Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mce Frigo
Uploaded by
Hich HarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mce Frigo
Uploaded by
Hich HarCopyright:
Available Formats
PowerPointPresentation
Chapter 6
Refrigeration Systems
Refrigeration Mechanical
Compression Refrigeration
Absorption Systems
Troubleshooting and Maintaining
Refrigeration Systems Refrigerant
Regulations Refrigerant Handling
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
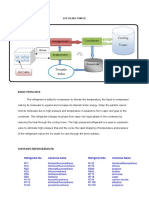
A refrigeration system
controls the absorption
and rejection of heat by
refrigerant to move heat
from inside a cooled
space to outside the
cooled space.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
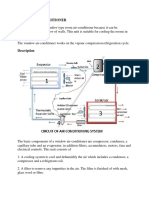
In a mechanical compression refrigeration system, a
compressor is used to produce the refrigeration
effect.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Refrigerant vapor
pressure charts list the
saturation temperature
and pressure of
refrigerants.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Refrigeration
compressors include
reciprocating, vane,
centrifugal, and screw
compressors.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Refrigerant compressors
are available in hermetic
and semi-hermetic
configurations.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
An air-cooled condenser
removes heat from highpressure refrigerant
vapor by air blown across
the condenser coils.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Water-cooled condensers
transfer heat from
refrigerant vapor to
water.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Evaporative condensers
reject heat through the
evaporation of water.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
A fin comb is used for
condenser maintenance
to straighten damaged or
bent fins, which limit
airflow and reduce
condenser efficiency.
Robinair Division, SPX Corporation
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
A thermostatic expansion
valve uses temperature
readings at the
evaporator outlet to
control the rate of
refrigerant flow into the
evaporator.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
The opening and closing of a
thermostatic expansion valve
is controlled by the pressure
in the remote bulb.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
An automatic expansion
valve controls the
temperature of the
refrigerant by controlling
the pressure in the
evaporator.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
As refrigerant is forced
through the capillary
tube, it loses pressure
until it is at the desired
evaporator pressure.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
An evaporator vaporizes
low-pressure refrigerant
liquid into a low-pressure
vapor.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
A hot-gas defrost uses hot gas from the compressor
to melt frost on the evaporator.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
An evaporator pressure regulating valve allows two
evaporators running from the same compressor to
maintain different temperatures.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Accessories are
used for maintaining
and controlling the
flow of refrigerant in
a refrigeration
system.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Pressure switches
control refrigeration
system temperature
through changes in
system pressure.
Ranco Inc.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Ammonia systems operate at high temperatures and
pressures and must have special controls and fittings
to control the release of ammonia gas.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
The direction of refrigerant flow in a heat pump is
controlled by a reversing valve.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Heat pumps may use air
or water as the heat
source.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Chillers use chilled water to cool large building
spaces.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
A cooling tower cools water from a condenser by the
evaporation of water as it cascades through the
tower.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Absorption systems
use a generator and
absorber in place of
the compressor to
raise system
pressure.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Gauge manifolds are
used to take pressure
readings, add or
remove refrigerant,
and remove air from a
system before it is
filled with refrigerant.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Service valves are frontseated for isolating parts
of the system, midseated for adding or
removing refrigerant or
taking system pressures,
and back-seated during
normal operation.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Refrigeration system pressure readings are taken by
connecting the blue hose to the low-pressure side
service valve and the red hose to the high-pressure
side service valve with both gauge manifold valves
front-seated.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
A head pressure
controller prevents the
condenser pressure from
falling too low and
starving the evaporator
for refrigerant.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
The EPA has established regulations under
Section 608 of the Clean Air Act to regulate the
handling of ozone-depleting substances.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
A recovery unit is used to
recover refrigerant for
reuse.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
A leak detector is a
device used to detect
refrigerant leaks in air
conditioning or
refrigeration systems.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
A vacuum pump
removes all air from a
refrigeration system.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
The vacuum pump is connected to the system
service valves using a gauge manifold and hoses.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
Electronic leak detectors are extremely sensitive and
indicate the general location of a leak.
Chapter6RefrigerationSystems
The refrigerant container
is placed upside down to
charge with liquid and
right side up to charge
with vapor.
