Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Burns
Uploaded by
bajaoc0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views25 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views25 pagesBurns
Uploaded by
bajaocCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 25
Burns
It is an injury involving the skin,
including the muscles, bones,
nerves and blood vessels. This
results from heat, chemical or
radiation. It may vary from depth,
size and severity and cause damage
cell in the affected area.
Kinds/Classifications of Burns due to source:
1.Thermal burns – most common type of burn is caused by
heat.
2.Chemical burns – occurs from any toxic substances that
come in contact with the body (e.g. strong acid, alkalis,
3. Electrical burns – occurs as a result of contact with
high/low voltage electricity.
4. Radioactive Agents –e.g chemotherapeutic agents
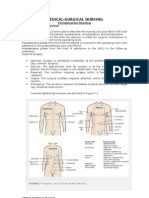
INFANT 5-9 Y/O
ANTERIOR POSTERIOR ANTERIOR POSTERIOR
HEAD 9.5 9.5 6.5 6.5
NECK 1 1 1 1
UPPER ARM 2 2 2 2
LOWER ARM 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.
5HAND 13 1.25 1.25 1.25
TRUNK 13 13
BACK 13 13
GENITAL 1 1
BUTTOCKS 2.5 2.5
THIGH 2.75 2.75 4 4
LEG 2.5 2.5 3 3
FOOT 1.75 1.75 1.75 1.75
Kinds/Classification of burns by depth:
st
1. 1 degree burn (superficial burns) – there’s redness, no
edema, blanches with pressure and is painful. It is soothed
by cooling (e.g. sunburn, flame) affected tissue is epidermis
nd
2 degree burn (partial thickness burns) – most painful type of
burn, hyperesthesia, blisters, moist and edema. Affected tissue:
epidermis, dermis
rd
1. 3 degree burn (ful thickness burn) – painless, symptoms
of shock, dry, pale, white/charred (discolored); broken skin
with fat exposed. Affected tissue : epidermis, dermis,
subcutaneous tissue and bones
1. The depth
2. The amount of surface area (total body surface area- TBSA)
3.Involvement of critical areas
4.the patient's age
5. patient's general health
FIRST AID (Pre-Hospital Emergency Care)
1.Stop the burning processand prevent injury
2.(For thermal burns and chemical burns)Burned areas and
adherent clothing are soaked with cold water briefly to
1.Cover the burned area with dry, sterile and non-adhesive
dressing.
2.Support the patient's vital body functions.(airway-
priority)
Never use ointment, lotion/antiseptic of any kind.
(ir itant)
Transport the patient promptly to the hospital that has
necessary capabilities to care for burns.
If finger or toes have burned, separate them with dry,
sterile, non-adhesive dressing.
for airway burns
MANAGEMENTS
1. FIR ST AID
a. put out flames by rollin g child on blanket
b. im merse burned part on cold water
c. remove burned clothin g of wit h sterile material
d. cover burn wit h sterile dressin g
d. cover burn wit h sterile dressin g
1. a/w
a. suction PRN, o2 wit h in creased humid ity
b. endotracheal in tubation
c. tracheostomy
1. PREVENTION OF SHOCK AND F&E INBALANCE
a. colloid s to expand blood volu me
3.PREVENTIO N OF SHOCK AND F&E INBALANCE
a. colloid s to expand blood volu me
c. tracheostomy
5.PREVENTIO N OF SHOCK AND F&E INBALANCE
a. colloid s to expand blood volu me
6. Teta nus toxoid boosters
6. relie f of pain wit h t h e use of IV analgesic morp hin e S04, needed for
nd
2 degree, very pain fu l
st
defense of body-in ta ct skin
PREVENTIO N OF WOUND INFECTIO N
A. cleanin g and debrid in g of wound
B. open or close method care
C. whirlp ool therapy, drum wit h solu tion
rd
7. kin graftin g- 3 degree, thigh or buttocks (a utograft), pigs/anim als ,
xenograft frozen cadaver, hallow graft .
