Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DC Motors Starters and Breaking Methods
Uploaded by
RukkuArun0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views25 pagesdc motor
Original Title
DC Machines Week
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdc motor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views25 pagesDC Motors Starters and Breaking Methods
Uploaded by
RukkuArundc motor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 25
KL3073
DC Motors Starters and Breaking
Methods
DC MOTOR STARTERS
In order for a dc motor to function
properly it must have some special
control and protection equipment
The purposes of this equipment are.
To protect the motor against damage
due to short circuits in the equipment
from long-term overloads
from excessive starting currents
To provide a convenient manner in which
to control the operating speed of the
Motor
DC Motor Problems on Starting
It must be protected from physical
damage during the starting period.
At starting conditions, the motor is not
turning, and so E
A
= 0 V.
The full-load current of this motor is:
Since the internal resistance of a normal
dc motor is very low a very high current
flows.
This current is over many times the
motor's rated full-load current. This may
damage the motor.
Solution to the problem of excess current
Insert a starting resistor in series with the
armature to limit the current flow.
Resistor must not be in the circuit
permanently.
because of: excessive losses
torque speed characteristic to
drop
Resistor must be removed again as the
speed of the motor builds up.
Solution to the problem of excess current
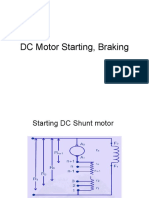
Shunt motor with an extra starting resistor.
In designing the starter it is important to
properly pick the size and number of
resistor segments.
Shuts the resistor bypass contacts at the
proper time
shunt motor with a
starting resistor
Selected Rstart so that the current flow
equals say twice the rated current.
the increasing EA decreases the IA in the
motor.
When the IA falls to rated current, a
section of the starting resistor must be
taken out to increase the starting current
back up to 200 percent of rated current
the increasing EA decreases the IA in the
motor.
Repeat until all segments are out
Solution to the problem of excess current
How many steps are required to
accomplish the current limiting?
R
tot
as the original resistance in the
starting circuit
The total resistance left in the starting
circuit after stages 1
Initial starting resistance must be
resistance R, must be switched out at 1
st
stage
How many steps are required to
accomplish the current limiting?
After switching that part of the resistance
out, the armature current must jump to
Equating previous 2 equation
By direct extension, the resistance left in
the circuit after the nth stage is switched
out is
How many steps are required to
accomplish the current limiting?
At the boundary where R
A
= R
tot,n
Equating previous 2 equation
Solving for n yields
Example
Example 6-7. Figure 6-24 shows a 100-hp 250-
V 350-A shunt de motor with an armature
resistance of 0.05 ohms. It is desired to design
a starter circuit for this motor which will limit the
maximum starting current to twice its rated
value and which will switch out sections of
resistance as the armature current falls to its
rated value.
(a) How many stages of starting resistance will
be required to limit the current to the range
specified?
(b) What must the value of each segment of the
resistor be? At what voltage should each stage
of the starting resistance be cut out?
DC Motor Starting Circuits
Devices commonly used in motor-control
circuits
DC Motor Starting Circuits
One common motor-starting circuit
DC Motor Starting Circuits
One common motor-starting circuit
THE WARD-LEONARD SPEED
CONTROLLER
The speed of a separately excited, shunt, or
compounded dc motor can be varied in one of
three ways:
by changing the field resistance,
changing the armature voltage, or
changing the armature resistance.
THE WARD-LEONARD SPEED
CONTROLLER
figure below shows an ac motor serving as a
prime mover for a dc generator, which in turn is
used to supply a dc voltage to a dc motor by
changing the field resistance.
This system is called Ward-Leonard system.
THE WARD-LEONARD SPEED
CONTROLLER
Controlling the field current of the dc generator
armature voltage can be controlled
This allows the motor's speed to be smoothly
varied between a very small value and the base
speed.
Higher speed can be achieved by reducing the
motor's field current
THE WARD-LEONARD SPEED
CONTROLLER
if the field current of the generator is reversed,
polarity of generated voltage also reversed.
This reverse the motor's direction of rotation.
If the torque or the speed alone of the motor
reverses while the other quantity does not, then
the machine serves as a generator.
