Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bearingcapacityofsoil
Uploaded by
Ajit Ji0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views46 pagesLoad - settlement curve in case of footing resting on surface of dense sand or stiff clay shows pronounced peak and failure occurs at very small stain. The shear strength of soil is not fully mobilized along planes and hence failure planes are not defined clearly. Failure occurs when the down ward pressure exerted by loads on the soil adjoining the inclined surfaces on soil wedge is equal to upward pressure.
Original Description:
Original Title
bearingcapacityofsoil.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLoad - settlement curve in case of footing resting on surface of dense sand or stiff clay shows pronounced peak and failure occurs at very small stain. The shear strength of soil is not fully mobilized along planes and hence failure planes are not defined clearly. Failure occurs when the down ward pressure exerted by loads on the soil adjoining the inclined surfaces on soil wedge is equal to upward pressure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views46 pagesBearingcapacityofsoil
Uploaded by
Ajit JiLoad - settlement curve in case of footing resting on surface of dense sand or stiff clay shows pronounced peak and failure occurs at very small stain. The shear strength of soil is not fully mobilized along planes and hence failure planes are not defined clearly. Failure occurs when the down ward pressure exerted by loads on the soil adjoining the inclined surfaces on soil wedge is equal to upward pressure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 46
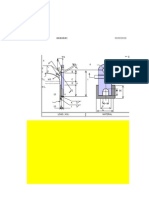
Strip footing resting on surface
Load settlement curve
of dense sand or stiff clay
* The load - Settlement curve in case of footing resting on surface of dense sand
or stiff clays shows pronounced peak & failure occurs at very small stain.
* A loaded base on such soils sinks or tilts suddenly in to the ground showing a
surface heave of adjoining soil
* The shearing strength is fully mobilized all along the slip surface & hence
failure planes are well defined.
* The failure occurs at very small vertical strains accompanied by large lateral
strains.
* ID > 65 ,N>35, > 360, e < 0.55
Strip footing resting on surface
Load settlement curve
Of Medium sand or Medium clay
* When load is equal to a certain value qu(1),
* The foundation movement is accompanied by sudden jerks.
* The failure surface gradually extend out wards from the foundation.
* The failure starts at localized spot beneath the foundation & migrates out
ward part by part gradually leading to ultimate failure.
* The shear strength of soil is not fully mobilized along planes & hence
failure planes are not defined clearly.
* The failure occurs at large vertical strain & very small lateral strains.
* ID = 15 to 65 , N=10 to 30 , <30, e>0.75
* The loaded base sinks into soil like a punch.
* The failure surface do not extend up to the ground surface.
* No heave is observed.
* Large vertical strains are involved with practically no lateral
deformation.
* Failure planes are difficult to locate 222
* The failure zones do not extend above the
horizontal plane passing through base of footing
* The failure occurs when the down ward pressure
exerted by loads on the soil adjoining the inclined
surfaces on soil wedge is equal to upward
pressure.
* Downward forces are due to the load (=qu B) &
the weight of soil wedge (1/4 B2 tan)
* Upward forces are the vertical components of
resultant passive pressure (Pp) & the cohesion (c)
acting along the inclined surfaces.
General Shear Failure
Local Shear Failure
Nc
Nq
Nr
Nc
Nq
Nr
5.7
1.0
0.0
5.7
1.0
0.0
15
12.9
4.4
2.5
9.7
2.7
0.9
45
172.3
173.3
297.5
51.2
35.1
37.7
* Surcharge term is not affected.
* Unit weight in term is
= sub +
y ( sub)
B
Thus,
qu = cNc + Df Nq + 0.5B Nr
When y = B ; W.T. at B below base of footing.
qu = cNc + Df Nq + 0.5 B Nr
Hence when ground water table is at b B, the equation is not
ZB
I2
S i C1C2 q q
E
Z 0 S
Sand & hard
Clay
Plastic clay
Max.Settle. Diff.Settl
Angular
distortion
Max.Settle
Diff.
Settle.
Angular
distortion
Isolated
foundation
i) steel struct
ii) RCC struct
50mm
50mm
0.0033L
0.0015L
1/300
1/666
50mm
75mm
0.0033L 1/300
0.0015L 1/666
Raft
foundation
i) steel struct
ii) Rcc struct.
75mm
75mm
0.0033L
0.002L
1/300
1/500
100mm
100mm
0.0033L 1/300
0.002L 1/500
Theoretically, no damage is done to the superstructure
if the soil settles uniformly.
However, settlements exceeding 150mm may cause
trouble to utilities such as water pipe lines, sewers,
telephone lines & also is access from streets.
