Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Retinoblastoma Cognitive Concept Map - DR Kumar Ponnusamy and DR Jegathambigai RN - Problem Based Learning (PBL) For Large Groups Medical Students
Uploaded by
Ponnusamy KumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Retinoblastoma Cognitive Concept Map - DR Kumar Ponnusamy and DR Jegathambigai RN - Problem Based Learning (PBL) For Large Groups Medical Students
Uploaded by
Ponnusamy KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
You must not lose faith in humanity.
Humanity is an ocean; a few drops of
the ocean are dirty the ocean does not become dirty_Mahatma Gandhiji.
COGNITIVE CONCEPT MAP ON RETINOBLASTOMA (Rb)
Problem Based Learning (PBL) for Large Groups Medical Students: e-Problem Solving Test: A Mutation Causing Retinoblastoma (Rb)
*International Medical University (IMU),
ST Matthews School of Medicine (SMU),
AIMST-U, MSU, Vinayaka Missions Med School
Dr Kumar Ponnusamy and Dr Jegathambigai Rameshwar Naidu
*
International Medical School (IMS), Management & Science University (MSU), Malaysia
*
Acknowledgements: The Authors Gratefully Acknowlwdges All On-Line Resources Including Google.com, PubMed, Elsieviers Ltd, Eye Cancer Network, Scriibd.com., ect.,.
Retinoblastoma (Rb): Problem Based Learning (PBL) for Large Groups Medical Students:
e-Problem Solving Test: A Mutation Causing Retinoblastoma (Rb). Abstract: Problem Based Learning (PBL) is an innovative
approach and emerging advances in the integrated medical curriculum to achieve the effective measurable outcomes for the large group of medical students in small groups with the on-line resources available (OLRA). Integrated
PBLs covers the clinical relevance of the particular disease with different disciplines of medicine which includes anatomy, pathophysiology, biochemistry-genetic basis of the disease, pathology, laboratory diagnosis, pharmacology,
community medicine, behavioural issues at the must know level of phase-1 medical students with much emphasize on self-directed learning with the OLRA and encourage the students to acquire up to date knowledge and clinicalcommunication skills right from the beginning of the medical curriculum and inculcate life-long learning. This present article emphasizes the achievement of the measurable learning outcomes with the reusable-on-line resources
available with the structured PBLs on a particular disorder which are not covered by any other mode of teaching-learning activities including didactic lectures and/or seminars and so on. Begining of the semester 1 hands-on
workshop on PBL-process to be provided to the students by the content experts of medical education. In this article provided with the case study on Retinoblastoma (Rb). Rb is a rare eye tumor of childhood that arises in the retina.
Rb is caused by a deletion of chromosomes 13, 14, 15, 21, and 22 and is a frame-shift deletion mutation. It is the most common intraocular malignancy of infancy and childhood; with an incidence of 1/15,00020,000 live births. The
two most frequent symptoms revealing Rb are leukocoria and strabismus. Pleotropy includes iris rubeosis, hypopyon, hyphema, buphthalmia, orbital cellulites and exophthalmia may also be observed. Sixty per cent of
retinoblastomas are unilateral and most of these forms are not hereditary (median age at diagnosis two years). Rb is bilateral in 40% of cases (median age at diagnosis one year). All bilateral and multifocal unilateral forms are
hereditary. Hereditary Rb constitutes a cancer predisposition syndrome: a subject constitutionally carrying an RB1 gene mutation has a greater than 90% risk of developing retinoblastoma but is also at increased risk of developing
other types of cancers. The PBL Process: Day-1:PBL-Induction: Step 1: Release of the digital copy of figure 1 shows the phenotype of patients with Rb and brain storming. Step-2: Figure-2-display of k aryotype of a person affected
by Rb and brain storming. Day 1-Step-3: Figure 3-display of pedigree chart-inheritance of Rb and discussion and division of labour. Day 1-Step 4: Research component on Rb-Review Article:
URLhttp://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140673611611379 : Day 1- Step 5: Matching and fine tuning of the learning outcomes arrived by the team, facilitated by tea leader. Day 2-Step 1: Presentations and