You might also like
- Functioning of ChillersDocument22 pagesFunctioning of ChillersAnonymous b9fcR5No ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance of Chillers: TopicsDocument10 pagesOperation and Maintenance of Chillers: TopicsMohammed AbbasNo ratings yet
- Basic Design Vapor-Compression Refrigeration SystemDocument20 pagesBasic Design Vapor-Compression Refrigeration Systemscarmathor90No ratings yet
- Types of ChillersDocument36 pagesTypes of ChillersKimsouen KorngNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Optimal Engine TemperatureDocument11 pagesMaintaining Optimal Engine TemperatureBird JacquesNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning - Building ServiceDocument12 pagesAir Conditioning - Building ServiceHarini Andal AgnihotramNo ratings yet
- Liquid Cooled SystemsDocument9 pagesLiquid Cooled Systemsananth k rNo ratings yet
- Scroll Chiller Systems Air & Water Cooled - NEW User ManualDocument85 pagesScroll Chiller Systems Air & Water Cooled - NEW User ManualBalaji Dhandapani71% (14)
- Refrigeration Systems - CompressorDocument11 pagesRefrigeration Systems - CompressorRidwan NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Water Chillers 83Document2 pagesWater Chillers 83Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Ec & Us Manual PDFDocument111 pagesEc & Us Manual PDFRamnarayan MeenaNo ratings yet
- Unit V Energy Conservation OpportunitiesDocument25 pagesUnit V Energy Conservation OpportunitiesRajesh BhaskarlaNo ratings yet
- Engine cooling system componentsDocument5 pagesEngine cooling system componentsAdnan ParkerNo ratings yet
- 4 - II. Innovative - Cascade, multi-VCRSDocument28 pages4 - II. Innovative - Cascade, multi-VCRSSumran ShahidNo ratings yet
- Ice Plant Theory RefrigerationDocument16 pagesIce Plant Theory RefrigerationArnulfo Jose Pi DiNo ratings yet
- Water Chillers 91Document2 pagesWater Chillers 91Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Good Afternoon Class, Today Our Group Will Be Present On Paper 1 Entitled Automotive Thermostat Valve Configurations Enhanced Warm-Up PerformanceDocument5 pagesGood Afternoon Class, Today Our Group Will Be Present On Paper 1 Entitled Automotive Thermostat Valve Configurations Enhanced Warm-Up PerformancesuperpeNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure - HVAC - V01 - 29082010Document10 pagesStandard Operating Procedure - HVAC - V01 - 29082010Karthik MandyaNo ratings yet
- 10air Con04Document7 pages10air Con04mister pogiNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit VDocument37 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit VA.R. Pradeep Kumar100% (1)
- Air Conditioning System ClassificationsDocument10 pagesAir Conditioning System ClassificationsPhạm Tấn PhátNo ratings yet
- Engine 4H SeriesDocument16 pagesEngine 4H SeriesRonny DiazNo ratings yet
- (545083214) Air-Cooled Chillers Heat Recovery 04-581041-01Document17 pages(545083214) Air-Cooled Chillers Heat Recovery 04-581041-01Pedro Vasquez Acevedo100% (1)
- Water Distribution - BetterBricksDocument11 pagesWater Distribution - BetterBricksdimchienNo ratings yet
- Evaporators by Doc and AlpineDocument41 pagesEvaporators by Doc and AlpineAeron Mathew VeloriaNo ratings yet
- Multi-Pressure Refrigeration SystemsDocument10 pagesMulti-Pressure Refrigeration SystemsCassie E. ZernaNo ratings yet
- AG09 - 5 - Marine CoolingDocument20 pagesAG09 - 5 - Marine Coolingkman548No ratings yet
- 06 PP T235 CoolingDocument29 pages06 PP T235 CoolingEzhil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Air Handling Unit: Temperature ControlDocument4 pagesAir Handling Unit: Temperature ControlNaveen Kumar VashistNo ratings yet
