Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Advanced Statistical Methods
Uploaded by
drkamesh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views38 pagesStatistical Methods
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentStatistical Methods
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views38 pagesAdvanced Statistical Methods
Uploaded by
drkameshStatistical Methods
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 38
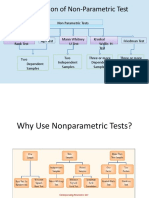
15-1 Introduction
Most of the hypothesis-testing and
confidence interval procedures discussed
in previous chapters are based on the
assumption that we are working with
random samples from normal populations.
These procedures are often called parametric
methods
In this chapter, nonparametric and distribution
free methods will be discussed.
We usually make no assumptions about the
distribution of the underlying population.
15-2 Sign Test
15-2.1 Description of the Test
The sign test is used to test hypotheses about the
median of a continuous distribution.
Let R+ represent the number of differences
~
Xi
0
that are positive.
15-2 Sign Test
15-2.1 Description of the Test
If the following hypotheses are being tested:
The appropriate P-value is
15-2 Sign Test
15-2.1 Description of the Test
If the following hypotheses are being tested:
The appropriate P-value is
15-2 Sign Test
15-2.1 Description of the Test
If the following hypotheses are being tested:
If r+ < n/2, then the appropriate P-value is
If r+ > n/2, then the appropriate P-value is
15-2 Sign Test
Example 15-1
Example 15-1
15-2 Sign Test
Example 15-1
15-2 Sign Test
The Normal Approximation
15-2 Sign Test
Example 15-2
15-2 Sign Test
Example 15-2
15-2 Sign Test
15-2.2 Sign Test for Paired Samples
15-2 Sign Test
Example 15-3
15-2 Sign Test
Example 15-3
15-2 Sign Test
Example 15-3
15-2 Sign Test
15-2.3 Type II Error for the Sign Test
Figure 15-1
Calculation of
for the sign test.
(a) Normal
distributions. (b)
Exponential
distributions
15-3 Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test
The Wilcoxon signed-rank test applies to the case
of symmetric continuous distributions.
Under this assumption, the mean equals the median.
The null hypothesis is H0: = 0
15-3 Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test
Example 15-4
Example 15-4
15-3 Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test
Example 15-4
15-3 Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test
15-3.2 Large-Sample Approximation
15-3 Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test
15-3.3 Paired Observations
Example 15-5
15-3 Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test
15-3.3 Paired Observations
Example 15-5
15-3 Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test
15-3.3 Paired Observations
Example 15-5
15-4 Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test
15-4.1 Description of the Test
We wish to test the hypotheses
15-4 Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test
15-4.1 Description of the Test
Test procedure:
Arrange all n1 + n2 observations in ascending
order of magnitude and assign ranks.
Let W1 be the sum of the ranks in the smaller
sample.
