Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Public Private Partnership: by Jared Aaron R. Cruz
Uploaded by
Jared Aaron CruzOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Public Private Partnership: by Jared Aaron R. Cruz
Uploaded by
Jared Aaron CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
P P P
Public
Private
Partnership
By Jared Aaron R. Cruz
Public = Government
Private = Non-Govt Companies
Partnership = Mutualism
What is Publicprivate partnership (PPP)
PublicPrivate Partnership describes a government service
or private business venture which is funded and operated
through a partnership of government and one or
more private sector companies. These schemes are
sometimes referred to as PPP, P3 or P
3
.
PPP involves a contract between a public sector authority and a private party
The private party provides a public service or project and assumes substantial financial,
technical and operational risk in the project.
In some types of PPP, the cost of using the service is borne exclusively by the users of the
service and not by the taxpayer. (Express ways)
In other types (notably the private finance initiative), capital investment is made by the
private sector on the strength of a contract with government to provide agreed services
and the cost of providing the service is borne wholly or in part by the government. (MRT-
LRT)
In projects that are aimed at creating public goods like in the infrastructure sector, the
government may provide a capital subsidy in the form of a one-time grant, so as to make it
more attractive to the private investors.
In some other cases, the government may support the project by providing revenue
subsidies, including tax breaks or by providing guaranteed annual revenues for a fixed
period.
PPP in the Philippines
The Philippines boasts of a long experience of public-private partnership
(PPP) initiatives, which serve as a rich basis for future investments.
With its aggressive PPP promotion, the government was and is able to
attract private partners to invest.
Through the partnership, the power crisis in the early 1990s was
addressed.
The partnership likewise helped improve road network quality, transport
linkages and social services. To date, approximately US$ 19.5 billion in
investment has already been generated since its inception.
Today, PPP can be credited in helping realize various development
projects both at the national and local levels across various infrastructure
sectors.
PPP in the Philippines
The Philippines boasts of a long experience of public-private partnership
(PPP) initiatives, which serve as a rich basis for future investments.
With its aggressive PPP promotion, the government was and is able to
attract private partners to invest.
Through the partnership, the power crisis in the early 1990s was
addressed.
The partnership likewise helped improve road network quality, transport
linkages and social services. To date, approximately US$ 19.5 billion in
investment has already been generated since its inception.
Today, PPP can be credited in helping realize various development
projects both at the national and local levels across various infrastructure
sectors.
Overview of the PPP program
The Philippine Government recognizes the essential role of the private
sector as the main engine for national growth and development.
The government is willing, on a case-to-case basis, to protect investors
from certain regulatory risk
Private sector investors will be selected through open competition under
fair and transparent terms.
All interested investors will be given a level playing field with reasonable
returns and appropriate sharing of risks without compromising the
protection of public interests.
Through this program, end-users will be provided with adequate, safe,
efficient, reliable, and reasonably-priced infrastructure services.
The projects under the PPP Program were selected based on the following criteria:
1. Project Readiness/Preparation
a. For 2011 Rollout
i. Feasibility Study to be completed within 2010 to 2011,
ii. Completed Feasibility Study being reconfigured for
PPP, and
iii. Ready to tender in 2011.
b. For Medium-Term Rollout and other PPP Projects
i. Included in the PPP pipeline projects of the
Implementing Agencies, and
ii. Initial preparation on-going, i.e., concept stage, hiring
of consultants for Feasibility Study preparation.
2. Responsiveness to the sectors needs (e.g., part of the transport
network system, water supply/sewerage, electric power capacity, etc); and
3. High Implementability (bankable, no major issues).
PHILIPPINE PUBLIC-PRIVATE
PARTNERSHIP (PPP) CENTER
The PPP Center, equipped with the technical know-how and
extensive experience in project development, provides various
services and assistance to:
implementing agencies (IAs)
government-owned and controlled corporations (GOCCs)
state universities (SUCs) and
local government units (LGUs) as well as to
the private sector
in the development and implementation of critical infrastructure
projects.
ROLE OF PPP CENTER
Project Development
Project Development and Monitoring Facility
Project Facilitation
Project Monitoring
Policy Advocacy
Information Management.
