Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH10 PPT NetworkNaming
Uploaded by
Antonius BlockOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH10 PPT NetworkNaming
Uploaded by
Antonius BlockCopyright:
Available Formats
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Network Naming
Chapter 10
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Objectives
Describe the function and
capabilities of DNS
Configure and troubleshoot WINS
Use common TCP/IP utilities to
diagnose problems with DNS and
WINS
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Overview
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Introduction to naming
Computers use IP addresses to
communicate
People remember names better
than numbers
Name resolution created to
convert names to IP addresses
(and vice versa)
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Name resolution has evolved
over the years
Main protocol is Domain Name
System (DNS)
Operating systems support old
and new
Windows, Linux, and Macintosh
OS X still support Windows
Internet Name Server (WINS)
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.1 Turning names into numbers
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Three parts to Chapter 10
DNS
WINS
Diagnosing TCP/IP networks
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
DNS
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
DNS
Early Internet use of HOSTS
file
One file copied to all hosts on
the Internet
Contained a list of IP addresses
for every computer, matched to
system names
Preceded rules for composing
Internet names
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
HOSTS file
Preceded DNS
Anyone could name computer
anything
Duplicate names not allowed
Sample old HOSTS file:
192.168.2.1 fred
201.32.16.4 SCHOOL2
123.21.44.16 SERVER
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
HOSTS file (cont.)
HOSTS file updated on every
system every morning at 2
a.m.
Impractical after Internet grew
to 5000
New name system, but HOSTS
file still exists
# symbol indicates a line is a
comment
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
HOSTS file (cont.)
Every OS first looks in HOSTS
file
Follow-up to Try This!
Every TCP/IP app looks at HOSTS file
If you altered the HOSTS file per the
Try This!, enter this command:
ping timmy
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
HOSTS file (cont.)
Some people place shortcut
names in a HOSTS file to avoid
typing a long name
into browser
DNS is more powerful and used
much more
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
How DNS works
No single computer can handle
all Internet name resolution
Delegation used
Top-dog DNS system delegates parts of
the job
Subsidiary DNS systems delegate parts
of their work
All DNS servers run a special DNS
server program
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
How DNS works (cont.)
Naming system facilitates
delegation
Top-dog DNS a bunch of
powerful systems
Dispersed around the world
Known collectively as the DNS root
servers (or DNS root)
The Internet name for DNS root is .
Below root are the top-level domain servers
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Name spaces
HOSTS file uses a flat name
space
DNS uses a hierarchical name
space
A hierarchy of DNS domains and
computer names
Hierarchical DNS name space is the
DNS Tree
Root is the holding area to which all
domains connect
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Name spaces (cont.)
Home-brewed DNS
Must not connect to the Internet
Set up a DNS server to be the root
server
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.2 Our People name space
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.3 Two DATA.TXT files in different
directories on the same system
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Name spaces (cont.)
DNS naming syntax
Opposite of disk folder/directory syntax
A complete DNS name is a fully
qualified domain name (FQDN)
Host and all domains in order
Root is far right
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.4 Private DNS network
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.5 Two DNS domains
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.6 Subdomains added
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Key players in DNS
DNS Name Server: running DNS
software
DNS Zone: A container for a
single DNS domain that gets
populated with records
DNS record: a line in the zone
data that maps an FQDN to an IP
address
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Name servers
One server is authoritative DNS
server for
a domain
a.k.a. Start of Authority (SOA)
Other name servers (NS) are
subordinate
All DNS servers know the address of
SOA and all NS servers in the domain
SOA keeps others updated
Name servers can host multiple
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Name servers (cont.)
Other systems send queries to
DNS servers
Request resolution of FQDNs to
IP addresses
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.7 A single SOA can support one or
more domains.
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.8 DNS flexibility
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.9 New information passed out
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.10 Root server in action
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.11 DNS domain
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Name resolution
DNS not required to access
Internet
DNS just makes it much easier
IP addresses required for
connections
Most people would not use
Internet without DNS name
resolution
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Name resolution (cont.)
Type Web address into a
browser
It must resolve the name to IP
address
Three ways to resolve a name
Broadcasting
HOSTS file
Querying a DNS server
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.12 Any TCP/IP-savvy program accepts
either an IP address or an FQDN.