Let W2 be the sum of the ranks in the other
sample. Then:
W2 = [(n1 + n2)(n1 + n2 + 1)]/2 W1
15-4 Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test
Example 15-6
15-4 Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test
Example 15-6
Example 15-6
15-4 Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test
Example 15-6
15-5 Nonparametric Methods in the
Analysis of Variance
The single-factor analysis of variance model for
comparing a population means is
The hypothesis of interest is
15-5 Nonparametric Methods in the
Analysis of Variance
The test statistic is
Computational method
15-5 Nonparametric Methods in the
Analysis of Variance
Example 15-7
Example 15-7
You might also like
- Signed Rank PDFDocument26 pagesSigned Rank PDFryanroncalesNo ratings yet
- Chi Square TestDocument52 pagesChi Square TestKlein Chris100% (1)
- Ken Black QA ch13Document56 pagesKen Black QA ch13Rushabh Vora100% (1)
- Statistical Analysis Using SPSS and R - Chapter 4 PDFDocument106 pagesStatistical Analysis Using SPSS and R - Chapter 4 PDFKarl LewisNo ratings yet
- Nonparametric TestDocument54 pagesNonparametric TestRajesh Dwivedi0% (1)
- Wilcoxon Signed-Ranks TestDocument16 pagesWilcoxon Signed-Ranks TestLayan MohammadNo ratings yet
- Non-Parametric Wilcoxon Signed Rank TestDocument10 pagesNon-Parametric Wilcoxon Signed Rank TestMH MerhiNo ratings yet
- 03 Statistics in Regrression AnalysisDocument24 pages03 Statistics in Regrression AnalysisXin NiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Non-Parametric and Robust TestDocument43 pagesChapter 6 Non-Parametric and Robust TestgirmaNo ratings yet
- Non Parametric StatisticsDocument20 pagesNon Parametric StatisticsshhanoorNo ratings yet
- Inferential Tests To Compare Two ConditionsDocument27 pagesInferential Tests To Compare Two ConditionsJess EjioforNo ratings yet
- TestDocument22 pagesTestHisham Mat SallehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document27 pagesChapter 15athirah jamaludinNo ratings yet
- Association of Attributes Chi-Square: Muhammad Usman ROLL 553-07-09Document31 pagesAssociation of Attributes Chi-Square: Muhammad Usman ROLL 553-07-09Muhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Time Series AnalysisDocument37 pagesTime Series AnalysisZiaNaPiramLiNo ratings yet
- MFM 5053 Chapter 2Document22 pagesMFM 5053 Chapter 2NivanthaNo ratings yet
- Eco 5Document30 pagesEco 5Nigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Nonparametric MethodDocument19 pagesNonparametric Methodsahuek100% (1)
- Nonparametric Hypothesis Testing Procedures ExplainedDocument54 pagesNonparametric Hypothesis Testing Procedures ExplainedYeshambel EwunetuNo ratings yet
- Point Estimation and Statistical Inference for Process ParametersDocument64 pagesPoint Estimation and Statistical Inference for Process ParametersCharmianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document26 pagesChapter 12maroof_mirNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Multiple Regression Analysis InferenceDocument25 pagesTopic 4 Multiple Regression Analysis InferenceHann YoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Non Parametric Slides Edited 2019Document29 pagesLecture 10 Non Parametric Slides Edited 2019gothai sivapragasamNo ratings yet
- Comparing Defective Items in Production LinesDocument19 pagesComparing Defective Items in Production LinesCarina JL0% (1)
- How To Test Hypothesis by T Model PDFDocument5 pagesHow To Test Hypothesis by T Model PDFRiz FahanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Hypothesis TestingDocument27 pagesChapter 5 Hypothesis Testingsolomon edaoNo ratings yet
- SM 38Document58 pagesSM 38ayushNo ratings yet
- Non-parametric Tests ExplainedDocument30 pagesNon-parametric Tests ExplainedKim Tat TehNo ratings yet
