Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Financialmanagement 1
Uploaded by
Padma Priya MuthukumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Financialmanagement 1
Uploaded by
Padma Priya MuthukumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Financial
Management
Definition of Financial
Management
Managerial activities which deals with
planning and controlling of firms and financial
sources.
Financial management is an area of financial
decision making, harmonsing individual
motives and enterprise goals.
- Weston Brigham
Scope of financial management
The scope and functions of financial
management is classified in two
categories.
- Traditional approach
- Modern approach
Traditional approach
According to this approach, the scope of the
finance function is restricted to procurement of
funds by corporate enterprise to meet their
financial needs.
The term procurement refers to raising of funds
externally as well as the inter related aspects of raising
funds.
Traditional approach
The inter related aspects are the institutional
arrangement for finance, financial instruments through
which funds are raised and legal and accounting
aspects between the firm and its sources of funds.
In traditional approach the resources
could be raised from the combination of
the available sources.
Limitations of traditional
approach
This approach is confirmed to
procurement of funds only.
It fails to consider an important aspects i.e.
allocation of funds.
It deals with only outside I.e. investors,
investment bankers.
Limitations of traditional
approach
The internal decision making is completely
ignored in this approach.
The traditional approach fails to consider the
problems involved in working capital
management.
The traditional approach neglected the issues
relating to the allocation and management of
funds and failed to make financial decisions.
Modern approach
The modern approach is an analytical way of
looking into financial problems of the firm.
According to this approach, the finance
function covers both acquisition of funds as
well as the allocation of funds to various uses.
Financial management is concerned with the
issues involved in raising of funds and efficient
and wise allocation of funds.
Main Contents of Modern
approach
How large should an enterprise be and how far
it should grow?
In what form should it hold its assets?
How should the funds required be raised?
- Financial management is concerned with
finding answer to the above problems.
Functions of Finance
There are three finance functions
Investment decision
Financing decision
Dividend decision
Investment Decision
Investment decision relates to selections of
asset in which funds will be invested by a firm.
The asset that can be acquired by a firm may
be long term asset and short term asset.
Investment Decision
Decision with regard to long term assets is
called capital budgeting.
Decision with regard to short term or current
assets is called working capital management.
Capital Budgeting
Capital budgeting relates to selection of an
asset or investment proposal which would yield
benefit in future. It involves three elements.
The measurement of the worth of the proposal
Capital Budgeting
Evaluation of the investment proposal in terms
of risk associated with it and
Evaluation of the worth of the investment
proposal against certain norms or standard. The
standard is broadly known as cost of capital
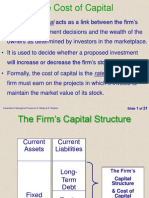
Financing Decision
Determination of the proportion of equity and
dept is the main issue in financing decision.
Once the best combination of debt and equity is
determined, the next step is raising appropriate
amount through available sources.
Working Capital Management
Working capital management or current asset
management is an important part of investment
decision.
Proper management of working capital ensures
firms liquidity and solvency.
A conflict exists between profitability and liquidity
while managing current asset.
Working Capital Management
If a firm does not invest sufficient funds in
current assets it may become illiquid and may
not meet its current obligations.
The financial manager should develop proper
techniques of managing current assets so that
neither insufficient nor unnecessary funds are
invested in current assets.
If the current asset are large, the firm would
lose its profitability and liquidity.
Management of Working Capital
The management of working capital has two
aspects.
- Efficient management of individual current
asset such as cash, receivable and inventory.
- Overview of working capital management and
Financing Decision
Financing decision is concerned with the
financing mix or capital structure.
The mix of debt and equity is known as capital
structure.
Dividend Decision
A firm distribute all profits or retain them or
distribute a portion and retain the balance with
it.
Which course should be allowed? The decision
depends upon the preference of the
shareholders and investment opportunities
available to the firm.
Dividend Decision
Dividend decision has a strong influence on the
market prize of the share.
So the dividend policy is to be determined in
terms of its impact on shareholders value.
The optimum dividend policy is one which
maximizes the value of shares and wealth of
the shareholders.
Dividend Decision
The financial manager should determine the
optimum pay out ratio I.e. the proportions of net
profit to be paid out to the shareholders.
The above three decisions are inter related. To
have an optimum financial decision the three
should be taken jointly.
Objectives of financial
management
The term objective refers to a goal or decision
for taking financial decisions.
Profit maximisation
Wealth maximisation
Profit maximisation
The term profit maximisation is deep rooted in
the economic theory.
It is need that when firms pursue the policy of
maximising profits.
Societys resources are efficiently utilised.
Profit maximisation
The firm should undertake those actions that
would profits and drop those actions that would
decrease profit.