8. diet- in crease CHON, in crease calo rie s
You might also like
- Tracheostomy & en Do Tracheal Tube SuctioningDocument35 pagesTracheostomy & en Do Tracheal Tube SuctioningbajaocNo ratings yet
- Pediatric NursingDocument55 pagesPediatric Nursingbajaoc100% (14)
- Maternity NursingDocument41 pagesMaternity Nursingbajaoc100% (1)
- Psych Nursing CompleteDocument31 pagesPsych Nursing CompletebajaocNo ratings yet
- Leadership MNGT ResearchDocument27 pagesLeadership MNGT ResearchbajaocNo ratings yet
- Spin ADocument25 pagesSpin AbajaocNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizattionDocument85 pagesUrinary Catheterizattionbajaoc100% (6)
- Management of Shock: Role of Inotropic & Vasoactive DrugsDocument50 pagesManagement of Shock: Role of Inotropic & Vasoactive DrugsbajaocNo ratings yet
- SuctioningDocument30 pagesSuctioningbajaoc60% (5)
- Prevention of Heart DiseaseDocument43 pagesPrevention of Heart DiseaseamitmokalNo ratings yet
- Re YesDocument12 pagesRe YesbajaocNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NursingDocument41 pagesPerioperative Nursingbajaoc100% (8)
- Nursing Leadership and ManagementDocument43 pagesNursing Leadership and Managementbajaoc95% (22)
- NebulizationDocument8 pagesNebulizationbajaocNo ratings yet
- Kinemati Cs of TraumaDocument62 pagesKinemati Cs of TraumabajaocNo ratings yet
- Managing Chest DrainageDocument63 pagesManaging Chest DrainagecarlalynneNo ratings yet
- HYDROCEPHADocument14 pagesHYDROCEPHAbajaocNo ratings yet
- Child DisordersDocument13 pagesChild DisordersbajaocNo ratings yet
- Why Worry About Electricity?Document18 pagesWhy Worry About Electricity?bajaocNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Patient EducationDocument96 pagesDiabetes Patient EducationbajaocNo ratings yet
- Eating Disorders: Anorexia vs. BulimiaDocument17 pagesEating Disorders: Anorexia vs. BulimiabajaocNo ratings yet
- Ecg/EkgDocument29 pagesEcg/EkgbajaocNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Rosario A. Respicio Clinical InstructorDocument52 pagesMrs. Rosario A. Respicio Clinical InstructorbajaocNo ratings yet
- CPRDocument29 pagesCPRbajaocNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument18 pagesCerebral PalsybajaocNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument17 pagesEmergency Drugsapi-3853350100% (12)
- Care of Patient On Pacemaker-SoniaDocument19 pagesCare of Patient On Pacemaker-SoniabajaocNo ratings yet
- Cardioversion & DefibrillationDocument14 pagesCardioversion & DefibrillationbajaocNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DisordersDocument71 pagesCardiac DisordersbajaocNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Supplier Development at Honda, Nissan and ToyotaDocument28 pagesSupplier Development at Honda, Nissan and Toyotapresidonsi100% (1)
- The Human Element is Critical in Personal SellingDocument18 pagesThe Human Element is Critical in Personal SellingArsalan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 HandoutDocument18 pagesChapter 10 HandoutChad FerninNo ratings yet
- The Role of Christian Education in Socia Group 6Document6 pagesThe Role of Christian Education in Socia Group 6Ṭhanuama BiateNo ratings yet
- Unpacking of StandardsDocument41 pagesUnpacking of StandardsJealf Zenia Laborada CastroNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesLiterature Reviewapi-549241187No ratings yet
- Scent of Apples: Does The Author Make Us Think Seriously of Life? Why Do You Say So?Document2 pagesScent of Apples: Does The Author Make Us Think Seriously of Life? Why Do You Say So?carl tom BondiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1-8Document39 pagesLecture Notes 1-8Mehdi MohmoodNo ratings yet
- Mansabdari SystemDocument10 pagesMansabdari SystemSania Mariam100% (8)
- 1022-Article Text-2961-1-10-20200120Document10 pages1022-Article Text-2961-1-10-20200120Zuber RokhmanNo ratings yet
- Adjustment DisordersDocument2 pagesAdjustment DisordersIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Neoclassicism: Romanticism Realism ImpressionismDocument16 pagesNeoclassicism: Romanticism Realism ImpressionismErika EludoNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument323 pagesFinancial MarketsSetu Ahuja100% (2)
- 2018 World Traumatic Dental Injury Prevalence and IncidenceDocument16 pages2018 World Traumatic Dental Injury Prevalence and IncidencebaridinoNo ratings yet
- Japanese Tea Cups LessonDocument3 pagesJapanese Tea Cups Lessonapi-525048974No ratings yet
- Atmospheres of Space The Development of Alvar Aalto S Free Flow Section As A Climate DeviceDocument18 pagesAtmospheres of Space The Development of Alvar Aalto S Free Flow Section As A Climate DeviceSebastian BaumannNo ratings yet
- Muhammad v. Hall, 10th Cir. (2017)Document12 pagesMuhammad v. Hall, 10th Cir. (2017)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by GerundsDocument10 pagesVerbs Followed by GerundsJhan MartinezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Vitamin C, (Chemistry STPM)Document2 pagesIntroduction To Vitamin C, (Chemistry STPM)NarmeenNirmaNo ratings yet
- June 2016 - QuestionsDocument8 pagesJune 2016 - Questionsnasir_m68No ratings yet
- 600 2 Sub-Zero Built-In Series Refrigerator Service ManualDocument188 pages600 2 Sub-Zero Built-In Series Refrigerator Service Manual911servicetechNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court: Lichauco, Picazo and Agcaoili For Petitioner. Bengzon Villegas and Zarraga For Respondent R. CarrascosoDocument7 pagesSupreme Court: Lichauco, Picazo and Agcaoili For Petitioner. Bengzon Villegas and Zarraga For Respondent R. CarrascosoLOUISE ELIJAH GACUANNo ratings yet
- Blaise PascalDocument8 pagesBlaise PascalBosko GuberinicNo ratings yet
- Extinction - WikipediaDocument14 pagesExtinction - Wikipediaskline3No ratings yet
- Analysing Context CluesDocument2 pagesAnalysing Context CluesSwathiNo ratings yet
- Marwar Steel Tubes Pipes StudyDocument39 pagesMarwar Steel Tubes Pipes Studydeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- Dwi Athaya Salsabila - Task 4&5Document4 pagesDwi Athaya Salsabila - Task 4&521Dwi Athaya SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- ASBMR 14 Onsite Program Book FINALDocument362 pagesASBMR 14 Onsite Program Book FINALm419703No ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument8 pagesNew Text DocumentDhaniNo ratings yet
- Bruno Latour: What Is Iconoclash?Document3 pagesBruno Latour: What Is Iconoclash?Clara HabibNo ratings yet