Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Innovation Workshop Brainstorming: Jonathan Weaver & Darrell Kleinke
Uploaded by
Ali M. ChehadehOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Innovation Workshop Brainstorming: Jonathan Weaver & Darrell Kleinke
Uploaded by
Ali M. ChehadehCopyright:
Available Formats
Brainstorming
Innovation Workshop
Brainstorming
Jonathan Weaver & Darrell Kleinke
UDM Mechanical Engineering
Brainstorming
References
Otto, Kevin and Wood, Kristin: Product Design Techniques in
Reverse Engineering and New Product Development. Prentice
Hall, 2001.
Dieter, George E.: Engineering Design A Materials and
Processing Approach. Third Edition. McGraw-Hill, 2000.
Ullman, David G.: The Mechanical Design Process. Second
Edition. McGraw-Hill, 1997.
Wright, Ian: Design Methods in Engineering and Product Design.
McGraw-Hill, 1998.
Dave Verduyn guest lectures at UDM.
Brainstorming
What is Brainstorming
Brainstorm: Sudden disturbance of the mind; sudden inspiration.
Brainstorming is an intuitive method of working as a team to
generate concepts where team members communicate ideas
verbally and with quick sketches
All team members are encouraged to be open and uninhibited
Goal is to comprehensively explore a breadth of solutions ideally
leaving no promising directions unexplored
Team members build upon each others ideas
Brainstorming
Advantages of Brainstorming
A set of individuals can collectively build on each other to
generate ideas that would not arise individually
Each member of the group contributes ideas from his or
her own viewpoint
Good team builder/morale booster
Its a great tool to start developing concepts (just dont
make it the only tool used!)
Brainstorming
Disadvantages of Brainstorming
The right idea may not come at the right time
Group conventions may sidetrack or inhibit original ideas (Best to
have each individual generate ideas beforehand)
The team may be distracted by a misdirected focus
Certain team members may dominate the discussion
Other than encouraging out of the box thinking, there is very
little direction to actively stimulate new ideas (well cover some
tools for systematic innovation to address this)
Brainstorming
Brainstorming Process
Form a group with 5 to 15 people (too few gives inadequate
ideas, too many can break down the group into multiple
conversations or inhibit participation)
Designate a group leader/facilitator who will solely direct
and record
Introduce the problem , then brainstorm ideas; wrap up
when stagnation is reached (30-45 minutes)
Record all the ideas generated
Brainstorming
Brainstorming Principles
1. No criticism
2. Focus on quantity (not quality)
3. Unusual ideas are welcomed
4. Combine and improve ideas
Brainstorming is a DIVERGENT technique, later on,
screening is used as a CONVERGENT technique.
Brainstorming Screening
Brainstorming
Brainstorming Guidelines
Provide a suitable working environment
Avoid hierarchically structured groups
Dont confine the group to experts in the area
Carefully define the problem beforehand (or at the start)
and allow time for individual thought
Do not allow the evaluation of ideas
Think wild and encourage humor
Practice applying brainstorming on real, but non-critical
problems to get good at it for the critical problems
Brainstorming
Brainstorming Guidelines
Avoid Idea-Killer Phrases
Thats a good idea, BUT .... (insert idea-killer here)
The Boss will never go for that.
Thats a good idea, in theory.
Thats not how its done around here.
If your idea is so good, why hasnt it been done
before?
Lets form a committee.
Brainstorming
10
Walt Disneys Imagineers
Brainstorming Rules
Rule 1 - There is no such thing as a bad idea. We never know how one
idea (however far-fetched) might lead into another one that is exactly
right.
Rule 2 - We dont talk yet about why not. There will be plenty of time for
realities later, so we dont want them to get in the way of good ideas now.
Rule 3 - Nothing should stifle the flow of ideas. Not buts or cants or
other stopping words. We want to hear words like and, or, and
what if?
Rule 4 - There is no such thing as a bad idea.
(We take that one very seriously.)
Source: http://www.techrepublic.com/blog/hiner/how-to-kill-innovation-in-five-easy-steps/8348
Brainstorming
11
Brainstorming
Exercise Evaluate These Brainstorming Assignments
Whats wrong with these assignments?
Use brainstorming to:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
determine the best mini-van on the market.
Use Benchmarking
suggest alternative genes for circadian rhythm.
Need Expertise
propose improvements to Dr. Weavers garage.
Lack of Data
decide which shop floor suggestions well use.
Use Pugh
come up with ideas on your own.
