Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Complete Oil Analysis
Uploaded by
Abhishek Prakash SrivastavaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Complete Oil Analysis
Uploaded by
Abhishek Prakash SrivastavaCopyright:
Available Formats
ANALYSIS & TESTING
OF
FUEL OIL
LUB OIL
INSULATING OIL
&
HYDRAULIC FLUIDS
DIFFERENT TYPES OF OILS USED IN
POWER PLANT
FUEL OIL
LUBRICATING OIL
FIRE RESISTANT FLUID
INSULATING OIL or TRANSFORMER
OIL
FUEL OIL
FUEL OILS BEING USED AT POWER STATIONS
- LDO
- HSD
- FO (FURNACE OIL)
- LSHS (LOW SULPHUR HEAVY STOCK)
LDO & HSD
LOW VISCOSITY
LOW FLASH POINT
COSTLY
NO NEED OF HEATING
NO STEAM REQUIRED
CV ~10720 KCAL/KG
IDEAL FOR STARTING OF BOILER FROM
COLD
FURNACE OIL
MUCH HIGHER VISCOSITY THAN LDO OR HSD
REQUIRES HEATING AT THE TIME OF UNLOADING &
PUMPING
PREHEATING UPTO 110 DEGC FOR USE
BETTER ATOMISED WITH STEAM
COMPARATIVELY CHEAPER THAN LDO & HSD
CV ~ 10270 KCAL/KG
**LSHS- HIGHLY VISCOUS, CHEAPER THAN FO
Parameters Monitored of Fuel oil
Standard: IS 1593/1971, Grades: LV-MV-HV
API gravity: 12 sp. 0.986 at 15 degc
Viscosity- 80-120-370 cst at 50 degc
Flash point- 66 degC (min)
Pour point
FO Monitoring
GCV: 10270 kcal/kg
Total Sulphur : 3.5-4.0-4.5% by weight
Water Content
Ash content
Sediments
FUNCTIONS OF FO
Coal fired units contains oil burners having
capacity of 15-20%
Ignition energy to light off coal burners
Stabilization of coal flame at low loads
Safe and reliable heat input source during
light up of boiler
PROPERTIES OF LUB OIL TO BE CHECKED
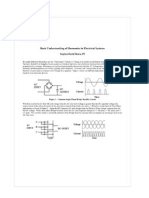
KINEMATIC VISCOSITY: The Redwood
viscometer determines the time usually
expressed in sec required for a standard
volume of oil to flow through a standard
orifice at specified pr. & temp.
Kinematic viscosity= const. x time
Moisture content: By Crackle test or
by Karl Fischer titration method
Mechanical Impurities: A fixed
volume of oil is dissolved in a solvent like
Toluene or Pet. Ether and passed through
pre weighed 45 micron filter paper.
MI is determined from difference in weight
Foaming Characteristics
Copper strip corrosion
Emulsion Characteristics
Cloud and pour point
Acidity
Oxidation Characteristics
Flash point
PROPERTIES OF LUBRICATING OIL
TO BE CHECKED
LIMIT OF DIFFERENT LUBE OIL
S.No Equipment Stage Name of
oil
Moisture
(ppm)
MI
(ppm)
Viscosity
(cst)
1 MOT/BFP/
ID/FD
I SERVO
PRIME-32
150 50 27.6-36.3
2 PA FAN I SP-68 150 50 60.8-79.2
3 CT
FAN/ASPH
I SERVO
SYSTEM-121
200 500 118-124
4 MILL GEAR
HOUSING
I SERVO
MESH SP-
320
1000 0.1% 320-350
LIMIT OF DIFFERENT LUBE OIL
S.N
o
Equipment Stage Name of
oil
Moisture
(ppm)
MI
(ppm)
Viscosity
(cst)
1 TURBINE II DAPHANE
SUPER
TURBINE-46
100 50 41.4-50.6
2 PA
FAN/SAPH
II SERVO
CYCLE-660
100 50 615-680
3 FD/ID II SERVO PM-
68
100 50 64-72
4 TDBFP BRG
& COUPLING
II SERVO PM-
46 T
300 50 43-48
5 MDBFP II SERVO
SYSTEM-
HLP32
300 50 29-39
6 MAIN MILL
LUBE UNIT
II SERVO
SYSTEM-460
500 500 440-500
FIRE RESISTANT FLUID
FIRE RESISTANT FLUID
FRF is known as phosphate ester
hydraulic fluids.
