Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diode Rectifiers
Uploaded by
AmineCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diode Rectifiers
Uploaded by
AmineCopyright:
Available Formats
1
MCT 4320
Power Electronics
Uncontrolled Rectifiers
2
Contents
Single-phase half-wave rectifiers,
Performance parameters,
Single-phase full-wave rectifiers,
Single-phase full-wave rectifier with RL
load,
Multiphase star rectifiers,
Three-phase bridge rectifiers,
Three-phase bridge rectifier with RL load.
3
Single-phase half-wave rectifiers
4
Performance parameters
Efficiency
Ripple factor
Form factor
Transformer utilization factor
Distortion factor
Harmonic factor
5
Performance parameters
2 2
dc rms ac
V V V =
ac dc
P P / = q
rectification effeciency
dc rms
V V FF / =
1 1
2
2
2
2 2
= =
= = FF
V
V
V
V V
V
V
RF
dc
rms
dc
dc rms
dc
ac
form factor
ripple factor
1
2
1
2
2
1
2
1
2
=
=
S
S
S
S S
i
I
I
I
I I
THD
1
2
1
2
2
1
2
1
2
=
=
S
S
S
S S
v
V
V
V
V V
THD
Faactor nt Displaceme Factor Distortion
I
I
I V
I V
I V
P
PF
S
S
S S
S S
S S
*
cos
cos
1
1 1 1
=
= = = |
|
Single-phase half-wave diode rectifier with resistive load.
}
= =
t
t
e e
t
0
sin
2
1
m
m dc
V
t d t V V
2
sin
2
1
0
2 2
m
m rms
V
t d t V V = =
}
t
e e
t
R
V
R
V
I
m dc
dc
t
= =
R
V
R
V
I
m rms
rms
2
= =
the load and diode currents
R
V
I I
m
D S
2
= =
Example 1: The rectifier shown in Fig.2.1 has a pure resistive load
of R Determine (a) The efficiency, (b) Form factor (c) Ripple factor
(d) Peak inverse voltage (PIV) of diode D1.
t
t
t
e e
t
t
m m
m dc
V V
t d t V V = = =
}
)) 0 cos( cos (
2
) sin(
2
1
0
R
V
R
V
I
m dc
dc
t
= =
2
) sin (
2
1
0
2 m
m rms
V
t V V = =
}
t
e
t
R
V
I
m
rms
2
=
% 53 . 40
2
*
2
*
*
*
= = = =
R
V V
R
V V
I V
I V
P
P
m m
m m
rms rms
dc dc
ac
dc
t t
q
57 . 1
2
2
= = = =
t
t
m
m
dc
rms
V
V
V
V
FF
211 . 1 1 57 . 1 1
2 2
= = = = FF
V
V
RF
dc
ac
(d) It is clear from Fig2.2 that the PIV is
.
m
V
Half Wave Diode Rectifier With R-L Load
Fig.2.3 Half Wave Diode Rectifier With
R-L Load
( ) ( )
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
|
e
| | e e
tan
sin sin ) (
t
m
e t
Z
V
t i
( ) ( ) 0 sin sin ) (
tan
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
|
|
| | | | e
Z
V
i
m
) cos 1 ( *
2
sin *
2
0
|
t
e e
t
|
= =
}
m m
dc
V
t d t
V
V
) 2 sin( 1 ( 5 . 0 *
2
) sin ( *
2
1
0
2
| |
t
e
t
|
+ = =
}
Vm
dwt t V V
m rms
Single-Phase Full-Wave Diode Rectifier
Center-Tap Diode Rectifier
t
e e
t
t
m
m dc
V
t d t V V
2
sin
1
0
= =
}
R
V
I
m
dc
t
2
=
( )
2
sin
1
0
2
m
m rms
V
t d t V V = =
}
t
e e
t
R
V
I
m
rms
2
=
PIV of each diode =
m
V 2
R
V
I I
m
D S
2
= =
Example 3. The rectifier in Fig.2.8 has a purely resistive load of R
Determine (a) The efficiency, (b) Form factor (c) Ripple factor (d)
TUF (e) Peak inverse voltage (PIV) of diode D1 and(f) Crest factor
of transformer secondary current.