Duhhhhhhh
End of Brainstorming Slides
Brainstorming
12
23 Reasons Why Nothing Happens After a
Brainstorming Session
Source: The Heart of Innovation, December 4, 2010
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
The output of the session is underwhelming.
No one has taken the time, pre-brainstorm, to consider follow-up.
No criteria is established to evaluate the output.
No next steps are established at the end of the session.
No champions (i.e. process owners) are identified.
The champions are not really committed.
The champions are committed, but under-estimate the effort.
The ideas are too threatening to key stakeholders.
No one is accountable for results.
The project leader doesn't stay in contact with key players and "out of sight, out
of mind" takes over.
11. The "steering committee" takes their hands off the wheel.
12. The next brainstorming session is scheduled too quickly.
Brainstorming
13
23 Reasons Why Nothing Happens After a
Brainstorming Session (Cont.)
Source: The Heart of Innovation, December 4, 2010
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
The output of the session is not documented.
No sponsors are on board.
Participants' managers are not supportive of the effort
It takes too long to document the output of the session.
The output is not distributed to stakeholders in a timely way.
Participants and stakeholders do not read the output.
Bureaucracy and company politics rule the day.
Somebody, in the session, is disengaged and sabotages the effort.
Teamwork and collaboration is in short supply.
Small wins are not celebrated. People lose heart.
Participants perceive follow-up as "more work to do" instead of a great
opportunity to really make a difference.
Brainstorming
14
"One thing to bear in mind about serendipity is that you
have to be looking for something in order to find
something else."
Lawrence Block (1938- ) is an acclaimed contemporary
American crime writer who was designated as a Grand Master
by the Mystery Writers of America in 1993.
Most people only become aware of their surroundings when
they are looking for something specific. But, by cultivating a
sense of "huntfulness" all day, every day, you will not only find
what you seek, but you will also discover all kinds of
unexpected things that otherwise would have gone overlooked.
This is one of the basic, yet most important attributes that
distinguish successful, prolific innovators from the average
person on the street.
Ideaologys Innovation Quote du Jour 20080410
You might also like
- Planning For Innovative Products: Planning For Innovative ProductsDocument48 pagesPlanning For Innovative Products: Planning For Innovative ProductsMuhammad HamayunNo ratings yet
- Brainstorming TechniquesDocument8 pagesBrainstorming TechniqueslettymcNo ratings yet
- L10 Conc Des Int p1v4Document43 pagesL10 Conc Des Int p1v4ahmedhamdiNo ratings yet
- 30 Minute .... To Brainstorm Great Ideas: Vinay KumarDocument16 pages30 Minute .... To Brainstorm Great Ideas: Vinay KumarVinay SoamNo ratings yet
- What Is Brainstorming 1Document3 pagesWhat Is Brainstorming 1YOUSAF KULACHINo ratings yet
- Importance of BrainstormingDocument4 pagesImportance of BrainstormingAmzionNo ratings yet
- Creativity & Innovation Brainstorming TechniquesDocument50 pagesCreativity & Innovation Brainstorming TechniquesFirdhaus SakaffNo ratings yet
- 7 Techniques for More Effective BrainstormingDocument8 pages7 Techniques for More Effective BrainstormingArshpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- PQMLec 05Document21 pagesPQMLec 05Maryam Bint E ImranNo ratings yet
- Boost Creativity with Brainstorming Rules and TipsDocument20 pagesBoost Creativity with Brainstorming Rules and TipsSab 1001No ratings yet
- Chap - 2 - Concept Generation - Sequenece - Sym - 1Document58 pagesChap - 2 - Concept Generation - Sequenece - Sym - 1Saurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- BrainstormingDocument11 pagesBrainstormingMM J30No ratings yet
- Brainstorming & Creative Thinking TechniquesDocument27 pagesBrainstorming & Creative Thinking TechniquesAdham YNo ratings yet
- BrainstormingDocument34 pagesBrainstormingShital ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- WIN SEM (2022-23) FRESHERS STS6001 TH AP2022237000730 Reference Material I 15-Mar-2023 Emotional Intelligence - All ContentDocument17 pagesWIN SEM (2022-23) FRESHERS STS6001 TH AP2022237000730 Reference Material I 15-Mar-2023 Emotional Intelligence - All ContentDendiNo ratings yet
