Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 15 Third Conditional
Uploaded by
Mind´s EyesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 15 Third Conditional
Uploaded by
Mind´s EyesCopyright:
Available Formats
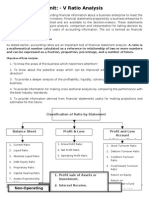
Understanding a Balance
Sheet
Basic Principles of a Balance
Sheet
Most businesses borrow money to help them
to operate.
A balance sheet has a special section called
liabilities. This shows how much money has
been borrowed or invested and where it came
from.
The term balance means that all the money
invested or borrowed must be accounted for in
another section, called assets.
What are Assets?
last a long time e.g., buildings, vehicles, computers.
cost a lot of money.
could be sold to increase capital (i.e. money owned
by the business).
Fixed assets are items owned by the company
which:
What are Assets?
Current assets include:
Items used and replaced regularly e.g., raw
materials or stock.
Customers who owe money (called debtors) for
goods they have bought.
Money in the current bank account.
What are Liabilities?
Current liabilities are:
Money the business owes to suppliers (called
creditors) for goods purchased on credit.
Short term loans.
What are Liabilities?
Liabilities also includes capital and reserves.
Share capital is money which shareholders have
invested in the business.
Reserves = profit from previous years which has
been kept to finance future developments.
Profit and loss account = money kept back from
the current years profits.
The structure of a Balance Sheet Assets
Fixed assets
Buildings 60,000
Equipment 20,000
Total fixed assets 80,000
Current assets
Stock 20,000
Debtors 10,000
Cash at bank 10,000
Total current assets 40,000
(Total assets = 120,000 but this figure doesnt show)
The structure of a Balance Sheet Current liabilities
LIABILITIES
Current liabilities
Creditors -10,000
Working Capital 30,000
(This is the current assets - 40,000 - minus the current liabilities)
Total Net Assets 110,000
(This is the total assets - 120,000 - minus the current liabilities)
The structure of a Balance Sheet Capital and Reserves
Financed By:
Accumulated Fund 70,000
Surplus of Income 40,000
Capital Employed 110,000
(This is the total amount in Capital and Reserves. It must equal
the same amount as the total assets minus current liabilities).
Putting it all together
ASSETS
Fixed assets (assets listed)
Total fixed assets
80,000 A
Current assets (assets listed)
Total current assets 40,000 B
LIABILITIES
Current liabilities 10,000 C
Working Capital 30,000 B C
Total Net Assets 110,000 A +B C
Financed By: (all listed)
Capital Employed 110,000 D
Reading a Balance Sheet
Both the balance sheet and the profit and loss
account show the health of the business
Shareholders, customers, suppliers, employees
and other groups of people will be interested in
both types of account.
Key aspects of a Balance Sheet
Fixed assets is there enough money secured
in items which could be sold to raise capital?
Cash in bank is there enough to cover a short-
term crisis?
Working Capital if this figure is negative, the
business hasnt enough money to pay all the
creditors in a reasonable time.
Shareholders funds are these increasing?
Shareholders want their investment to grow.
Contents of Profit and Loss
Account
Revenues : Turnover
Other income
Sale of fixed assets
Expenses
Profit / Loss
Revenues
Revenue is defined as the income that
accrues to the firm by sale of goods and
services or through investments
Sales Revenue is the amount earned
through sale of goods/services
Gross sales is the total sales, while Net
sales is gross sales minus the trade
discounts
Revenue (Contd.)
Other income is earned through other
sources of investments
Examples: Interest, dividend, royalty,
commission, fee, etc
Sale of Fixed Assets are the revenues
which come into the business when
unused / unwanted assets are sold and
money recovered by the company
Expenses
The cost of earning the revenues are the
expenses
Examples: variable expenses like cost of
manufacture, cost of selling, fixed
expenses like salaries, administrative
expenses
Expenses (Contd.)
Cost of goods consumed
This is the value of the inputs used to
manufacture the final product
It is calculated as
Opening stock
+ Purchases
- Closing Stock
Expenses (Contd.)
Manufacturing expenses
These include all expenses related to plant and
manufacturing operations like power and fuel,
repairs and maintenance, stores consumed,
water consumed, etc
Excise Duty
This is the amount paid to the Govt. as a tax,
before the goods are dispatched from the factory
Expenses (Contd.)
Salaries and Wages
These are the cost of labour and other
staff and will also include all other
employee benefits and amenities.
The other benefits include Provident Fund,
ESI contributions, medical benefits, LTC,
bonus, gratuity, pension, other
superannuation benefits, etc
Expenses (Contd.)