% 05 . 81
2
*
2
2
*
2
*
*
= = = =
R
V V
R
V V
I V
I V
P
P
m m
m m
rms rms
dc dc
ac
dc
t t
q
11 . 1
2 2
2
2
= = = =
t
t
m
m
dc
rms
V
V
V
V
FF
483 . 0 1 11 . 1 1
2 2
= = = = FF
V
V
RF
dc
ac
The PIV is
m
V 2
Single-Phase Full Bridge Diode Rectifier With Resistive Load
Example 4 single-phase diode bridge rectfier has a purely resistive load of R=15
ohms and, VS=300 sin 314 t and unity transformer ratio. Determine (a) The
efficiency, (b) Form factor, (c) Ripple factor, (d) The peak inverse voltage, (PIV)
of each diode, , and, (e) Input power factor.
V
V
t d t V V
m
m dc
956 . 190
2
sin
1
0
= = =
}
t
e e
t
t
A
R
V
I
m
dc
7324 . 12
2
= =
t
( ) V
V
t d t V V
m
m rms
132 . 212
2
sin
1
2 / 1
0
2
= =
(
(
=
}
t
e e
t
% 06 . 81 = = =
rms rms
dc dc
ac
dc
I V
I V
P
P
q
11 . 1 = =
dc
rms
V
V
FF
482 . 0 1 1
2
2
2
2 2
= = =
= = FF
V
V
V
V V
V
V
RF
dc
rms
dc
dc rms
dc
ac
The PIV=300V
Input power factor =
1
cos Re
= =
S S
S S
I V
I V
Power Apperant
Power al |
Full Bridge Single-phase Diode Rectifier with DC Load Current
| |
| | ... .......... , 5 , 3 , 1
4
cos 0 cos
2
cos
2
sin *
2
0
0
= = =
= =
}
n for
n
I
n
n
I
t n
n
I
t d t n I b
o o
o
o n
t
t
t
e
t
e e
t
t
t
) .......... 9 sin
9
1
7 sin
7
1
5 sin
5
1
3 sin
3
1
(sin *
4
) ( + + + + + = t t t t t
I
t i
o
e e e e e
t
% 46
15
1
13
1
11
1
9
1
7
1
5
1
3
1
)) ( (
2 2 2 2 2 2 2
=
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
= t I THD
s
t 2
4
1
o
S
I
I =
% 34 . 48 1
4
2
1
2
4
1 )) ( (
2
2
2
1
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
t
t
o
o
S
S
s
I
I
I
I
t I THD
Example 5 solve Example 4 if the load is 30 A pure DC
From example 4 V
dc
= 190.986 V, V
rms
=212.132 V A I
dc
30 = and
rms
I = 30 A
% 90 = = =
rms rms
dc dc
ac
dc
I V
I V
P
P
q
11 . 1 = =
dc
rms
V
V
FF
482 . 0 1 1
2
2
2
2 2
= = =
= = FF
V
V
V
V V
V
V
RF
dc
rms
dc
dc rms
dc
ac
The PIV=V
m
=300V
A
I
I
o
S
01 . 27
2
30 * 4
2
4
1
= = =
t t
Input Power factor=
=
Power Apperant
Power al Re
Lag
I
I
I V
I V
S
S
S S
S S
9 . 0 1 *
30
01 . 27 cos * cos *
1 1
= = =
| |
Effect Of LS On Current Commutation Of Single-Phase Diode Bridge Rectifier.
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
m
o s
V
I L
u
e 2
1 cos
1
o S
o S
rd
I L f
I L
V 4
2
4
=
=
t
e
o s
m
rd
ce induc source without
dc
actual
dc
I fL
V
V V V 4
2
tan
= =
t
(
=
3 2
2
2
u I
I
o
s
t
t
2
sin *
2
8
1
u
u
I
I
o
S
t
=
( )
(
=
3 2
sin 2
u
u
u
pf
t
t
Example 6 Single phase diode bridge rectifier connected to 11 kV, 50 Hz, source
inductance Ls=5mH supply to feed 200 A pure DC load, find: (i) Average
DC output voltage, (ii) Power factor. And (iii) Determine the THD of
the utility line current.