- Creativity and Innovation in Organ Is at Ions - Black BoardDocument20 pagesCreativity and Innovation in Organ Is at Ions - Black BoardAmar BhattNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document14 pagesChapter 4isma farizNo ratings yet
- Brainstorming Is A: Group Creativity Technique Ideas Problem Alex Faickney OsbornDocument19 pagesBrainstorming Is A: Group Creativity Technique Ideas Problem Alex Faickney OsbornАндрей СГNo ratings yet
- Brain Storming: Making The Impossible PossibleDocument24 pagesBrain Storming: Making The Impossible Possibleneha3ietmba2010No ratings yet
- What Is Brainstorming?Document2 pagesWhat Is Brainstorming?Yasmin khanNo ratings yet
- Conducting A Brainstorming Session ChecklistDocument4 pagesConducting A Brainstorming Session ChecklistNilesh KurleNo ratings yet
- Brainstorming Process PDFDocument2 pagesBrainstorming Process PDFrajiNo ratings yet
- Brainstorm - 8 RulesDocument6 pagesBrainstorm - 8 RulesAbhilash Lodhi RajpootNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document26 pagesWeek 4FarisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: The Requirements Workshop: Group 2: Andrew DennerDocument51 pagesChapter 11: The Requirements Workshop: Group 2: Andrew DennerAndrew DennerNo ratings yet
- Brainstorming TechniquesDocument4 pagesBrainstorming TechniquesImran Maqsood0% (1)
- Ir. Siow Yun Tong: Miem, PengDocument59 pagesIr. Siow Yun Tong: Miem, PengShafiq MahadiNo ratings yet
- Pod HandlerDocument53 pagesPod HandlerLean Ashly MacarubboNo ratings yet
- Brainstorming 2Document19 pagesBrainstorming 2Fol FightNo ratings yet
- Design Thinking 2324 5Document35 pagesDesign Thinking 2324 5Diogo MadalenoNo ratings yet
- 5 Techniques To Conduct A Successful Ideation ProcessDocument14 pages5 Techniques To Conduct A Successful Ideation ProcessJignesh RayNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving - Brainwriting Is Brainstorming On SteroidsDocument3 pagesProblem Solving - Brainwriting Is Brainstorming On SteroidsathanasiusNo ratings yet
- 01 Prepare For Brainstorming SuccessDocument7 pages01 Prepare For Brainstorming SuccessKaka DNo ratings yet
- Guide To Brainstorming: Islamic University of MadinahDocument13 pagesGuide To Brainstorming: Islamic University of MadinahAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- What Is BrainstormingDocument3 pagesWhat Is BrainstormingMary MillareNo ratings yet
- Productive Brainstorming - Just Pay Attention To Your Surroundings - AttentionableDocument10 pagesProductive Brainstorming - Just Pay Attention To Your Surroundings - AttentionableramkryNo ratings yet
- Brainstorming Techniques ExplainedDocument13 pagesBrainstorming Techniques ExplainedAyaz KaziNo ratings yet
- History and Use of BrainstormingDocument14 pagesHistory and Use of BrainstormingNanda GiftaninaNo ratings yet
- Idea Generation TechniquesDocument5 pagesIdea Generation TechniquesmansoormbaNo ratings yet
- Brain Storming TechniquesDocument25 pagesBrain Storming TechniquesMostafa Gamal El DeepNo ratings yet
- Brainstorming: Amritpal SinghDocument17 pagesBrainstorming: Amritpal SinghAnand RathourNo ratings yet
- Brain Storming Assi 1Document2 pagesBrain Storming Assi 13126328310No ratings yet
- BrainstormingDocument9 pagesBrainstormingibrahimNo ratings yet
- Brainstorming!Document11 pagesBrainstorming!111111No ratings yet
- Creative ThinkingDocument30 pagesCreative Thinkingmonirba48No ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 3aDocument4 pagesASSIGNMENT 3a68 DEEPAK GAUND100% (1)
- 10 Tips For Effective Creative Brainstorming - Design ShackDocument8 pages10 Tips For Effective Creative Brainstorming - Design ShackraajmrkNo ratings yet
- BrainstormingDocument194 pagesBrainstormingArvind Ranganathan100% (3)
- Creative Thinking: Techniques and Tools For SuccessDocument7 pagesCreative Thinking: Techniques and Tools For SuccesslaliipalmeirasNo ratings yet
- Fourth Session September 2016Document30 pagesFourth Session September 2016Chesya NichitaNo ratings yet
- Desgining AlternativesDocument38 pagesDesgining AlternativesAnishNo ratings yet
- BrainstormingDocument18 pagesBrainstormingAkshay MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Creativity & Problem SolvingDocument26 pagesCreativity & Problem Solvingprashantk_106No ratings yet
