Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flash Memory: Technical Seminar Report
Uploaded by
uname0708Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Flash Memory: Technical Seminar Report
Uploaded by
uname0708Copyright:
Available Formats
National Institute of Science & Technology
TECHNICAL SEMINAR REPORT
FLASH MEMORY
Presented by
Rajnikant Bal
Roll no:IT200118159
Under the Guidance
of
Mr. Pradeep Kumar Jena.
National Institute of Science & Technology
FLASH MEMORY
INTRODUCTION
Flash memory provides exciting opportunities to
increase the flexibility of an embedded product.
Flash Memory is solid state non-volatile memory.
It stores electrical charges rather than magnetic
media.
Flash memory is light, compact, energy efficient and
less expensive.
It is a ideal storage medium for digital camera, smart
card etc.
Presented By: Rajnikant Bal, IT200118159
National Institute of Science & Technology
FLASH MEMORY
WHAT IS FLASH MEMORY?
Flash memory is electronically erasable,
electronically programmable, (generally) readonly memory.
From an embedded
system
designers
perspective, the key difference between flash
memory and EEPROM is that flash devices are
block structured; that is, while flash memory
locations are individually programmable, they
are not individually erasable the way they are
with EEPROM.
Presented By: Rajnikant Bal, IT200118159
Cont..
3
National Institute of Science & Technology
FLASH MEMORY
Flash memory is erased in sections whose
sizes and locations in the chip are defined by
the parts manufacturer.
As a result, once a flash memory location is
programmed, the entire section containing the
location must be erased before that location
can be programmed again.
Presented By: Rajnikant Bal, IT200118159
National Institute of Science & Technology
FLASH MEMORY
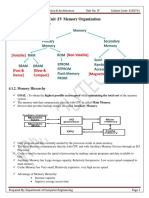
FLASH MEMORY ARCHITECTURE
National Institute of Science & Technology
FLASH MEMORY
HOW FLASH MEMORY WORKS
Flash memory is a type of EEPROM chip.
Flash memory cell consists of two transistors and
these transistors are separated by a thin oxide
layer.
One transistor is called floating and other one is
control gate.
A cell censor monitor the level of charge passing
through floating gate. if the flow through the gate is
greater than 50%of charge its value is 1. If charge
passing drops below 50% threshold its value is 0.
Presented By: Rajnikant Bal, IT200118159
National Institute of Science & Technology
FLASH MEMORY
HOW TO ERASE & WRITE TO FLASH?
Flash memory is a type of EEPROM chip. It has a
grid of columns and rows with a cell that has two
transistors at each intersection . The two transistors
are separated from each other by a thin oxide layer.
Programming algorithms specified to Flash controller
is used to control Flash memory.
Presented By: Rajnikant Bal, IT200118159
National Institute of Science & Technology
FLASH MEMORY
FLASH APPLICATIONS
FLASH Memory for Data Storage
The flash can also be used for configuration data and mass
storage. Since flash is non-volatile these systems can restore
configuration parameters after a power failure or reset.
Presented By: Rajnikant Bal, IT200118159
National Institute of Science & Technology
FLASH MEMORY
FLASH APPLICATIONS
Various Types of Flash Memories Products
1. Data flash memories are used as flexible data storage
devices in mobile telephones, PDAs, digital cameras,
MP3 players .
2. Program flash memories (or Code Flash) are used as
memories for software in personal computers, mobile
telephones and other electronic devices.
3. Embedded flash memories are used to equip chip
cards,which are increasingly utilized as cash cards and ID
cards. Flash memory is often used in MP3 players and
digital cameras, magazines.
9
National Institute of Science & Technology
FLASH MEMORY
FLASH APPLICATIONS
Products needing reduced service costs
A product with in-circuit programmable flash
memory
is
easier
to
service
than
an
otherwise identical product built with UVerase
EPROM,
since
no
disassembly
is
required to update the firmware or insert test
functions.
Presented By: Rajnikant Bal, IT200118159
10
National Institute of Science & Technology
FLASH MEMORY
FLASH APPLICATIONS
Nonvolatile storage needed but battery
not desirable
In an application where long-term data storage
is required but a battery is not desirable, flash
provides an ideal alternative to battery-backed
static RAM.