- GETrans - GEVO Tier 4 Locomotive Support SystemsDocument142 pagesGETrans - GEVO Tier 4 Locomotive Support SystemsTim MarvinNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Central Air-Conditioning System With Air Cooled Chiller of Multi-Storey Office BuildingDocument16 pagesDesign and Analysis of Central Air-Conditioning System With Air Cooled Chiller of Multi-Storey Office BuildingSajjad HasanNo ratings yet
- Cooling Distribution Septic SystemsDocument22 pagesCooling Distribution Septic SystemsShiela Louisianne AbañoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Chap 9Document35 pagesChapter - Chap 9SimphiweNo ratings yet
- For Duct Work Services and Its Insulation, Colour Triangle May BeDocument11 pagesFor Duct Work Services and Its Insulation, Colour Triangle May BeManjeet CinghNo ratings yet
- Study of Refrigeration SystemsDocument28 pagesStudy of Refrigeration SystemsAkhil ShettyNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance of HVAC Water SystemDocument8 pagesOperation and Maintenance of HVAC Water SystemHenry SuarezNo ratings yet
- Chilled Water Systems GuideDocument31 pagesChilled Water Systems Guide123john123100% (1)
- Lab Manual: RGPV University (Bhopal)Document6 pagesLab Manual: RGPV University (Bhopal)Pushpendra KushwahaNo ratings yet
- HPLDocument10 pagesHPLJoy KumarNo ratings yet
- How To Recharge Air Conditioner: Purpose, Do's and Don'ts, and Some AdviceDocument11 pagesHow To Recharge Air Conditioner: Purpose, Do's and Don'ts, and Some AdviceSanjay OhriNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration System For Food StoragesDocument46 pagesRefrigeration System For Food StoragesFiseha Mengisteab100% (2)
- Solar RefrigerationDocument19 pagesSolar RefrigerationPradhyumna CkNo ratings yet
- 3 Dk2831 - ch35 EvaporadoresDocument10 pages3 Dk2831 - ch35 EvaporadoresHarold Valle ReyesNo ratings yet
- HVAC Handbook New Edition Part 4 Refrigerant Brines OilsDocument71 pagesHVAC Handbook New Edition Part 4 Refrigerant Brines OilsShakir Ahmed Kalkundri100% (3)
- Chiller UnitDocument85 pagesChiller Unitchandra sriramNo ratings yet
- Bu ResearchDocument10 pagesBu ResearchToteng TanglaoNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Water Cooled Scroll Chiller SDocument93 pagesAir Cooled Water Cooled Scroll Chiller SSaleem BashaNo ratings yet
- Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument4 pagesSteam Jet Refrigeration SystemChristian D. AllanaNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document32 pagesCH 1beila.amu.22No ratings yet
- WAC and VCRSDocument8 pagesWAC and VCRSShubham MishraNo ratings yet
- Cooling System Guide for CarsDocument26 pagesCooling System Guide for CarsDalton WiseNo ratings yet
- Unit6 N 7Document46 pagesUnit6 N 7Shanku Raajashree100% (1)
- Group 2 Basic Refrigerationsystem and ComponentsDocument25 pagesGroup 2 Basic Refrigerationsystem and ComponentsVipin VetriNo ratings yet
- Coolingsystem 141121065724 Conversion Gate02Document30 pagesCoolingsystem 141121065724 Conversion Gate02rinku sainiNo ratings yet
- Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle ExplainedDocument16 pagesVapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle ExplainedDiether RigorNo ratings yet
- ChillersDocument7 pagesChillersaldz5100% (1)
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Lab: Mansoura University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Power Department 4 YearDocument9 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Lab: Mansoura University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Power Department 4 YearKhaled HakimNo ratings yet
- HARAMAYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITIONINGDocument108 pagesHARAMAYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITIONINGMoges AsefaNo ratings yet
