Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Material Properties 2
Uploaded by
Prabath De SilvaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Material Properties 2
Uploaded by
Prabath De SilvaCopyright:
Available Formats
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2-SJ
MATERIAL PROPERTIES
Classification of Materials
Metals and Alloys
Ceramic, Glass, and Glass-ceramics
Polymers (plastics) and Thermoplastics
Semiconductors
Composite Materials
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Types of Loadings
Tensile Loading
Compressive Loading
Shear Loading
Torsion Loading
Tension Compression
Shear
Torsion
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Stress
A stress is a measure of the force in a
component relative to the cross-sectional
area over which the force is applied.
= Force per unit area
F
A
s = F/A
(units: N/m
2
or Pascal (Pa), psi)
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Strain
Strain is a measure of deformation (either elastic or
permanent).
= Change in length per unit original length
e = DL / L0
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Important Properties of Material
Strength
Elasticity
Ductility
Hardness
Resilience
Toughness
Creep
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Tensile Test
The most common way to assess the mechanical
property of a material (strength and ductility) is the
tensile test which measures the resistance of material to
a static or slowly applied force.
(b)
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Sequence of Events of a Tensile-
Test Specimen
(a) Early stage of necking
(b) Small voids begin to form within the necked region;
(c) Voids coalesce, producing an internal crack;
(d) Rest of the cross-section begins to fail at the periphery,
by shearing
(e) Final fracture surfaces, known as cup- (top fracture
surface) and cone- (bottom surface) fracture.
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Tensile Stress-Stain Curve
STRAIN
S
T
R
E
S
S
The resulting information is used to plot a graph which is
called stress strain curve to assess strength and
deformability
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Elastic Deformation
Associated with stretching
but not breaking the
chemical bonds between
atoms in a solid
Elastic deformation is
recovered immediately
upon unloading.
LOAD
UNLOAD
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Plastic Deformation
Atoms change neighbors,
returning to a stable
configuration with new
neighbors after the
dislocation has passed.
Plastic deformation is not
recovered upon unloading
and is therefore
permanent.
LOAD
UNLOAD
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Elastic Vs Plastic Deformation
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Proportional Limit
PROPORTIONAL LIMIT
A
ELASTIC DEFORMATION
Beyond this stress level A:
stress & strain are no longer
proportional to each other.
The metal is no longer completely
elastic.
E
L
A
S
T
I
C
R
A
N
G
E
STRAIN
S
T
R
E
S
S
Elastic Range is the:
Stress up to the proportional limit.
The max stress developed which causes no
permanent deformation when the force is
removed.
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Modulus of Elasticity
PROPORTIONAL LIMIT
A
E
L
A
S
T
I
C
R
A
N
G
E
ELASTIC DEORMATIOON
S
T
R
E
S
S
STRAIN
Slope of the straight line portion
Mod of Elasticity is the ratio b/w
Proportional limit stress and the
corresponding strain.
Tan = E = a/b
MODULUS OF
ELASTICITY
E
a
b
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Resilience
PROPORTIONAL LIMIT
A
E
L
A
S
T
I
C
R
A
N
G
E
ELASTIC DEORMATIOON
S
T
R
E
S
S
STRAIN
Ability to absorb energy in elastic
range.
Area under the stress strain curve
up to the proportional limit.
a
b
RESILIENCE
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Yield Stress
YIELD POINT
A
ELASTIC DEORMATIOON
The stress at which rapid increase
in permanent strain occurs.
Y
I
E
L
D
S
T
R
E
S
S
S
T
R
E
S
S
STRAIN
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Ultimate Stress
A
MODULUS OF
ELASTICITY
RESILENCE U
L
T
I
M
A
T
E
S
T
R
E
N
G
T
H
The highest engineering stress
that a material can with stand before
fracture.
FRACTURE POINT
PLASTIC RANGE
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Strength
Strength is the ability of a material to resist stress
without failure.
It is the ability of a material to return to its original size
and shape after removal of a applied force.
Elasticity
Ductility
A measure of a materials ability to be stretched or
drawn (plastically)
Measurements: Percent elongation or reduction in
area
The higher the %elongation, the more ductile and
formable the material is.
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Ductile Fracture Surface
ANSI 304 SS
1000x
Microvoids
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Cup-and-cone Fracture in Al
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2-SJ
Brittle
It is opposite to ductility.
Brittle materials don't change shape readily under load.
Normally they fail with little or no warning.