- Performing a Paired Data Nonparametric TestDocument7 pagesPerforming a Paired Data Nonparametric TestAzriNexusNo ratings yet
- Malhotra 15Document99 pagesMalhotra 15Satyajeet ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Non Parametric TestsDocument27 pagesNon Parametric TestsAndrea MéndezNo ratings yet
- Non Parametric TestsDocument43 pagesNon Parametric TestsTumabang Divine100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Hypothesis TestingDocument27 pagesChapter 5 Hypothesis Testingkidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Chi-Square T Z TestDocument72 pagesModule 6 Chi-Square T Z TestLavanya Shetty100% (1)
- Linear Correlation 1205885176993532 3Document102 pagesLinear Correlation 1205885176993532 3Anonymous 7Un6mnqJzNNo ratings yet
- Hypotheses testingDocument25 pagesHypotheses testingEsai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing and Ttest 2Document29 pagesHypothesis Testing and Ttest 2Nathan DrakeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7.descriptive and Inferential StatisticsDocument44 pagesLecture 7.descriptive and Inferential StatisticsKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Test of SignificanceDocument22 pagesTest of SignificanceKathiravan GopalanNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing With T Tests Edited 1Document31 pagesHypothesis Testing With T Tests Edited 1Katharine MalaitNo ratings yet
- Types of Inferential Statistics and Choosing Statistical ProceduresDocument14 pagesTypes of Inferential Statistics and Choosing Statistical ProceduresSophie SchrödingerNo ratings yet
- 4.hypothesis TestingDocument31 pages4.hypothesis Testingjbsimha3629No ratings yet
- Assignment Educational Statistics Course Code: 8614Document21 pagesAssignment Educational Statistics Course Code: 8614AmjadNo ratings yet
- Non Parametric Tests Unit 5Document21 pagesNon Parametric Tests Unit 5Juan Antonio VeraNo ratings yet
- QTM Cycle 7 Session 6Document76 pagesQTM Cycle 7 Session 6OttilieNo ratings yet
- Y. Conducting Small Sample Tests About A Population Mean Myu PDFDocument34 pagesY. Conducting Small Sample Tests About A Population Mean Myu PDFBrian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Sign TestDocument10 pagesSign TestShubhamMaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing. Chi-Square Test: Georgi Iskrov, Mba, MPH, PHD Department of Social MedicineDocument31 pagesHypothesis Testing. Chi-Square Test: Georgi Iskrov, Mba, MPH, PHD Department of Social MedicineKARTHIK SREEKUMARNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution and Regression NotesDocument71 pagesNormal Distribution and Regression Notescassandraolson.kya07No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Data Analysis AbDocument56 pagesChapter 5 Data Analysis AbGatluak Thalow KuethNo ratings yet
- Exp 3Document35 pagesExp 3Bakchodi WalaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis: A Hypothesis Is An Assumption (Or Claim) About TheDocument85 pagesHypothesis: A Hypothesis Is An Assumption (Or Claim) About Theaishwarya desaiNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument17 pagesHypothesis TestingshivaniNo ratings yet
- Exploring StatisticsDocument33 pagesExploring StatisticsYet Barreda BasbasNo ratings yet
- Introductory Statistics for Psychology: The Logic and the MethodsFrom EverandIntroductory Statistics for Psychology: The Logic and the MethodsNo ratings yet
- IJOHD - 1 (1) - 11-15 (1) ArticleDocument5 pagesIJOHD - 1 (1) - 11-15 (1) ArticledrkameshNo ratings yet
- Instructions for Sedation Dental CareDocument2 pagesInstructions for Sedation Dental CaredrkameshNo ratings yet
- TNMRB RecruitmentDocument1 pageTNMRB RecruitmentTopRankersNo ratings yet
