Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Manufacturing-Accounts Teaching Guide
Uploaded by
kimringineCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Manufacturing-Accounts Teaching Guide
Uploaded by
kimringineCopyright:
Available Formats
1
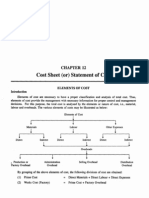
Chapter 7:
Manufacturing Account
TYPES OF INVENTORY
Raw materials
Work in progress
Finished goods/completed goods
TYPES OF PRODUCTION COST
3
Prime cost/
Direct cost
Overhead
cost/
Indirect cost
Production
cost
Cost incurred in the
manufacturing process, but
they cannot be traced
directly to the goods being
produced.
Direct materials
Direct labor
Direct expenses
Indirect materials
Indirect labor
Indirect expenses
PRIME COST
4
1. Direct materials
Costs of the materials used during the period.
Include the purchase price of the raw materials
and the acquisition costs related to the purchase.
Examples: Purchase of raw materials,
Carriage inwards / freight charges on raw
materials
5
2. Direct labour
Wages paid to the people who are
directly involved in the manufacturing
process.
Example: Direct labour, Direct wages,
Factory wages, Production wages,
Manufacturing wages
6
3. Direct expenses
They refer to the expenses paid
according to each unit of production.
Examples: Royalties, hire purchase of
special materials
7
1. Indirect materials
Lubricants
Loose tools
2.Indirect labour
wages, salaries, bonus or commission to
cleaners, crane drivers, foremen, supervisors
and production managers.
OVERHEAD COST
8
3. Indirect expenses related to the factory,
machinery and vehicles
Rent and rates
Depreciation
Insurance
Repairs and maintenance
Factory power / electricity
Internal transport
Loss on disposal
FINANCIAL STATEMENT
9
1. Manufacturing Account
2. Income Statement
3. Balance Sheet
1) Manufacturing Account
10
It shows the production cost or transfer price of
goods completed during the accounting period.
Direct materials
Direct labour
Direct expenses
Factory overhead expenses
Work in progress
Factory profit
11
Manufacturing Account for the year ended.
Opening stock of Raw Materials X
Add: Purchases of Raw Materials X
Return Outwards (raw materials) (X)
Carriage inwards (raw materials) (X)
Drawings (raw materials) (X)
X
X
Less: Closing stock of Raw Materials (X)
Cost of Raw Materials Consumed X
Direct Labor Wages X
Royalties X
Prime Cost X
Factory Overhead Expenses:
Production Managers salaries X
Factory Power X
Maintenance of Plant & Machinery X
Depreciation of Plant & Machinery X X
Direct material
Direct labour
Direct Expenses
Overhead
12
Add: Opening Work in Progress X
Less: Closing Work in Progress X
Production Cost of finished goods X
Factory profit (% PCFG) X
Transfer price of finished goods X
2) Income Statement
13
Profit or loss of the whole business during the
accounting period.
Includes all the expenses and income related to
the office and the running of the whole business
such as:
Gross profit / loss from the trading account
Factory profit / loss
Administration expenses
Selling and distribution expenses
Financial expenses
Increase / decrease in the provision for unrealized
profit
14
Sales X
Less: Returns inwards (X)
X
Less: Cost of Goods Sold
Opening stock of finished goods X
add: Transfer price of Finished goods X
Less: Drawings (finished goods) (X)
Returns outwards (X)
X
less: Closing stock of finished goods (X)
(X)
Gross Profit X
Add: Factory Profit X
Add: Other revenue
Discount Received X
Reduction in provision for unrealized profit X
X
Income Statement for the year ended
15
Less: Other Expenses
Selling expenses
commissions on sales XXX
salesman salaries XXX
carriage outwards XXX
depreciation of delivery van XXX
Administrative expenses
rental XXX
depreciation of office equipment XXX
printing XXX
postage XXX
Financial charges
bad debts XXX
discount allowed XXX
interest XXX
increase in provision for unrealized profit XXX
XXX
Net profit XXX
3) Balance Sheet
16
It shows the assets, liabilities and equities of the
Whole business on a specific date of the accounting
period.