Summarization on RB: Day 2-Step 2: Display of video clip on RB, U Tube URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FOnZKtupBYg [5]. Day 2-Step 3: Construction of cognitive concept mapping and discussion, Day 2-Step 4: Spot
test on matching questions. Terms to be familiar with before you start to solve the test: Retinoblastoma (Rb), RB1 gene on chromosome 13 (first tumor suppressor gene discovered), genetic disorder, Oncogenes, tumor suppressor
genes, DNA-repair genes, epidemiology, mode of inheritance-X-linked, autosomal dominant (AD) transmission, penetrance, pedigree analysis, karyo-type of Rb, frame shift-deletion-mutation, deletion of parts of chromosomes at 13,
14, 15, 21, and 22 [1]. Alfred Knudsons two-hit hypothesis (1971) [2], biochemical-molecular basis of retinoblastoma, sporadic (non-hereditary) Rb, familial (hereditary) Rb, consanguinity, risk factors of Rb, signs and symptoms,
pathophysiology, clinical presentation of RB, congenital anomalies-dysmorphism, differential diagnosis, molecular etiopathogenesis, bridge to pharmacology, management of Rb, treatment options, preventive medicine, prenatal
diagnosis, amniocentesis, genetic counselling, behavioural issues, ethics, referral to Ssspeciality clinics URL [3]:http://edit.mskcc.org/pediatrics/childhood/retinoblastoma Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, Research
component in Rb, model review article on Retinoblastoma URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140673611611379[4].
PBL Process Keywords: Problem based learning, USMLE-Preparatory curriculum, learning outcomes, on-line reusable resources, clinical skills, BIO-GEN Inno-vision, content experts, PBL-process, PBL-facilitation, group leader
as facilitator, small group learning, integrated medical curriculum, measurable learning outcomes, on-line resources, e-learning, self-directed learning, audio-visual facility, medical dictionary, group dynamics, brain storming, team
work, peer value-review, division of labour, group dynamics, leadership quality and team player, group leader as a facilitator, communication skills, time-management, mono-acting as a simulated patient, parts of the PBLs: Step
wise release of the parts of the PBL-Step 1, 2 and 3, video clips, construction of high-yield cognitive concept mapping, spot test-matching questions. Learning Outcomes: Retinoblastoma, karyo-type of Rb, Alfred Knudsons two-hit
hypothesis, risk factors of Rb, histopathology of Rb, differential diagnosis of leukocoria, genetic counselling on Rb and ethics.
Location of RB1 Gene: Cytogenetic Location:
13q14.2 . Molecular Location on Chromosome 13:
Base Pairs 48,303,746 to 48,481,889.
Osteosarcoma
Leukocoria
4
5
FISH
Variable expressivity
D. Tumor suppressor gene (TSG) loss.
E.RB1 mutation is present in all of the somatic
cells.
F. Within a single individual or tissue, the
occurrence of two or more cell lines with
different genetic or chromosomal constitutions.
G. The presence of an altered gene within the
egg or sperm (germ cell), such that the altered
gene can be passed to subsequent generations.
Germinal retinoblastoma
Hereditary pattern of familial
retinoblastoma
Mosaicism
H. Two separate loss of function mutations are
required to inactivate both the homologous loci
of the RB gene for malignant phenotype to be
expressed.
The critical events has most likely resulted
from an aberration involving chromosome
13 leads to a 5-month-old girl has bilateral
retinoblastoma
I. Condition characterized by a whitish reflex
within the pupil. It is secondary to cataract,Coats
'disease, retinoblastoma, retrolental fibroplasia,
persistent hyperplastic primaryvitreous, etc.
G
M
J. Autosomal dominant (AD).
K. Multiple, often seemingly unrelated, physical
effects caused by a single altered gene or pair of
altered genes.
10 Germline mutation
11 Cytogenetic Location of Retinoblastoma
12 Pleotrophy
L. The proportion of individuals with a
mutation causing a particular disorder who
exhibit clinical symptoms of that disorder; most
often refers to autosomal dominant (AD).
13 Penetrance
L M. 13q14.2.
Ans: 1-H ; 2-A ; 3-I ; 4-C ; 5-B ; 6-E ; 7-J ; 8-F ; 9-D ; 10-G; 11-M; 12-K; 13-M .