Presented By: Rajnikant Bal, IT200118159
11
National Institute of Science & Technology
FLASH MEMORY
ADVANTAGES
Flash memory is noise less.
It allows faster access.
It is smaller size and lighter.
It has no moving parts.
Embedded applications can take advantage of Flash
memory by both storing application data in it and by
allowing modifications of the application code itself .
Presented By: Rajnikant Bal, IT200118159
12
National Institute of Science & Technology
FLASH MEMORY
LIMITATIONS
Flash memory costs five to ten times more
than standard DRAM.
Another downside is the overabundance of
formats.
Huge premium to pay power saving of flash
memory.
Presented By: Rajnikant Bal, IT200118159
13
National Institute of Science & Technology
FLASH MEMORY
CONCLUSION
Flash memory thus can provide an alternative
to conventional DRAM memory. But its cost
has to be decreased drastically to ensure that
it replays the DRAM quickly.
It is a ideal storage medium for digital
camera,smart card etc.
Presented By: Rajnikant Bal, IT200118159
14
National Institute of Science & Technology
FLASH MEMORY
THANKYOU
THANKYOU !!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!
Presented By: Rajnikant Bal, IT200118159
15
You might also like
- Theoretical FrameworkDocument11 pagesTheoretical FrameworkMark AbadiesNo ratings yet
- App NandDocument30 pagesApp NandRajesh MedampudiNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Part2Document84 pagesMicroprocessor Part2مهند عدنان الجعفريNo ratings yet
- Application: Chip Non-Volatile Floating-Gate Transistors Ultraviolet Fused Quartz Silicon UltravioletDocument4 pagesApplication: Chip Non-Volatile Floating-Gate Transistors Ultraviolet Fused Quartz Silicon UltravioletfeysalnurNo ratings yet
- Embedded System of Shibu K VDocument10 pagesEmbedded System of Shibu K Vshahebgoudahalladamani0% (1)
- Embedded ImpDocument9 pagesEmbedded Impajs3313746No ratings yet
- Raghu Institute of Technology: UNIT-5Document32 pagesRaghu Institute of Technology: UNIT-5Krishna BoreddyNo ratings yet
- Syit ES Unit 4Document23 pagesSyit ES Unit 4truptiNo ratings yet
- Polymer MemoryDocument23 pagesPolymer MemorySumit DiwakerNo ratings yet
- Memory CardDocument9 pagesMemory CardPrakash NatarajanNo ratings yet
- SYIT ES CH 5 & 6 PDFDocument26 pagesSYIT ES CH 5 & 6 PDFtruptiNo ratings yet
- 2 PLDDocument42 pages2 PLDlalap5727No ratings yet
- Introduction To Programming TechnologiesDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Programming TechnologiesSwetha VanamNo ratings yet
- Flash MemoryDocument18 pagesFlash Memoryamit.c.parekh131786% (7)
- FRAM MCUS For Dummies Part 2Document5 pagesFRAM MCUS For Dummies Part 2rodrigo935874No ratings yet
- Non Volatile Memory1Document14 pagesNon Volatile Memory1Jane D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Cte 421 Material Batch3Document10 pagesCte 421 Material Batch3DivineNo ratings yet
- Polymer MemoryDocument27 pagesPolymer MemorysansureNo ratings yet
- Ovonic Unified Memory PPT1Document20 pagesOvonic Unified Memory PPT1pankaja143No ratings yet
- Unit 5Document71 pagesUnit 5Dr.G.Nirmala PriyaNo ratings yet
- Polymer Memory: Bachelor of Technology IN Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument25 pagesPolymer Memory: Bachelor of Technology IN Electronics and Communication EngineeringSateesh Kuna100% (1)
- ControllerDocument142 pagesControllerlyalashwanyNo ratings yet
- Gain-Cell Embedded DRAMs for Low-Power VLSI Systems-on-ChipFrom EverandGain-Cell Embedded DRAMs for Low-Power VLSI Systems-on-ChipNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Cache Management TechniqueDocument31 pagesDynamic Cache Management TechniqueJohn ElekwaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Memory ReportDocument31 pagesPlastic Memory ReportAjit Padmarajan100% (2)
- مسيطرات كاملDocument101 pagesمسيطرات كاملahmed aliraqiNo ratings yet