V V
m
15556 2 * 11000 = =
V V
actual
dc
9703 200 * 005 . 0 * 50 * 4
15556 * 2
= =
t
. 285 . 0
15556
200 * 005 . 0 * 50 * * 2 * 2
1 cos
2
1 cos
1 1
rad
V
I L
u
m
o s
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
t e
( ) ( )
917 . 0
3
285 .
2
285 . 0
285 . 0 sin * 2
3 2
sin * 2
2
cos *
1
=
(
=
(
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
t
t
t
t
u
u
u u
I
I
pf
S
S
A
u I
I
o
S
85 . 193
3
285 . 0
2
200 * 2
3 2
2
2 2
=
(
=
(
=
t
t
t
t
A
u
u
I
I
o
S
46 . 179
2
285 . 0
sin *
285 . 0 * 2
200 * 8
2
sin *
2
8
1
=
|
.
|
\
|
= =
t t
% 84 . 40 1
46 . 179
85 . 193
1
2
2
1
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
S
S
i
I
I
THD
Three-Phase Half Wave Rectifier
m
m
m dc
V
V
t d t V V 827 . 0
2
3 3
sin
2
3
6 / 5
6 /
= = =
}
t
e e
t
t
t
R
V
R
V
I
m m
dc
* 827 . 0
* * 2
3 3
= =
t
( )
m m m rms
V V t d t V V 8407 . 0
8
3 * 3
2
1
sin
2
3
6 / 5
6 /
2
= + = =
}
t
e e
t
t
t
R
V
I
m
rms
8407 . 0
=
R
V
R
V
I I
m m
S r
4854 . 0
3
08407
= = =
ThePIV of the diodes is
m LL
V V 3 2 =
Example 7 The rectifier in Fig.2.21 is operated from 460 V
50 Hz supply at secondary side and the load O resistance is
R=20. If the source inductance is negligible, determine (a)
Rectification efficiency, (b) Form factor (c) Ripple factor (d)
Peak inverse voltage (PIV) of each diode.
V V V V
m S
59 . 375 2 * 58 . 265 , 58 . 265
3
460
= = = =
m
m
dc
V
V
V 827 . 0
2
3 3
= =
t R
V
R
V
I
m m
dc
0827
2
3 3
= =
t
m rms
V V 8407 . 0 =
R
V
I
m
rms
8407 . 0
=
% 767 . 96 = = =
rms rms
dc dc
ac
dc
I V
I V
P
P
q
% 657 . 101 = =
dc
rms
V
V
FF
% 28 . 18 1 1
2
2
2
2 2
= = =
= = FF
V
V
V
V V
V
V
RF
dc
rms
dc
dc rms
dc
ac
The PIV=
3
V
m
=650.54V
Three-Phase Half Wave Rectifier With DC Load Current and zero source
induct
N
e
w
a
x
i
s
3 2
1
3 /
3 /
0
o
o
I
t d I a
}
= =
t
t
e
t
| |
harmonics treplean all for
n for
n
I
n for
n
I
t n
n
I
dwt t n I a
o
o
o
o n
0
17 , 16 , 11 , 10 , 5 , 4 3 *
,.... 14 , 13 , 8 , 7 , 2 , 1 3 *
sin cos *
1
3 /
3 /
3 /
3 /
=
= =
= =
= =
}
t
t
e
t
e
t
t
t
t
t
|
.