- NIT PATNA SEMINAR ON REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITIONINGDocument31 pagesNIT PATNA SEMINAR ON REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITIONINGShashi Bhushan KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Inventions Make Life EasierDocument11 pagesChapter 2 Inventions Make Life EasierAsh ArtNo ratings yet
- Capilary Tube For Ac and RefrigeratorDocument4 pagesCapilary Tube For Ac and RefrigeratorJoko SubagyoNo ratings yet
- 3-25 Tons TZ Rooftop Units: Plug and Play Comfort Solutions For Residential and Commercial ApplicationsDocument2 pages3-25 Tons TZ Rooftop Units: Plug and Play Comfort Solutions For Residential and Commercial ApplicationsHazem HassonNo ratings yet
- 1995 Toyota Camry Cooling System Technical ManualDocument30 pages1995 Toyota Camry Cooling System Technical ManualKevin Reilly100% (1)
- L Yo Phil IzationDocument2 pagesL Yo Phil IzationvishaNo ratings yet
- TWR / TWZ: Split System Heat Pumps Single PhaseDocument6 pagesTWR / TWZ: Split System Heat Pumps Single PhaseDavid CollinsNo ratings yet
- Engine Cooling System: 1988 Toyota CelicaDocument12 pagesEngine Cooling System: 1988 Toyota CelicaToua YajNo ratings yet
- Unit V Cooling SystemDocument20 pagesUnit V Cooling SystemRavindra_1202No ratings yet
- Details Model: Cooling PerformanceDocument2 pagesDetails Model: Cooling Performanceعامر شیخ100% (1)
- Indesit Error Messages and Error CodesDocument4 pagesIndesit Error Messages and Error CodesFlori IonitaNo ratings yet
- Refrigerator: Prasad Murumkar Simran Jagtap Prasanna GramopadhyeDocument13 pagesRefrigerator: Prasad Murumkar Simran Jagtap Prasanna GramopadhyeSHREYAS JOSHINo ratings yet
- Single Zone Inverter Service ManualDocument67 pagesSingle Zone Inverter Service ManualasparagushaterNo ratings yet
- TE - Mech - RAC - Chapter 4 - VCC Cycles-1Document98 pagesTE - Mech - RAC - Chapter 4 - VCC Cycles-1Aniket MandalNo ratings yet
- NIRATA Members DirectoryDocument48 pagesNIRATA Members DirectoryDevasyruc100% (1)
- Ice Skating Rink Product GuideDocument8 pagesIce Skating Rink Product GuidecashloverNo ratings yet
- 2020 Full Catalogue - HitachiDocument221 pages2020 Full Catalogue - HitachiIsmael Perez100% (1)
- GSX1300R - 99500-39187-03E - Pag 257Document1 pageGSX1300R - 99500-39187-03E - Pag 257Tarso BrasilNo ratings yet
- New DuctDocument122 pagesNew DuctAndrei ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Building ServicesDocument19 pagesBuilding ServicesRitu ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- المصطلحات الإنجليزية المستخدمة في مهنة التبريد والتكييفDocument9 pagesالمصطلحات الإنجليزية المستخدمة في مهنة التبريد والتكييفRania HazezNo ratings yet
- Class Notes For Centrifugal BlowersDocument9 pagesClass Notes For Centrifugal BlowersaryannNo ratings yet
- The American Institute of Indian Studies, Gurgaon. Space Design Consultants, ArchitectsDocument2 pagesThe American Institute of Indian Studies, Gurgaon. Space Design Consultants, ArchitectsNishit ChadhaNo ratings yet
- TVL Diagrama Calefaccion CXU613Document2 pagesTVL Diagrama Calefaccion CXU613ricardoNo ratings yet
- Airwide International-China (A) Key Account SellingDocument6 pagesAirwide International-China (A) Key Account SellingFahad ParvezNo ratings yet
- Converted 277031216Document57 pagesConverted 277031216Daniel SoseNo ratings yet
- HW 2 - 2Q1314 - QuestionaireDocument1 pageHW 2 - 2Q1314 - Questionairejenninajuban0% (2)
- Car Park Ventilation CalculationDocument2 pagesCar Park Ventilation CalculationJojolas100% (1)
- Hvac TechnicianDocument3 pagesHvac Technicianapi-79087437No ratings yet
- Indwell Construction November Erection ProgrammeDocument6 pagesIndwell Construction November Erection ProgrammeAlanka PrasadNo ratings yet
- Mcquay SWTDocument109 pagesMcquay SWTmarcp22No ratings yet