Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Integumentary System 343
Uploaded by
Spenz TañalasCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Integumentary System 343
Uploaded by
Spenz TañalasCopyright:
Available Formats
1
2
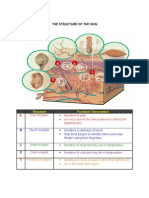
The Integumentary System
3
General Anatomy
The largest organ;
composed of 4 tissue
types
18 square feet
1-2 mm thick
Weight 10 lbs.
Skin and its accessory structures
structure
function
growth and repair
development
aging
disorders
4
Overview
2 Major layers of skin
epidermis is epithelial
tissue only
dermis is a layer of
connective tissue,
nerve & muscle
5
Overview of Epidermis
Stratified squamous
epithelium
Contains no blood vessels
4 types of cells
5 distinct strata (layers) of
cells
6
Cell types of the Epidermis
Keratinocytes--90%
produce keratin
Melanocytes-----8 %
produces melanin pigment
melanin transferred to other cells
with long cell process
Langerhan cells
from bone marrow
provide immunity
Merkel cells
in deepest layer
form touch receptor with sensory
neuron
7
Layers (Strata) of the Epidermis
Stratum corneum
Stratum lucidum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum basale
8
Stratum Basale
Deepest single layer of cells
Called stratum germinativum
Combination of merkel cells,
melanocytes, keratinocytes &
stem cells that divide
repeatedly
9
Stratum Spinosum
8 to 10 cell layers held together
by desmosomes
During slide preparation, cells
shrink and look spiny
Melanin taken in by phagocytosis
from nearby melanocytes
10
Stratum Granulosum
3 - 5 layers of flat dying
cells
Show nuclear
degeneration
Contain dark-staining
keratohyalin granules
Contain lamellar granules
that release lipid that
repels water
11
Stratum Lucidum
Seen in thick skin on
palms & soles of feet
Three to five layers of
clear, flat, dead cells
Contains precursor of
keratin
12
Stratum Corneum
25 to 30 layers of flat
dead cells filled with
keratin and surrounded
by lipids
Continuously shed
Barrier to light, heat,
water, chemicals &
bacteria
Friction stimulates callus
formation
13
Keratinization & Epidermal
Growth
Stem cells divide to produce keratinocytes
As keratinocytes are pushed up towards the
surface, they fill with keratin
4 week journey unless outer layers removed
in abrasion
Psoriasis = chronic skin disorder
cells shed in 7 to 10 days as flaky silvery scales
abnormal keratin produced
14
Skin Grafts
New skin cannot regenerate if stratum
basale and its stem cells are destroyed
Skin graft is covering of wound with piece
of healthy skin
autograft from self
isograft from twin
autologous skin
transplantation of patients skin grown in culture
15
Dermis
Connective tissue layer composed of collagen
& elastic fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages &
fat cells
Contains hair follicles, glands, nerves & blood
vessels
Major regions of dermis
papillary region
reticular region
16
Papillary Region
Top 20% of dermis
Composed of loose CT & elastic fibers
Finger like projections called dermal papillae
Functions
anchors epidermis to dermis
contains capillaries that feed epidermis
contains Meissners corpuscles (touch) & free
nerve endings (pain and temperature)
17
Reticular Region
Dense irregular connective tissue
Contains interlacing collagen and elastic fibers
Packed with oil glands, sweat gland ducts, fat & hair
follicles
Provides strength, extensibility & elasticity to skin
stretch marks are dermal tears from extreme
stretching
Epidermal ridges form in fetus as epidermis conforms
to dermal papillae
fingerprints are left by sweat glands open on ridges
increase grip of hand
18
Skin Color Pigments (1)
Melanin produced in epidermis by melanocytes
same number of melanocytes in everyone, but
differing amounts of pigment produced
results vary from yellow to tan to black color
melanocytes convert tyrosine to melanin
UV in sunlight increases melanin production
19
Skin Color Pigments (2)
Carotene in dermis
yellow-orange pigment (precursor of vitamin A)
found in stratum corneum & dermis
Hemoglobin
red, oxygen-carrying pigment in blood cells
if other pigments are not present, epidermis is
translucent so pinkness will be evident
20
Accessory Structures of
Skin
Epidermal derivatives
Cells sink inward during
development to form:
hair
oil glands
sweat glands
nails
21
Structure of Hair
Shaft -- visible
Root -- below the surface
Follicle surrounds root
external root sheath
internal root sheath
base of follicle is bulb
blood vessels
germinal cell layer
22
Hair Related Structures
Arrector pili
smooth muscle in
dermis contracts
with cold or fear.
