Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pesit Hvac
Uploaded by
pdatscribd123Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pesit Hvac
Uploaded by
pdatscribd123Copyright:
Available Formats
PES Institute of Technology
Objective
Goal: To develop an automotive air-conditioning system
that is smaller and lighter than with conventional technology.
The Challenge: The system must be capable of
keeping a temperature of 22C inside a stationary black
vehicle with four occupants, with an outside temperature
of 40C. Also, the system must be an efficient heating
system, keeping an internal temperature of 15C with an
outside temperature of 0C.
H.V.A.C
H.V.A.C Heating, Ventilation and Air
Conditioning system
The HVAC regulates:
Room Temperature
Humidity
Air Quality
Air Flow
Refrigeration Cycle
4
1
2
3
Enthalpy kJ/kg
Vapour Compression Cycle
Design Parameters & Considerations
Heat Load on the HVAC = 5.287 kW
Cabin Relative Humidity = 40%
Evaporator Temperature = 4C
Refrigerant Used = R134a
Refrigeration Cycle : Vapour Compression
Cabin design cooling and heating requirements
Temperature and Humidity range
Placement of Vents and Ducts
Space considerations
Effect on car performance
Efficiency
Environmental Impact
Cycle Analysis & Heat Load
Assumptions:
Compression process is isentropic.
No pressure losses in piping.
Condenser temperature = 46C.
Evaporator Temperature = 4 C.
Refrigerant is not sub cooled.
Heat Load Calculations:
Heat due to opaque surfaces = 3598.2 W
Heat due to fenestration = 1229.66 W
Internal Loads ( human ) = 460 W
Total Load = 5.287 kW
Results
Evaporator Pressure = 3.38 bar
Condenser Pressure = 11.9 bar
Heat Load = 5.287 KW
Condenser Cooling Load= 6.308 KW
Compressor Work = 1.02 KW
Mass Flow Rate = 1.94 l/min
Selection Basis
Scroll Compressors
Compact design and High Volumetric Efficiency (
around 98% ).
Refrigerant R134a
Minimized environmental impact.
Plate-Fin Heat Exchanger-
Compact size, Higher heat transfer capability.
Simple design incorporated to minimize cost.
Heart of the system, belt driven pump that fastened to engine.
Responsible for compressing and transferring refrigerant.
Two interleaved scrolls with involute geometry.
One scroll fixed while the other orbits eccentrically to compress fluid
Advantage:
Very high volumetric efficiency (almost 98%)
Lesser Noise and lighter compared to rotary compressor.
Compressor
Weight 5.8 kg
Displacement 90 ml/ revolution
Maximum Speed 12000 rpm
Rated Voltage 12 V
Responsible for heat dissipation
The condenser is designed to radiate heat.
Located in front of the radiator
Require good air flow when system is in operation
Plate fin type heat exchanger with micro channels
used.
Very compact and better heat transfer capability.
Hot compressed refrigerant vapour cools at constant
pressure to liquid.
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient = 92 W/m
2
K
Area = 6.87 m
2
Condenser
Depending on the vehicle, the A/C system will either have a receiver dryer
or an accumulator.
Components contain a desiccant, chemical that attracts moisture.
Prevents formation of corrosive acids on mixture of water and acid.
Also act as temporary storage for refrigerant to prevent starving of
evaporator
Accumulator
Heat absorption component.
Used remove heat from the inside of vehicle.
Secondary benefit - dehumidification.
Unconditioned air passes through a filter before entering the evaporator.
Plate-fin evaporator with micro channels used.
Overall heat transfer coefficient = 98 W/m
2
K
Area calculated = 3.04 m
2
Fan Flow Rate = 90 l/s
Evaporator
Layout of Components
Looking Ahead
Finalize and validate results based on
inputs from other teams.
Improvise on the current design and form
a cost effective solution.
Documentation and reports.
Thank You !