Capacity Building
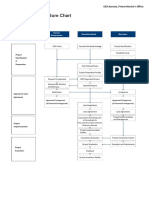
PPP Process Flow Chart
Under Republic Act 7718 and its IRR, the implementing agency/local government
units (IAs/LGUs) can implement their PPP/BOT projects through any of the following
implementation modes:
Public Bidding (Solicited Mode)
The IA/LGU chooses to procure their priority infrastructure and development
projects through transparent and competitive public bidding process.
Unsolicited Mode
The IA/LGU may accept unsolicited proposal from project proponent to undertake
infrastructure or development projects on a negotiated basis provided that:
1) Project involves new concept or technology and/or is not part of the list of priority
projects;
2) No direct government guarantee, subsidy or equity is required; and
3) The IA/LGU has invited by publication, for three (3) consecutive weeks, in a
newspaper of general circulation, comparative or competitive proposals.
PPP Process Flow Chart
Under Republic Act 7718 and its IRR, the implementing agency/local government
units (IAs/LGUs) can implement their PPP/BOT projects through any of the following
implementation modes:
Public Bidding (Solicited Mode)
The IA/LGU chooses to procure their priority infrastructure and development
projects through transparent and competitive public bidding process.
Unsolicited Mode
The IA/LGU may accept unsolicited proposal from project proponent to undertake
infrastructure or development projects on a negotiated basis provided that:
1) Project involves new concept or technology and/or is not part of the list of priority
projects;
2) No direct government guarantee, subsidy or equity is required; and
3) The IA/LGU has invited by publication, for three (3) consecutive weeks, in a
newspaper of general circulation, comparative or competitive proposals.
DPWH PPP PROJECTS
See pdf file
You might also like
- Outline Specifications For FitoutDocument11 pagesOutline Specifications For FitoutJared Aaron CruzNo ratings yet
- IKEA Organisational Analysis - Startegic HR DocumentDocument24 pagesIKEA Organisational Analysis - Startegic HR DocumentAssignment ConsultancyNo ratings yet
- SPG BallotDocument4 pagesSPG BallotLeonorBagnison55% (11)
- Planning Administration - Presentation1-NEDA Appraisal and Funding PPP-JOM-7 May 2017Document160 pagesPlanning Administration - Presentation1-NEDA Appraisal and Funding PPP-JOM-7 May 2017Aris TesoroNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary Garden Vista E-VersionDocument1 pageExecutive Summary Garden Vista E-VersionNdank SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- EDCF Loan Procedure ChartDocument1 pageEDCF Loan Procedure Chartvinavzenir100% (1)
- Letter of Invitation Sample - Oct 6 2011 - Design Consultancy Servs. 63ooosf ICT BLDG (MBFZ)Document14 pagesLetter of Invitation Sample - Oct 6 2011 - Design Consultancy Servs. 63ooosf ICT BLDG (MBFZ)Daniel EvansNo ratings yet
- Sub-Clause 4.17 - Notice of Consent For Removal of Contractor's EquipmentDocument2 pagesSub-Clause 4.17 - Notice of Consent For Removal of Contractor's Equipmentkhiem440% (1)
- 2006 BOT Law IRR PresentationDocument19 pages2006 BOT Law IRR PresentationRenzNo ratings yet
- Deped MouDocument5 pagesDeped MouJanna Carmela L. ObiernaNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE Letter of Intent 1.11.11Document1 pageSAMPLE Letter of Intent 1.11.11batambintanNo ratings yet
- CMO No. 61 Series 2017 Policies Standards and Guidelines For The Bachelor of Science in Architecture BS ArchiDocument56 pagesCMO No. 61 Series 2017 Policies Standards and Guidelines For The Bachelor of Science in Architecture BS ArchiJared Aaron Cruz100% (3)
- Policy Brief UPolicy Brief Unsolicited Proposals 2009-2012 Nsolicited Proposals 20092012Document31 pagesPolicy Brief UPolicy Brief Unsolicited Proposals 2009-2012 Nsolicited Proposals 20092012Gerrysaudi Dzme-epNo ratings yet