forms goose bumps
as hair is pulled
vertically
Hair root plexus
detect hair
movement
23
Hair Growth
Growth cycle = growth stage & resting stage
Growth stage
lasts for 2 to 6 years
matrix cells at base of hair root producing
length
Resting stage
lasts for 3 months
matrix cells inactive & follicle atrophies
Old hair falls out as growth stage begins again
normal hair loss is 70 to 100 hairs per day
24
Hair Color
Result of melanin produced in melanocytes
in hair bulb
Dark hair contains true melanin
Blond and red hair contain melanin with iron
and sulfur added
Graying hair is result of decline in melanin
production
White hair has air bubbles in the medullary
shaft
25
Functions of Hair
Prevents heat loss
Decreases sunburn
Eyelashes help
protect eyes
Touch receptors (hair
root plexus) senses
light touch
26
Glands of the Skin
Specialized exocrine glands found in
dermis
Sebaceous (oil) glands
Sudiferous (sweat) glands
Ceruminous (wax) glands
Mammary (milk) glands
27
Sebaceous (oil) glands
Secretory portion in the dermis
Most open onto hair shafts
Sebum
combination of cholesterol, proteins, fats &
salts
keeps hair and skin from soft & pliable
inhibits growth of bacteria & fungi(ringworm)
Acne
bacterial inflammation of glands
secretions stimulated by hormones at puberty
28
Sudoriferous (sweat)
glands
Eccrine (sweat) glands
most areas of skin
secretory portion in dermis with duct to
surface
regulate body temperature with perspiration
Apocrine (sweat) glands
armpit and pubic region
secretory portion in dermis with duct that
opens onto hair follicle
secretions more viscous
29
Ceruminous glands
Modified sweat glands produce waxy
secretion in ear canal
Cerumin contains secretions of oil and
wax glands
Helps form barrier for entrance of foreign
bodies
Impacted cerumen may reduce hearing
30
Nails
Tightly packed, keratinized cells
Nail body is pink due to underlying
capillaries
Lunula appears white due to thickened
stratum basale in that area
Cuticle (eponychium) is stratum corneum
Nail matrix deep to the nail root is the
region from which the nail growth occurs
Growth is 1mm per week--faster in summer
& on most-used hand
31
Structure of Nails
Tightly packed keratinized
cells
Nail body
visible portion pink due to
underlying capillaries
free edge appears white
Nail root
buried under skin layers
lunula is white due to
thickened stratum basale
Eponychium (cuticle)
stratum corneum layer
32
Nail Growth
Nail matrix below nail root produces growth
Cells transformed into tightly packed keratinized
cells
1 mm per week
33
Types of Skin
Thin skin
covers most of body
thin epidermis (.1 to .15 mm.) that lacks
stratum lucidum
lacks epidermal ridges, has fewer sweat glands
and sensory receptors
Thick skin
only on palms and soles
thick epidermis (.6 to 4.5 mm.) with distinct
stratum lucidum & thick stratum corneum
lacks hair follicles and sebaceous glands
34
General Functions of the
Skin
Regulation of body temperature
Protection as physical barrier
Sensory receptors
Excretion and absorption
Synthesis of vitamin
35
Thermoregulation
Releasing of sweat onto the skin
perspiration & its evaporation lowers body
temperature
Adjusting flow of blood to the body surface
in moderate exercise, more blood brought to
surface helps lower temperature
with extreme exercise, blood is shunted to
muscles and body temperature rises
Shivering and constriction of surface vessels
raise internal body temperature as needed
36
Protection
Physical, chemical and biological barrier
tight cell junctions prevent bacterial invasion
lipids released retard evaporation
pigment protects somewhat against UV light
langerhans cells alert immune system
37
Cutaneous Sensations
Touch, temperature, pressure, vibration,
tickling and some pain sensations arise
from the skin.