The operating range of a Ward-
Leonard motor-control system
SOLID-STATE SPEED CONTROLLERS
The average voltage applied to the armature of
the motor can be controlled by fraction of the
time the supply voltage is applied to the
armature.
fast on and off of the supply can be done by
modern solid state devices such as SCR.
A simple dc armature voltage controller circuit
using SCR is shown below
A two-quadrant solid-state dc motor controller
SOLID-STATE SPEED CONTROLLERS
A more advanced circuit capable of supplying
an armature voltage with either polarity is
shown below. This armature voltage control
circuit can permit a current flow out of the
positive terminals of the generator, so a motor
with this type of controller can regenerate
A 4-quadrant solid-state dc motor controller
DC MOTOR BREAKING METHODS
There are three kinds of electric breaking, namely:
Rheostatic or dynamic breaking
Plugging and
Regenerative breaking
Electric breaking for shunt motors
The armature of the shunt motor is disconnected
from the supply and it is connected across a
variable resistor R.
The field winding is kept undisrupted and this
breaking is controlled by varying the series
resistor R.
This method used generator action.
Rheostatic or dynamic breaking
Electric breaking for shunt motors
the armature terminals are reversed to rotate the
motor in the reverse direction
V
T
and the back E
b
start acting in the same
direction.
Plugging or Reverse Breaking
Electric breaking for shunt motors
In regenerative breaking, E
b
is greater than Vt.
The direction of I
A
and the armature torque Tb
are reversed
Regenerative Breaking
Electric breaking for series motors
In this method the motor is disconnected from
supply. The field connection is reversed and the
motor is connected through a variable resistance
R.
Rheostatic or dynamic breaking
Electric breaking for series motors
it is similar to that of shunt motor.
Plugging or Reverse Current Breaking
You might also like
- DC Motors Starters and Breaking MethodsDocument25 pagesDC Motors Starters and Breaking Methodskrishnareddy_chintalaNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Drives Unit-II GuideDocument32 pagesDC Motor Drives Unit-II GuidesangsangicnuNo ratings yet
- 3 - Starter, Braking, EtcDocument22 pages3 - Starter, Braking, EtcAtul Jaysing PatilNo ratings yet
- Question No 1: Speed Control of DC MotorDocument10 pagesQuestion No 1: Speed Control of DC MotorProxima YusNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document31 pagesLecture 6amanuel abrehaNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC MotorDocument19 pagesSpeed Control of DC MotorVijaya LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Electrical interview questions on motor principles and power electronicsDocument26 pagesElectrical interview questions on motor principles and power electronicsNavdeepNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC MotorDocument18 pagesSpeed Control of DC Motorkrishnareddy_chintalaNo ratings yet
- Class DutyDocument58 pagesClass DutyHarsha AnantwarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDeepak BansalNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 SSDDocument85 pagesUnit - 2 SSDAkshat SaxenaNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Starting, Braking Aug18Document25 pagesDC Motor Starting, Braking Aug18Ashwini Singh100% (1)
- Chapter-2: Dynamic Behavior of Electric DrivesDocument43 pagesChapter-2: Dynamic Behavior of Electric DrivesMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- DC Motor S: Anand 08338958770Document79 pagesDC Motor S: Anand 08338958770Rohit AvasthiNo ratings yet
- Guerra, John Nichol N. Bsme 3C (Ac and DC Ass.2)Document22 pagesGuerra, John Nichol N. Bsme 3C (Ac and DC Ass.2)John Nichol GuerraNo ratings yet
- Electric Drives ControlDocument29 pagesElectric Drives ControlNebyou DanielNo ratings yet
- Regenerative Braking of Induction MotorDocument27 pagesRegenerative Braking of Induction MotorcoolkannaNo ratings yet