Examples : - Glass and Concrete etc
Brittle Fracture
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Ductile vs. Brittle Failure
Adapted from Fig. 8.3, Callister 7e.
cup-and-cone fracture brittle fracture
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Comparison of Graph
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2-SJ
Hardness
Hardness is the ability of material
to resist indentation or abrasion.
It is most commonly measured by
the Brinell Test
BRINELL HARDNESS
TESTER
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2-SJ
Resilience
x
YS
PL x
Resilience
Amount of energy necessary
to deform the material to the
proportional limit (PL).
The resistance of a material
to permanent deformation.
= Area under the elastic
portion of the S-S curve.
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Amount of energy necessary to cause fracture
The resistance of a material
to fracture
= Area under the elastic and
plastic portions of the S-S
curve.
Unit = N
.
m/m
3
, Joule/m
3
(energy per unit volume of material)
PL x
x
YS
Toughness
Toughness
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Creep
Creep is that property which
causes some material under
stress to deform slowly but
progressively over a period
of time.
It is Time-dependent
inelastic deformation.
(c)2003 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Thomson Learning
is a trademark used herein under license.
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2-SJ
Malleability
Malleability is that property of
a material that enable it to
undergo great change in shape
without rupture under
compressive stress.
For example, copper,
aluminum, or wrought iron
being hammered into various
shapes or steel being rolled
into structural shapes or sheets
Institute of Air Safety-PAF
TI-2- SJ
Can you find .?
Most brittle material
Compare strength
Yield strength
Ultimate strength
Fractural strength
Toughest material
Most resilience
material
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Design of Circular Base Plate Under Large Bending MomentDocument5 pagesDesign of Circular Base Plate Under Large Bending MomentAntonioMonteroNo ratings yet
- Calibration ProceduresDocument24 pagesCalibration Procedurestingpadu83% (6)
- Welding Metallurgy IIW Presentation ANB Program Dec 2011Document88 pagesWelding Metallurgy IIW Presentation ANB Program Dec 2011Asad Bin Ala Qatari100% (4)
- Battery ManualDocument76 pagesBattery ManualPrabath De Silva0% (1)
- ASTM International Constructuring Smooth Hot Mix Asphalt 2003 PDFDocument274 pagesASTM International Constructuring Smooth Hot Mix Asphalt 2003 PDFNur Yanta100% (1)
- Nursing Division BudgetingDocument5 pagesNursing Division BudgetingPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- MSL Technical Guide 25 Calibrating Balances: Ing and Calibration Laboratories by International AccrediDocument7 pagesMSL Technical Guide 25 Calibrating Balances: Ing and Calibration Laboratories by International AccrediPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- CalibrateDocument33 pagesCalibrateazurananNo ratings yet
- Combined Torsion and BendingDocument3 pagesCombined Torsion and BendingShepherd Nhanga0% (1)
- Dry-Block Calibrator Immersion Test GuideDocument3 pagesDry-Block Calibrator Immersion Test GuidePrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- EntebeDocument20 pagesEntebePrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- The Origins of Aerial HijackingDocument5 pagesThe Origins of Aerial HijackingPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Good Practice GuideDocument14 pagesGood Practice GuidePrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- JH Wascator FlyerDocument1 pageJH Wascator FlyerPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- 3501e JDocument18 pages3501e JPartsGopher.comNo ratings yet
- Surface Sensor SDocument8 pagesSurface Sensor SPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Manometros WikaDocument20 pagesManometros WikaDavid VargasNo ratings yet
- DS - In0002 - GB - 1372. en 837 PDFDocument4 pagesDS - In0002 - GB - 1372. en 837 PDFAldrin HernandezNo ratings yet
- 258 - VeriVide Product Guide June09Document16 pages258 - VeriVide Product Guide June09Prabath De Silva0% (1)
- Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument17 pagesCorporate Social ResponsibilityPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Introducing Microsoft Project 2007Document226 pagesIntroducing Microsoft Project 2007Prof. Dr. Abdalla ElDaoushyNo ratings yet