38
Excretion and Absorption
Only a minor role is played by the skin
400 mL of water evaporates from it
daily
Small amounts salt, CO2, ammonia and
urea are excreted
Lipid soluble substances can be
absorbed through the skin
39
Transdermal Drug Administration
Method by which drugs in a patch enter the
body
Drug absorption most rapid in areas where
skin is thin (scrotum, face and scalp)
Examples
nitroglycerin (prevention of chest pain from
coronary artery disease)
scopolamine ( motion sickness)
estradiol (estrogen replacement therapy)
nicotine (stop smoking alternative)
40
Synthesis of Vitamin D
Sunlight activates a precursor to vitamin D
Enzymes in the liver and kidneys
transform that molecule into calcitriol
(most active form of vitamin D)
Necessary vitamin for absorption of
calcium from food in the gastrointestinal
tract
41
Age Related Structural Changes
Collagen fibers decrease in number & stiffen
Elastic fibers become less elastic
Fibroblasts decrease in number
Langerhans cells and macrophages decrease in
number and become less-efficient phagocytes
Oil glands shrink and the skin becomes dry
Walls of blood vessels in dermis thicken so
decreased nutrient availability leads to thinner
skin as subcutaneous fat is lost
42
Photodamage
Ultraviolet light (UVA and UVB) both
damage the skin
Acute overexposure causes sunburn
DNA damage in epidermal cells can lead to
skin cancer
UVA produces oxygen free radicals that
damage collagen and elastic fibers and
lead to wrinkling of the skin
43
Skin Cancer
1 million cases diagnosed per year
3 common forms of skin cancer
basal cell carcinoma (rarely metastasize)
squamous cell carcinoma (may metastasize)
malignant melanomas (metastasize rapidly)
most common cancer in young women
arise from melanocytes ----life threatening
key to treatment is early detection watch for
changes in symmetry, border, color and size
risks factors include-- skin color, sun exposure,
family history, age and immunological status
44
Burns
Destruction of proteins of the skin
chemicals, electricity, heat
Problems that result
shock due to water, plasma and plasma protein
loss
circulatory & kidney problems from loss of
plasma
bacterial infection
45
Types of Burns
First-degree
only epidermis (sunburn)
Second-degree burn
destroys entire epidermis & part of dermis
fluid-filled blisters separate epidermis & dermis
epidermal derivatives are not damaged
heals without grafting in 3 to 4 weeks & may scar
Third-degree or full-thickness
destroy epidermis, dermis & epidermal derivatives
damaged area is numb due to loss of sensory
nerves
46
Pressure Sores
Caused by constant deficiency of blood
flow to tissue
Areas affected is skin over bony
prominence in bedridden patients
Preventable with proper care
Other Diseases
Acne
Athletes Foot
Dermatitis
Psoriasis
Vitiligo
Warts
Alopecia Areata
47
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Paronychia
Integration of Faith, Values and
Learning
Psalms 139: 14
I praise you because I am fearfully
and wonderfully made; your works are
wonderful, I know that fully well.
48
QUIZ
1.Give at least 2 Stratas (Layers) of the
Epidermis
2.What is epidermis?
3.Give at least 2 types of cells found in the
Epidermis.
4.Differentiate epidermis from dermis
5.Give two functions of hair
49
6. forms goose bumps as hair is pulled vertically
A. Arrector Pili B. Shaft C. Hair
7. Produces melanin pigments.
A. Melanocytes B. Keratinocytes C. Merkel Cells
8. The skin is ____ square feet
A.17 B. 18 C. 20
50
9.Burn only in the epidermis
A. First Degree B. Second Degree C. Third Degree
10. From the bone marrow and provides immunity
A. Keratinocytes B. Melanocytes C. Langerhan Cells
51
BONUS QUESTION:
It serves AS barriers for the prisoners,
the security of government, and
the cell membrane of our body.
52
Were done!