|
\
|
+ + + + = ... 8 sin
8
1
7 sin
7
1
5 sin
5
1
4 sin
4
1
2 sin
2
1
sin
3
3
) ( t t t t t t
I I
t I
O O
s
e e e e e e
t
% 24 . 109 0924 . 1 1
9
* 2
1
2
3
3 /
1 )) ( (
2
2
2
1
= = =
|
|
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
t
t
O
o
S
S
s
I
I
I
I
t I THD
Example 8 Solve example 7 if the load current is 100 A pure DC
V V
V
V
m
m
dc
613 . 310 827 . 0
2
3 3
= = =
t
A I
dc
100 =
V V V
m rms
759 . 315 8407 . 0 = =
A I
rms
100 =
% 37 . 98
100 * 759 . 315
100 * 613 . 310
= = = =
rms rms
dc dc
ac
dc
I V
I V
P
P
q
% 657 . 101 = =
dc
rms
V
V
FF
% 28 . 18 1 1
2
2
2
2 2
= = =
= = FF
V
V
V
V V
V
V
RF
dc
rms
dc
dc rms
dc
ac
The PIV=
3
V
m
=650.54V
Three-Phase Full Wave Rectifier With Resistive Load
1
3
5
4 6 2
b
c
I
L
V
L
I
s
I
p
a
LL m
LL m
m dc
V V
V V
t d t V V 3505 . 1 654 . 1
2 3 3 3
sin 3
3
3 / 2
3 /
= = = = =
}
t t
e e
t
t
t
R
V
R
V
R
V
R
V
I
LL LL m m
dc
3505 . 1 2 3 654 . 1 3 3
= = = =
t t
( )
LL m m m rms
V V V t d t V V 3516 . 1 6554 . 1
4
3 * 9
2
3
sin 3
3
3 / 2
3 /
2
= = + = =
}
t
e e
t
t
t
R
V
I
m
rms
6554 . 1
=
R
V
R
V
I
m m
r
9667 . 0
3
6554 . 1
= =
R
V
I
m
S
2 9667 . 0 =
Example 10 The rectifier shown in Fig.2.30 is operated from 460 V
50 Hz supply and the load resistance is R=20ohms. If the source
inductance is negligible, determine (a) The efficiency, (b) Form
factor (c) Ripple factor (d) Peak inverse voltage (PIV) of each diode
.
V V
V
V
m
m
dc
226 . 621 654 . 1
3 3
= = =
t
A
R
V
R
V
I
m m
dc
0613 . 31
654 . 1 3 3
= = =
t
V V V V
m m rms
752 . 621 6554 . 1
4
3 * 9
2
3
= = + =
t
A
R
V
I
m
rms
0876 . 31
6554 . 1
= =
% 83 . 99 = = =
rms rms
dc dc
ac
dc
I V
I V
P
P
q
% 08 . 100 = =
dc
rms
V
V
FF
% 4 1 1
2
2
2
2 2
= = =
= = FF
V
V
V
V V
V
V
RF
dc
rms
dc
dc rms
dc
ac
The PIV=
3
V
m
=650.54V
Three-Phase Full Wave Rectifier With DC Load Current
| |
.... ,......... 15 , 14 , 12 , 10 , 9 , 8 , 6 , 4 , 3 , 2 , 0
..... ),........ 3 (
13
2
), 3 (
11
2
), 3 (
7
2
), 3 (
5
2
, 3
2
cos
2
sin *
2
13 11 7 5 1
6 / 5
6 /
6 / 5
6 /
= =
= = = = =
= =
}
n for b
I
b
I
b
I
b
I
b
I
b
t n
n
I
t d t n I b
n
o o o o o
o
o n
t t t t t
e
t
e e
t
t
t
t
t
|
.
|
\
|
+ + = t t t t v t
I
t I
o
s
e e e e e
t
13 sin
13
1
11 sin
11
1
7 sin
7
1
5 sin
5
1
sin
3 2
) (
% 31
25
1
23
1
19
1
17
1
13
1
11
1
7
1
5
1
)) ( (
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
=
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
= t I THD
s
o S
I I
3
2
=
o S
I I
t
3 * 2
1
=
% 01 . 31 1
/ 3 * 2
3 / 2
1 )) ( (
2
2
1
= =
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
t
S
S
s
I
I
t I THD
Power Factor =
S
S
S
S
I
I
I
I
1 1
) 0 cos( * =
(
=
LL
o S
V
I L
u
e 2
1 cos
1
o
o
rd
fLI
LI
V 6
2
6
= =
t
e
o LL rd
ce induc source without
dc
actual
dc
fLI V V V V 6 35 . 1
tan
= =
(
=
6 3
2
2
u I
I
o
S
t
t
|
.