Assets (closing inventory : raw materials, WIPs,
and finished goods)
Liabilities
Equities
17
Non-current Assets X
Current Asset
Inventory :-raw materials X
-work in progress X
-finished goods X
less: provision for unrealized profit (X) X
Total assets X
Financed by:
Owner`s capital
Opening capital X
Add: net profit X
Less: drawings (X)
X
Non-current liabilities X
Current liabilities X
Total liabilities and owner`s capital X
Balance Sheet as at.
18
Some expenses are related to both the
manufacturing process and the administration
of the office such as: Rent, electricity, insurance,
depreciation on premises, motor vehicles etc.
These expenses should be allocated to the
factory and office and debited to the
manufacturing account and the profit and loss
account respectively.
In the event of examinations, the bases of
allocation are usually given.
IMPORTANT TO NOTE
Production cost Vs. Transfer price
19
Stock of raw materials, work in progress and
other finished goods are valued at cost.
However, the stock of manufactured goods
can be valued at production cost or the
transfer price of goods completed.
Provision of unrealized profit of on stock
should be made if closing stock of
manufactured goods is valued at transfer
price.
Provision of Unrealized Profit
20
Mark up%
100%+ Mark up(%)
= Stock (at transfer price) x
Increase/ Decreased in Provision of Unrealized
Profit
Increase in Provision
(other expenses)
Reduction in Provision
(other revenues)
Dr Profit and Loss
Cr Provision for
Unrealized Profit
Dr Provision for
Unrealized Profit
Cr Profit and Loss
Expenses
Balance b/d (prepaid)
Balance b/d (accrued)
Balance c/d (prepaid) Balance c/d (accrued)
Cash/Bank
Income Statement
Drawings (expenses)
Acc. Rec. ( for dis.
allowed)
Adjustment on expenses
Income Statement
Income statement (admin)
Manufacturing account (factory)
Revenue
Balance b/d (prepaid) Balance b/d (accrued)
Balance c/d (prepaid)
Balance c/d (accrued)
Cash/Bank Income Statement
Acc. Pay (for
dis.received)
Adjustment on revenue
Income Statement
Income statement (admin)
Manufacturing account (factory)
Accum. depreciation of non-current assets
Balance b/d) Balance c/d
Income Statement
Depreciation for current years
1.Policy given
2.No policy (cost-NBV)
Accum. depreciation for previous years
1.Stated in question
2.cost-NBV
Adjustment on depreciation
24
A company manufactures and sells it own products.
It also purchases and sells other finished goods.
Production 100 units $1@ $100
Sales 80 units $2@ $160
Closing stock 20 units $1@ $20
Expenses for this period $50
Prepare manufacturing, trading and profit and loss
account for the following 2 situations would be
shown:
1. The factory output is transferred to the trading
account at factory cost.
2. The factory output is transferred to the trading
account at factory cost plus 20% factory profit, and
the stock of manufactured goods is valued at
transfer price.
25
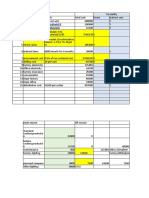
1.
$ $
Production cost of Gd completed (100 units*$1) 100
Sales (80 units*$2) 160
Less: COGS
Production cost of Gd completed 100
Less: Closing stock(at cost) (20 units*$1) 20 80
Gross Profit 80
Less: Expenses
Expenses 50
30
Manufacturing, trading and profit and loss account (extract)
26
2.