- Brainstorming: The Step by Step Guide ToDocument11 pagesBrainstorming: The Step by Step Guide TomanishphyNo ratings yet
- Pb4mat Umc05 P7-8Document38 pagesPb4mat Umc05 P7-8Metta Niyamacitta ExeliemNo ratings yet
- 4.2 What Is BrainstormingDocument4 pages4.2 What Is BrainstormingD.K.Sreekantha NMAMIT - Computer Science & EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Brainstorming Rules & Steps for Generating Creative IdeasDocument20 pagesBrainstorming Rules & Steps for Generating Creative IdeasNithin ThalibNo ratings yet
- Quality Tools and Techniques-Brainstorming - Fall20Document14 pagesQuality Tools and Techniques-Brainstorming - Fall20Ashik ShariarNo ratings yet
- BrainstormingDocument17 pagesBrainstormingNurain XuNo ratings yet
- CE 351 Part 3 Chapter 4 B Pipe Network PDFDocument31 pagesCE 351 Part 3 Chapter 4 B Pipe Network PDFAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- CE 351 Part 5 Chapter 7 Groundwater PDFDocument75 pagesCE 351 Part 5 Chapter 7 Groundwater PDFAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- CE 351 Part 1 CH 3 PDFDocument108 pagesCE 351 Part 1 CH 3 PDFAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Jordan University of Science and Technology Department of Civil EngineeringDocument1 pageJordan University of Science and Technology Department of Civil EngineeringAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Jordan University of Science and Technology Department of Civil EngineeringDocument1 pageJordan University of Science and Technology Department of Civil EngineeringAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Exp09 - California Bearing Ratio (CBR) and Stripping TestDocument6 pagesExp09 - California Bearing Ratio (CBR) and Stripping TestAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Exp11 - CKE MS-2 and Dynamic CreepDocument4 pagesExp11 - CKE MS-2 and Dynamic CreepAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Stress - Penetration RelationshipDocument4 pagesStress - Penetration RelationshipAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document5 pagesBook 1Ali M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Cover Page 05 and 06 and 07Document1 pageCover Page 05 and 06 and 07Ali M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Exp05 and 06 and 07 - Marshall Test MethodDocument12 pagesExp05 and 06 and 07 - Marshall Test MethodAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Vs. Unit Weight vs. %AV vs. Stability vs. Flow vs. VFADocument3 pagesVs. Unit Weight vs. %AV vs. Stability vs. Flow vs. VFAAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Exp05 and 06 and 07 - Marshall Test Method (Tables)Document1 pageExp05 and 06 and 07 - Marshall Test Method (Tables)Ali M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Exp08 - Extraction and ViscosityDocument6 pagesExp08 - Extraction and ViscosityAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
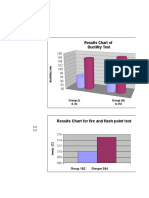
- Results Chart of Ductility TestDocument2 pagesResults Chart of Ductility TestAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Jordan University of Science and Technology Department of Civil EngineeringDocument1 pageJordan University of Science and Technology Department of Civil EngineeringAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Extraction & ViscosityDocument6 pagesExtraction & ViscosityAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Stripping OnlyDocument7 pagesStripping OnlyAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Solu BilityDocument7 pagesSolu BilityAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Skynet3 1Document8 pagesSkynet3 1Ali M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Creep & UTMDocument4 pagesCreep & UTMAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Summary:: Stability: Is The Maximum Load Resistance in Newton (LB.) That TheDocument10 pagesSummary:: Stability: Is The Maximum Load Resistance in Newton (LB.) That TheAli M. Chehadeh100% (1)