Administrative Expenses
These include office expenses, secretarial costs,
postage and telephones, directors remuneration
and other administrative expenses
Selling Expenses
These include freight, advertising and sales
promotion, commissions and discounts and
other selling and distribution costs
Expenses (Contd.)
Interest
The interest costs consist of interest on long
term loans, debentures, bank loans for working
capital, interest on public deposits and other
loans
Depreciation
This represents a non cash expenditure as it is
only an accounting provision. This amount is not
paid to an outside party
Other expenses
This includes auditors remuneration, petty
expenses, donations, etc
Profit / Loss
The difference between the revenue and
expense is profit
When expense exceeds the revenue, the
company ends up with a loss.
PBID: Profit before Interest and
Depreciation
PBT: Profit before Tax
PAT: Profit after Tax
The Profit Appropriations
Profit after Tax (PAT) is available for
appropriations for
Debenture Redemption Reserve
General Reserve
Dividend on Preference Share
Dividend on Equity Share
Profit or Loss carried over
After appropriating the taxes and
dividends, the balance surplus is
transferred to Reserves and Surplus in the
Balance Sheet
The net loss reduces the Reserves and
Surplus in the Balance Sheet
IF CLAUSES: THIRD
CONDITIONAL
Conditional sentences describe situations that
occur (or do not occur) because of certain
conditions.
In conditional sentences, the clauses can come in
either order.We place a comma after the if clause
if it is comes first.We dont generally place a
comma after the result clause if it comes first.
There are five types of if clause:
TYPES OF IF CLAUSE
Type 0
Type 1
Type 2
Type 3
Mixed Type
Type 3
This is the only type of condition which deals
with past situations. The action mentioned
did not really happen.
*** If + past perfect + would have verb3
e.g. If it had rained yesterday, I would have
stayed at home.
Basic structures used in conditional sentences
Situation If Clause Main Clause
True in the present /
future
Simple present Simple present
Simple future
Untrue in the present /
future
Simple past Would + verb 1
Untrue in the past Past perfect Would + have verb 3
EXERCISES
1. If I ___(be) stronger, I'd help you carry the piano.
2. If we'd seen you, we ___(stop).
3.If we ___(meet) him tomorrow, we'll say hello.
4.He would have repaired the car himself if he
___(have) the tools.
5.If you drop the vase, it ___(break).
6.If you hadnt studied, I ___(not pass) the exam.
7.I wouldnt go to school by bus, if I ___(have) a
driving licence.
8.If she ___(not see) him everyday, shed be
lovesick.
Answers: 1)were 2)would have stopped 3)meet 4)had had 5)will
break 6)would not have passed 7)had 8)didnt see
EXERCISES
1. If I ___(be) stronger, I'd help you carry the piano.
2. If we'd seen you, we ___(stop).
3.If we ___(meet) him tomorrow, we'll say hello.
4.He would have repaired the car himself if he
___(have) the tools.
5.If you drop the vase, it ___(break).
6.If you hadnt studied, I ___(not pass) the exam.
7.I wouldnt go to school by bus, if I ___(have) a
driving licence.
8.If she ___(not see) him everyday, shed be
lovesick.
Answers: 1)were 2)would have stopped 3)meet 4)had had 5)will
break 6)would not have passed 7)had 8)didnt see
WISHES
We often use unreal conditionals to
express regret or sadness. In a similar
way, we use wish + noun clause to
express sadness or a desire for different
situation.
e.g. I wish (that) I had a better job.
(If I had a better job, Id earn more.)
a) wish + would / could
To express a wish about the future.
e.g. I wish you would change your mind about
buying that house.
I wish she could visit us.
b) wish + simple past
To express a wish about the present.
e.g. My wife wishes I helped her with the house
work.
I wish I lived in a big city.
** If only has a meaning similar to that of wish. If only
is followed by a noun clause without that.
e.g. I wish (that) I were good at sports.
If only I were good at sports.
** Use simple past after if only to express a wish
about something that is contrary to fact at present.
e.g. If only we werent so busy.
** Use past perfect after if only to express a wish that
something had happened differently in the past.
e.g. If only I hadnt said that.
Be careful!
Dont confuse if only with only if.
e.g. If only Jerry studied more.
( = I wish he would study more.)
Only if Jerry studied more would he have a
chance of passing.
( = This would be the only way for him to
pass.)
Basic Structures Used in Wish Clauses
situation
Subject + wish
main clause
A wish about
the future
would + verb1
A wish about
the present
verb2
A wish about
the past
verb3
c) wish + past perfect
To express a wish about the past.
e.g. My son wishes he hadnt taken that job.