$ $
Production cost of Gd completed (100 units*$1) 100
Add: Manufacturing profit (100*0.2) 20
Transfer price of Gds completed 120
Sales (80 units*$2) 160
Less: Cost of goods sold
Transfer price of Gd completed 120
Less: Closing stock(at transfer price) (20+20*0.2) 24 96
Gross Profit 64
Add: Manufacturing profit 20
84
Less: Expenses
Expenses 50
Provision for unrealized profit (24*20/120) 4 54
Net Profit 30
Cost + profit
You might also like
- Manufacturing AccountDocument2 pagesManufacturing Accountmeelas123100% (2)
- Cost Accounting Fundamentals for Manufacturing BusinessesDocument21 pagesCost Accounting Fundamentals for Manufacturing Businessesabdullah_0o0No ratings yet
- Absorption vs Marginal Costing: Worked ExamplesDocument5 pagesAbsorption vs Marginal Costing: Worked ExamplesSUHRIT BISWASNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing SolutionsDocument8 pagesManufacturing SolutionsMothusi M NtsholeNo ratings yet
- Cost Sheet: Solutions To Assignment ProblemsDocument3 pagesCost Sheet: Solutions To Assignment ProblemsNidaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing AccountDocument15 pagesManufacturing Accountbalachmalik50% (2)
- Cost Sheet: Learning OutcomesDocument15 pagesCost Sheet: Learning OutcomesshubNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Cost Sheet or Statement of CostDocument16 pagesChapter 12 Cost Sheet or Statement of CostNeelesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Control Accounts Q8 PDFDocument3 pagesControl Accounts Q8 PDFRyanNo ratings yet
- Pearson LCCI Level 2 Certifi Cate in Cost Accounting (ASE20094)Document60 pagesPearson LCCI Level 2 Certifi Cate in Cost Accounting (ASE20094)Pinky PinkyNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Frame Work of AccountingDocument7 pagesConceptual Frame Work of AccountingashiqNo ratings yet
- 06 Overhead (OH) Costs - Allocations, Apportionment, Absorption CostingDocument34 pages06 Overhead (OH) Costs - Allocations, Apportionment, Absorption CostingAyushNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing AccountDocument36 pagesManufacturing AccountSaksham RainaNo ratings yet
- 6Document459 pages6sunildubey02100% (1)
- 9706 Y16 SP 3Document10 pages9706 Y16 SP 3Wi Mae RiNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing AccountsDocument11 pagesManufacturing Accountslukamasia100% (1)
- JOB, BATCH AND SERVICE COSTING-lesson 11Document22 pagesJOB, BATCH AND SERVICE COSTING-lesson 11Kj NayeeNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Depreciation PDFDocument50 pagesAssignment of Depreciation PDFMuhammad Arslan0% (2)
- Wages ( (Accounting For Labour)Document18 pagesWages ( (Accounting For Labour)Jitendra Patel100% (1)
- Absorption and Marginal CostingDocument6 pagesAbsorption and Marginal Costingberyl_hst100% (1)
- Add or Drop Product DecisionsDocument6 pagesAdd or Drop Product DecisionsksnsatishNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Paper: Cost Accounting McqsDocument8 pagesQuestion Bank Paper: Cost Accounting McqsNikhilNo ratings yet
- F2 Past Paper - Ans12-2006Document8 pagesF2 Past Paper - Ans12-2006ArsalanACCANo ratings yet
- Depreciation AssignmentDocument13 pagesDepreciation AssignmentfarisktsNo ratings yet
- ADL 56 Cost & Management Accounting 2V3Document20 pagesADL 56 Cost & Management Accounting 2V3Deepesh100% (1)
- Financial StatementsDocument18 pagesFinancial Statementswajeeha.arfat008No ratings yet
- CIMA Process Costing Sum and AnswersDocument4 pagesCIMA Process Costing Sum and AnswersLasantha PradeepNo ratings yet