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.13 Routers dont forward broadcasts!
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.14 A host contacts its local DNS server.
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.15 DNS information in Windows
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.16 Entering DNS information in Ubuntu
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.17 ipconfig /all showing DNS information
in Windows
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.18 Checking the DNS cache
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.19 Talking to a root server
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.20 Talking to the .com server
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.21 Talking to microsoft.com DNS server
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
DNS servers (in action)
Most OSes have built-in DNS
server software
Server versions of Windows
Most versions of UNIX/Linux
Third-party DNS servers
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
DNS Servers (in action) (cont.)
Three special storage areas
Cached lookups
Forward lookup zones
Reverse lookup zones
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.22 DNS server main screen
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.23 Inspecting the DNS cache
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
DNS servers (in action) (cont.)
Cache-only DNS servers
Do not store lookup zones
Talk to other DNS servers to resolve for
clients
Are never the authoritative server for a
domain
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.24 Authoritative vs. cache-only DNS server
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Totalhome domain example
Does not comply with Internet
rules
None of the computers is visible
on Internet
Only usable on private network
Forward lookup is named
totalhome
All the DNS servers listed under
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Totalhome forward lookup
zone
Each system in the domain has an
A record
An alias for a system is a canonical
name (CNAME)
SMTP servers use MX records (Mail
eXchanger)
AAAA records are for IPv6
addresses
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.25 Forward lookup zone totalhome
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.26 Less common DNS record types
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Forward lookup zones
Two types of forward lookup
zones:
Primary zone and Secondary zone
Resolve FQDN to IP address with
Reverse lookup zone
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.27 Two DNS servers with updating
taking place
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.28 Reverse lookup zone
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Windows DNS server
Performs most functions exactly
like UNIX/Linux DNS servers
Adds a Windows-only Active
Directory-integrated zone
Avoids problems of standard
DNS servers
All domain controllers are DNS
servers
All DNS servers are equal
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Enter Windows
1980s Microsoft
NetBIOS/NetBEUI
1990s Microsoft created
NetBIOS over TCP/IP added
NetBIOS naming to DNS
Old sharing protocol Server
Message Block (SMB)
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.29 NetBIOS broadcast
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Enter WindowsNetBIOS over
TCP/IP
New sharing protocol Common
Internet File System (CIFS)
SMB/CIFS adopted by UNIX/Linux
and Mac OS X
CIFS and DNS work together
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.30 Samba on Ubuntu (its so common that the OS
doesnt even use the term in the dialog box)
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Living with the legacy of CIFS
Networks using CIFS use two
name systems
CIFS broadcast to find local
server
DNS query to find TCP/IP host
CIFS and DNS work together
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Living with the legacy of CIFS
(cont.)
CIFS organizes computers into
workgroups
Computer joins a workgroup
Flat name space
See workgroups in Network/My
Network Places
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.31 Joining a workgroup
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.32 Two workgroups in Network folder
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Living with the legacy of CIFS
(cont.)
Computers controlled by
Windows domain controller
server are grouped in a
Windows domain
Windows computers join a
domain
Computers (and users)
authenticate to the domain
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.33 Logging in to the domain
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Living with the legacy of CIFS
(cont.)
An Active Directory domain is an
organization of computers that
shares one or more Windows
domains
All Active Directory Windows
domain controllers are DNS
servers
All domain controllers are equal
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.34 If one domain controller goes down,
another automatically takes over.
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Active Directory-integrated
zones
DNS info is stored in the AD
database, instead of text files
AD is stored across several
domain controllers, so theres
no longer only one copy
Domain controllers
automatically replicate DNS
zone information along with
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Dynamic DNS (DDNS)
DNS previously required manual
updates to zone files
This became very problematic as
the Internet and organizations
computers grew in numbers
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) enables a
DNS server to talk to a DHCP
server and get IP addressing
info on its clients
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Dynamic DNS (cont.)
Most modern DNS software can
use DDNS
Windows clients can also update
DNS server files automatically
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Dynamic DNS on the Web
High-speed connections now
enable home computers to run
as web and file servers, and
enable remote connections to it
Problem existed with home or
office
router-assigned DNS names
Dynamic DNS maps home or
office router
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Dynamic DNS on the Web
(cont.)