You might also like
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Lesson Notes Lecture 14Document5 pagesLesson Notes Lecture 14Quantum SaudiNo ratings yet
- ReagentsDocument12 pagesReagentsKimscey Yvan DZ SulitNo ratings yet
- WL4000Document1 pageWL4000Laser PowerNo ratings yet
- Practical 3.1 Determining The Specific Heat CapacityDocument3 pagesPractical 3.1 Determining The Specific Heat CapacityiAlex11No ratings yet
- 2019 - High Levels of Polypharmacy in RheumatoidDocument7 pages2019 - High Levels of Polypharmacy in RheumatoidGustavo ResendeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5, Abdominal TraumaDocument41 pagesChapter 5, Abdominal TraumaRandy HarrisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Jun 2010 Mark Scheme Unit 3Document15 pagesChemistry Jun 2010 Mark Scheme Unit 3dylandonNo ratings yet
- Greek ArchitectureDocument16 pagesGreek ArchitectureXlyth RodriguezNo ratings yet
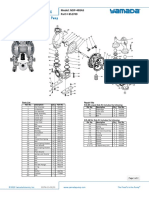
- Exploded View & Parts Listing Air Operated Double Diaphragm PumpDocument2 pagesExploded View & Parts Listing Air Operated Double Diaphragm PumpCarlos AvalosNo ratings yet
- South Valley University Faculty of Science Geology Department Dr. Mohamed Youssef AliDocument29 pagesSouth Valley University Faculty of Science Geology Department Dr. Mohamed Youssef AliHari Dante Cry100% (1)
- A Collection of Ideas For The Chemistry Classroom by Jeff HepburnDocument14 pagesA Collection of Ideas For The Chemistry Classroom by Jeff HepburnPaul SchumannNo ratings yet
- PositioningDocument2 pagesPositioningKishan AndureNo ratings yet
- Moldex Realty, Inc. (Linda Agustin) 2.0 (With Sound)Document111 pagesMoldex Realty, Inc. (Linda Agustin) 2.0 (With Sound)Arwin AgustinNo ratings yet
- Titan GelDocument6 pagesTitan GelVladi Salas100% (1)
- SFT PresentationDocument16 pagesSFT Presentationapna indiaNo ratings yet
- Osce05ans 110918053819 Phpapp01Document20 pagesOsce05ans 110918053819 Phpapp01masood alamNo ratings yet
- Nissan 720 L4-2.0-Z20 1983-86 Manual PDFDocument641 pagesNissan 720 L4-2.0-Z20 1983-86 Manual PDFEduardo Ariel JuarezNo ratings yet
- Veg Dum Biryani - Hyderabadi Veg Biryani Recipe - Hyderabadi Biryani - Hebbar's KitchenDocument2 pagesVeg Dum Biryani - Hyderabadi Veg Biryani Recipe - Hyderabadi Biryani - Hebbar's KitchenmusicalcarpetNo ratings yet
- The Gingerbread Man-1 EnglishareDocument40 pagesThe Gingerbread Man-1 EnglishareamayalibelulaNo ratings yet
- Foldable HelmetDocument16 pagesFoldable Helmetharsha kotewarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Course FileDocument81 pagesHydraulics Course FileSwarna LathaNo ratings yet
- English 3 Avicenna Graded Test 1Document11 pagesEnglish 3 Avicenna Graded Test 1Mohd FarisNo ratings yet
- Scalextric Arc One GuideDocument46 pagesScalextric Arc One GuidenotifyatpriNo ratings yet
- LINEAR INDUCTION MOTOR 6981660.ppsxDocument56 pagesLINEAR INDUCTION MOTOR 6981660.ppsxFalley FasterNo ratings yet
- The Latent Phase of LaborDocument8 pagesThe Latent Phase of LaborLoisana Meztli Figueroa PreciadoNo ratings yet
- Biasing Opamps Into Class ADocument11 pagesBiasing Opamps Into Class AsddfsdcascNo ratings yet
- List ToolingDocument10 pagesList Toolingyohanes adi saputroNo ratings yet
- Load Distribution Flow Chart For Bridge DesignDocument1 pageLoad Distribution Flow Chart For Bridge DesignBunkun15No ratings yet
- ForewordDocument96 pagesForewordkkcmNo ratings yet
- Case Study (Co2 Flooding)Document10 pagesCase Study (Co2 Flooding)Jessica KingNo ratings yet