- Chinese Lunar CalendarDocument1 pageChinese Lunar CalendarPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Material Properties 1Document39 pagesMaterial Properties 1Prabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Back Side of ChinaDocument30 pagesBack Side of ChinaPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- In The Name of The Most Gracious, The Most Merciful: AllahDocument27 pagesIn The Name of The Most Gracious, The Most Merciful: AllahPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Failure TerminologiesDocument24 pagesFailure TerminologiesPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Elementry Stresses & Stress Concentration 36 TIDocument39 pagesElementry Stresses & Stress Concentration 36 TIPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Elementry Stresses & Stress Concentration 36 TIDocument39 pagesElementry Stresses & Stress Concentration 36 TIPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of QualityDocument18 pagesBasic Concept of QualityPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Metrology Lab Manual DimensionDocument30 pagesMetrology Lab Manual DimensionPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Integrated CircuitsDocument28 pages8 - Integrated CircuitsPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Corrosion For Off & Tech July 2010Document49 pagesAircraft Corrosion For Off & Tech July 2010Prabath De Silva100% (1)
- A Guide To Effective Human Resources ManagementDocument39 pagesA Guide To Effective Human Resources ManagementPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Parker White Paper Developments in Stainless Steel Instrumentation Tube FittingsDocument6 pagesParker White Paper Developments in Stainless Steel Instrumentation Tube FittingskkaranagNo ratings yet
- Crystal Dislocations - Their Impact On Physical Properties of Crystals PDFDocument318 pagesCrystal Dislocations - Their Impact On Physical Properties of Crystals PDFshaileshNo ratings yet
- 15CV 32 Module 3Document56 pages15CV 32 Module 3Karthik A KulalNo ratings yet
- ENG Oiles 500 SJDocument6 pagesENG Oiles 500 SJRendra Maha Putra JfNo ratings yet
- Mohr - Coulumb Failure CriteronDocument5 pagesMohr - Coulumb Failure CriteronTahir KhanNo ratings yet
- Liquid Metals Chem ProjectDocument14 pagesLiquid Metals Chem ProjectHarshath RagavendraNo ratings yet
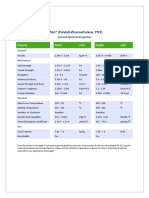
- TeflonDocument1 pageTeflonSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- c70 Data Sheet AIREXDocument2 pagesc70 Data Sheet AIREXestecoboatNo ratings yet
- Background TheoryDocument13 pagesBackground TheoryJayminNo ratings yet
- Engg Thermodynamics-GKVDocument18 pagesEngg Thermodynamics-GKVPradap TeddyNo ratings yet
- Chap 10Document45 pagesChap 10NhanNo ratings yet
- Tu 2 7 4 PDFDocument11 pagesTu 2 7 4 PDFIvanUribeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Materials and Methods 2Document30 pagesLecture 2 Materials and Methods 2Jefferson AltarNo ratings yet
- Buckling and Vibration of Laminated Composite Plates Using Various Plate TheoriesDocument10 pagesBuckling and Vibration of Laminated Composite Plates Using Various Plate TheoriesahoramehriNo ratings yet
- Me307 Formula Sheet5423Document19 pagesMe307 Formula Sheet5423Gazi FıratNo ratings yet
- Ansys Shell 63 Elementansys Shell 63 Elementansys Shell 63 ElementDocument10 pagesAnsys Shell 63 Elementansys Shell 63 Elementansys Shell 63 ElementvilukNo ratings yet
- Wood-Based Structural Panels in Compression: Standard Test Methods ForDocument6 pagesWood-Based Structural Panels in Compression: Standard Test Methods ForAnvit GadkarNo ratings yet
- Photonic Material (Polymer)Document24 pagesPhotonic Material (Polymer)Shofi Dhiya UlhaqNo ratings yet
- 2.1.2.a Beamdeflection 2Document7 pages2.1.2.a Beamdeflection 2Bailey RodriguezNo ratings yet
- EMT 3253-Solid and Structural Mechanics IDocument1 pageEMT 3253-Solid and Structural Mechanics IezraNo ratings yet
- BFC 32102Document14 pagesBFC 32102Zuliyah ZakariaNo ratings yet
- High-Rise Shear Wall Strength and DuctilityDocument6 pagesHigh-Rise Shear Wall Strength and Ductilitymr.xinbombayNo ratings yet
- STAAD Pro - Lesson 07 - SpecificationsDocument7 pagesSTAAD Pro - Lesson 07 - SpecificationsEBeeNo ratings yet
- NTSB Pipeline Accident ReportDocument101 pagesNTSB Pipeline Accident ReportkoushkiNo ratings yet
- Hughes, Owen F. Paik, Jeom Kee Ship Structural Analysis and Design 2010Document42 pagesHughes, Owen F. Paik, Jeom Kee Ship Structural Analysis and Design 2010Muh Kurniawan S100% (2)