|
\
|
=
2
sin
6 2
1
u
u
I
I
o
S
t
( )
(
=
|
.
|
\
|
(
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
6 3
sin * 3
2
cos
6 3
2
2
sin
6 2
2
cos
2
1
u
u
u u
u I
u
u
I
u
I
I
pf
o
o
S
S
t
t
t
t
t
Example 11 Three phase diode bridge rectifier connected to tree phase
33kV, 50 Hz supply has 8 mH source inductance to feed 300A pure DC
load current Find;
Commutation time and commutation angle.
DC output voltage.
Power factor.
Total harmonic distortion of line current.
o
rad u 61 . 14 . 2549 . 0 = =
(
=
LL
o S
V
I L
u
e 2
1 cos
1
d LL rd
ce induc source without
dc
actual
dc
fLI V V V V 6 35 . 1
tan
= =
V V
dcactual
43830 300 * 008 . * 50 * 6 33000 * 35 . 1 =
=
( ) ( )
9644 . 0
6
2549 . 0
3
* 2549 . 0
2549 . 0 sin 3
6 3
sin * 3
=
(
=
(
=
t
t
t
t
u
u
u
pf
A
u I
I
d
s
929 . 239
6
2549 . 0
3
*
300 * 2
6 3
2
2 2
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
(
=
t
t
t
t
A
u
u
I
I
o
S
28 . 233
2
2549 . 0
sin *
2 * 2549 . 0 *
300 * 3 4
3 2 *
2
sin
2
3 4
1
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
t t
9644 . 0
2
2549 . 0
cos *
929 . 239
28 . 233
2
cos *
1
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
u
I
I
pf
s
S
% 05 . 24 1
28 . 233
929 . 239
1
2
2
1
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
S
S
i
I
I
THD
46
With R-L Load
Without Freewheeling diode
47
RL load
With freewheeling diode
Commutation of Diode D1
(at et=t) the current from
D1 is transferred to Dm.
48
Half wave rectifier: RC Load
49
Role of the Capacitor
C is initially uncharged. Switch is turned on at wt=0.
Diode becomes forward biased as the source become
positive.
When diode is ON the output is the same as source
voltage. C charges until Vm.
After et= t/2, C discharges into load R.
The source becomes less than the output Voltage.
The output voltage decays exponentially.
50
Full wave rectifier
Center-tapped (CT) rectifier
requires center-tap
transformer and 2 diodes.
51
Bridge rectifier
52
With RL load
If the load current is continuous
53
With RL load
If the load current is discontinuous
54
Multiphase Rectifier
A multi-phase rectifier increases the dc component and
lowers the harmonic components.
55
Output of Multiphase Rectifier
56
Three Phase Star rectifier
57
Three Phase Star rectifier
58
3 phase Bridge rectifier
Sequence of conduction:
D1-D2, D3-D2, D3-D4, D5-D4, D5-D6
59
3 phase Bridge rectifier
Sequence of conduction:
D1-D2, D3-D2, D3-D4, D5-D4, D5-D6
60
3 phase Bridge rectifier
Wave shape with R load
61
Explanation using phase voltage
62
Three-phase waveforms
Top group: diode with its anode at the highest
potential will conduct. The other two will be reversed.
Bottom group: diode with the its cathode at the lowest
potential will conduct. The other two will be reversed.
For example, if D1 (of the top group) conducts, v
p
(+)
is connected to v
an
. If D6 (of the bottom group)
conducts, v
n
(-) connects to v
bn
. All other diodes are
off.
The resulting output waveform is given as: v
o
=v
p
-v
n
For peak of the output voltage is equal to the peak of
the line to line voltage v
ab
.
63
Comparisons of Diode Rectifiers
1- phase
Half wave
1- phase
Full wave
3- phase
star
3- phase
bridge
efficiency 40.5% 81% 96.77% 99.83%
RF 121% 48.2% 18.24% 4%
TUF 28.6% 57.32% 66.43% 0.9542
PIV Vm 2Vm/ Vm \3Vm \3Vm
FF 157% 111% 101.65% 100.08%
64
Summary
An inductive load can make the load current
continuous.