- De La Salle University - Dasmarinas College of Engineering, Architecture and Technology Technology DepartmentDocument7 pagesDe La Salle University - Dasmarinas College of Engineering, Architecture and Technology Technology DepartmentHennesey LouriceNo ratings yet
- Ovonic Unified Memory PPT1Document20 pagesOvonic Unified Memory PPT1Vinod YadavNo ratings yet
- Cost-Efficient Memory Architecture Design of NAND Flash Memory Embedded SystemsDocument5 pagesCost-Efficient Memory Architecture Design of NAND Flash Memory Embedded SystemsHarikrishnaChinthalaboyinaNo ratings yet
- Architecture and Programming of 8051 MCUDocument111 pagesArchitecture and Programming of 8051 MCUbbshir0No ratings yet
- Unit 6 Programmable Logic DevicesDocument21 pagesUnit 6 Programmable Logic DevicessharvarictamaneNo ratings yet
- What Is Flash Memory and How Does It WorkDocument13 pagesWhat Is Flash Memory and How Does It WorkAman KukarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Embedded Systems ByshibukvDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Embedded Systems ByshibukvNyein NyeinNo ratings yet
- Flash MemoryDocument12 pagesFlash MemoryPriyadarshini SahooNo ratings yet
- Flash MemoryDocument13 pagesFlash MemoryRam021No ratings yet
- Memory Devices JayjeetDocument53 pagesMemory Devices JayjeetmansurNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document10 pagesUnit 4kisu kingNo ratings yet
- Esd 1Document40 pagesEsd 1154Soyal LonareNo ratings yet
- My Final ReportDocument51 pagesMy Final ReportManoj SethiNo ratings yet
- Technical Seminar On Polymer Memory: Presented by - 18AG1A04G5Document14 pagesTechnical Seminar On Polymer Memory: Presented by - 18AG1A04G5afsdfdsaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and Embedded SystemsDocument32 pagesMicroprocessors and Embedded SystemsEmmanuel MupingaNo ratings yet
- Computer RAM CourseworkDocument3 pagesComputer RAM CourseworkEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- Polymer MemoryDocument22 pagesPolymer Memoryakkamahadevi_m_b67% (3)
- Flash Mem BasicsDocument9 pagesFlash Mem BasicsananthNo ratings yet
- Automatic Room Light ControllerDocument41 pagesAutomatic Room Light Controllervipul22150% (2)
- Microcontroller: Micro-ControllerDocument14 pagesMicrocontroller: Micro-ControllerGarima JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To HCS12/MC9S12 The HCS12 Microcontroller Han-Way Huang Minnesota State University, Mankato September 2009Document31 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To HCS12/MC9S12 The HCS12 Microcontroller Han-Way Huang Minnesota State University, Mankato September 2009Omar LopezNo ratings yet
- (A) Six Characteristics of A USB (Universal Serial Bus)Document4 pages(A) Six Characteristics of A USB (Universal Serial Bus)Leonard BreezyNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR REPORT On Swap Space Management For NAND Flash MemoryDocument23 pagesSEMINAR REPORT On Swap Space Management For NAND Flash MemoryVinod BhaskarNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument9 pagesMemoryKufaNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor - M B RajparaDocument67 pages8085 Microprocessor - M B RajparaSS0% (1)
- Architecture and Programming of 8051 MCU's: Chapter1: Introduction To MicrocontrollersDocument360 pagesArchitecture and Programming of 8051 MCU's: Chapter1: Introduction To MicrocontrollersNarendra BholeNo ratings yet
- Eeprom: Stmicro M24C02 (HTTP://WWW - St.Co M/Resource/En/Datasheet/M24C02-F. PDF) I C Serial Type EepromDocument9 pagesEeprom: Stmicro M24C02 (HTTP://WWW - St.Co M/Resource/En/Datasheet/M24C02-F. PDF) I C Serial Type EepromAndrés Alejandro PereiraNo ratings yet
- Cpu Primary and Secondary Storage TheDocument2 pagesCpu Primary and Secondary Storage TheAmy IshNo ratings yet
