Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bomba Dagua
Uploaded by
Fernando Ferreira De AlmeidaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bomba Dagua
Uploaded by
Fernando Ferreira De AlmeidaCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGINEERING LESSON
GUIDE 4
PUMPS, VALVES, AND FANS
VALVES
TYPES OF VALVES
Globe valves - common type of stop
valve
the disk seats on the seating ring
commonly used in, steam, air, water, and
oil lines
also used as throttle valves
TYPES OF VALVES
Gate valve - used for straight line
flow and when minimum flow
restriction are needed
not used for throttling
rising stem or nonrising stem
steam systems have flexible gates
TYPES OF VALVES
Butterfly valve - light weight,
relatively small and quick-acting
has a body, resilient seat, butterfly disk, a
stem, packing, a notched position plate,
and a handle
very versatile - can be used for fresh water,
salt water, JP-5, lube-oil, and chill water
systems
Relief
Valve
VALVE OPERATING
DEVICES
Manual
Hydraulic
Motor (electric or air operated)
Solenoid
PUMPS
PUMP COMPONENTS
Drive
Steam, electric, or gear
Pump Shaft
Impeller or Piston
Casing
PUMP TYPES
CENTRIFUGAL
Single Stage
Multi-staged centrifugal pumps
POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT
Reciprocating
Rotary Gear
Screw
Moving vane
JET PUMP
Eductor
Ejector
POSITIVE
DISPLACEMENT PUMP
Fixed Volume
Volumetric Flow rate is proportional to
speed
A relief valve will always be on the
discharge end of the pump
E
X
A
M
P
L
E
S
PRESSURE HEAD
( Hp = ft lbf/ lbm)
CAPACI TY
( V= GPM)
N
1 N
2
Actual
I deal
Reciprocating Pump
Characteristic Curve
NON-POSITIVE
DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
BERNOULLIS THEOREM
Z
1
+ P
1
/D + 1/2(V
1
2
/g) =Z
2
+P
2
/D + 1/2(V
2
2
/g)
+ g
c
/g(wk) + H
L
Where:
Z : Elevation (ft)
P : Pressure (lbs/ft
2
)
D : Density (lb/ft
3
)
V : Velocity (ft/sec)
g : acceleration
(32.2 ft/sec
2
)
wk: work (ft-lbs)
H
L
: Head Loss
= f(L/D)(V
2
/2Zg)
where
f : friction factor
L: Length
D: Diameter
BERNOULLIS PRINCIPLE
Basically: as the velocity (speed) of a
fluid increases, its pressure decreases,
and visa versa
PUMPS
Net Positive Suction Head: that
pressure required at the suction of a
pump to prevent cavitation.
cavitation: the formation of bubbles due to
area where P < P
SAT
, and the subsequent
collapse of those bubbles.
causes noise and damage due to erosion and
fatigue failure.
Pressure
Head
V = GPM
.
HP =
( ft lbf) / lbm
V
N
Hp
N
2
Pw
N
3
.