They are used in 500 MW turbine
control system
They are fire resistant, exhibit
good resistance to oxidation
hydrolysis, adequate air release
and low foaming properties when
compared to petroleum oil.
PARAMETERS OF FRF MONITORED
Water Content-Potential for Hydrolysis
Fluid Cleanliness/ Particle Count
Total Acid No-Hydrolysis that has
occurred
Mineral oil content
Air release
Viscosity
Resistivity
FRF POLISHING UNIT
Mechanical filter and strainers
removes mechanical impurities
Fuller earth and activated alumina
treatment to remove acidic ions. They
acts as ion exchangers.
Air drier or desiccant breather to
remove moisture-moisture filter.
LIMIT OF DIFFERENT PARAMETERS
S.N Parameter Test Method Permissible
Limit
1 Viscosity ASTM D-445 30-50 cst
2 Acid Number ASTM D-974 0.2 mg
KOH/gm
3 Water Content ASTM D-1744 1500 ppm
4 Sediments AFNORE-48652 5 mg/100 ml
5 Particle Count ASTMF-662/322 Class 16/13
INSULATING OIL
USE OF INSULATING OIL
Insulating oils are derived from mineral oil.
Insulating oils are used in transformers,
reactors switchgear and cables.
It quenches arcs when switching.
Prevents glow discharge.
Act as a cooling agent.
AGEING OF OIL DURING OPERATION
Increased temperature.
Absorption of gases mainly oxygen.
Absorption of water from atmosphere.
Ageing through contacts with metal plates
like copper and iron
High temperature decomposition.
Dielectric breakdown test.
Dielectric dissipation factor or tan-d.
Specific resistances.
Water content test.
Acidity Test.
PARAMETERS OF INSULATING OIL
MONITORED
RECONDITIONING OF INSULATING
OIL
Reconditioning of oil means removal of water
and solid particles from oil.
This is done by using several available type of
filters, centrifuge and vacuum dehydrators.
Filter removes mechanical impurities.
The centrifuge is used when there is large
amount of water or other contamination present.
Vacuum dehydrator removes water and
dissolved gases.
Condition Monitoring of HV
Transformers and Reactors by
DGA technique
Degradation of insulating oil
Electrical discharges or thermal
stresses in the oil or solid insulator of
an oil filled transformer produces gases.
The most significant gases produced
are hydrogen, methane, ethane,
ethylene and actylene.
The relative quantity of various gases
depends on the energy available.
GASES GENERATED UNDER
DIFFERENT CONDITION
S.N Phenomenon Gases
Generated
1 Partial discharge H2 gas (mainly)
2 Little heating CH4,H2
3 Low temp. hotspot CH4
4 Moderately high temp
hotspot
C2H4,C2H6
5 Very high temp hotspot C2H2 in significant
amount.
Steps involved in D G Analysis
Sampling of oil - Stainless steel oil
sampling containers of capacity up to 1000
ml with needle valves and tube adaptors
at both ends can be used for sampling.
Gas Extraction from oil Dissolved gases
are extracted by degassing flask attached
with a vacuum pump assembly. The
extracted gas is then compressed to
atmospheric pressure and volume of the
gas is measured.
Steps involved in D G Analysis
Analysis of gas extracted- The gas extracted can
be analyzed by a Gas Chromatograph fitted with
a thermal conductivity cell detector. The carrier
gas is helium. The column used is poropak N and
Molecular sieve 5A.The gases determined are
Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, methane, ethane,
ethylene, acetylene, propane, propylene, CO,
CO2 etc.
