Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SR05 - Amruth Pavan Davuluri - How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy
Uploaded by
amruthpavan090 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views14 pagesCompetition for profits goes beyond established industry rivals to include four other competitive forces as well. A buyer group is more powerful if: 1. It is concentrated or purchased in large volumes 2. It earns low profits 3. It is unimportant to the quality of the buyers' products or services 6. It poses a credible threat to integrating backward to make the industry's products or services better.
Original Description:
Original Title
SR05_Amruth Pavan Davuluri_How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCompetition for profits goes beyond established industry rivals to include four other competitive forces as well. A buyer group is more powerful if: 1. It is concentrated or purchased in large volumes 2. It earns low profits 3. It is unimportant to the quality of the buyers' products or services 6. It poses a credible threat to integrating backward to make the industry's products or services better.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views14 pagesSR05 - Amruth Pavan Davuluri - How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy
Uploaded by
amruthpavan09Competition for profits goes beyond established industry rivals to include four other competitive forces as well. A buyer group is more powerful if: 1. It is concentrated or purchased in large volumes 2. It earns low profits 3. It is unimportant to the quality of the buyers' products or services 6. It poses a credible threat to integrating backward to make the industry's products or services better.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Amruth Pavan Davuluri
140101017
Section A
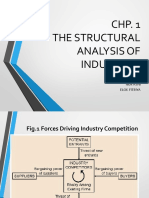
Forces of competition are not only limited to
direct competitors.
Competition for profits goes beyond established
industry rivals to include four other competitive
forces as well
Five forces collective strength determine the
competition in the market
New entrants may bring new capacity, the
desire to gain market share, and often
substantial resources
The seriousness of the threat of entry depends on
the barriers present and on the reaction from
existing competitors that entrants can expect
If the barriers to entry are high and newcomers
can expect sharp retaliation from the entrenched
competitors.
1.
2.
3.
Economies of scale which force a new aspirant
to come in on a large scale or to accept a cost
disadvantage.
Product differentiation which creates a barrier by
forcing entrants to spend heavily to overcome
customer loyalty.
Capital requirements which create the need to
invest large financial resources in order to
compete.
4.
5.
6.
Cost disadvantages independent of size due to
experience curves, proprietary technology,
access to the best raw materials, etc.
Access to distribution channels that are tied up
by existing competitors which makes it more
difficult for new entrants to get started.
Government policy which can limit or even
foreclose entry by controlling such items as
license requirements and limits on the access to
raw materials.
A supplier group is more powerful if:
1. It
is dominated by a few companies
2. It is more concentrated than the industry it sells to
3. Its product is unique or at least differentiated
4. The supplier has built up switching costs
5. It does not contend with other products for sale to
the industry
6. It poses a credible threat of integrating forward
into the industrys business
7. The industry is not an important customer of the
supplier group
A buyer group is more powerful if:
1. It is a concentrated or purchased in large volumes
2. The products it purchases from the industry are standard
and undifferentiated
3. The products it purchases form a component of its
products and represent a significant fraction of its costs
4. It earns low profits, which creates great incentive to
lower its purchasing costs
5. The industrys product is unimportant to the quality of
the buyers products or services
6. The industrys products do not save the buyer money
7. The buyer poses a credible threat to integrating
backward to make the industrys product
Substitute products and services can have an
impact on the industry because:
By placing a ceiling on the prices it can charge,
substitute products or services limit the potential
of an industry
Substitutes not only limit profits in normal times
but also reduce the bonanza an industry can reap
in boom times
Substitute products that deserve the most
attention strategically are those that are
a. subject to trends improving their priceperformance trade-off with the industrys
product or
b. produced by industries earning high profits
Intense rivalry occurs when:
Competitors are numerous or are roughly equal
Industry growth is slow, precipitating fights for
market share that involve expansion
The product or service lacks differentiation or
switching costs
Fixed costs are high or the product is perishable,
creating strong temptation to cut prices
Capacity normally is augmented in large
increments
Exit barriers are high
Rivals are diverse in strategy, origin, and
personality
1.
2.