Where
V = volumetric flow rate
N = Speed of rotation
Hp= Pump Head ( discharge pressure
Pw= Power required ( prime mover)
N
2
= 2N
1
Characteristic curve for centrifugal pump
N
1
N
2
PUMPS
Centrifugal:
Parallel pumps:
1 pump
2 pumps
H
P
V
GPM
V
2
= 2V
1
H
P2
= H
P1
PUMPS
Series (called staging):
H
P
V
GPM
1 pump
2 pumps
Fans
Same Principle as Non-positive
displacement pumps
Types:
Centrifugal: majority used for compressors
Axial (like propeller): cooling fans
QUESTIONS
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Io ListDocument122 pagesIo ListCahyanti Dwi WinartiNo ratings yet
- Session GuideDocument6 pagesSession GuideLuisa GarcillanNo ratings yet
- Sharp CD Dh950pDocument74 pagesSharp CD Dh950pJuan Carlos PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Universal JointDocument17 pagesUniversal Jointakmalzuhri96No ratings yet
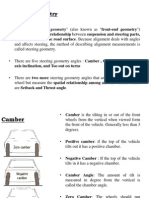
- Steering GeometryDocument23 pagesSteering GeometryChetanPrasadSevana100% (1)
- Digital Logic GatesDocument41 pagesDigital Logic Gatessurafel5248No ratings yet
- SKF Single Plane Graphical Balancing Tutorial ENDocument13 pagesSKF Single Plane Graphical Balancing Tutorial ENVili KamenovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5001Document32 pagesChapter 5001jangra014100% (1)
- Kode Program Untuk Led Matrix p10Document5 pagesKode Program Untuk Led Matrix p10IlmisyabanaNo ratings yet
- Landslides and Engineered Slopes - Chen 2008 PDFDocument2,170 pagesLandslides and Engineered Slopes - Chen 2008 PDFLupu Daniel100% (2)
- RAB & Spek LiftDocument2 pagesRAB & Spek Liftfatwa1985No ratings yet
- Experiment #1 Audio MonitorDocument7 pagesExperiment #1 Audio MonitorDaniel CafuNo ratings yet
- Continuous Functions and LimitsDocument9 pagesContinuous Functions and LimitsQurban HanifNo ratings yet
- Big Bang Theory: The-Origin-Of-The-UniverseDocument33 pagesBig Bang Theory: The-Origin-Of-The-UniverseMayank Kumar LodhiNo ratings yet
- 10 1108 - BFJ 06 2022 0466Document21 pages10 1108 - BFJ 06 2022 0466l.scheunertNo ratings yet
- Australia: AiracDocument3 pagesAustralia: AiracPero PericNo ratings yet
- Functions Modeling Change: A Precalculus CourseDocument239 pagesFunctions Modeling Change: A Precalculus CourseDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Precision Echosounder for Easy Hydrographic SurveyDocument13 pagesPrecision Echosounder for Easy Hydrographic SurveyMujahid SukarnoNo ratings yet
- Lab Scope Certificate ISO 17025-2017Document33 pagesLab Scope Certificate ISO 17025-2017Khan SattrakulvongNo ratings yet
- Shearwall Design of RCCCC Structure 111111222222298909Document77 pagesShearwall Design of RCCCC Structure 111111222222298909Shams KhattakNo ratings yet
- Logic Game 73rd Facebook nr2 With Key Games - 105593Document2 pagesLogic Game 73rd Facebook nr2 With Key Games - 105593azzarroNo ratings yet
- FVM - CFDDocument44 pagesFVM - CFDgrkguptaNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Long Quiz in ScienceDocument2 pages4th Quarter Long Quiz in ScienceEderlina Bentilanon FagtananNo ratings yet
- Yamaha Supermax English ManualDocument6 pagesYamaha Supermax English ManualanaloggeekNo ratings yet
- Discretization Methods of Fractional Parallel PIDDocument4 pagesDiscretization Methods of Fractional Parallel PIDBaherNo ratings yet
- MDVT v140w Drn1 CabinDocument49 pagesMDVT v140w Drn1 CabinambuenaflorNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra and its Applications: Functions of a matrix and Krylov matrices聻Document16 pagesLinear Algebra and its Applications: Functions of a matrix and Krylov matrices聻krrrNo ratings yet
- Vitiello - Io e Il Mio Doppio. Il Modello Quantistico Dissipativo Del CervelloDocument42 pagesVitiello - Io e Il Mio Doppio. Il Modello Quantistico Dissipativo Del Cervellorobyx71No ratings yet
- Survey Questions and Answers For Colleges, Professional Exams and Promotion InterviewDocument57 pagesSurvey Questions and Answers For Colleges, Professional Exams and Promotion InterviewAnthony ManadongNo ratings yet
- Design, Construction and Test of Prop System of Solar UAVDocument126 pagesDesign, Construction and Test of Prop System of Solar UAVNitin SharmaNo ratings yet