Ho
Ho
Sf sf
( mv
)
i
(
)
i
(
z )mv
i ........(2
)z
SF
0
i 1
if both mv & are cons tan t ,
SF mv Ho ........ ( 1)
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unseelie Prince Maze of Shadows Book 1 by Kathryn AnnDocument267 pagesThe Unseelie Prince Maze of Shadows Book 1 by Kathryn Annanissa Hri50% (2)
- Mid Term Business Economy - Ayustina GiustiDocument9 pagesMid Term Business Economy - Ayustina GiustiAyustina Giusti100% (1)
- Astm A182Document2 pagesAstm A182fastenersworldNo ratings yet
- Method Statement Pressure TestingDocument15 pagesMethod Statement Pressure TestingAkmaldeen AhamedNo ratings yet
- A) Shear Capacity of BoltsDocument30 pagesA) Shear Capacity of BoltsAjit JiNo ratings yet
- A) Shear Capacity of BoltsDocument30 pagesA) Shear Capacity of BoltsAjit JiNo ratings yet
- Boat DesignDocument8 pagesBoat DesignporkovanNo ratings yet
- TheSun 2008-11-04 Page16 Asian Stocks Rally Continues On Policy HopesDocument1 pageTheSun 2008-11-04 Page16 Asian Stocks Rally Continues On Policy HopesImpulsive collectorNo ratings yet
- NGFERUIKJJHDocument42 pagesNGFERUIKJJHAjit JiNo ratings yet
- NGFERUIKJJHDocument42 pagesNGFERUIKJJHAjit JiNo ratings yet
- NGFERUIKJJHDocument42 pagesNGFERUIKJJHAjit JiNo ratings yet
- NGFERUIKJJHDocument42 pagesNGFERUIKJJHAjit JiNo ratings yet
- NGFERUIKJJHDocument42 pagesNGFERUIKJJHAjit JiNo ratings yet
- NGFERUIKJJHDocument42 pagesNGFERUIKJJHAjit JiNo ratings yet
- Design of Padeye for Beam LiftingDocument28 pagesDesign of Padeye for Beam LiftingAjit JiNo ratings yet
- CCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCDocument24 pagesCCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCAjit JiNo ratings yet
- CCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCDocument24 pagesCCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCAjit JiNo ratings yet
- CCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCDocument24 pagesCCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCAjit JiNo ratings yet
- CCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCDocument24 pagesCCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCAjit JiNo ratings yet
- CCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCDocument24 pagesCCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCAjit JiNo ratings yet
- CCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCDocument24 pagesCCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCAjit JiNo ratings yet
- Book 1 SDDDocument3 pagesBook 1 SDDAjit JiNo ratings yet
- CCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCDocument16 pagesCCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCAjit JiNo ratings yet
- CCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCDocument12 pagesCCCCCCCCC Aaaaaac CCCCCCCCAjit JiNo ratings yet
- LIFT Ana PDFDocument2 pagesLIFT Ana PDFAjit JiNo ratings yet
- 1 SDD DDFDocument8 pages1 SDD DDFAjit JiNo ratings yet
- PC 1Document2 pagesPC 1Azam Islam KhanNo ratings yet
- Ballari City Corporation: Government of KarnatakaDocument37 pagesBallari City Corporation: Government of KarnatakaManish HbNo ratings yet
- Vortex: Opencl Compatible Risc-V Gpgpu: Fares Elsabbagh Blaise Tine Priyadarshini Roshan Ethan Lyons Euna KimDocument7 pagesVortex: Opencl Compatible Risc-V Gpgpu: Fares Elsabbagh Blaise Tine Priyadarshini Roshan Ethan Lyons Euna KimhiraNo ratings yet
- Construction Internship ReportDocument8 pagesConstruction Internship ReportDreaminnNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing FiguresDocument34 pagesStrategic Marketing FiguresphuongmonNo ratings yet
- Import Sample 2Document63 pagesImport Sample 2akkyNo ratings yet
- 935 Ubi PBK Statement PDFDocument20 pages935 Ubi PBK Statement PDFTECHNO ACCOUNTNo ratings yet
- Product 243: Technical Data SheetDocument3 pagesProduct 243: Technical Data SheetRuiNo ratings yet
- Communication Networks Chapter 1 SolutionsDocument10 pagesCommunication Networks Chapter 1 SolutionsJ PrakashNo ratings yet
- 10 Compactness in Function Spaces: Ascoli-Arzel A TheoremDocument5 pages10 Compactness in Function Spaces: Ascoli-Arzel A TheoremronalduckNo ratings yet
- DRUG LISTDocument45 pagesDRUG LISTAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Name: Chakshu Purohit Course: BBA LLB Subject: Legal Research and Methodology Submitted To: Utkarsh MishraDocument5 pagesName: Chakshu Purohit Course: BBA LLB Subject: Legal Research and Methodology Submitted To: Utkarsh Mishrachakshu purohitNo ratings yet
- CHEMOREMEDIATIONDocument8 pagesCHEMOREMEDIATIONdeltababsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Lease DecisionsDocument51 pagesChapter 9 Lease Decisionsceoji25% (4)
- Nigerian Romance ScamDocument10 pagesNigerian Romance ScamAnonymous Pb39klJNo ratings yet
- Bylaw 16232 High Park RezoningDocument9 pagesBylaw 16232 High Park RezoningJamie_PostNo ratings yet
- Nistha Tamrakar Chicago Newa VIIDocument2 pagesNistha Tamrakar Chicago Newa VIIKeshar Man Tamrakar (केशरमान ताम्राकार )No ratings yet
- 2018 JC2 H2 Maths SA2 River Valley High SchoolDocument50 pages2018 JC2 H2 Maths SA2 River Valley High SchoolZtolenstarNo ratings yet
- Canary TreatmentDocument117 pagesCanary TreatmentRam KLNo ratings yet
- Inventory of Vacant Units in Elan Miracle Sector-84 GurgaonDocument2 pagesInventory of Vacant Units in Elan Miracle Sector-84 GurgaonBharat SadanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Earth & SpaceDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Earth & SpaceSol Vega PagdangananNo ratings yet
- DISADVANTAGESDocument3 pagesDISADVANTAGESMhd MiranNo ratings yet
- Guidelines To MAS Notice 626 April 2015Document62 pagesGuidelines To MAS Notice 626 April 2015Wr OngNo ratings yet
- New Pacific Timber v. Señeris, 101 SCRA 686Document5 pagesNew Pacific Timber v. Señeris, 101 SCRA 686Ishmael AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Schedule For Semester III, Class of 2021Document7 pagesSchedule For Semester III, Class of 2021Jay PatelNo ratings yet