With highly inductive load the input current of
a rectifier becomes an ac square wave.
With high value of capacitance the output
voltage remains almost constant.
##### ##### ##### ##### ##### #####
Exercise: Example
You might also like
- Uncontrolled RectifiersDocument43 pagesUncontrolled RectifiersAbhijeet Singh KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document33 pagesLecture 7Mohamad SyazwanNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Tugas FajarDocument11 pagesTugas FajarFajar Alya RahmanNo ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Eq SheetDocument1 pageEq Sheetuama87No ratings yet
- PSIM Tutorial 2Document12 pagesPSIM Tutorial 2Milena Novato SilvaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- JNTUK EDC-Unit-IV Notes PDFDocument32 pagesJNTUK EDC-Unit-IV Notes PDFkarthiha12No ratings yet
- Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsDocument18 pagesWorkbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsarunNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- Multi Stage Amplifier (L 1)Document21 pagesMulti Stage Amplifier (L 1)Asheque IqbalNo ratings yet
- Class Test - 2016: Power ElectronicsDocument9 pagesClass Test - 2016: Power ElectronicsarunNo ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Class-A Source Follower With External Resistor Output StageDocument23 pagesClass-A Source Follower With External Resistor Output StagelaksologinNo ratings yet
- Ee 435 2Document43 pagesEe 435 2EdamEdamNo ratings yet
- Power Electronic Module - Chapter 2Document43 pagesPower Electronic Module - Chapter 2jayxcellNo ratings yet
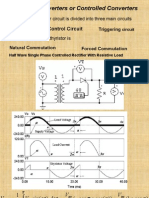
- Thyristor Converters or Controlled Converters: Control CircuitDocument62 pagesThyristor Converters or Controlled Converters: Control CircuitDilip TheLipNo ratings yet
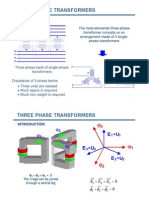
- Three Phase TransformersDocument26 pagesThree Phase TransformersElardZP100% (1)
- "Supply Independent" Current Source: Notice That This Circuit Is A Temperature Detector!Document14 pages"Supply Independent" Current Source: Notice That This Circuit Is A Temperature Detector!Bruno SilvaNo ratings yet
- Saturation CT Because of DC OffsetDocument20 pagesSaturation CT Because of DC OffsetAngga Wira PramanaNo ratings yet
- CH4Document55 pagesCH4Mohamad SyazwanNo ratings yet
- Switch Mode Power Supplies: SPICE Simulations and Practical DesignsDocument9 pagesSwitch Mode Power Supplies: SPICE Simulations and Practical Designscms124dNo ratings yet
- HNEE 105 Electrical and Electronic PrincipleDocument31 pagesHNEE 105 Electrical and Electronic PrincipleShaikh FarhaNo ratings yet
- Formula BookletDocument11 pagesFormula BookletAzfar UmarNo ratings yet
- Class Test - 2016: Electrical EngineeringDocument6 pagesClass Test - 2016: Electrical EngineeringarunNo ratings yet
- Ee366 Chap 2 5Document25 pagesEe366 Chap 2 5Michael Adu-boahenNo ratings yet
- Rahman Tutorial 1Document5 pagesRahman Tutorial 1John Wanyoike MakauNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase Half Wave ConverterDocument3 pages3-Phase Half Wave ConverterAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- Alternative Current Theory - EDocument12 pagesAlternative Current Theory - Ethinkiit100% (3)
