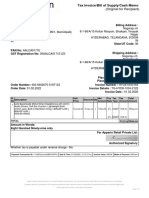
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4 Project Execution
Uploaded by
czuberek0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
120 views16 pagesProject execution Management
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProject execution Management
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
120 views16 pagesChapter 4 Project Execution
Uploaded by
czuberekProject execution Management
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
The Project Management Life Cycle
A Complete Step-by-Step Methodology for
Initiating, Planning, Executing and Closing a Project Successfully
Welcome to the Project Management Life Cycle
We have provided this unique CD to help you gain an appreciation of the phases, activities and tasks
included within The Project Management Life Cycle. This CD and book reveal the Method123 Project
Management Methodology (MPMM) which is used by more than 45,000 people around the world.
To purchase MPMM and the complete set of project management templates upon which this book is
based, please visit www.Method123.com. There you will find all of the software, reports, checklists,
forms, templates and case studies required to manage projects successfully.
Whether youre a project manager, business owner, team member, consultant, lecturer or student, you
will greatly enhance your chances of success by adopting MPMM for your projects.
If you have questions regarding the content contained within this book or CD, please e-mail us at:
support@method123.com.
This CD and its contents are copyright protected.
All copyright rights remain with Method123 Ltd.
Chapter 4
Project Execution
What is project execution?
- it is the third phase in the project life
cycle;
- it involves creating project deliverables
- within this phase the deliverables are
built and signed off by the customer.
The project manager monitors and
controls the project by executing a suite
of management processes.
Which activities are undertaken?
The following diagram depicts the
activities involved in executing a project:
Step 1: Build deliverables
A deliverable is:
A quantifiable outcome of a project which results
in the partial or full achievement of the project
objectives.
To build project deliverables, you need to:
- delegate the building of deliverables to project staff;
- physically construct each project deliverable;
- measure the deliverables against the quality targets set;
- request acceptance of deliverables by the customer.
Build
Deliverables
Step 2: Monitor and control
During the execution of the project, you need to monitor
and control the project delivery by performing:
- time management;
- cost management;
- quality management;
- change management;
- risk management;
- issue management;
- procurement management;
- acceptance management;
- communications management.
Monitor &
Control
Perform time management
Time management is:
The process of recording and
quantifying time spent completing
tasks on a project.
Time management involves:
- completing and approving timesheets;
- recording time spent, within a timesheet
register and project plan;
- identifying and resolving exceptions.
Perform cost management
Cost management is:
The process by which costs (ie
expenses) incurred on a project are
identified, approved and paid.
Cost management involves:
- completing and approving expense forms;
- recording expenditure, within an
expense register and project plan;
- resolving expense issues.
Perform quality management
Quality management is:
The process by which the
quality of the deliverables
and management processes
is assured and controlled.
Quality management involves:
- setting quality targets;
- measuring deliverable quality;
- performing quality assurance;
- performing quality control;
- resolving quality issues.
Perform change management
Change management is:
The process by which changes to
the project scope, deliverables,
timescales or resources are approved
and managed.
Change management involves:
- completing change requests;
- assessing change feasibility;
- approving change requests;
- scheduling change requests;
- implementing change requests.
Perform risk management
Risk management is:
The process of identifying, quantifying
and mitigating risks throughout a
project.
Risk management involves:
- identifying project risks;
- completing risk forms;
- reviewing and assessing risks;
- implementing risk mitigation actions;
- constantly reviewing the risk status.
Perform issue management
Issue management is:
The process by which issues are
formally identified, reviewed and
resolved.
Issue management involves:
- identifying project issues;
- completing issue forms;
- reviewing and assessing issues;
- implementing issue resolution actions;
- constantly reviewing the issue status
Perform procurement management
Procurement management is:
The process of
procuring products
from external
suppliers.
Procurement management
involves:
- issuing purchase orders;
- fulfilling purchase orders;
- managing supplier contracts.
Perform acceptance management
Acceptance management is:
The process by which project
deliverables are reviewed and
accepted by the customer.