- Nonsurgical Management of Large Periapical Lesion in Mature and Immature Teeth Using Different Calcium Hydroxide Formulations Case SeriesDocument6 pagesNonsurgical Management of Large Periapical Lesion in Mature and Immature Teeth Using Different Calcium Hydroxide Formulations Case SeriesdrkameshNo ratings yet
- Portable Dental Chair With Unit & Stool: Mobile Unit Includes (Briefcase)Document1 pagePortable Dental Chair With Unit & Stool: Mobile Unit Includes (Briefcase)drkameshNo ratings yet
- Decision Trees For Management of An Avulsed Permanent ToothDocument2 pagesDecision Trees For Management of An Avulsed Permanent ToothdrkameshNo ratings yet
- Criterion VI - Governance, Leadership and Management (100) Key Indicator - 6.2 Strategy Development and DeploymentDocument5 pagesCriterion VI - Governance, Leadership and Management (100) Key Indicator - 6.2 Strategy Development and DeploymentdrkameshNo ratings yet
- Parthamitraglobaleconomyresearchpaper 121016222806 Phpapp02Document20 pagesParthamitraglobaleconomyresearchpaper 121016222806 Phpapp02drkameshNo ratings yet
- Picture Tells The Thousand Words: An Unexplored Path: Eview RticleDocument4 pagesPicture Tells The Thousand Words: An Unexplored Path: Eview RticledrkameshNo ratings yet
- Gap Arthroplasty With Custom Made Acrylic Mouth Opener: Case ReportDocument3 pagesGap Arthroplasty With Custom Made Acrylic Mouth Opener: Case ReportdrkameshNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Conditions Considered For ProphylaxisDocument5 pagesCardiac Conditions Considered For ProphylaxisdrkameshNo ratings yet
- Artikel AbsesDocument4 pagesArtikel AbsesPurnaNo ratings yet
- Esthetic and Functional Rehabilitation of Missing Anterior Teeth With A Conservative Treatment Approach A Clinical Case Series 2247 2452.1000646Document5 pagesEsthetic and Functional Rehabilitation of Missing Anterior Teeth With A Conservative Treatment Approach A Clinical Case Series 2247 2452.1000646drkameshNo ratings yet
- Pulp Therapy in Pediatric DentistryDocument131 pagesPulp Therapy in Pediatric DentistrydrkameshNo ratings yet
- Ejpd 2014 3 8Document6 pagesEjpd 2014 3 8drkameshNo ratings yet
- JIndianSocPedodPrevDent344348-3624096 100400Document6 pagesJIndianSocPedodPrevDent344348-3624096 100400drkameshNo ratings yet
- Looking For Green Jobs The Impact of Green Growth On EmploymentDocument32 pagesLooking For Green Jobs The Impact of Green Growth On EmploymentdrkameshNo ratings yet
- Alternative/renewable Energy PresentationDocument20 pagesAlternative/renewable Energy Presentationdasilvabobo90% (21)
- Arch Length Loren Mills PDFDocument6 pagesArch Length Loren Mills PDFdrkameshNo ratings yet
- Esthetic and Functional Rehabilitation of Missing Anterior Teeth With A Conservative Treatment Approach A Clinical Case Series 2247 2452.1000646Document5 pagesEsthetic and Functional Rehabilitation of Missing Anterior Teeth With A Conservative Treatment Approach A Clinical Case Series 2247 2452.1000646drkameshNo ratings yet
- Employment Effects of Green Energy PoliciesDocument10 pagesEmployment Effects of Green Energy PoliciesdrkameshNo ratings yet
- Looking For Green Jobs The Impact of Green Growth On EmploymentDocument32 pagesLooking For Green Jobs The Impact of Green Growth On EmploymentdrkameshNo ratings yet
- Nonsurgical Management of Large Periapical Lesion in Mature and Immature Teeth Using Different Calcium Hydroxide Formulations Case SeriesDocument6 pagesNonsurgical Management of Large Periapical Lesion in Mature and Immature Teeth Using Different Calcium Hydroxide Formulations Case SeriesdrkameshNo ratings yet
- Kahler Trauma 2016 PDFDocument15 pagesKahler Trauma 2016 PDFdrkameshNo ratings yet
- Amazing Indian Herbs - Akarkara or Pellitory or Anacyclus PyrethrumDocument7 pagesAmazing Indian Herbs - Akarkara or Pellitory or Anacyclus PyrethrumdrkameshNo ratings yet
- Tooth Numbering SystemDocument11 pagesTooth Numbering SystemdrkameshNo ratings yet