3.
Positioning the company: Strategy can be
viewed as building defense against the
competitive forces or as finding positions in the
industry where the competitive forces are
weakest
Exploiting and expecting industry change:
Industry evolution is important strategically
because we want to know how these changes
are effecting the sources of competition
Shaping the Industry Structure: Use tactics
that are designed specifically to reduce the
share of profits leaking to other companies
In a world of more open competition and
relentless change, it is important than ever to
think structurally about the competition
Awareness of the Five forces can help a
company stakeout a position in its industry
that is less vulnerable to others
Whatever their collective strength is, the
corporate strategists goal is to find a position
in the industry where his or her company can
best defend itself against these forces or can
influence them in its favor
Defining the industry too broadly or too
narrowly
Paying equal attention to all the forces rather
than digging deeply into the important one
Using static analysis that ignores industry
trend
Using the framework to declare an industry
attractive or unattractive rather than using it
to guide strategic choices
You might also like
- Porter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionFrom EverandPorter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- How Competitive Forces Shape StrategyDocument13 pagesHow Competitive Forces Shape StrategyReshmi Varma100% (1)
- Industry AnalysisDocument13 pagesIndustry AnalysisKasiira HatimuNo ratings yet
- Michael Porter's Industry Structural AnalysisDocument12 pagesMichael Porter's Industry Structural AnalysisRenell John Maglalang100% (1)
- 5 ForceDocument5 pages5 ForceMichael YongNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Assignment 1 Group 2Document11 pagesStrategic Management Assignment 1 Group 2Ani889No ratings yet
- Michael Porter 5 Forces Model AnalysisDocument4 pagesMichael Porter 5 Forces Model AnalysisSheetal Siyodia100% (2)
- The Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyDocument14 pagesThe Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyatulpvermaNo ratings yet
- The Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyDocument14 pagesThe Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyronNo ratings yet
- Notes On Compettive StartegiesDocument6 pagesNotes On Compettive Startegiesdivya8955No ratings yet
- Competitive Strategy: (Summary)Document11 pagesCompetitive Strategy: (Summary)Jason Patrick PastranaNo ratings yet
- Porter (2008) The Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyDocument5 pagesPorter (2008) The Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategySachin AntonyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Compre 1Document30 pagesReviewer Compre 1Dexter AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- 2.the Structural Analysis of IndustriesDocument27 pages2.the Structural Analysis of IndustriesEric Parilla0% (1)
- Development and Cost Reduction Efforts. Price and Service Would Become MoreDocument9 pagesDevelopment and Cost Reduction Efforts. Price and Service Would Become More2B Ma. Lyn BrenNo ratings yet
- The Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyDocument5 pagesThe Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyAmol Deherkar67% (3)
- Porters 5 ForcesDocument20 pagesPorters 5 ForcesMaruti Nandan DubeyNo ratings yet
- Industry Handbook: Porte: R's 5 Forces AnalysisDocument20 pagesIndustry Handbook: Porte: R's 5 Forces AnalysisAnitha GirigoudruNo ratings yet
- Porter's Five Forces: A Model For Industry AnalysisDocument6 pagesPorter's Five Forces: A Model For Industry AnalysiskimsrNo ratings yet
- Industry Analysis: Positioning The FirmDocument5 pagesIndustry Analysis: Positioning The FirmDonrost Ducusin Dulatre100% (1)
- Porter's Five Five Force Analysis (Part-1)Document4 pagesPorter's Five Five Force Analysis (Part-1)Pooja Rani-48No ratings yet