The financial decisions should be oriented to the
maximisation of profits.
Profit provides the yardstick for measuring
performance of firms.
Profit maximisation
It makes allocation of resources to profitable
and desirable areas.
It also ensures maximum social welfare.
Wealth maximisation
Wealth maximisation or net present value
maximisation provides an appropriate and
operationally feasible decision criterion for
financial management decisions.
Sources of Finance
Capital required for a business can be classified
under two main categories, viz.,
- Fixed Capital, and
- Working Capital.
- every business needs funds for two purposes.
- for its establishment and to carry out its day-to-
day operations.
Sources of Finance
Long term funds are required to create production
facilities through purchase of fixed assets such as
- plant,
- machinery,
- land,
- building,
- furniture, etc.
Sources of Finance
- Investment in these asset represent that part of
firms capital which is blocked on permanent or
fixed basis and is called fixed capital.
Funds are also needed for short-term purposes
for the purchase of raw materials, payment of
wages and other day to day expenses, etc. These
funds are known as working capital.
Sources of Finance/Funds
In our present day economy, finance is defined
as the provision of money at the time when it is
required.
Every enterprise, whether big or medium or
small, needs finance to carry on its operations
and to achieve its targets.
Sources of Finance/Funds
In fact finance is so indispensable today that is
rightly said that it is the life blood of enterprise.
With out adequate finance, no enterprise can
possibly accomplish its objectives.
In every concern there are two methods of raising
finance, viz.,
- Raising of owned capital,
- Rising of borrowed capital
Sources of Finance/Funds
The financial requirements may be for a long term, medium term or short term.
Financial Requirements
Short-Term Medium-Term Long-Term
Bank Credit
Customer advances
Trade Credit
Issue of Debentures
Issue of Preference shares
Bank Loan
Public deposit / Fixed deposit
Loans from financial institutions
Issue of shares
Issue of Debentures
Ploughing back of
profits
Loan from
spec.financial
institutions
Issue of shares
The companys owned capital is split into
large number of equal parts,such a part
being called a share.
The person holding the share as shareholder
and becomes part-owner of the company.
For this reason, the capital so raised is known
as owned capital and the shares are called
ownership securities.
Issue of shares
The share capital of the company is ideal
for meeting the long term requirements.
It need not be paid back to the shareholders
within the life time of the company.
The only exception is the sum raised by the
issue of redeemable preference shares.
Types of shares
A public company can issue two types of
share.
Equity share
Preference share
Equity share
Equity share has number of special
features
The dividend on these shares are paid after the
dividend on preference share has been paid.
The rate of dividend depends upon the amount
of profits available and the intention of
directors.
Equity share
The Equity shareholders have the chance
of earning good dividends in times of
prosperity and run the risk of earning
nothing in times of adversity.
The equity shareholders have a residual claim
on the companys asset in case of liquidation.
The company is controlled by the equity
shareholders and they are entitled to vote in
the meetings of the company.
Preference shares
Preference shares are those which carry
preferential right over other class of shares
with regard to payment of dividend and
repayment of capital.
The rate of dividend on preference share is a
fixed one.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Dimensional Fund Advisors 2002 Case SolutionDocument10 pagesDimensional Fund Advisors 2002 Case SolutionRohit Kumar80% (5)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Chapter 5 Final Income Taxation Summary BanggawanDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Final Income Taxation Summary Banggawanyours truly,100% (3)
- Question of Chapter 2Document7 pagesQuestion of Chapter 2carlos chavesNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Cash and Cash Equivalents ReviewerDocument4 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents ReviewerEileithyia KijimaNo ratings yet
- ch6 100917000852 Phpapp01Document24 pagesch6 100917000852 Phpapp01Aakansha SinghNo ratings yet
- Measurement of CostDocument20 pagesMeasurement of CostPadma Priya MuthukumarNo ratings yet
- Financialmanagement 1Document39 pagesFinancialmanagement 1Padma Priya MuthukumarNo ratings yet