If routers external IP address
changes, it notifies the dynamic
DNS service and makes the
change
Allows home or office network to
be contacted via domain name
regardless of IP address
changes
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Troubleshooting DNS
Client is source of most DNS
problems
DNS servers rarely go down
If a DNS server is down, clients
use secondary DNS server
Symptom: server not found
error
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.35 DNS error
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Troubleshooting DNS (cont.)
Eliminate any local DNS caches
Do not use Web browser for
troubleshooting
On Windows, run ipconfig /flushdns
Ping the name of a well-known Web
site
Does it return an IP address?
If not, ping an IP address
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.36 Using ping to check DNS
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Troubleshooting DNS (cont.)
If the previous steps indicate a
problem with the DNS server,
run nslookup utility
Queries functions of DNS servers
Depends on proper permission level
Use to change how your system uses
DNS
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Troubleshooting DNS (cont.)
Run nslookup without parameters
to get
IP address and name of default DNS
server
Error indicates primary DNS server is
down or client has wrong IP for DNS
server
nslookup has own prompt
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Troubleshooting DNS (cont.)
UNIX/Linux tool: domain
information groper (DIG)
Similar to nslookup
Non-interactive
Ask it a question; it answers
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
WINS
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
WINS
Legacy NetBIOS
Current versions of Windows
use DNS and/or CIFS
NetBIOS names supported for
backwards compatibility
NetBIOS system broadcasts its
name
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Prior to CIFS
LMHOSTS file
Works for NetBIOS like HOSTS does for
DNS
Microsoft OSes still support
Every Windows systems has an
LMHOSTS file
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Windows Internet Naming
Service (WINS)
WINS server for legacy Windows
No broadcasting: NetBIOS hosts
register with WINS
Allows NetBIOS to function in a
routed network
WINS proxy agent for legacy
Windows
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.37 WINS server
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.38 Proxy agent
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Configuring WINS clients
Enter IP address of WINS server
WINS information can be added
to DHCP
WINS clients register NetBIOS
names with WINS server
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Troubleshooting WINS
Most WINS problems are
NetBIOS problems
Two systems sharing same name
Change name of one system
NBTSTAT
Check name cache with nbtstat c
Determine if WINS server has given inaccurate
info
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Diagnosing TCP/IP
networks
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Improper configuration
causes most problems
Ping anyone you want to
connect to
Regardless of what the user
cannot connect to, you
perform the same steps
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Use common sense
If one system behaves differently
than others, the problem is with the
client
Before starting steps (below) check
the network connections and
protocols
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Steps for troubleshooting
TCP/IP
Diagnose the NIC
Diagnose locally
Check IP address and subnet mask
Run netstat with no options
Run netstat s
Diagnose to the gateway
Diagnose to the Internet
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.39 The net view command in action
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.40 The netstat command in action
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mike Meyers CompTIA Network+ Guide to Managing
and Troubleshooting Networks, Third Edition (Exam
N10-005)
Figure 10.41 Using tracert
2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- DoCoMo Japan - S Wireless TsunamiDocument256 pagesDoCoMo Japan - S Wireless TsunamiAntonius BlockNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems and IotDocument5 pagesEmbedded Systems and IotAntonius BlockNo ratings yet
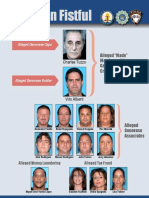