Anterior segment invasion
Bridge to Mol-Biology
& Genetics
Secondary glaucoma
Orbital inflammation
Orbital invasion
3 4
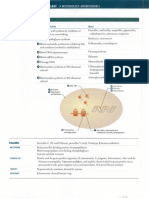
The left eye is enlarged. The cornea is
opacified, the conjunctiva is injected,
while tumor cells can be seen on the
corneal endothelium (arrows).
.Molecular Basis of Low-Penetrance
Retinoblastoma. Arch Ophthalmol.
2001;119(11):1699-1704.
CT demonstrates intratumoral
calcifications consistent with Rb
(black arrows). The left optic nerve
is enlarged and retrobulbar
opacities suggest extrascleral
extention (white arrow).
Day 1-Step 2:Trigger-2:Fig.2: Display of Digital Copy of RB Karyotype
Day 1-Step 3:Trigger 3: Display of Pedigree Chart on Retinoblastoma
Leukocoria or
White Pupil
Rb is either sporadic or familial
Sporadic cancer in 55-65% of all cases.
Sporadic cancers are unilateral.
Hereditary childhood cancer
bilateral tumors in ~75% of cases.
unilateral tumors in ~25% of cases.
1/20,000 children; 300 /yr Average
age is 18 months. Treatment:
enucleation. Prognosis is good after
enucleation over 90% survival with
early detection and treatment.
Day 1- Step 4: Research Component on Retinoblastoma [4].
URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140673611611379
Research Component on Rb
Fig.3: Genetic Features of Heritable Rb-A Model AD Pattern of
Review Article on Rb [4]
Inheritance in Cancer Patients with a Family History of Rb
Molecular Pathogenesis of Rb
MANAGEMENT
Step 4: MCQ 1. 6-24. A newborn child is being Eye Cancer Network Case #13: Retinoblastoma
History: This 16-month old patient was referred for bilateral leukocoria (white pupil),
examined. During ophthalmologic evaluation, acute glaucoma OS, with evidence of anterior chamber seeding and possible optic
it is noticed that the red reflex is absent.
nerve/orbital invasion. The left pupil was nonreactive. Impression: Retinoblastoma.
Which of the following could this indicate?
*Note* This risks and benefits of observation, enucleation, chemotherapy and external
beam radiation therapy were discussed in detail. Single agent cisplatinum chemotherapy (3
A.Congenital cataracts.
cycles due to definite choroidal and possible orbital and optic nerve involvement) and
B.Chorioretinitis.
enucleation of the left eye was performed. Histopathologic evaluation of the left eye
C.Retinitis pigmentosa.
revealed retinoblastoma without optic nerve or orbital extension. The right eye was
D.Optic atrophy.
enucleated after failure of systemic chemoreduction to produce a treatable tumor.
E.Holoprosencephaly.
PATHOGENESIS
6-24. The answer is A. (Swaiman, p 82.) On shining a light through the pupil of the normal newborn, the normal color of the retina is perceived as an orange-red reflection of the light. Failure to perceive
that reflection usually indicates opacification of the pathway of light transmission. Several types of intrauterine infections, including rubella and CMV infection, may produce congenital cataracts and impair
light transmission in this way. The presence of a distinctive white reflex usually indicates disease behind the lens, such as a scar from retinopathy of prematurity or a retinoblastoma. Reference: Pre Test:
Clinical Vignettes for the USMLE Step 2 CK, PreTestTM Self-Assessment and Review, 5th Edition.
19. A 5-month-old girl has bilateral retinoblastoma. Neither parent has a history of having had retinoblastoma. Chromosomal analysis of the patient's stimulated peripheral blood lymphocytes is
done; the photograph is of a representative karyotype. Which of the following critical events has most likely resulted Genetic Counselling on Rb: Parents having a child with RB (at the time of
from an aberration involving chromosome 13? Biochemical Calculation:
enucleation or during treatment) & patients with family history of Rb should
A.Proto-oncogene activation
undergo genetic counselling (blood sample only).
1+1=1; 1+2=2; 5+5=5
B.Proto-oncogene amplification
Recommendation: examination at birth & 4-mo thereafter until
Can U Solve This?