- M1. Introduction To Cost and Management AccountingDocument11 pagesM1. Introduction To Cost and Management AccountingLara Camille CelestialNo ratings yet
- 6int 2006 Dec QDocument9 pages6int 2006 Dec Qrizwan789No ratings yet
- 02 MA1 LRP Questions 2014Document34 pages02 MA1 LRP Questions 2014Yahya KaimkhaniNo ratings yet
- Service CostingDocument2 pagesService CostingMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri Attari100% (1)
- Past Papers For Single Entry and Incomplete RecordsDocument2 pagesPast Papers For Single Entry and Incomplete RecordsMahreena IlyasNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Materials ManagementDocument40 pagesChapter Two Materials ManagementYeabsira WorkagegnehuNo ratings yet
- Joint Cost Apportionment MethodsDocument16 pagesJoint Cost Apportionment MethodsAnmol AgalNo ratings yet
- Cost and Management AccountingDocument84 pagesCost and Management AccountingKumar SwamyNo ratings yet
- Harsh ElectricalsDocument7 pagesHarsh ElectricalsR GNo ratings yet
- Job Costing CADocument13 pagesJob Costing CAmiranti dNo ratings yet
- Igcse Accounting Control Accounts - Questions AnswersDocument24 pagesIgcse Accounting Control Accounts - Questions AnswersOmar WaheedNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Notes Fall 19-1Document11 pagesCost Accounting Notes Fall 19-1AnoshiaNo ratings yet
- Product Mix Decision: IllustrationDocument2 pagesProduct Mix Decision: IllustrationMeghan Kaye LiwenNo ratings yet
- Cost SheetDocument20 pagesCost SheetKeshviNo ratings yet
- ManufacturingDocument6 pagesManufacturingapi-3034896990% (1)
- 02 MA2 LRP QuestionsDocument36 pages02 MA2 LRP QuestionsKopanang Leokana50% (2)
- Cost SheetDocument6 pagesCost SheetAishwary Sakalle100% (1)
- MCQ'S: EconomicsDocument73 pagesMCQ'S: EconomicsHabib MughalNo ratings yet
- Functional BudgetsDocument12 pagesFunctional BudgetsAyush100% (1)
- Test of Labour Overheads and Absorption and Marginal CostingDocument4 pagesTest of Labour Overheads and Absorption and Marginal CostingzairaNo ratings yet
- 35 Resource 11Document16 pages35 Resource 11Anonymous bf1cFDuepPNo ratings yet
- Past Papers - Partnership ChangesDocument10 pagesPast Papers - Partnership ChangesFarhan JehangirNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting 2013Document3 pagesCost Accounting 2013GuruKPO0% (1)
- Assignment 4 - Variances - 50140Document9 pagesAssignment 4 - Variances - 50140Hafsa HayatNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Managerial Accounting: Submitted By-Ghayoor Zafar Submitted To - DR MohsinDocument11 pagesAssignment 3 Managerial Accounting: Submitted By-Ghayoor Zafar Submitted To - DR Mohsinjgfjhf arwtr100% (1)
- Overhead and Absorption Costing: Prepared By: Talha Majeed Khan (M.Phil), Lecturer UCP, Faculty of Management StudiesDocument20 pagesOverhead and Absorption Costing: Prepared By: Talha Majeed Khan (M.Phil), Lecturer UCP, Faculty of Management StudieszubairNo ratings yet
- MGT402 Cost & Management Accounting Midterm ExamDocument279 pagesMGT402 Cost & Management Accounting Midterm ExamRamchandra MurthyNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management (2021)Document8 pagesInventory Management (2021)JustyNo ratings yet
- Question-Ias 2 - Ias 16 and Ias 40 - Admin-2019-2020-1Document6 pagesQuestion-Ias 2 - Ias 16 and Ias 40 - Admin-2019-2020-1Letsah BrightNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Marginal Costing and Absorption CostingDocument7 pagesChapter 9 Marginal Costing and Absorption CostingLinyVatNo ratings yet