- Pr20160427a Op-FistDocument1 pagePr20160427a Op-FistAntonius BlockNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Business Intelligence (2015)Document361 pagesFundamentals of Business Intelligence (2015)asceric436392% (13)
- Gov Fratto MemoDocument71 pagesGov Fratto MemoAntonius BlockNo ratings yet
- Linux FilesystemDocument16 pagesLinux FilesystemAntonius BlockNo ratings yet
- PharmagheddonDocument315 pagesPharmagheddonAntonius BlockNo ratings yet
- Screenplay GoodfellasDocument127 pagesScreenplay GoodfellasJonas BarrosNo ratings yet
- The Spycraft Manual - Barry DaviesDocument191 pagesThe Spycraft Manual - Barry DaviesAkar Aha Ahershu100% (31)
- Ocbars 2Document105 pagesOcbars 2Antonius BlockNo ratings yet
- EMU8086 TutorialDocument81 pagesEMU8086 TutorialGaurav Arora50% (4)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Internet Domain Name SystemDocument5 pagesInternet Domain Name SystemVenkat Ramana CHNo ratings yet
- How to Configure DHCP in Cisco Packet Tracer: Configure DHCP ServicesDocument12 pagesHow to Configure DHCP in Cisco Packet Tracer: Configure DHCP ServicesLuis FfNo ratings yet
- Subnetting tasksDocument9 pagesSubnetting tasksHafizuraNo ratings yet
- Domain Name SystemDocument8 pagesDomain Name SystemSrishti AroraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 02 ADocument8 pagesTutorial - 02 AChanduni GamageNo ratings yet
- IPv4 and IPv6 subnet cheat sheetDocument5 pagesIPv4 and IPv6 subnet cheat sheetJumaniyoz BotirovNo ratings yet
- IP AddressingDocument48 pagesIP AddressingDaniel VargasNo ratings yet
- PROTECT - How To Combat Fake Emails (August 2019)Document14 pagesPROTECT - How To Combat Fake Emails (August 2019)Evil Terms OnlyNo ratings yet
- Tencent DNS IP addresses and hostnamesDocument88 pagesTencent DNS IP addresses and hostnamesLukman Fafa0% (1)
- New Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationDocument25 pagesNew Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationTsuna DrameNo ratings yet
- IP Addresses: Understanding IPv4 Classes, Networking, and SubnettingDocument65 pagesIP Addresses: Understanding IPv4 Classes, Networking, and SubnettingFiroz kumarNo ratings yet
- Challenge 6.4.5 Instructors VersionDocument10 pagesChallenge 6.4.5 Instructors VersionMadsKDK100% (1)
- Config Cisco 887Document5 pagesConfig Cisco 887Manuel ArellanoNo ratings yet
- IAP Assignment1 PDFDocument1 pageIAP Assignment1 PDFAbdul MananNo ratings yet
- IP addressing fundamentals worksheetDocument8 pagesIP addressing fundamentals worksheetkerya ibrahimNo ratings yet
- 1.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge OSPF Instructions - IG PDFDocument6 pages1.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge OSPF Instructions - IG PDFDairo Mauricio Suarez PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Meezan Bank CEO: Irfan SiddiquiDocument5 pagesMeezan Bank CEO: Irfan SiddiquiJamesNo ratings yet
- NTP Server Reachability FaultDocument2 pagesNTP Server Reachability FaultSARBJIT BHANGUNo ratings yet
- Subnetting Summary Youtube - Com-Romeroc24Document40 pagesSubnetting Summary Youtube - Com-Romeroc24Hector AndresNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - VLSM Design and Implementation Practice TopologyDocument3 pagesPacket Tracer - VLSM Design and Implementation Practice TopologyL HammeRNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 Activity 1Document6 pagesLab 7 Activity 1bonspspNo ratings yet
- Slides 99 Edu Sessh DNS Privacy Tutorial 00Document89 pagesSlides 99 Edu Sessh DNS Privacy Tutorial 00Manny OrtizNo ratings yet
- LCTN0016 Configuring Dynamic DNSDocument7 pagesLCTN0016 Configuring Dynamic DNSProxicastNo ratings yet
- IPv4 and IPv6 DNS provider optionsDocument4 pagesIPv4 and IPv6 DNS provider optionsIt babaNo ratings yet
- IP Addressing, Subnetting, SupernettingDocument65 pagesIP Addressing, Subnetting, SupernettingFiroz kumarNo ratings yet
- 8.1.4.8 Lab RespuestasDocument4 pages8.1.4.8 Lab RespuestasJesús David DíazNo ratings yet
- IP Addressing and Subnetting AssignmentDocument4 pagesIP Addressing and Subnetting AssignmentZeeshan AjmalNo ratings yet
- IP Addressing and Subnetting Workbook, Version 2.0 Student EditionDocument12 pagesIP Addressing and Subnetting Workbook, Version 2.0 Student EditionmanuelNo ratings yet
- DNS Translates Domain Names to IP AddressesDocument3 pagesDNS Translates Domain Names to IP AddressesLayla AfidatiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Content:: Sec 1.2.2 IP AddressesDocument16 pagesSyllabus Content:: Sec 1.2.2 IP Addressesapi-470106119No ratings yet