C.Proto-oncogene loss
4 yrs of age. Tumor tissue & blood required in sporadic cases w
GOD Cant Come in Person to Help You. He Will Send Some One in the
D.Tumor-suppressor gene activation Form of Homosepian, Believe it. The Only Thing What You Are Going to
hile only blood sample sufficient in inherited cases.
Take Away is Karma _Educate_Dr P Kumar, BIO-GEN.
E.Tumor-suppressor gene loss
Molecular tests: Direct analysis of the constitutional mutation of
RB11. The following are true about retinoblastoma (Rb):
gene performed on constitutional DNA. Indirect analysis of the allele
A. in familial retinoblastoma, the hereditary pattern is that of an AD mutation.
carrying the mutation. Tumor cell LOH evaluation. Patients should be
B. the genetic defect is recessive at the cellular level.
informed about the risk of transmission and of second primary malignant
C. retinoblastoma results from a dominant mutant onco-gene
tumor development (20% at 10 years , 50% at 20 years & 90% at 30 years).
D. both germinal or somatic mutation can give rise to retinoblastoma
E. osteosarcoma is associated with retinoblastoma containing deletion of chromosome 13. Answers: TTFTT.
11
Strabismus - 20%
PATHO -PHYSIOLOGY
or mutation of the RB gene occurs in either the germline or a somatic cell (eg, retinoblast). The second hit, which is always a somatic event that disrupts the remaining RB allele,
usually involves one of the indicated mechanisms (their approximate frequencies in retinoblastoma tumors are indicated). The predicted result of the 2 hits (tumor vs no tumor)
is indicated when the first hit involves a full-penetrance vs a low-penetrance mutation. These predictions are based on the assumption that 2 copies of a low-penetrance mutation
are sufficient to suppress tumorigenesis. This mechanism could help to explain the phenomenon of low-penetrance retinoblastoma, since approximately 60% of second hits that
are tumorigenic with full-penetrance mutations may not cause tumors with low-penetrance mutations. RB indicates RB gene mutation; wt, wild type.
Ans
Column B
H A. Associated with retinoblastoma containing
deletion of chromosome 13.
A B. Variation in clinical features (type and
severity) of a genetic disorder between affected
individuals, even with n same family.
I C. A technique used to identify the presence of
specific chromosomes or chromosomal regions
through hybridization (attachment) of
fluorescently-labelled DNA probes to denatured
chromosomal DNA. Examination under
fluorescent lighting detects the presence of the
hybridized fluorescent signal (and hence
presence of the chromosomal material) or
absence of the hybridized fluorescent signal (and
hence absence of the chromosome material).
C
B
Leukocoria - 60%
Knudsons Double Hit Hypothesis:Chromosomal events leading to tumorigenesis in retinoblastoma (Rb) according to the Knudsen 2-hit hypothesis. The first hit
Matching Questions 1 on Retinoblastoma ((Rb) Inheritance
No
Column A
1 Alfred Knudsons two-hit hypothesis
Elsevier Ltd URL: ?.
Leukocoria with tumor
visible through the right
pupil. Note the clear cornea
and lack of orbital signs.
GENETICS : ETIOLOGY
12
GENETICS
The PBL Process: Day 1-Step 1-Trigger 1: Release of the Digital Copy of
Fig.1 Shows the Presentations of Retinoblastoma Phenol Type URL: Google Images:
DIAGNOSIS
The Self-Directed PBL Process Overall (Day-1-Induction; Day -2 Presentation)
DAY 1: Induction of PBL on Retinoblastoma (Rb)
1 Day 1-Step 1-Trigger 1: Release of the Digital Copy of Picture 1 Shows
the Presentations of Retinoblastoma Phenotype.
2 Day 1-Step 2: Fig 2-Trigger 2: Display of Digital Copy of Karyotype of Rb.
3 Day 1- Step 3:Trigger 3: Display of Pedigree Chart on Rb. Figure 3: Genetic
Features of Heritable Retinoblastoma.
4 Day 1-Step 4: Research Component on Retinoblastoma-Review Article: URL:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140673611611379
5 Day 1- Step 5: Matching and Fine Tuning of the Learning Outcomes Arrived by
the Team, Facilitated by Team Leader (Chair-Person of PBL Process).