- CMA Inventory Management New HandoutDocument10 pagesCMA Inventory Management New HandoutahmedNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing AccountDocument50 pagesManufacturing AccountfarissaharNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Cost of Goods ProducedDocument1 pageSchedule of Cost of Goods Producedalena persadNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument20 pagesCash Flow StatementKarthik Balaji100% (1)
- Company AccountsDocument116 pagesCompany AccountskimringineNo ratings yet
- APT Lecture6Document48 pagesAPT Lecture6Pandit Ramakrishna AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Agribusiness Meaning, Nature and ScopeDocument5 pagesAgribusiness Meaning, Nature and ScopeAmarendra Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Company AccountsDocument116 pagesCompany AccountskimringineNo ratings yet
- Financial Inclusion in AfricaDocument148 pagesFinancial Inclusion in AfricakimringineNo ratings yet
- The Financial and Economic Crisis of 2008-2009 and Developing CountriesDocument340 pagesThe Financial and Economic Crisis of 2008-2009 and Developing CountriesROWLAND PASARIBU100% (2)
- Ch13-Cash Flow STMDocument44 pagesCh13-Cash Flow STMAnonymous zXWxWmgZENo ratings yet
- Parity Conditions and Currency Forecasting-VVGG IllustrDocument36 pagesParity Conditions and Currency Forecasting-VVGG IllustrkimringineNo ratings yet
- International Tax StructuringDocument19 pagesInternational Tax StructuringkimringineNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument254 pagesFinancial Managementkimringine50% (2)
- Audit Committee Quality and Agency TheoryDocument19 pagesAudit Committee Quality and Agency TheorykimringineNo ratings yet
- Creative AgricultureDocument6 pagesCreative AgriculturekimringineNo ratings yet
- Value Chain Vs Supply ChainDocument7 pagesValue Chain Vs Supply Chainsornapudi472No ratings yet
- Formal Verus Informal Finance Evidence From ChinaDocument68 pagesFormal Verus Informal Finance Evidence From ChinakimringineNo ratings yet
- Demand Factors That Influence Fin InclusionDocument23 pagesDemand Factors That Influence Fin InclusionkimringineNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Formal and Informal Sector Interms of EmploymentDocument87 pagesRelationship Between Formal and Informal Sector Interms of EmploymentkimringineNo ratings yet
- Geometric MeanDocument2 pagesGeometric Meanarchangel655No ratings yet
- Cash Vs AccrualDocument4 pagesCash Vs AccrualkimringineNo ratings yet
- Summary of Accounting ConceptsDocument21 pagesSummary of Accounting ConceptskimringineNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Incomplete Accounting RecordsDocument49 pagesAccounting For Incomplete Accounting RecordskimringineNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument0 pagesCost Volume Profit Analysisprasathm873900No ratings yet
- Secondary MarketsDocument59 pagesSecondary MarketskimringineNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio AnalysisDocument14 pagesFinancial Ratio AnalysisPrasanga WdzNo ratings yet
- CAP1 Finance Session 2 SlidesDocument41 pagesCAP1 Finance Session 2 SlideskimringineNo ratings yet
- Poor LiteracyDocument3 pagesPoor LiteracykimringineNo ratings yet
- Note On Financial Ratio FormulaDocument5 pagesNote On Financial Ratio FormulaRam MohanreddyNo ratings yet
- Calculating Profit or Loss Under Incpmplete Records Scenario-GoodDocument7 pagesCalculating Profit or Loss Under Incpmplete Records Scenario-GoodkimringineNo ratings yet
- A Summary of Key Financial RatiosDocument4 pagesA Summary of Key Financial Ratiosroshan24No ratings yet