- Indirect Tensile & UTMDocument2 pagesIndirect Tensile & UTMAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Student Name & Number: Wael Asim AlarajiDocument1 pageStudent Name & Number: Wael Asim AlarajiAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- PenetrationDocument6 pagesPenetrationAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- ExtractionDocument5 pagesExtractionAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Ductilityand Flash and FireDocument4 pagesDuctilityand Flash and FireAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Stripping & CBRDocument8 pagesStripping & CBRAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Friction & British Pendulum 1Document6 pagesFriction & British Pendulum 1Ali M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Serial # 17 Evaluation Form: Salah JA ARADocument1 pageSerial # 17 Evaluation Form: Salah JA ARAAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Review Sheet Answer KeyDocument2 pagesUnit 6 Review Sheet Answer KeyMia RoaNo ratings yet
- Policy BriefDocument3 pagesPolicy BriefDAVID EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Role of NGOs before and during CovidDocument47 pagesRole of NGOs before and during CovidAnkush ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Rule Book Technical EventsDocument26 pagesRule Book Technical EventsGud GuyNo ratings yet
- 4 English Prototype Syllabi CompendiumDocument328 pages4 English Prototype Syllabi CompendiumBiblanias Rayel FinaNo ratings yet
- The 8 Models of CommunicationDocument4 pagesThe 8 Models of CommunicationEd Ali L. Magondacan100% (1)
- RPMS Template - T1-T3Document29 pagesRPMS Template - T1-T3Deslene CasugayNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Value of The Duckweed Species of The Genus Wolffia (Lemnaceae) As Human FoodDocument13 pagesNutritional Value of The Duckweed Species of The Genus Wolffia (Lemnaceae) As Human FoodSiriporn PansriNo ratings yet
- World History 1: Five Characteristics of CivilizationDocument3 pagesWorld History 1: Five Characteristics of CivilizationHenry BilanNo ratings yet
- Physics Ch3 Energy Resources NewDocument2 pagesPhysics Ch3 Energy Resources NewAnais AnnNo ratings yet
- Sci Worksheet W5 Act 1Document4 pagesSci Worksheet W5 Act 1Mae GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Building Learning Commitment - Perdalin-Project HopeDocument18 pagesBuilding Learning Commitment - Perdalin-Project Hopesusy kusumawardaniNo ratings yet
- Goniophotometer For Automotive and Signal Lamps 1950sDocument6 pagesGoniophotometer For Automotive and Signal Lamps 1950sLisun GroupNo ratings yet
- Reynold Equation and Hydrodynamic Thrust Bearing 0Document5 pagesReynold Equation and Hydrodynamic Thrust Bearing 0Kosgi LavanyaNo ratings yet
- SpectroscopieBasseResolution enDocument43 pagesSpectroscopieBasseResolution enMarco Aurelio MinozzoNo ratings yet
- Charlemagne's War MachineDocument46 pagesCharlemagne's War MachineHistoryRepeating100% (1)
- Urea-Formaldehyde Adhesive Resins: Anthony H. ConnerDocument8 pagesUrea-Formaldehyde Adhesive Resins: Anthony H. ConnerAditiya Muchsin SobariNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of Education That Is Learner CenteredDocument5 pagesPhilosophies of Education That Is Learner CenteredPrincess zamora100% (1)
- Differences Between Solids and FluidsDocument4 pagesDifferences Between Solids and FluidsgknindrasenanNo ratings yet
- Chemfile Mini-Guide To Problem Solving Chapter 14Document13 pagesChemfile Mini-Guide To Problem Solving Chapter 14MANDARAW100% (1)
- Finding Life in Space: British Scientists Plan New HuntDocument18 pagesFinding Life in Space: British Scientists Plan New HuntLê Thanh ThảoNo ratings yet
- Q4 - W1-SHS Humss-Diss-Module 1Document102 pagesQ4 - W1-SHS Humss-Diss-Module 1Russell AngelesNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Business Ethics, The Changing Environment, and Stakeholder ManagementDocument23 pagesChapter One: Business Ethics, The Changing Environment, and Stakeholder ManagementAbdullah MujahidNo ratings yet
- Sierra SeriesDocument292 pagesSierra SeriesHéctor VanzNo ratings yet
- B Som and FM Lab ManualDocument101 pagesB Som and FM Lab ManualGANESH GOMATHINo ratings yet
- GRAPHITE SAFETYDocument7 pagesGRAPHITE SAFETYakbar macheteNo ratings yet
- 1801-Article Text-7307-1-10-20220201Document10 pages1801-Article Text-7307-1-10-20220201LEO LESTERE TAO TAONo ratings yet
- FactorisingExercises132 PDFDocument4 pagesFactorisingExercises132 PDFCassandra LauNo ratings yet
- Operation of AutoclavesDocument7 pagesOperation of AutoclavesTawanda Precious SingiziNo ratings yet
- Engineering-Physics-Notes 3 U8 PDFDocument78 pagesEngineering-Physics-Notes 3 U8 PDFKarthik KumarNo ratings yet