Day 2: Presentation on Retinoblastoma
1 Day 2-Step 1: Presentations and Summarization on Retinoblasma.
2 Day 2-Step 2: Display of Video Clip on Retinoblastoma.
URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FOnZKtupBYg.
3 Day 2-Step 3: Construction of cognitive concept mapping. Model Map
on RB: URL.?
4 Day 2-Step 4: Spot Test on Matching Questions on Retinoblastoma.
10
ETHICS: GENETIC
COUNSELING & REFERRAL
TO SPECILITY CLINICS
RB SUPPORT GROUPS.
Bajaj A, Bajaj SK, Bajaj N. Bilateral retinoblastoma in early
infancy: A case report. Kathmandu University Medical Journal
(2007), Vol. 5, No. 4, Issue 20, 550-551.
Rb Inheritance: Rb is inherited as a
AD, but it is recessive at the cellular level. People with familial Rb
carry one mutated copy in all their cells. Cells that would get a 2 nd hit will develop Rb or later, other cancers.
13
References: [1] [1]. Isabelle Aerts, Livia Lumbroso-Le Rouic, Marion Gauthier-Villars, Herv Brisse 4, Franois Doz and Laurence
Desjardins. Review. Retinoblastoma. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2006, 1:31, 1-11.
[2]. Alfred G. Knudson, JR. Mutation and Cancer: Statistical Study of Retinoblastoma. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 68, No. 4, 820-823.
[3]:http://edit.mskcc.org/pediatrics/childhood/retinoblastoma Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center.
[4] Helen Dimaras, Kahaki Kimani, Elizabeth A O Dimba, Peggy Gronsdahl, Abby White, Helen S L Chan, Brenda L Gallie. Retinoblastoma.
is the ONLY Visible GOD I Know.
Lancet 2012; 379: 14361446. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140673611611379 Mother
The Most Beautiful Woman in This World is Mother Therasa
The Most Handsome Man in This World is Nelson Mondala
[5]. Retinoblastoma-U Tube URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FOnZKtupBYg
You might also like
- Dreams and Destiny Adventure HookDocument5 pagesDreams and Destiny Adventure HookgravediggeresNo ratings yet
- Liquid Hydrogen As A Propulsion Fuel, 1945-1959Document341 pagesLiquid Hydrogen As A Propulsion Fuel, 1945-1959Bob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- DNA Viruses: P P P A H H PDocument2 pagesDNA Viruses: P P P A H H PKimberly KanemitsuNo ratings yet
- 100 Concepts - MCBDocument316 pages100 Concepts - MCBNisreen SalameNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionDocument58 pagesConic SectionNailah Sakinah100% (1)
- Pathology Test I Diseases GuideDocument6 pagesPathology Test I Diseases GuideBahaa Ibrahim HelmiNo ratings yet
- UW (Step 1) Biochemistry - Educational ObjectivesDocument41 pagesUW (Step 1) Biochemistry - Educational ObjectivesUsama BilalNo ratings yet
- Group 4: Urine Screening for Metabolic DisordersDocument41 pagesGroup 4: Urine Screening for Metabolic DisordersBrent LagartoNo ratings yet
- The Army Crew Team Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesThe Army Crew Team Case Analysisarshdeep199075% (4)
- Disease Pathognomonic Sign: Muddy Brown CastsDocument1 pageDisease Pathognomonic Sign: Muddy Brown CastsRafey AhmedNo ratings yet
- DRUG ALLERGY GUIDEDocument61 pagesDRUG ALLERGY GUIDEadysti100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal & NutritionBlock3 PDFDocument170 pagesGastrointestinal & NutritionBlock3 PDFTed DoyleNo ratings yet
- Onsemi ATX PSU DesignDocument37 pagesOnsemi ATX PSU Designusuariojuan100% (1)
- Pathology - 2Document99 pagesPathology - 2lusia playzNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Block 1Document258 pagesPediatrics Block 1Ghada ElhassanNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure - Notes From "Cardiology" (Timmis Et Al) : Main CausesDocument3 pagesHeart Failure - Notes From "Cardiology" (Timmis Et Al) : Main CausesPrarthana Thiagarajan100% (3)