- P 4 110920142923 Phpapp02Document24 pagesP 4 110920142923 Phpapp02Vishal VegadaNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Management: A PerspectiveDocument21 pagesWorking Capital Management: A PerspectiveSanthosh Philip GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Share ValuationDocument9 pagesShare ValuationAsad TahirNo ratings yet
- Accounting ProcessDocument25 pagesAccounting ProcessPadma Priya MuthukumarNo ratings yet
- Share ValuationDocument9 pagesShare ValuationAsad TahirNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Company AccountsDocument9 pagesChapter - Company AccountsPadma Priya MuthukumarNo ratings yet
- Subsidiary BooksDocument30 pagesSubsidiary BooksanuradhaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CompaniesDocument32 pagesIntroduction To CompaniesPadma Priya MuthukumarNo ratings yet
- Std11 Acct EMDocument159 pagesStd11 Acct EMniaz1788100% (1)
- Final AccountsDocument43 pagesFinal AccountsPadma Priya Muthukumar100% (1)
- Std10 Maths EM 1Document180 pagesStd10 Maths EM 1eezeebzNo ratings yet
- Ping BricksDocument2 pagesPing BricksPadma Priya MuthukumarNo ratings yet
- Accounting ProcessDocument25 pagesAccounting ProcessPadma Priya MuthukumarNo ratings yet
- Std10 English 2Document117 pagesStd10 English 2Venkat RaamNo ratings yet
- Std10 English 1Document75 pagesStd10 English 1gvasangNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentPadma Priya MuthukumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Computation of Total Income and Tax PayableDocument8 pagesChapter 8 Computation of Total Income and Tax PayablePrabhjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Bharti Airtel India AssignmentDocument21 pagesBharti Airtel India Assignmentwintoday01No ratings yet
- IDBIDocument10 pagesIDBIArun ElanghoNo ratings yet
- Definition of Capital BudgetingDocument6 pagesDefinition of Capital Budgetingkaram deenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Weighing Net Present Value and Other Capital Budgeting Criteria QuestionsDocument21 pagesChapter 13 - Weighing Net Present Value and Other Capital Budgeting Criteria QuestionsAhmad RahhalNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Financial Management in The WorkshopDocument27 pagesTopic 6 Financial Management in The Workshopjohn nderitu100% (1)
- R Money Sip Presentation by Ravish Roshandelhi 1223401016149009 9Document19 pagesR Money Sip Presentation by Ravish Roshandelhi 1223401016149009 9Yukti KhoslaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic & Industrial AnalysisDocument10 pagesMacroeconomic & Industrial AnalysisFrans AlfianNo ratings yet
- The Deeper The Love, The Deeper The Hate 2017Document7 pagesThe Deeper The Love, The Deeper The Hate 2017Luquiitas LasernaNo ratings yet
- FM4, Exercises 17, Black-ScholesDocument54 pagesFM4, Exercises 17, Black-Scholeswenhao zhouNo ratings yet
- Indiabulls Housing Finance Annual Report Fy 2019 20 0253611001597460978 PDFDocument300 pagesIndiabulls Housing Finance Annual Report Fy 2019 20 0253611001597460978 PDFArun KanagarajNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Financial Statements & Decision MakingDocument31 pagesTopic 2 Financial Statements & Decision MakingajayNo ratings yet
- A Study On Carbon CreditDocument38 pagesA Study On Carbon CreditSaurabh Jhaveri100% (1)
- Samsung The Fast Adoption StrategyDocument14 pagesSamsung The Fast Adoption StrategyAminul Daffodil100% (1)
- Internship Report of Sjibl-GbDocument45 pagesInternship Report of Sjibl-GbsaminbdNo ratings yet
- Trading Psychology ManualDocument19 pagesTrading Psychology ManualOgechinwankwo100% (1)
- Lec 4 Optimal Portfolio Selection A Few Analytical Results 20170923102633 PDFDocument12 pagesLec 4 Optimal Portfolio Selection A Few Analytical Results 20170923102633 PDFMassimiliano RizzoNo ratings yet
- BondsDocument12 pagesBondsSai Hari Haran100% (1)
- Business Plan For SalonDocument34 pagesBusiness Plan For Salonvandanam1367% (6)
- Edelbrock Gets 40 Days in Kalida Theft: The Delphos HeraldDocument16 pagesEdelbrock Gets 40 Days in Kalida Theft: The Delphos HeraldThe Delphos HeraldNo ratings yet
- Delegate List - TradeDocument145 pagesDelegate List - TradeFummy Omnipotent67% (3)
- Chapter 6 Net Present ValueDocument20 pagesChapter 6 Net Present ValueAhmed AlfaitoryNo ratings yet
- 04 Quiz 1 - Ca2Document8 pages04 Quiz 1 - Ca2Jen DeloyNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 2 - Alaeto Henry Emeka (2020) - Determinants - of - Dividend - Polic - NigeriaDocument31 pagesJurnal 2 - Alaeto Henry Emeka (2020) - Determinants - of - Dividend - Polic - NigeriaGilang KotawaNo ratings yet
- Ethics Professionalism and Corpoarate GoDocument26 pagesEthics Professionalism and Corpoarate GoRajkumar VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- BCC BR 112 14Document4 pagesBCC BR 112 14Nitesh varmaNo ratings yet