- PDTN FXNDocument9 pagesPDTN FXNrachmmmNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court Rules in Favor of Airline Employees in 13th Month Pay DisputeDocument13 pagesSupreme Court Rules in Favor of Airline Employees in 13th Month Pay DisputeRogie ToriagaNo ratings yet
- Employee Welfare TriveniDocument74 pagesEmployee Welfare TriveniAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- ARCHITECTURE PROFESSION-2proff PracticeDocument83 pagesARCHITECTURE PROFESSION-2proff PracticeKoti BoddyNo ratings yet
- SH INDUSTRIAL 11 2023.02.03 Labour Tribunal ENGDocument4 pagesSH INDUSTRIAL 11 2023.02.03 Labour Tribunal ENGthe advantis lkNo ratings yet
- Labor Stan - Week 4Document16 pagesLabor Stan - Week 4Andrew LastrolloNo ratings yet
- Srinagar Municipal Corporation: Office of The Executive Engineer Right River Works DivisionDocument7 pagesSrinagar Municipal Corporation: Office of The Executive Engineer Right River Works DivisionBeigh Umair ZahoorNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management (HRM) Practices: A Case Study On Arcadia Group, UKDocument10 pagesHuman Resource Management (HRM) Practices: A Case Study On Arcadia Group, UKAshutosh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Salary and WagesDocument13 pagesSalary and WagesIrfan FarooqNo ratings yet
- Some Costing Questions PDFDocument85 pagesSome Costing Questions PDFHarshit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Labor Code Maternity BenefitsDocument21 pagesBangladesh Labor Code Maternity BenefitsTarikul IslamNo ratings yet
- Note For PF PDFDocument3 pagesNote For PF PDFMilind MohapatraNo ratings yet
- AXON/2013/CIVILSITE/672 Labour Supply Work OrderDocument4 pagesAXON/2013/CIVILSITE/672 Labour Supply Work Ordervijayabhaskar kilariNo ratings yet
- AISATS Payslip April 2023Document1 pageAISATS Payslip April 2023Sahil shahNo ratings yet
- Employee Welfare ProjectDocument110 pagesEmployee Welfare ProjectJithin ShajiNo ratings yet
- The Constitutional Legal FrameworkDocument32 pagesThe Constitutional Legal FrameworkStarlette Kaye Badon100% (1)
- Learning Guide: Nefas Silk Poly Ntechnic CollegeDocument27 pagesLearning Guide: Nefas Silk Poly Ntechnic CollegeNigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Sibal Vs Notre Dame of Greater Manila GR 75093Document7 pagesSibal Vs Notre Dame of Greater Manila GR 75093Beverlyn JamisonNo ratings yet
- Labor Relations GuideDocument1 pageLabor Relations GuideRoselle Jarden AñesNo ratings yet
- Assess BSBHRM602 Manage HR SP v1.3-1Document38 pagesAssess BSBHRM602 Manage HR SP v1.3-1Maykiza NiranpakornNo ratings yet
- Accouc Payroll CH3Document15 pagesAccouc Payroll CH3Nimona Beyene50% (2)
- Kool KingDocument9 pagesKool KingAnuj PeepreNo ratings yet
- HRM Assignment Compensations MethodsDocument21 pagesHRM Assignment Compensations MethodsAbd Majid Bin Bachok100% (1)
- LABOR Compilation 4-B - Collective Bargaining and Administration of AgreementDocument33 pagesLABOR Compilation 4-B - Collective Bargaining and Administration of AgreementgracedorsgracedorsNo ratings yet
- Service ContractDocument6 pagesService ContractMarian Santos100% (1)
- Wages and Salary Admin - Wage Boards - Q4Document7 pagesWages and Salary Admin - Wage Boards - Q4bageemurthyNo ratings yet
- The Manila Hotel Corp vs. NLRCDocument6 pagesThe Manila Hotel Corp vs. NLRCiamchurky100% (1)
- Iran vs. NLRCDocument8 pagesIran vs. NLRCRichard Irish AcainNo ratings yet
- Living Conditions of Tea Plantation WorkersDocument4 pagesLiving Conditions of Tea Plantation WorkersRAGHUBALAN DURAIRAJUNo ratings yet
- Introduction ManagementDocument16 pagesIntroduction ManagementAbdullah Al Mamun TusherNo ratings yet