- USMLE NotesDocument165 pagesUSMLE NotesHerliani HalimNo ratings yet
- Lippin NotesDocument8 pagesLippin Noteswalt65100% (1)
- Word Formation - ExercisesDocument4 pagesWord Formation - ExercisesAna CiocanNo ratings yet
- NEUROLOGY Goljan FootnotesDocument10 pagesNEUROLOGY Goljan FootnotesPrince DuNo ratings yet
- The Forty Nine StepsDocument312 pagesThe Forty Nine Stepsoldnic67% (3)
- The Islam Question - Should I Become A Muslim?Document189 pagesThe Islam Question - Should I Become A Muslim?Aorounga100% (1)
- BIO-GEN INNO-VISION 2012 - DR Kumar Ponnusamy 1 Min Papers On Inborn Errors of AA Metab & DNA RNADocument12 pagesBIO-GEN INNO-VISION 2012 - DR Kumar Ponnusamy 1 Min Papers On Inborn Errors of AA Metab & DNA RNADr Kumar PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- PENCITRAAN PADA KEADAAN GAWAT DARURAT (EMERGENCY RADIOLOGYDocument93 pagesPENCITRAAN PADA KEADAAN GAWAT DARURAT (EMERGENCY RADIOLOGYLeonardus William KuswaraNo ratings yet
- Relevant physiology signs of early pregnancyDocument29 pagesRelevant physiology signs of early pregnancyDiwakesh C BNo ratings yet
- First Aid Step 1 2017 Sample RevisionsDocument9 pagesFirst Aid Step 1 2017 Sample RevisionsFirst Aid/USMLE-Rx100% (2)
- QuizletDocument104 pagesQuizletS.No ratings yet
- Anatomy of the Large IntestineDocument16 pagesAnatomy of the Large IntestinePriya GKNo ratings yet
- Chest X-RayDocument39 pagesChest X-Rayendah cahya sufianyNo ratings yet
- Shift of Heart and Trachea To Left: Tension PneumothoraxDocument44 pagesShift of Heart and Trachea To Left: Tension PneumothoraxlettasamudraNo ratings yet
- Protein Synth Inhibs Target Bact RibosomeDocument61 pagesProtein Synth Inhibs Target Bact RibosomegirNo ratings yet
- Guidance Khurram Irshad ChatthaDocument5 pagesGuidance Khurram Irshad ChatthaMuhammad Aamir IqbalNo ratings yet
- Social Sciences PDFDocument122 pagesSocial Sciences PDFوصال القريتليNo ratings yet
- Block 13 Patho SlidesDocument62 pagesBlock 13 Patho SlidesLennon Ponta-oyNo ratings yet
- RespiDocument58 pagesRespiIshani PatelNo ratings yet
- WWW - Natures.Ir: More Free Usmle, Mccee, Mcqe and Amq FlashcardsDocument54 pagesWWW - Natures.Ir: More Free Usmle, Mccee, Mcqe and Amq FlashcardsNixon GoyalNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb TransDocument18 pagesUpper Limb Transashley nicholeNo ratings yet
- Brenner and Stevens, Pharmacology 3 © 2010Document5 pagesBrenner and Stevens, Pharmacology 3 © 2010PharAwayNo ratings yet
- DR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry-Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On-Line Resources For Large Group Teaching-Learning in Relatively Short TimeDocument1 pageDR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry-Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On-Line Resources For Large Group Teaching-Learning in Relatively Short TimeDr Kumar Ponnusamy100% (1)
- Female Genital Tract Infections and PathologyDocument16 pagesFemale Genital Tract Infections and Pathologymiguel cuevasNo ratings yet
- 2 Renal Buzzword ChartDocument6 pages2 Renal Buzzword ChartTyler KingNo ratings yet
- Surgery - FirecrackerDocument73 pagesSurgery - FirecrackerLucas HoldereggerNo ratings yet
- UWorld question analysis reportDocument29 pagesUWorld question analysis reportFeroz RaZa SoomrOoNo ratings yet
- GI and Hemagology & Oncology QuizDocument41 pagesGI and Hemagology & Oncology Quizwalt65No ratings yet
- ReproductiveDocument8 pagesReproductiveMedSchoolStuffNo ratings yet