- Porter XXXDocument7 pagesPorter XXXAmol DeherkarNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis - Chp02 - Summary NotesDocument6 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis - Chp02 - Summary NotesBrainNo ratings yet
- Notes For Assignment 2Document15 pagesNotes For Assignment 2phyu trezaNo ratings yet
- Porter's Five Force ModelDocument27 pagesPorter's Five Force ModelKushagra SethiNo ratings yet
- SM WK 4 - External AnalysisDocument43 pagesSM WK 4 - External AnalysisPard TeekasapNo ratings yet
- Porter's Framework of Competitive Strategies (Generic Strategies)Document14 pagesPorter's Framework of Competitive Strategies (Generic Strategies)Adil Bin Khalid100% (1)
- Offensive Competitive Strategy: Objectives of Offensive StrategiesDocument29 pagesOffensive Competitive Strategy: Objectives of Offensive Strategiesjagan rathodNo ratings yet
- PESTLE AnalysisDocument13 pagesPESTLE AnalysisAlzen Marie DelvoNo ratings yet
- Industry AttractivenessDocument9 pagesIndustry AttractivenessSakshi DangiNo ratings yet
- The Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyDocument2 pagesThe Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategySubash AcharyaNo ratings yet
- The Porter Five-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesThe Porter Five-WPS Officehammad khatri0% (1)
- Competitor AnalysisDocument9 pagesCompetitor Analysisvarsha raichalNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 STMGMTDocument3 pagesQuiz 3 STMGMTJoetta BlevinsNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Business StrategyDocument5 pagesCH 6 Business StrategyfirasNo ratings yet
- 5 Force ModelDocument14 pages5 Force Modelsrilatha212No ratings yet
- Barriers To Entering An Industry: Entry Barriers and The Other 4 Porter Competitive ForcesDocument11 pagesBarriers To Entering An Industry: Entry Barriers and The Other 4 Porter Competitive ForcesFasi RaoNo ratings yet
- How Competitive Forces Shape StrategyDocument11 pagesHow Competitive Forces Shape StrategyErwinsyah RusliNo ratings yet
- Petitive Strategy - Industry StructureDocument12 pagesPetitive Strategy - Industry StructuredevendrakhaleNo ratings yet
- Extra Topics:: 1. Strategies For Different Industries 2. Ge Matrix 3. Turnaround Strategies 4. 7S ModelDocument14 pagesExtra Topics:: 1. Strategies For Different Industries 2. Ge Matrix 3. Turnaround Strategies 4. 7S Model51095BRizwana KhojaNo ratings yet
- Porter Analysis ReportingDocument5 pagesPorter Analysis ReportingMinini NestNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document7 pagesChapter 5ERICKA MAE NATONo ratings yet
- Chap 3,4Document22 pagesChap 3,4Sadman KabirNo ratings yet
- Porter's Generic StrategiesDocument3 pagesPorter's Generic StrategiesAhmed ElGeoshyNo ratings yet
- Bab 1-5 PorterDocument31 pagesBab 1-5 PorterNur AsniNo ratings yet
- BCG MATRIX Boston Consulting GroupDocument16 pagesBCG MATRIX Boston Consulting GroupDana DrNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document19 pagesCH 02Muhammad Shahadat HossainNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Strengthening A Company's Competitive PositionDocument20 pagesStrategic Management: Strengthening A Company's Competitive PositiontonmoyNo ratings yet
- Generic Strategies PDFDocument13 pagesGeneric Strategies PDFDikshita MahadikNo ratings yet
- "Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyDocument32 pages"Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategySahrish TahirNo ratings yet
- Otd 2Document4 pagesOtd 2ramshaNo ratings yet
- Porters Five ForcesDocument5 pagesPorters Five ForcesDhairya BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Strategy + Five Forces ModuleDocument56 pagesBlue Ocean Strategy + Five Forces ModuleWolf's Rain100% (1)
- Diversification & Porters Generic StategiesDocument11 pagesDiversification & Porters Generic StategiesvaryushNo ratings yet