HYDRAULIC FLUIDS
MINERAL OIL HYD FLUIDS
SOLUBLE IN WATER, FORMING EMULSIONS
USED WHERE NOT MANY MOVING PARTS ARE
INVOLVED
CHEAP
IF LEAK OCCURS, PRESENT A DEFINITE FIRE
HAZARD AT ELEVATED TEMP
WATER/GLYCOL HYD FLUID
BETTER OILLINESS THAN MINERAL OIL HF
ARE REASONABLY FIRE RESISTANT
FLUID BECOMES THICKER & STICKY AT HIGH TEMP
WATER CAN BE ADDED TO RESTORE ITS ORIGINAL
CONSISTENCY
MORE EXPENSIVE THAN THE SOLUBLE MINERAL OIL HF
SYNTHETIC HYDRAULIC FLUID
MAN-MADE PRODUCT
CHEMICAL NAMES SUCH AS CHLORINATED HC &
PHOSPHATE ESTERS
HIGH RESISTANCE TO FIRE
USED IN BOILER DAMPERS & OTHER SYSTEMS
WHERE HIGH TEMP ARE ENCOUNTERED
COSTS ABOUT 8 TIMES AS MUCH AS MOHF
THANK YOU
You might also like
- 3boiler Steam Water Chemistry in Power PlantsDocument22 pages3boiler Steam Water Chemistry in Power PlantsAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Turbine Lub Oil SysDocument32 pagesTurbine Lub Oil SysAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ProtectiveDocument1 pageProtectiveAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Generator Excitaion & AVRDocument70 pagesGenerator Excitaion & AVRashumanu427100% (2)
- Water Chemistry IN Thermal Power Plants (An Overview) : O.P.RangwaniDocument24 pagesWater Chemistry IN Thermal Power Plants (An Overview) : O.P.RangwaniAbhishek Prakash Srivastava100% (1)
- Transmission LineDocument34 pagesTransmission LineAbhishek Prakash Srivastava100% (1)
- 2dm Plant OprDocument25 pages2dm Plant OprAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- AOP JOP EOP turbine interlock functionsDocument27 pagesAOP JOP EOP turbine interlock functionsAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Presentation RIPDocument26 pagesPresentation RIPAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- CCGTDocument74 pagesCCGTAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- KVVidyanandan document 12-21-2011Document35 pagesKVVidyanandan document 12-21-2011Abhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- SWGRDocument26 pagesSWGRAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- NTPC DLN Systems VamsiDocument13 pagesNTPC DLN Systems VamsiAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- FACT DevicesDocument28 pagesFACT DevicesAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Process Control (SPC)Document28 pagesStatistical Process Control (SPC)Abhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- GT Mtc. PracticesDocument59 pagesGT Mtc. PracticesAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- HVDC ManojDocument81 pagesHVDC ManojAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Power GenDocument59 pagesPower GenAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Petrol Pump Hazards Risk Assessment ControlDocument6 pagesPetrol Pump Hazards Risk Assessment ControlAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ATRS Optimizes Turbine StartupDocument47 pagesATRS Optimizes Turbine StartupAbhishek Prakash Srivastava100% (1)
- Energy Audit in IndustriesDocument14 pagesEnergy Audit in IndustriesAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical CBIP 30-05-12Document81 pagesBasic Electrical CBIP 30-05-12Abhishek Prakash Srivastava100% (1)
- Article 3: What Is Reactive Power?Document8 pagesArticle 3: What Is Reactive Power?MAT JIBRUDNo ratings yet
- 2 Boiler HydroDocument16 pages2 Boiler HydroAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- HarmonicsDocument2 pagesHarmonicsAbhishek Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- ASTM MNL77 - Analysis of Biofuels - A Laboratory Resource, by R. A. Kishore Nadkarni, 2016Document212 pagesASTM MNL77 - Analysis of Biofuels - A Laboratory Resource, by R. A. Kishore Nadkarni, 2016NinyasumergidoNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic For Marine EngineersDocument45 pagesBasic Electronic For Marine EngineersŞansal DikmenerNo ratings yet