Acceptance management involves:
- identifying the completion of deliverables;
- requesting customer acceptance tests;
- completing acceptance tests;
- accepting final deliverables.
Perform communications management
Communications management is:
The process of keeping stakeholders
informed of the progress of the project.
Communications management involves:
- identifying communication required;
- creating communications messages;
- dispatching communications messages;
- reviewing communication effectiveness.
Step 3: Perform a stage gate
A stage gate is:
A checkpoint at the end of the project phase to ensure
that the project has achieved its stated objectives and
deliverables.
To perform a stage gate, you need to:
- identify the stage-gate review criteria;
- undertake the stage-gate review;
- complete the stage-gate review form;
- seek approval to proceed.
Perform
Stage-Gate
You might also like
- General Principles of Project ManagementDocument6 pagesGeneral Principles of Project ManagementCopet FxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Project Procurement ManagementDocument40 pagesChapter 12 Project Procurement ManagementMohamed El ArabiNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Project and Programme Management - P2M For Enterprise Innovation StructureDocument12 pagesUnit 8 Project and Programme Management - P2M For Enterprise Innovation StructurebevinjNo ratings yet
- Management of Project Communication Pub3711Document13 pagesManagement of Project Communication Pub3711Tsholofelo Majipos StlhanohNo ratings yet
- 10 - PM - Communication ManagementDocument16 pages10 - PM - Communication ManagementEmran HossainNo ratings yet
- Project Closeout Report InstructionsDocument2 pagesProject Closeout Report InstructionstohemaNo ratings yet
- Project Management Proj - LifecycleDocument5 pagesProject Management Proj - LifecycleSohini DasNo ratings yet
- PROJECT CHARTER DOCUMENTnDocument3 pagesPROJECT CHARTER DOCUMENTnMiyuranga W.H.D.D. en17081344No ratings yet
- Contract ManagementDocument3 pagesContract ManagementAB AgostoNo ratings yet
- Project Closeout TemplateDocument6 pagesProject Closeout Templatejeyn100% (1)
- Braindump JK0-017Document87 pagesBraindump JK0-017cremer.rikeNo ratings yet
- Project Monitoring ControlDocument28 pagesProject Monitoring Controlsarah smithNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Project CycleDocument16 pagesCH 2 Project CycleMebratu SimaNo ratings yet
- Monitoring ControllingDocument22 pagesMonitoring ControllingGio BattadNo ratings yet
- PM CommunicationManagement14 PDFDocument32 pagesPM CommunicationManagement14 PDFsamii7362No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Project Procurement ManagementDocument37 pagesChapter 12 Project Procurement ManagementFederico KeselmanNo ratings yet
- Project Monitoring PlanDocument2 pagesProject Monitoring PlanharithaNo ratings yet
- Integrated Project Management Solution For Automotive Supplier (Case Study)Document4 pagesIntegrated Project Management Solution For Automotive Supplier (Case Study)Angie Fer.No ratings yet
- Organizational Breakdown StructureDocument25 pagesOrganizational Breakdown StructureAnni Lou BordiosNo ratings yet
- Procurement ReportDocument12 pagesProcurement ReportMwasNo ratings yet
- Terms of ReferenceDocument2 pagesTerms of ReferenceSeble GetachewNo ratings yet
- Network DiagramsDocument8 pagesNetwork Diagramscrystal50% (2)
- Stakeholder RegisterDocument4 pagesStakeholder Registerapi-3388834090% (1)
- p2 AssignmentDocument5 pagesp2 AssignmentmulugetaNo ratings yet
- Contract Award To IBI GroupDocument3 pagesContract Award To IBI GroupsebastienperthNo ratings yet
- PPM 641A2Sample1Document12 pagesPPM 641A2Sample1Alison BennettNo ratings yet