- Goljan Blue NotesDocument1 pageGoljan Blue NotesCarl NieweldNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine #1Document167 pagesInternal Medicine #1Nikhil RayarakulaNo ratings yet
- LOOK! Neuroscience Brainstorm 2010Document32 pagesLOOK! Neuroscience Brainstorm 2010genome12345No ratings yet
- Introduction of Neonatal Disease-Bi GuangliangDocument43 pagesIntroduction of Neonatal Disease-Bi GuangliangsinghNo ratings yet
- Blueprints - Radiology PDFDocument134 pagesBlueprints - Radiology PDFBenny KMNo ratings yet
- ERRATA 2020 First Aid For The USMLE Step 1Document4 pagesERRATA 2020 First Aid For The USMLE Step 1Rakesh TiwaryNo ratings yet
- My Step 1 Experience - 261Document7 pagesMy Step 1 Experience - 261Mohamed Medhat0% (1)
- By DR - Mohammad Z. Abu Sheikha@: +pigmented Stones (Black Stone - Non Infected) (Brown Stone - Infected)Document11 pagesBy DR - Mohammad Z. Abu Sheikha@: +pigmented Stones (Black Stone - Non Infected) (Brown Stone - Infected)Nisreen Al-shareNo ratings yet
- Usmle RX NotesDocument1 pageUsmle RX NotesmNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument3 pagesAtelectasisLouis FortunatoNo ratings yet
- All Forms of Shock - Lactic Acid Via Tissue Hypoxia Tubulare Nec Via Coagulation in PT TALDocument10 pagesAll Forms of Shock - Lactic Acid Via Tissue Hypoxia Tubulare Nec Via Coagulation in PT TALlynk787No ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases Case StudiesDocument28 pagesInfectious Diseases Case StudiesAnukriti MamgainNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Physiology and Sexual DifferentiationDocument11 pagesReproductive Physiology and Sexual DifferentiationAbeebs SalahouNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 DiseasesDocument1 pageExam 1 DiseasesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Step 1 Express 2018-RenalDocument14 pagesStep 1 Express 2018-RenalPratik JadhavNo ratings yet
- Diseases - BiochemDocument4 pagesDiseases - BiochemJay FeldmanNo ratings yet
- DR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On Line Resources For Large Group Teaching Learning in Relatively SHDocument2 pagesDR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On Line Resources For Large Group Teaching Learning in Relatively SHPonnusamy KumarNo ratings yet
- TreatmentDocument13 pagesTreatmentAnastasiafynnNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument41 pagesAnemiabekthyNo ratings yet
- Mnemonic of Some Rare Genetic Disease PDFDocument9 pagesMnemonic of Some Rare Genetic Disease PDFfaraz100% (1)
- Step1 Journey-To 271Document7 pagesStep1 Journey-To 271Nilay BhattNo ratings yet
- Spider Model E-Cognitive Concept Map - Cystic Fibrosis (CF) - DR Kumar Ponnusamy, Siddarth Srigkul & DR Jegathambigai RN - BIO-GEN PEARLS 2016Document2 pagesSpider Model E-Cognitive Concept Map - Cystic Fibrosis (CF) - DR Kumar Ponnusamy, Siddarth Srigkul & DR Jegathambigai RN - BIO-GEN PEARLS 2016Ponnusamy Kumar100% (1)
- Cognitive Concept Map - Case of The Week - USMLE Genetics - All About Cystic Fibrosis (CF) - DR Kumar Ponnusamy & DR Jegathambigai RNDocument2 pagesCognitive Concept Map - Case of The Week - USMLE Genetics - All About Cystic Fibrosis (CF) - DR Kumar Ponnusamy & DR Jegathambigai RNPonnusamy KumarNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Concept Map - Rheumatoid Arthritis & Gout - DR P Kumar & Senthilkumar Rajasekaran - ST Matthew's Uni School of MedicineDocument1 pageCognitive Concept Map - Rheumatoid Arthritis & Gout - DR P Kumar & Senthilkumar Rajasekaran - ST Matthew's Uni School of MedicinePonnusamy Kumar100% (1)