- Shell Lubricants Bangladesh - v1.1 PDFDocument118 pagesShell Lubricants Bangladesh - v1.1 PDFWaliur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Aux PRDS SystemDocument22 pagesAux PRDS SystemKhan Ahmed MuradNo ratings yet
- 080 Frascold Chillventa-2020 1015Document46 pages080 Frascold Chillventa-2020 1015Prince RajaNo ratings yet
- 2024 03 22 Platts PriceDocument9 pages2024 03 22 Platts PriceIbrahim JaleelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Duties and Responsibilities AutosavedpdfDocument53 pagesLesson 5 Duties and Responsibilities AutosavedpdfMarian Ninyel S. TAMAYONo ratings yet
- DNV Alternative Fuels For Containerships Methanol-Ammonia Web FinalDocument100 pagesDNV Alternative Fuels For Containerships Methanol-Ammonia Web Finalbjarne9800No ratings yet
- Annex B BSMarE Course Specifications For Industrial Chemistry and TribologyDocument7 pagesAnnex B BSMarE Course Specifications For Industrial Chemistry and TribologyRoy June CaadanNo ratings yet
- MUNIN Final BrochureDocument12 pagesMUNIN Final BrochureMyo Zin AungNo ratings yet
- Pretect Hot Tapping Download - WebDocument84 pagesPretect Hot Tapping Download - WebEliseo Porcel Huayra100% (1)
- Marine Fuels DatasheetDocument29 pagesMarine Fuels DatasheetLondonguyNo ratings yet
- 11.30 Wim GroenendijkDocument13 pages11.30 Wim Groenendijkds92davidNo ratings yet
- Domestic Shipping License Exemption (DSLE) : Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)Document17 pagesDomestic Shipping License Exemption (DSLE) : Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)m3t4ph0RNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Refinery Products PDFDocument23 pagesUnit 1 Refinery Products PDFDeep SinojiyaNo ratings yet
- 4.furnaces: What Is A Furnace?Document36 pages4.furnaces: What Is A Furnace?aravind grandhiNo ratings yet
- Fuel Oil SpecificationDocument7 pagesFuel Oil Specificationmichael_forraNo ratings yet
- ECG72 Energy Consumption in Hospitals 1999 PDFDocument16 pagesECG72 Energy Consumption in Hospitals 1999 PDFMohamed RiyaazNo ratings yet
- STS Extract From MarineDocument7 pagesSTS Extract From MarineWirote Archeepkosol100% (1)
- KMPCL 6 x 600 MW Subcritical Coal-fired Power Plant Project Boiler Operating RulesDocument162 pagesKMPCL 6 x 600 MW Subcritical Coal-fired Power Plant Project Boiler Operating Rulesjust_4_u_dear_in9549No ratings yet
- Diesel Fuels & Diesel Fuel Systems: Application and Installation GuideDocument58 pagesDiesel Fuels & Diesel Fuel Systems: Application and Installation Guidedimaomar100% (1)
- Gas Aegean - Q88Document7 pagesGas Aegean - Q88David SilverNo ratings yet
- 1 28 SafetyDocument28 pages1 28 SafetyLiam WoodredNo ratings yet
- Green Blue Ammonia Value ChainDocument8 pagesGreen Blue Ammonia Value ChainIvanakbar PurwamaskaNo ratings yet
- 2018 - 05 - 25-12-49-44 - Watermarked HM 50Document32 pages2018 - 05 - 25-12-49-44 - Watermarked HM 50Prashant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Operating Mannua2Document96 pagesOperating Mannua2Ajay Kumar0% (1)
- Astm d4176Document3 pagesAstm d4176PAURUSHNo ratings yet
- Refinería Kirkuk PDFDocument11 pagesRefinería Kirkuk PDFcesarinarragaNo ratings yet
- 2016 So Las CompleteDocument76 pages2016 So Las CompleteJohn MondalaNo ratings yet
- American Institute of Chemical EngineersDocument35 pagesAmerican Institute of Chemical EngineersPathik PandyaNo ratings yet