- Training Project PlanDocument8 pagesTraining Project PlangolfohNo ratings yet
- 2010-06-14 1300 Project Management Broad Spectrum Overview WikibookDocument522 pages2010-06-14 1300 Project Management Broad Spectrum Overview WikibookKits Sri100% (1)
- Basics of Project Scheduling: Create A Schedule Using CPMDocument11 pagesBasics of Project Scheduling: Create A Schedule Using CPMWali RahmanNo ratings yet
- Coursework 1 - CPDocument15 pagesCoursework 1 - CPMufeez Lebbe0% (1)
- Stakeholder Engagement Plan Guide and TemplateDocument3 pagesStakeholder Engagement Plan Guide and TemplateDan RadaNo ratings yet
- PrimaveraP6 Training - 24hrsDocument1 pagePrimaveraP6 Training - 24hrsespee29No ratings yet
- C4384 - Assignment 2Document26 pagesC4384 - Assignment 2iamaffandiNo ratings yet
- Part A Memorandum of ProcedureDocument24 pagesPart A Memorandum of ProcedureSyed Umair HashmiNo ratings yet
- Critical Path MethodDocument53 pagesCritical Path MethodFrst-Ngwazi Prince Christopher Manda100% (1)
- Form K - Item 1 - Nigerian Content Execution PlanDocument8 pagesForm K - Item 1 - Nigerian Content Execution PlanBALARISI ENGINEERNo ratings yet
- Planning A ProjectDocument33 pagesPlanning A ProjectLjuba SindzirevicNo ratings yet
- Building House-Critical Path MethodDocument7 pagesBuilding House-Critical Path MethodDavid MechuraNo ratings yet
- 8 - Project Risk ManagementDocument64 pages8 - Project Risk ManagementMohammed AdelNo ratings yet
- Construction Phase Commissioning ActivitiesDocument2 pagesConstruction Phase Commissioning ActivitiesclaudelgoNo ratings yet
- Project Procurement Management: 1 WWW - Cahyo.web - Id IT Project Management, Third Edition Chapter 12Document28 pagesProject Procurement Management: 1 WWW - Cahyo.web - Id IT Project Management, Third Edition Chapter 12cahyodNo ratings yet
- Template - Financial PlanDocument10 pagesTemplate - Financial PlanGryswolfNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents Group Final ProjectDocument4 pagesTable of Contents Group Final ProjectGian adhit19No ratings yet
- Risk Management PlanDocument9 pagesRisk Management PlanLinus100% (1)
- Schedule Management PlanDocument3 pagesSchedule Management PlanGeeta RamsinghNo ratings yet
- Issue LogDocument1 pageIssue LogoliverapopovicNo ratings yet
- Pmi Rep HandbookDocument31 pagesPmi Rep HandbookNirupan KumarNo ratings yet
- Playbook Mobilisation Phase ChecklistDocument2 pagesPlaybook Mobilisation Phase Checkliststimayo010809No ratings yet
- Project Execution PlanDocument17 pagesProject Execution PlanAmadi LawrenceNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 Project-Quality-Management1Document52 pagesMODULE 4 Project-Quality-Management1Tewodros TadesseNo ratings yet
- Cemp ReportDocument75 pagesCemp ReportTAHER AMMARNo ratings yet
- Project Management Practices: The Criteria For Success or FailureDocument8 pagesProject Management Practices: The Criteria For Success or Failurerenjith100% (1)
- Rizal Technological University: Department of ArchitectureDocument5 pagesRizal Technological University: Department of ArchitectureMharcianeMaxineMagoNo ratings yet
- Swan Mundaring Reform Project Management Plan LGNSW Amalgamation ToolkitDocument140 pagesSwan Mundaring Reform Project Management Plan LGNSW Amalgamation ToolkitSyed Mujahid AliNo ratings yet
- Critical Path Method and Its SignificancDocument66 pagesCritical Path Method and Its Significancdarl1100% (1)
- Project Procurement ManagementDocument72 pagesProject Procurement ManagementSamsun GalaxNo ratings yet
- Cost Management Plan-Template1Document5 pagesCost Management Plan-Template1Zac Usaf100% (1)