- Cognitive Concept Map - Rheumatoid Arthritis & Gout - DR P Kumar & Senthilkumar Rajasekaran - ST Matthew's Uni School of MedicineDocument1 pageCognitive Concept Map - Rheumatoid Arthritis & Gout - DR P Kumar & Senthilkumar Rajasekaran - ST Matthew's Uni School of MedicinePonnusamy Kumar100% (1)
- Cognitive Concept Map - XERODERMA PIGMENTOSUM - DR P Kumar, Et Al, 2015Document1 pageCognitive Concept Map - XERODERMA PIGMENTOSUM - DR P Kumar, Et Al, 2015Ponnusamy Kumar100% (1)
- DR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On Line Resources For Large Group Teaching Learning in Relatively SHDocument2 pagesDR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On Line Resources For Large Group Teaching Learning in Relatively SHPonnusamy KumarNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Concept Map - XERODERMA PIGMENTOSUM - DR P Kumar, Et Al, 2015Document1 pageCognitive Concept Map - XERODERMA PIGMENTOSUM - DR P Kumar, Et Al, 2015Ponnusamy Kumar100% (1)
- Sri Dakshinamurthy Stotram - Hindupedia, The Hindu EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesSri Dakshinamurthy Stotram - Hindupedia, The Hindu Encyclopediamachnik1486624No ratings yet
- Merry Almost Christmas - A Year With Frog and Toad (Harmonies)Document6 pagesMerry Almost Christmas - A Year With Frog and Toad (Harmonies)gmit92No ratings yet
- Wjec Gcse English Literature Coursework Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesWjec Gcse English Literature Coursework Mark Schemef6a5mww8100% (2)
- A Cautionary Tale of Psychoanalysis and SchizophreniaDocument30 pagesA Cautionary Tale of Psychoanalysis and SchizophreniaJona JoyNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense The Elves and The Shoemaker Short-Story-Learnenglishteam - ComDocument1 pageSimple Past Tense The Elves and The Shoemaker Short-Story-Learnenglishteam - ComgokagokaNo ratings yet
- Fractional GradingDocument7 pagesFractional Gradingapi-355619062No ratings yet
- Operations Management 2Document15 pagesOperations Management 2karunakar vNo ratings yet
- Unit Test, Part 2: Literature With A Purpose: Total Score: - of 40 PointsDocument3 pagesUnit Test, Part 2: Literature With A Purpose: Total Score: - of 40 PointsAriana Stephanya Anguiano VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 To 12 English Amplified PamphletDocument59 pagesGrade 10 To 12 English Amplified PamphletChikuta ShingaliliNo ratings yet
- Ariel StoryDocument2 pagesAriel StoryKKN Pasusukan2018No ratings yet
- EY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseDocument2 pagesEY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseAayushi AroraNo ratings yet
- H-1 Nationalism in Europe NotesDocument5 pagesH-1 Nationalism in Europe Noteskanishk kumarNo ratings yet
- 4th Singapore Open Pencak Silat Championship 2018-1Document20 pages4th Singapore Open Pencak Silat Championship 2018-1kandi ari zonaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Deuteronomy On Its Own TermsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Deuteronomy On Its Own TermsAlberto RodriguesNo ratings yet
- DRF1301 1000V 15A 30MHz MOSFET Push-Pull Hybrid DriverDocument4 pagesDRF1301 1000V 15A 30MHz MOSFET Push-Pull Hybrid DriverAddy JayaNo ratings yet
- Soal Paket 1Document10 pagesSoal Paket 1Nurul HayatiNo ratings yet
- Prayer BuddyDocument42 pagesPrayer BuddyJoribelle AranteNo ratings yet
- Test Unit 3Document2 pagesTest Unit 3RAMONA SECUNo ratings yet
- CBCP Monitor Vol. 17 No. 9Document20 pagesCBCP Monitor Vol. 17 No. 9Areopagus Communications, Inc.No ratings yet
- Neoclassicism: Romanticism Realism ImpressionismDocument16 pagesNeoclassicism: Romanticism Realism ImpressionismErika EludoNo ratings yet
- GII-07 Training MaterialDocument191 pagesGII-07 Training MaterialIris Amati MartinsNo ratings yet