDocument27 pagesJyotirao PhuleAnkit RajputNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)