- Chapter 12 Introduction To Cost Management SystemsDocument6 pagesChapter 12 Introduction To Cost Management SystemsAnne Marieline BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Boat Bassheads 950v2 1feb 2023Document1 pageBoat Bassheads 950v2 1feb 2023Ranjan ThegreatNo ratings yet
- 1968 Hypogene Texture and Mineral Zoning in A Copper Granodiorite Porphyry Stock NielsenDocument14 pages1968 Hypogene Texture and Mineral Zoning in A Copper Granodiorite Porphyry Stock NielsenKevin Hiram Torres Montana100% (1)
- NEM326 HW 1 PDFDocument2 pagesNEM326 HW 1 PDFyaprak dönerNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Probable Cause: ArresteeDocument3 pagesAffidavit of Probable Cause: ArresteeMcKenzie StaufferNo ratings yet
- Strange Inhabitants of The ForestDocument36 pagesStrange Inhabitants of The Forestmacaquinho.No ratings yet
- Master Nilai RDM Semseter Gasal 2020 Kelas 1Document50 pagesMaster Nilai RDM Semseter Gasal 2020 Kelas 1Ahmad Syaihul HNo ratings yet
- Inventory Control Software Business PlanDocument28 pagesInventory Control Software Business Planhemansh royalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Urdu and Regional Languages Urdu LanguageDocument10 pagesChapter 5: Urdu and Regional Languages Urdu LanguageAdnan Qureshi100% (1)
- 2019-04-01 BESTPRAC Financial Management of H2020 Projects - Guide To Best Practice PDFDocument87 pages2019-04-01 BESTPRAC Financial Management of H2020 Projects - Guide To Best Practice PDFDes Des Z MottaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Urban Design and Cultural Diversity, by Nada Lazarevic Bajec, Marija MarunaDocument141 pagesStrategic Urban Design and Cultural Diversity, by Nada Lazarevic Bajec, Marija MarunaArhitektonski fakultet100% (1)
- A Summer Internship Report On Online ResearchDocument58 pagesA Summer Internship Report On Online ResearchSaurav Kumar0% (1)
- Kashmir DisputeDocument13 pagesKashmir DisputeAmmar ShahNo ratings yet
- Kove Food MenuDocument6 pagesKove Food MenusafinditNo ratings yet
- CASE DIGEST - Metrobank vs. CADocument7 pagesCASE DIGEST - Metrobank vs. CAMaria Anna M Legaspi100% (1)
- Globalization DesglobalizationDocument10 pagesGlobalization DesglobalizationFarhadNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Bahasa InggrisDocument18 pagesPresentasi Bahasa InggrisIndraPrawiroAdiredjoNo ratings yet
- Goodyear (Veyance)Document308 pagesGoodyear (Veyance)ZORIANNYEGLNo ratings yet
- C4ISR Architecture Framework PDFDocument231 pagesC4ISR Architecture Framework PDFdiomsgNo ratings yet
- 7 Wonders of ANCIENT World!Document10 pages7 Wonders of ANCIENT World!PAK786NOONNo ratings yet
- LorealDocument2 pagesLorealviaraNo ratings yet
- RPS Energy Savings UpdateDocument9 pagesRPS Energy Savings UpdateinforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Financial Accounting 12th Edition Thomas Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Financial Accounting 12th Edition Thomas Test Bank PDFhetero.soothingnnplmt100% (15)
- Reviewer in Mapeh: African-AmericansDocument4 pagesReviewer in Mapeh: African-Americanszephyra neithNo ratings yet
- SSS Disability BenefitsDocument5 pagesSSS Disability BenefitsJason TiongcoNo ratings yet
- Circular 64 - KG I Sibling Admissions For The AY 2024-25Document2 pagesCircular 64 - KG I Sibling Admissions For The AY 2024-25Inderpaal SinghNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - (Template) Understanding The Black Death Student MaterialsDocument4 pagesKami Export - (Template) Understanding The Black Death Student Materialscookniya1No ratings yet
- LESSON 1-3 HistoryDocument13 pagesLESSON 1-3 HistoryFLORIVEN MONTELLANONo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Persons and Family Relations 2019 PDFDocument6 pagesSyllabus For Persons and Family Relations 2019 PDFLara Michelle Sanday BinudinNo ratings yet