I wish you had told me about the dance.
** If only has a meaning similar to that of wish. If only
is followed by a noun clause without that.
e.g. I wish (that) I were good at sports.
If only I were good at sports.
** Use simple past after if only to express a wish
about something that is contrary to fact at present.
e.g. If only we werent so busy.
** Use past perfect after if only to express a wish that
something had happened differently in the past.
e.g. If only I hadnt said that.
Be careful!
Dont confuse if only with only if.
e.g. If only Jerry studied more.
( = I wish he would study more.)
Only if Jerry studied more would he have a
chance of passing.
( = This would be the only way for him to
pass.)
EXERCISES
1.What a beautiful view! I wish I (bring) ___ my
camera with me.
2.If only Mr. Blake (not, interrupt) ___ the speaker
all the time, the presentation would have been
enjoyable.
3.I quite like this flat, but I wish the people above
us (not, be) ___ so noisy.
4.If only I (have) ___ better eyesight.I cant read
anything now without my glasses.
5.Later on today, I ---- a cake for tea if we---- all of the necessary
ingredients , of course.
A) would bake/were having
B) will bake/have
C) could have baked/had
D) will have baked/have had
E) were to have baked/would have
6.If people ---- any opium-related drug often enough, they ----
physically dependent, or addicted, to the drug.
A) take/become
B) took/became
C) would take/had become
D) were taking/may become
E) are taking/have become
Answers: 1C-2D-3A-4C-5B-6A
You might also like
- RatiosDocument4 pagesRatiosSoham SubhamNo ratings yet
- A. Li Quidity Ratios:-: 1. Current RatioDocument5 pagesA. Li Quidity Ratios:-: 1. Current RatioGyanam SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Business Finance IBBA 2023Document16 pagesBusiness Finance IBBA 2023mohamed taha elgharibNo ratings yet
- Finance For Non FinanceDocument21 pagesFinance For Non FinanceHari PurwadiNo ratings yet
- Livelihood Evaluation ModuleDocument5 pagesLivelihood Evaluation ModuleSumit TripathiNo ratings yet
- 10 Basic Financial Terms - PDFDocument17 pages10 Basic Financial Terms - PDFkutty kusumbanNo ratings yet
- Basic Financial Terms - PDFDocument16 pagesBasic Financial Terms - PDFgaurav singhNo ratings yet
- ACCA FA1 Practice Question 4Document15 pagesACCA FA1 Practice Question 4arslan.ahmed8179No ratings yet
- For Balance Sheet and Retained Earnings Statement - Follow The Format in The BookDocument7 pagesFor Balance Sheet and Retained Earnings Statement - Follow The Format in The Booknhtsng123No ratings yet
- Bookkeeping & Accounting Chapter 1Document29 pagesBookkeeping & Accounting Chapter 1Joan FerreiraNo ratings yet
- A) Liquidity Ratios: - Current Ratio - Acid Test Ratio - Working CapitalDocument3 pagesA) Liquidity Ratios: - Current Ratio - Acid Test Ratio - Working CapitalFariha MaqboolNo ratings yet
- Record Week 6 - ALKDocument11 pagesRecord Week 6 - ALKLeona Vierman Al-ZuraNo ratings yet
- Week 1: Financial Statement Analysis : Assignment 001Document2 pagesWeek 1: Financial Statement Analysis : Assignment 001Marilou Arcillas PanisalesNo ratings yet
- Ratio - Basics: Liquidity Ratios (Short Term Solvency Ratios)Document5 pagesRatio - Basics: Liquidity Ratios (Short Term Solvency Ratios)Avijash ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Application EngDocument8 pagesApplication EngHassan AmintuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Nature of Financial Accounting Principles: 3.8 Matching ConceptsDocument6 pagesChapter 2: Nature of Financial Accounting Principles: 3.8 Matching ConceptsRavikumar GandhiNo ratings yet
- The Role of BusinessDocument117 pagesThe Role of BusinessEd LappNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet Analysis Sources of FundsDocument4 pagesBalance Sheet Analysis Sources of FundsMohammad Asraf Ul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Accounting: Lect. Dr. Sorina Chiper Lect. Dr. Anca Irina CecalDocument22 pagesAccounting: Lect. Dr. Sorina Chiper Lect. Dr. Anca Irina CecalAlly BogoaNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument63 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisHarsh DalmiaNo ratings yet