- Porter's Generic StrategiesDocument4 pagesPorter's Generic StrategiesAshish PereNo ratings yet
- Porter 5 Forces AnalysisDocument3 pagesPorter 5 Forces AnalysisWaleed AshourNo ratings yet
- Externalanch 02Document24 pagesExternalanch 02api-228377429No ratings yet
- SM Mod 05Document60 pagesSM Mod 05Kavi_3788No ratings yet
- The Competitive EnvironmentDocument8 pagesThe Competitive EnvironmentElaine MorenoNo ratings yet
- The General, Industry, and Competitor EnvironmentsDocument6 pagesThe General, Industry, and Competitor EnvironmentsUlfa ZhafirahNo ratings yet
- Sped'Ers C.A.R.E Organization Financial Statement: Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State UniversityDocument2 pagesSped'Ers C.A.R.E Organization Financial Statement: Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State Universitychenee liezl horarioNo ratings yet
- A Study On Credit Risk Management at Canara BankDocument10 pagesA Study On Credit Risk Management at Canara BankBhaswani33% (6)
- Business Plan Aprils Group 1Document19 pagesBusiness Plan Aprils Group 1Lealyn Alupay YagaoNo ratings yet
- The Comparison Between LG and Samsung in Satisfaction and AwarenessDocument37 pagesThe Comparison Between LG and Samsung in Satisfaction and AwarenessChandan SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- "The New Science of Salesforce Productivity": Reading SummaryDocument2 pages"The New Science of Salesforce Productivity": Reading SummarypratyakshmalviNo ratings yet
- Drain of Wealth JrPUzLp PreviewDocument3 pagesDrain of Wealth JrPUzLp PreviewAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Bnmit ConferenceDocument4 pagesBnmit ConferenceBhavani B S PoojaNo ratings yet
- Cips Fees - February 2019Document2 pagesCips Fees - February 2019edd bazNo ratings yet
- Journal of Financial Economics: Progress PaperDocument17 pagesJournal of Financial Economics: Progress PapersaidNo ratings yet
- Bài Báo Thu MuaDocument10 pagesBài Báo Thu MuaMinh TânNo ratings yet
- WJEC Economics AS Unit 2 QP S19Document7 pagesWJEC Economics AS Unit 2 QP S19angeleschang99No ratings yet
- RELIANCE - Investor Presentation - 06-May-22 - TickertapeDocument70 pagesRELIANCE - Investor Presentation - 06-May-22 - TickertapeAhaana guptaNo ratings yet
- Amit SinghDocument111 pagesAmit Singhashish_narula30No ratings yet
- LSCM Assignment 1 - Diet 1 2020 - 21Document7 pagesLSCM Assignment 1 - Diet 1 2020 - 21Ronisha ShresthaNo ratings yet
- 2023 HSC Business StudiesDocument22 pages2023 HSC Business StudiesSreemoye ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - AnswerDocument10 pagesChapter 03 - AnswerGeomari D. BigalbalNo ratings yet
- South-East Journal Sept 2023Document56 pagesSouth-East Journal Sept 2023unworahNo ratings yet
- PST AAA 2015 2022Document45 pagesPST AAA 2015 2022mulika99No ratings yet
- Mohammed Ariful Islam Saimon Chowdhury: BankerDocument2 pagesMohammed Ariful Islam Saimon Chowdhury: BankerAriful SaimonNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide To Financial PlanningDocument160 pagesThe Complete Guide To Financial PlanningVikas Acharya100% (2)
- Crack The Case 6.0Document6 pagesCrack The Case 6.0SIDDHARTH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Tomato ProductsDocument5 pagesTomato ProductsDan Man100% (1)
- Angelo Wardana 349655122Document5 pagesAngelo Wardana 349655122Green Sustain EnergyNo ratings yet
- Sambhav 2023Document8 pagesSambhav 2023prachi singhNo ratings yet
- FM Report On Ultratech Cement (Sem 2)Document22 pagesFM Report On Ultratech Cement (Sem 2)mital208No ratings yet
- Financial Controller 1 Pre-Final QuestionsDocument2 pagesFinancial Controller 1 Pre-Final QuestionsWen CapunoNo ratings yet
- Global RRL of AbesnteeismDocument4 pagesGlobal RRL of AbesnteeismelijahjosephhmesadaNo ratings yet
- Enron ReflectionDocument2 pagesEnron ReflectionRanie MonteclaroNo ratings yet
- MedMen CFO Lawsuit PDFDocument48 pagesMedMen CFO Lawsuit PDFsandydocs100% (2)
- HRP Case StudyDocument1 pageHRP Case Studymruga_123No ratings yet