- Dental TraumatologyDocument6 pagesDental TraumatologydrkameshNo ratings yet
- Dental Sys Permanent TeethDocument2 pagesDental Sys Permanent TeethatcommaNo ratings yet
- G Antibioticprophylaxis PDFDocument6 pagesG Antibioticprophylaxis PDFDian Purbasari NugrahaningrumNo ratings yet
- Dental Sys Primary Teeth PDFDocument2 pagesDental Sys Primary Teeth PDFdrkameshNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Modelling & Simulation GuideDocument96 pagesReservoir Modelling & Simulation GuideyouungNo ratings yet
- Quizlet-Philippine Electrical CodeDocument2 pagesQuizlet-Philippine Electrical Codena zafira0% (1)
- QNX Neutrino RTOS Building Embedded SystemsDocument248 pagesQNX Neutrino RTOS Building Embedded SystemsLarken BradynNo ratings yet
- Fractional Brownian Motions in Financial Models, Simulation and PricingDocument111 pagesFractional Brownian Motions in Financial Models, Simulation and Pricingnahv_08No ratings yet
- EC424 Monetary Economics (Michaelmas Term) Additional QuestionsDocument5 pagesEC424 Monetary Economics (Michaelmas Term) Additional QuestionsSteamPunkNo ratings yet
- Step 1: State The Null and Alternative HypothesisDocument3 pagesStep 1: State The Null and Alternative HypothesisChristine Joyce BascoNo ratings yet
- Profit Signals How Evidence Based Decisions Power Six Sigma BreakthroughsDocument262 pagesProfit Signals How Evidence Based Decisions Power Six Sigma BreakthroughsM. Daniel SloanNo ratings yet
- G5 Fi 125 (Sr25aa) PDFDocument122 pagesG5 Fi 125 (Sr25aa) PDF陳建璋No ratings yet
- P18 Probability in The CourtroomDocument14 pagesP18 Probability in The CourtroomYehiaNo ratings yet
- Components of A BarrageDocument21 pagesComponents of A BarrageEngr.Hamid Ismail CheemaNo ratings yet
- Pipe Flow Expert BrochureDocument2 pagesPipe Flow Expert BrochurecristinelbNo ratings yet
- STATS Shortcut FormulaDocument3 pagesSTATS Shortcut Formulajeet sighNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document76 pagesUnit 2Mithila100% (1)
- DRV IpDocument23 pagesDRV IpTim MarshallNo ratings yet
- The Market and Budget ConstraintsDocument8 pagesThe Market and Budget ConstraintsSnehaNo ratings yet
- Emphatic Struct and InversionDocument11 pagesEmphatic Struct and InversionMaria Veronica BustosNo ratings yet
- Recent Developments in Ultrasonic NDT Modelling in CIVADocument7 pagesRecent Developments in Ultrasonic NDT Modelling in CIVAcal2_uniNo ratings yet
- Black HoleDocument2 pagesBlack HoleLouis Fetilo Fabunan0% (1)
- FOUNDATION REPAIR AND REGROUT FOR BODYMAKER AT CARNDAUD METALBOX SINGAPOREDocument15 pagesFOUNDATION REPAIR AND REGROUT FOR BODYMAKER AT CARNDAUD METALBOX SINGAPORETrúc NguyễnNo ratings yet
- State-Of-The-Art CFB Technology For Utility-Scale Biomass Power PlantsDocument10 pagesState-Of-The-Art CFB Technology For Utility-Scale Biomass Power PlantsIrfan OmercausevicNo ratings yet
- Flender Technical HandbookDocument69 pagesFlender Technical HandbookAhmed Emad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Alili M S PDFDocument20 pagesAlili M S PDFStatsitika ITNo ratings yet
- Use Jinja2 To Create TemplatesDocument44 pagesUse Jinja2 To Create TemplatesmNo ratings yet
- Sandvik DL311Document4 pagesSandvik DL311Anonymous Dm7iMmtNo ratings yet
- Migrating Your SQL Server Workloads To PostgreSQL - Part 3 - CodeProjectDocument6 pagesMigrating Your SQL Server Workloads To PostgreSQL - Part 3 - CodeProjectgfgomesNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement Detailing in BeamsDocument9 pagesReinforcement Detailing in Beamssaheed tijaniNo ratings yet
- Foundation DetailsDocument29 pagesFoundation DetailsSUSOVAN BISWASNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Friction Losses in PipesDocument34 pagesExperiment 1 - Friction Losses in PipesKhairil Ikram33% (3)
- Ab5 PDFDocument93 pagesAb5 PDFbhavani nagavarapuNo ratings yet