- Embedded SystemDocument20 pagesEmbedded Systempra0408No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document21 pagesChapter 6adeepadeepNo ratings yet
- Polymer MemoryDocument27 pagesPolymer Memoryapi-3827000100% (4)
- An ASIC Low Power Primer: Analysis, Techniques and SpecificationFrom EverandAn ASIC Low Power Primer: Analysis, Techniques and SpecificationNo ratings yet
- 18cs34 SolutionDocument9 pages18cs34 SolutionsantoshNo ratings yet
- Sapnote 973227 - Aix Virtual Memory Management Tuning RecommendationsDocument3 pagesSapnote 973227 - Aix Virtual Memory Management Tuning Recommendationssup1959113694No ratings yet
- Types of MemoryDocument3 pagesTypes of MemoryVenkatareddy Mula0% (1)
- Study of Programmable Logic Controller (Simatic S7-200 in Paper Mill)Document55 pagesStudy of Programmable Logic Controller (Simatic S7-200 in Paper Mill)b_sravaniprasadNo ratings yet
- PDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial Version: Page Title of Schematic: Title TitleDocument40 pagesPDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial Version: Page Title of Schematic: Title TitleÔng MậpNo ratings yet
- ADSP-21060 21060L InstructionDocument47 pagesADSP-21060 21060L Instructionapi-3817711100% (4)
- DmaDocument19 pagesDmaManjunath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Connect User Guide Armv8-A Address TranslationDocument32 pagesConnect User Guide Armv8-A Address TranslationKhusal PhogatNo ratings yet
- Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory (MRAM)Document29 pagesMagnetoresistive Random Access Memory (MRAM)sanjeevshrestyNo ratings yet
- PSPCL LDC (23 Dec 2019 Shift 2)Document21 pagesPSPCL LDC (23 Dec 2019 Shift 2)Prdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- WWW Mikroe Com Chapters View 67 Chapter 4 At89s8253 MicroconDocument51 pagesWWW Mikroe Com Chapters View 67 Chapter 4 At89s8253 Microconramnag4No ratings yet
- Xerox B1022 B1023 IAD - SOV v1 0Document32 pagesXerox B1022 B1023 IAD - SOV v1 0Abdel AdimNo ratings yet
- Flash MemoriesDocument52 pagesFlash MemoriesJeff GicharuNo ratings yet
- Allen-Bradley Parts: Installation InstructionsDocument76 pagesAllen-Bradley Parts: Installation InstructionsSting EyesNo ratings yet
- Lista Precios202305Document5 pagesLista Precios202305multicompecNo ratings yet
- Seth 740 Fall13 Module3.5 Main Memory Part1Document69 pagesSeth 740 Fall13 Module3.5 Main Memory Part1Ermin SehicNo ratings yet
- Accessoryd-2020-07-31-185359.ips 2Document20 pagesAccessoryd-2020-07-31-185359.ips 2Richard GarciaNo ratings yet
- Addition of 8 Bit and 16 Bit Data For Control Surface DeflectionDocument11 pagesAddition of 8 Bit and 16 Bit Data For Control Surface DeflectionReena RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The AVR Microcontroller and Embedded Systems Using Assembly and CDocument32 pagesChapter 1 The AVR Microcontroller and Embedded Systems Using Assembly and Chobbes002100% (4)
- ICT 2nd PrelimDocument2 pagesICT 2nd PrelimAngelo M LamoNo ratings yet
- Embedded System MCQDocument11 pagesEmbedded System MCQARPAN KUMAR BHANDARINo ratings yet
- Spartan 6 Memory ResourcesDocument30 pagesSpartan 6 Memory ResourcesSugar BluesNo ratings yet
- Lista Precios201608Document5 pagesLista Precios201608HugoNo ratings yet
- TCS It Quiz 2018Document63 pagesTCS It Quiz 2018cv bnmmksNo ratings yet
- Toshiba 8x TranslateDocument7 pagesToshiba 8x TranslatealexandrNo ratings yet
- cs744 DC PDFDocument31 pagescs744 DC PDFNisarg ShahNo ratings yet
- De Thi HSG Tieng Anh 10 Cum Truong Huyen Son DongDocument8 pagesDe Thi HSG Tieng Anh 10 Cum Truong Huyen Son DongTiếng Anh ThíchNo ratings yet
- II IIitDocument39 pagesII IIitnigusNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Komputer EPPD 1063Document6 pagesAplikasi Komputer EPPD 1063Alim AhmadNo ratings yet
- Mtfddaa200mar 1k1abDocument31 pagesMtfddaa200mar 1k1ablepicane7No ratings yet