- Profit & Loss AccountDocument38 pagesProfit & Loss AccountAbhirup Sengupta100% (1)
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS NotesDocument20 pagesFINANCIAL STATEMENTS NotesAbisellyNo ratings yet
- Chart of AccountsDocument35 pagesChart of AccountsbatowiiseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Chapter 2 10th January 2016Document74 pagesLecture 5 Chapter 2 10th January 2016Miraz AzadNo ratings yet
- Ms.K.GOWRI, Associate Professor in Management Studies, Excel Business SchoolDocument82 pagesMs.K.GOWRI, Associate Professor in Management Studies, Excel Business Schoolvishwavichu100% (1)
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument10 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisAli Gokhan Kocan100% (1)
- Corporate Financial Analysis NotesDocument19 pagesCorporate Financial Analysis NotesWinston WongNo ratings yet
- Engine90 Suuberg Financial StatementsDocument47 pagesEngine90 Suuberg Financial StatementssshreyasNo ratings yet
- The Three Financial Statements:: Profit and Loss (P&L)Document7 pagesThe Three Financial Statements:: Profit and Loss (P&L)Bruno DomingosNo ratings yet
- S Totalshare Dividends PFD Netincome: Debt (Solvency) RatiosDocument3 pagesS Totalshare Dividends PFD Netincome: Debt (Solvency) RatiosFarin KaziNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting TermsDocument12 pagesBasic Accounting TermsNathan DavidNo ratings yet
- Strategic Capital Group Workshop #5: Financial Statement AnalysisDocument39 pagesStrategic Capital Group Workshop #5: Financial Statement AnalysisUniversity Securities Investment TeamNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements Aim at Providing Financial Information About A Business Enterprise To Meet The Information Needs of The DecisionDocument7 pagesFinancial Statements Aim at Providing Financial Information About A Business Enterprise To Meet The Information Needs of The Decisionrupeshdahake8586No ratings yet
- Final Exams Business EnglishDocument10 pagesFinal Exams Business EnglishKhayla CitraNo ratings yet
- Finance For Non FinanceDocument146 pagesFinance For Non Financehithr1No ratings yet
- Lesson 22 - FinanceDocument9 pagesLesson 22 - FinanceStyven KyomenNo ratings yet
- CSC Chapter 2Document85 pagesCSC Chapter 2Afif JaziminNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet PDFDocument7 pagesBalance Sheet PDFGaureesh NaikNo ratings yet
- FIN 201 Chapter 02 TheoryDocument24 pagesFIN 201 Chapter 02 TheoryAhmed ShantoNo ratings yet
- CIE Chapter 1 The Purpose of AccountingDocument22 pagesCIE Chapter 1 The Purpose of AccountingHsu Lae NandarNo ratings yet
- Welcome: Corporate Financial StatementDocument23 pagesWelcome: Corporate Financial StatementTanmay GargNo ratings yet
- Capital & RevenueDocument14 pagesCapital & RevenueNeha KumariNo ratings yet
- Rules of Determining Debit & Credit PDFDocument26 pagesRules of Determining Debit & Credit PDFasadurrahman40100% (1)
- Financial RatiosDocument3 pagesFinancial Ratiospv12356No ratings yet
- WS9-1 31 2013Document37 pagesWS9-1 31 2013University Securities Investment TeamNo ratings yet
- Personal MNGMT ClassDocument49 pagesPersonal MNGMT ClassthemalksNo ratings yet
- LS4-7 (3) MARIANO - EditedDocument16 pagesLS4-7 (3) MARIANO - EditedarnelNo ratings yet
- Finance Interview QuestionsDocument40 pagesFinance Interview QuestionsOmkar JangamNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 1 Interdependence of Major Sectors, Markets and Flows in A Mixed EconomyDocument16 pagesStudy Unit 1 Interdependence of Major Sectors, Markets and Flows in A Mixed EconomyVinny HungweNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document9 pagesWeek 4Christopher LiNo ratings yet
- What Is Meant by ? by by ? By: "Short-Run"Document23 pagesWhat Is Meant by ? by by ? By: "Short-Run"Rafik RafikNo ratings yet
- Ecnomic Notes 1Document26 pagesEcnomic Notes 1ehnzdhmNo ratings yet
- CHP 3.2 Costs and RevenuesDocument19 pagesCHP 3.2 Costs and RevenuesDana MneimneNo ratings yet