- Motors and Motor StartersDocument32 pagesMotors and Motor StartersbmshivakumarNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor BrakingDocument26 pagesInduction Motor BrakingAshwini Singh100% (3)
- Unit 7electric TractionDocument35 pagesUnit 7electric TractionVinod KohliNo ratings yet
- Em 1 TestingDocument13 pagesEm 1 TestingAravindNo ratings yet
- Synchronous MotorDocument5 pagesSynchronous Motornaga531No ratings yet
- Power Supply Description:: The Power Supply Circuit Comprises of Four Basic PartsDocument19 pagesPower Supply Description:: The Power Supply Circuit Comprises of Four Basic PartsEr. Piush Jindal100% (1)
- AC motors starting and protection guideDocument32 pagesAC motors starting and protection guideTarek MohamedNo ratings yet
- AST 117 - Industrial Power ElectronicsDocument16 pagesAST 117 - Industrial Power ElectronicsKrieczek DoyuganNo ratings yet
- Mcqs (Transformers) : Electrical Machine Final RevisionDocument5 pagesMcqs (Transformers) : Electrical Machine Final Revisionmoooo yii trrhjNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 & 3 EM-I (REE 402) : DC MachinesDocument48 pagesUnit 2 & 3 EM-I (REE 402) : DC MachinesAnanya Srivastava100% (1)
- DC MOTOR STARTER GUIDEDocument25 pagesDC MOTOR STARTER GUIDESrinivasan PrakashNo ratings yet
- DC MACH - Chapter 5Document53 pagesDC MACH - Chapter 5marryjohnopalla05No ratings yet
- Motor StartersDocument14 pagesMotor StartersairamNo ratings yet
- IDS NewDocument128 pagesIDS NewShahbaz Ali100% (1)
- How Is Ac Voltage Produced?Document4 pagesHow Is Ac Voltage Produced?Mariappan NaNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Drive ChaacteristicsDocument26 pagesUnit Ii Drive Chaacteristicssaravanakmar vNo ratings yet
- Fig. 2 (A) Self Excited Induction GeneratorDocument7 pagesFig. 2 (A) Self Excited Induction GeneratorLaxmikant BagaleNo ratings yet
- Purpose of Variable Frequency DrivesDocument25 pagesPurpose of Variable Frequency DrivesGaurav MobarNo ratings yet
- Motor StartersDocument9 pagesMotor Startersanon_896479742No ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed Control: Bayan University For Science & TechnologyDocument12 pagesDC Motor Speed Control: Bayan University For Science & TechnologyAltayeb AbdulhameedNo ratings yet
- EE 448 Laboratory Experiment 4 Introduction To DC MotorsDocument10 pagesEE 448 Laboratory Experiment 4 Introduction To DC MotorsjegjegtNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Motor Drives: Open Loop V/F Control of Synchronous MotorDocument11 pagesSynchronous Motor Drives: Open Loop V/F Control of Synchronous MotorSaish Dalvi100% (1)
- ExcitationsysDocument5 pagesExcitationsysDan GrayNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines I: Week 13: Ward Leonard Speed Control and DC Motor BrakingDocument15 pagesElectrical Machines I: Week 13: Ward Leonard Speed Control and DC Motor Brakingmansoor.ahmed100No ratings yet
- DC Motors Starting MethodsDocument6 pagesDC Motors Starting MethodsSai Teja KondraNo ratings yet
- ExcitationRDocument4 pagesExcitationRDan GrayNo ratings yet
- ExcitationDocument4 pagesExcitationDan GrayNo ratings yet
- Ain Shams University Faculty of Engineering Chep Energy SeniorDocument12 pagesAin Shams University Faculty of Engineering Chep Energy Seniorbanana_26No ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC MotorsDocument27 pagesSpeed Control of DC MotorsBabuKannanNo ratings yet
- Starting Methods of A DC MotorDocument8 pagesStarting Methods of A DC Motoragreykato100% (1)
- Motorola Application NotesDocument10 pagesMotorola Application Notesvasudeva yasasNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed System Modeling (Final Report)Document41 pagesDC Motor Speed System Modeling (Final Report)Khubaib Ahmed80% (5)
- DC Motors: - Construction Very Similar To A DC GeneratorDocument35 pagesDC Motors: - Construction Very Similar To A DC GeneratorDeepak Ganachari100% (1)