- Half-Wave RL Circuit With A Free-Wheeling DiodeDocument7 pagesHalf-Wave RL Circuit With A Free-Wheeling Diodehamza abdo mohamoud100% (2)
- Unit 3Document37 pagesUnit 3h2o_kazzike50% (2)
- Formula ShhetDocument10 pagesFormula Shhetandres2chNo ratings yet
- Power in AC Circuit Lab ReportDocument8 pagesPower in AC Circuit Lab ReportJEJUNG67% (3)
- Lec2 Frequency ResponseDocument79 pagesLec2 Frequency ResponseAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- ZZ - Electricity & MagnetismDocument137 pagesZZ - Electricity & Magnetismvenkyrocker777750% (4)
- Single-Machine Infinite Bus SystemDocument18 pagesSingle-Machine Infinite Bus SystemMuhammad FajraNo ratings yet
- Full-Wave Controlled Rectifier RL Load (Continuous Mode)Document6 pagesFull-Wave Controlled Rectifier RL Load (Continuous Mode)hamza abdo mohamoud100% (1)
- 2.-Electrotecnia Unit2 PDFDocument12 pages2.-Electrotecnia Unit2 PDFJayaraj LathaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam SEE3433 Mei (Solution)Document9 pagesFinal Exam SEE3433 Mei (Solution)Fizah Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument37 pagesRectifierMahendra Mandalapu MNo ratings yet
- Formula Rio 2014Document2 pagesFormula Rio 2014Alberto García WatsonNo ratings yet
- Basic 3 PhaseDocument17 pagesBasic 3 PhaseUnknownNo ratings yet
- Lecture13 BJT Transistor Circuit AnalysisDocument24 pagesLecture13 BJT Transistor Circuit Analysisazur33nNo ratings yet
- Stw57N65M5-4: N-Channel 650 V, 0.056 Typ., 42 A, Mdmesh™ V Power Mosfet in A To247-4 PackageDocument14 pagesStw57N65M5-4: N-Channel 650 V, 0.056 Typ., 42 A, Mdmesh™ V Power Mosfet in A To247-4 PackageCristiano BruschiniNo ratings yet
- ET1006 1112S2Exam Formulae SheetsDocument4 pagesET1006 1112S2Exam Formulae SheetstestniaNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering Midterm Test Answer: Subject Code: Course Title: Date: Time AllowedDocument8 pagesCollege of Engineering Midterm Test Answer: Subject Code: Course Title: Date: Time AllowedMohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- EE42 100 Wb-Lecture18 080513-FDocument44 pagesEE42 100 Wb-Lecture18 080513-FozanistzNo ratings yet
- Esercitazione amp-BJT - PpsDocument22 pagesEsercitazione amp-BJT - PpsLuckyLuke981No ratings yet
- Ee366 Chap 5 2Document28 pagesEe366 Chap 5 2Michael Adu-boahenNo ratings yet
- Class E Resonant InverterDocument28 pagesClass E Resonant InverterSenthil Kumar0% (1)
- Extra AC-DCDocument34 pagesExtra AC-DCAhmed AbuNasserNo ratings yet
- Exercicios 8Document3 pagesExercicios 8douglas.julianiNo ratings yet
- 03 AC MetersDocument18 pages03 AC MetersKenneth KuokNo ratings yet
- Aula Conversores CC-CC BásicosDocument44 pagesAula Conversores CC-CC BásicosVirgílio TávoraNo ratings yet
- Harvindar & Masyitah (Revised) Research Paper SampleDocument15 pagesHarvindar & Masyitah (Revised) Research Paper SampleAmineNo ratings yet
- Tae Kwan Doo AssignmentDocument14 pagesTae Kwan Doo AssignmentAmineNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Logic ScriptDocument28 pagesFuzzy Logic ScriptDalia MuraddNo ratings yet
- Trig Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesTrig Cheat Sheetapi-284574585No ratings yet
- Towards A Brain-Computer Interface Based Control For Next Generation Electric WheelchairsDocument5 pagesTowards A Brain-Computer Interface Based Control For Next Generation Electric WheelchairsAmineNo ratings yet