- 01 Financial Management and The Firm and Review of Financial Statements (Session 1)Document68 pages01 Financial Management and The Firm and Review of Financial Statements (Session 1)creamellzNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet Analysis PPT at Bec Doms BDocument25 pagesBalance Sheet Analysis PPT at Bec Doms BAARTI GUPTANo ratings yet
- Introduction To AccountingDocument87 pagesIntroduction To AccountingEllegor Eam Gayol (girl palpak)No ratings yet
- Economics Is Too Learn Scarcity (NoDocument7 pagesEconomics Is Too Learn Scarcity (NoFluffy MvNo ratings yet
- Closing Entry For Service Concern BusinessDocument6 pagesClosing Entry For Service Concern BusinessEzekiel LapitanNo ratings yet
- BV2018 - MFRS 5 Non Current Assets Held For Sale and Discontinued OperationsDocument22 pagesBV2018 - MFRS 5 Non Current Assets Held For Sale and Discontinued OperationsAndrew ChongNo ratings yet
- Dampak Penerapan Psak No 50 Dan 55 Revisi 2006 TerDocument21 pagesDampak Penerapan Psak No 50 Dan 55 Revisi 2006 TerAsfa AsfiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Separate and Consolidated FS - Date of AcquisitionDocument21 pagesChapter 2 Separate and Consolidated FS - Date of AcquisitioneiaNo ratings yet
- Chapt 5. Internal ReconstructionDocument12 pagesChapt 5. Internal ReconstructionAnoop Mishra100% (1)
- Comparing Merchandising and Manufakturing CompanyDocument3 pagesComparing Merchandising and Manufakturing CompanyHermanNo ratings yet
- Difficult Level Corpo-Drill3Document4 pagesDifficult Level Corpo-Drill3julsNo ratings yet
- BF SG 12 0203Document31 pagesBF SG 12 0203JOSHUA GABATERONo ratings yet
- Dac 511: Corporate Financial Reporting & Analysis Group 5 Cash Flow AnalysisDocument44 pagesDac 511: Corporate Financial Reporting & Analysis Group 5 Cash Flow AnalysisJan Dave Ogatis100% (1)
- Chapter 12 Exercise E12-7 SOLUTION Fall 2018Document2 pagesChapter 12 Exercise E12-7 SOLUTION Fall 2018Areeba QureshiNo ratings yet
- Ia3 Midterm ExamDocument7 pagesIa3 Midterm ExamJalyn Jalando-onNo ratings yet
- Parcor ExerciseDocument2 pagesParcor ExerciseLacson DennisNo ratings yet
- Final Accounts With Adjustments - Principles of AccountingDocument9 pagesFinal Accounts With Adjustments - Principles of AccountingAbdulla Maseeh100% (1)
- Performance Task BUSINESS-and-ACCOUNTINGDocument3 pagesPerformance Task BUSINESS-and-ACCOUNTINGSallyContiBolorNo ratings yet
- Gaurav Enterprises: College Road KhesmiDocument18 pagesGaurav Enterprises: College Road KhesmiPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Prelimx No AnswersDocument7 pagesPrelimx No Answerscarl fuerzasNo ratings yet
- Ch16 Answer KeyDocument30 pagesCh16 Answer KeyWed Cornel0% (1)
- Accouts ReceivableDocument2 pagesAccouts Receivablerhysakhil catamponganNo ratings yet
- Week 3 PowerpointDocument35 pagesWeek 3 PowerpointAnka MaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1: Introduction To Accounting and BookkeepingDocument37 pagesQuiz 1: Introduction To Accounting and BookkeepingDiana Rose BassigNo ratings yet
- Google Form Model A.A University 1Document96 pagesGoogle Form Model A.A University 1Tesfu HettoNo ratings yet
- Advance Chapter OneDocument15 pagesAdvance Chapter OneAhmedNo ratings yet
- QUIZ1Document2 pagesQUIZ1Samantha CabugonNo ratings yet
- Given The P&L and Balance Sheet Assumptions, Calculate The FollowingDocument37 pagesGiven The P&L and Balance Sheet Assumptions, Calculate The FollowingSuvid0% (1)
- Ratio Analysis For Nissan (2008) : Liquidity Ratios RatiosDocument2 pagesRatio Analysis For Nissan (2008) : Liquidity Ratios Ratiosatifrazzaq007No ratings yet
- Financial Reporting and AnalysisDocument50 pagesFinancial Reporting and AnalysisGeorge Shevtsov83% (6)
- 1T Siñel ACTIVITY7Document10 pages1T Siñel ACTIVITY7Von Jaurdan SinelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NPO BasicsDocument32 pagesChapter 1 NPO BasicsTejasva GargNo ratings yet
- Q3 2019 Standard Industries Financial StatementsDocument29 pagesQ3 2019 Standard Industries Financial StatementsMiguel RamosNo ratings yet
- FY2020 Rhea County Annual Financial ReportDocument232 pagesFY2020 Rhea County Annual Financial ReportNewsChannel 9 StaffNo ratings yet