- Unit V: DC MotorsDocument28 pagesUnit V: DC Motorskrishnareddy_chintalaNo ratings yet
- Starting and Braking of Induction MotorDocument15 pagesStarting and Braking of Induction MotorSOURABH MONGRANo ratings yet
- DC Serv O-Mo TOR: Engr. M.BILALDocument28 pagesDC Serv O-Mo TOR: Engr. M.BILALBilalNo ratings yet
- The Advantages and Hazards of DC MotorsDocument6 pagesThe Advantages and Hazards of DC MotorsGalco IndustrialNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Bicotest Model-T272-US-A4v2 PDFDocument2 pagesBicotest Model-T272-US-A4v2 PDFJusril HidayatNo ratings yet
- Medical Student Amnesia USMLE Step 1 - Flash Cards by CueFlashDocument13 pagesMedical Student Amnesia USMLE Step 1 - Flash Cards by CueFlashMuhammad Farhan KhaliqNo ratings yet
- Ig2 of Bikas 00691520 x123Document20 pagesIg2 of Bikas 00691520 x123Engr. Imran Hasan Pathan100% (4)
- LDRRMPDocument39 pagesLDRRMPMarlon VillenaNo ratings yet
- 2018-06-21 Calvert County TimesDocument24 pages2018-06-21 Calvert County TimesSouthern Maryland OnlineNo ratings yet
- Re Insurance BrochureDocument12 pagesRe Insurance BrochureQBE European OperationsNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Notebook: Aquatic Ecology and ResourcesDocument7 pagesLaboratory Notebook: Aquatic Ecology and ResourcesAireen Diamsim MaltoNo ratings yet
- Homemade Litmus Paper ExperimentDocument3 pagesHomemade Litmus Paper ExperimentEmmanuelle NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Bams 1st Rachna Sharir Joints and Their Classification 16-05-2020Document15 pagesBams 1st Rachna Sharir Joints and Their Classification 16-05-2020Sanjana SajjanarNo ratings yet
- Advanced GeomorphologyDocument30 pagesAdvanced GeomorphologyCarlos Letras100% (3)
- Bureau Corrections ManualDocument55 pagesBureau Corrections ManualEugene UCNo ratings yet
- HVAC Control ModuleDocument2 pagesHVAC Control ModuleData TécnicaNo ratings yet
- Kelas 7 Bahasa Inggris Semester GenapDocument8 pagesKelas 7 Bahasa Inggris Semester GenapTaty ErdianingsihNo ratings yet
- Aafreen Project Report SIPDocument19 pagesAafreen Project Report SIPshubham moonNo ratings yet
- Single and Double Volute Casing - RodeltaDocument3 pagesSingle and Double Volute Casing - Rodeltamasood_me60No ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument16 pagesMini ProjectMr. Y. RajeshNo ratings yet
- Cherry Circle Room Main MenuDocument8 pagesCherry Circle Room Main MenuAshok SelvamNo ratings yet
- Is.1446.2002 Class of Dang GoodsDocument88 pagesIs.1446.2002 Class of Dang GoodsMD ParthiNo ratings yet
- Isc BUX82/83: Isc Silicon NPN Power TransistorsDocument2 pagesIsc BUX82/83: Isc Silicon NPN Power TransistorsCarlos HCNo ratings yet
- Ethics Case StudyDocument5 pagesEthics Case StudyCian MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument39 pagesBiochemistryapi-290667341No ratings yet
- ICAEW Professional Level Business Planning - Taxation Question & Answer Bank March 2016 To March 2020Document382 pagesICAEW Professional Level Business Planning - Taxation Question & Answer Bank March 2016 To March 2020Optimal Management SolutionNo ratings yet
- Bladder StonesDocument20 pagesBladder StonesRiean AuliaNo ratings yet
- I-WEB - Com.vn Manual 498031910Document94 pagesI-WEB - Com.vn Manual 498031910IBJSC.comNo ratings yet
- Memoir of Glicerio Abad - 2005 - v2Document6 pagesMemoir of Glicerio Abad - 2005 - v2Jane JoveNo ratings yet
- Bolivia CSRDocument1 pageBolivia CSRDaniel Andrade SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Event Details Report - Algoma SteelDocument66 pagesEvent Details Report - Algoma SteelThe NarwhalNo ratings yet
- Endangered Species Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesEndangered Species Lesson PlanIrena Stamenova100% (1)
- Bio Brain Review Q S PDFDocument22 pagesBio Brain Review Q S PDFtehilashiftehNo ratings yet
- Water Plant SOPDocument6 pagesWater Plant SOPIndrie AgustinaNo ratings yet