- 0809 Sem 2Document21 pages0809 Sem 2AmineNo ratings yet
- PSV PDFDocument3 pagesPSV PDFKasnowo DiponegoroNo ratings yet
- Informacion Motor KomatsuDocument8 pagesInformacion Motor KomatsuKike HernandezNo ratings yet
- 04443720AA Masterpact NW User ManualDocument1 page04443720AA Masterpact NW User ManualdaywalkeryNo ratings yet
- Car Engine PartsDocument20 pagesCar Engine PartsHealth Club100% (2)
- Server RakitanDocument22 pagesServer RakitanadebsbNo ratings yet
- HPR-2Document12 pagesHPR-2v2nssysy6fNo ratings yet
- Standard Pilot, Steel Seat, Pilot-To-Open Check Valve Ckeb: 30 GPM (120 L/min.)Document4 pagesStandard Pilot, Steel Seat, Pilot-To-Open Check Valve Ckeb: 30 GPM (120 L/min.)Alex RamirezNo ratings yet
- VP395299 - NA-WPS-00 100912.12 Nabiac Borefield Stage 2B Pump Stations Pre Tender Meeting Minutes With Q&ADocument7 pagesVP395299 - NA-WPS-00 100912.12 Nabiac Borefield Stage 2B Pump Stations Pre Tender Meeting Minutes With Q&AAshNo ratings yet
- 22m Boom - Circuit + Bom-Vr-0628 (1) - 1Document7 pages22m Boom - Circuit + Bom-Vr-0628 (1) - 1MuthuNo ratings yet
- E3301 p5k3 Deluxe v3Document176 pagesE3301 p5k3 Deluxe v3Daniel AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Paper Manufacturing 3Document2 pagesPaper Manufacturing 3Masroor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Act 1&2Document10 pagesAct 1&2John Neil Bibera100% (4)
- A SectionDocument102 pagesA Sectionmarc5278No ratings yet
- Cookworks Mini OvenDocument9 pagesCookworks Mini Ovensum0n3No ratings yet
- Babylock BL18 SMDocument22 pagesBabylock BL18 SMDavid GarnerNo ratings yet
- Digger Cal UTSDocument61 pagesDigger Cal UTSConnor TabainNo ratings yet
- DHW - LC Series Factsheet - AUS NZ NOV 2019 - DHW00025 PDFDocument2 pagesDHW - LC Series Factsheet - AUS NZ NOV 2019 - DHW00025 PDFjustforaspinNo ratings yet
- 2011 Nissan Versa®: ShiftDocument3 pages2011 Nissan Versa®: ShiftYudyChen100% (1)
- AER BAER CatalogDocument20 pagesAER BAER Catalogadis.machadoNo ratings yet
- ACL TOP 500 Service Manual Rev 01Document764 pagesACL TOP 500 Service Manual Rev 01suny8781No ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1ngokhanhtNo ratings yet
- Ryobi Hand Planer Model No. HPL51 Repair SheetDocument4 pagesRyobi Hand Planer Model No. HPL51 Repair SheetJL AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Outdoor Box Isolated AP300 AP400 2012-03Document29 pagesOutdoor Box Isolated AP300 AP400 2012-03Alfian LinuxNo ratings yet
- PH TransmitterDocument23 pagesPH TransmitterDarwin LealNo ratings yet
- KONICAMINOLTA 7145 7222 7228 7235 Service Manual PagesDocument8 pagesKONICAMINOLTA 7145 7222 7228 7235 Service Manual PagesKanchanNo ratings yet
- Analysis Tequiniques For Racecar Data AcquisitionDocument191 pagesAnalysis Tequiniques For Racecar Data AcquisitionAnderson Luiz Dias100% (2)
- 78d33 DatasheetDocument4 pages78d33 DatasheetJorge AdrianNo ratings yet
- 7 - V-0801 P-0801 ABC HOT OIL SYSTEM PUMPS - Rev 0Cx PDFDocument1 page7 - V-0801 P-0801 ABC HOT OIL SYSTEM PUMPS - Rev 0Cx PDFMariaNo ratings yet
- DSP2 Manual PDFDocument147 pagesDSP2 Manual PDFEcaterina Irimia100% (2)
- EPB With Preload: Ep B 20 05 - 6 QZ RR G0 +650L C3Document2 pagesEPB With Preload: Ep B 20 05 - 6 QZ RR G0 +650L C3Radinal Fernandez SimanjuntakNo ratings yet