XD
53
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Service Learning Program Portfolio : SmokingDocument1 pageService Learning Program Portfolio : SmokingSpenz TañalasNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Critique Paper.Document4 pagesCritique Paper.Spenz TañalasNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Biblical Grounds For DivorceDocument1 pageBiblical Grounds For DivorceSpenz TañalasNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Family Centered Matulungin Magalang Katapangan Hospitable MatapatDocument1 pageFamily Centered Matulungin Magalang Katapangan Hospitable MatapatSpenz TañalasNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Teacher EditedDocument2 pagesA Teacher EditedSpenz TañalasNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- AbstractDocument3 pagesAbstractSpenz TañalasNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- John Spencer Tañalas Newton'S Second Law of MotionDocument3 pagesJohn Spencer Tañalas Newton'S Second Law of MotionSpenz TañalasNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- An Instrument For God.Document1 pageAn Instrument For God.Spenz TañalasNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Teacher EditedDocument2 pagesA Teacher EditedSpenz TañalasNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- AbstractDocument3 pagesAbstractSpenz TañalasNo ratings yet
- Riberal ReportDocument9 pagesRiberal ReportSpenz TañalasNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Teacher EditedDocument2 pagesA Teacher EditedSpenz TañalasNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Filip inDocument1 pageFilip inSpenz TañalasNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Forensic 2 - Midterm - Chapter 3 Part 1Document3 pagesForensic 2 - Midterm - Chapter 3 Part 1Ihra CastilloNo ratings yet
- Earwax As An Alternative Specimen For Forensic AnalysisDocument11 pagesEarwax As An Alternative Specimen For Forensic AnalysisNAYARA MOREIRA DAMASCENONo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Biology Questions and Answers Form 2Document41 pagesBiology Questions and Answers Form 2Zubin Jammaa FulaniNo ratings yet
- DLaboratory Actiivty 5 - Integumentary System AnswerDocument6 pagesDLaboratory Actiivty 5 - Integumentary System AnswerSYDNEY JILL ACHAINo ratings yet
- Skin and Body Membranes: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDocument73 pagesSkin and Body Membranes: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeCath TabasNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Physical and Personal Development in The Arts: Quarter 1 The Anatomy of An Artist: Integumentary SystemDocument13 pagesPhysical and Personal Development in The Arts: Quarter 1 The Anatomy of An Artist: Integumentary SystemCarl Benedict RevillaNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Health Assesment Exam ObjectivesDocument119 pagesHealth Assesment Exam ObjectivesMartha TreviñoNo ratings yet
- Sweat Glands Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument72 pagesSweat Glands Anatomy and PhysiologyDr Daulat Ram DhakedNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Pre Board Exam On Forensic CriminalisticDocument16 pagesPre Board Exam On Forensic CriminalisticNoli BencaloNo ratings yet
- Histology of The SkinDocument23 pagesHistology of The Skinshmirtb100% (1)
- Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of DermatologyDocument19 pagesLookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatologyputri theresia50% (2)
- ! Chemical Processes of DigestionDocument9 pages! Chemical Processes of DigestionВася СінчакNo ratings yet
- Apocrine Sweat Glands: E. NailDocument2 pagesApocrine Sweat Glands: E. NailGeenaNo ratings yet
- Criminalistics 3Document4 pagesCriminalistics 3Mohaimen G. EsmailNo ratings yet
- Etas Mcqs 2019 PlusDocument1,569 pagesEtas Mcqs 2019 PlusSally dossNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Part 7Document7 pagesPart 7Anna Marie Ventayen MirandaNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Skin and FunctionDocument2 pagesThe Structure of Skin and FunctionSiti Aliyah KarimNo ratings yet
- Aging Skin Histology Physiology and PathologyDocument6 pagesAging Skin Histology Physiology and PathologyyadNo ratings yet
- Medicaltreatment Discoveryand Hint 01Document17 pagesMedicaltreatment Discoveryand Hint 01Seid MuhammedNo ratings yet
- 01 01Document2 pages01 01sagitawidiyastutiNo ratings yet
- Dermatoven MCQDocument30 pagesDermatoven MCQsajithaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System-GRADE 6 MARCOSDocument41 pagesIntegumentary System-GRADE 6 MARCOSCRISTILE ANN GESMAN100% (1)
- Unit 2 The Integumentary System (2 Hours LEC/3 Hours LAB)Document4 pagesUnit 2 The Integumentary System (2 Hours LEC/3 Hours LAB)Cherry Urmanita BucalingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Integumentary System PDFDocument54 pagesChapter 5 Integumentary System PDFStefanie Henry100% (1)
- Clinical and Dermoscopic Features of Eccrine Poroma Features of Eccrine PoromaDocument2 pagesClinical and Dermoscopic Features of Eccrine Poroma Features of Eccrine PoromajmuhilanNo ratings yet
- Nail FolliclesDocument16 pagesNail FollicleshannaleigmactalNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Science6 ST1 Q2Document2 pagesScience6 ST1 Q2Joseph PederisoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Skin and Its DerivativesDocument39 pagesIntegumentary System: Skin and Its DerivativesGlory Ann BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lookingbill and Marksâ Principles of Dermatology (PDFDrive)Document320 pagesLookingbill and Marksâ Principles of Dermatology (PDFDrive)Alexander Hartono100% (5)
- CRMTC 2NLDocument120 pagesCRMTC 2NLdulce amor herdilesNo ratings yet