- Pawb Technical Bulletin NO. 2013-05: (Caves and Cave Resources Conservation, Management and Protection)Document6 pagesPawb Technical Bulletin NO. 2013-05: (Caves and Cave Resources Conservation, Management and Protection)Billy RavenNo ratings yet
- Notice To Proceed DoneDocument14 pagesNotice To Proceed DoneRandy ViolaNo ratings yet
- Sub - Contract AgreementDocument3 pagesSub - Contract AgreementRamon SottaNo ratings yet
- Confirmation of Lease / Authority To Construct For Smart CellsiteDocument2 pagesConfirmation of Lease / Authority To Construct For Smart CellsiteJan Brian Guillena BangcayaNo ratings yet
- Notice of AGM 2019 - FinalDocument10 pagesNotice of AGM 2019 - FinalAnonymous PJjFPTNo ratings yet
- Modernized Transport AgreementDocument7 pagesModernized Transport AgreementGrace Abayon LaczaNo ratings yet
- SCC Special ConditionsDocument4 pagesSCC Special ConditionsEmmanuel Sto TomasNo ratings yet
- EPC Template: Engineering, Procurement and Construction AgreementDocument59 pagesEPC Template: Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreementjunaid112No ratings yet
- Contract Drafting Structure ChecklistDocument4 pagesContract Drafting Structure ChecklistsdysangcoNo ratings yet
- Remove Personal Items from Common Areas by Mar 22Document1 pageRemove Personal Items from Common Areas by Mar 22dandan tanNo ratings yet
- Checklist for Job Contractor RegistrationDocument1 pageChecklist for Job Contractor RegistrationCarmela CalangiNo ratings yet
- Calaex - Drainage Sub ContractDocument6 pagesCalaex - Drainage Sub ContractMhonn Bulanguit PadillaNo ratings yet
- Central Office: ManilaDocument106 pagesCentral Office: ManilaJhon Jezar CalumagNo ratings yet
- Amending PCAB RequirementsDocument5 pagesAmending PCAB RequirementsrubydelacruzNo ratings yet
- Malitubog-Maridagao Irrigation Project, Phase IIDocument5 pagesMalitubog-Maridagao Irrigation Project, Phase IIBeth HtebNo ratings yet
- Citing The Sourcebook On Administrative Offenses in The Civil Service Published by The Civil Service Commission and Some Actual Supreme Court Decided Cases As My ReferencesDocument2 pagesCiting The Sourcebook On Administrative Offenses in The Civil Service Published by The Civil Service Commission and Some Actual Supreme Court Decided Cases As My ReferencesKapitan BilangNo ratings yet
- Form of Agreement Between Client and Consultant ForDocument18 pagesForm of Agreement Between Client and Consultant Forjunaid112No ratings yet
- Philippine Exploration Permit RequirementsDocument3 pagesPhilippine Exploration Permit RequirementsMAHARLIKA CONSTRUCTION AND AGGREGATES SUPPLY, OPCNo ratings yet
- NTP Irr - SignedDocument24 pagesNTP Irr - SignedPalanas A. VinceNo ratings yet
- CDC 2015 Annual ReportDocument69 pagesCDC 2015 Annual ReportPipoy ReglosNo ratings yet
- Project Execution: What Happens During This PhaseDocument5 pagesProject Execution: What Happens During This PhaseRussell EndoyNo ratings yet
- Bizmanualz Construction Management Policies and Procedures SampleDocument5 pagesBizmanualz Construction Management Policies and Procedures SampleShahalaNo ratings yet
- Qatar Tenancy Contract DetailsDocument2 pagesQatar Tenancy Contract DetailsCarlos Arellano ArceNo ratings yet
- Certificateofcompletion MechanicalDocument1 pageCertificateofcompletion Mechanicaljoneth torresNo ratings yet
- Boq TenderDocument30 pagesBoq TenderLeilani JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Construction Contract SummaryDocument13 pagesConstruction Contract SummaryMelanoleuca PandaNo ratings yet
- Turnkey CMP Modality (For Developer)Document39 pagesTurnkey CMP Modality (For Developer)Cherry Duldulao50% (2)
- BLDG Notice of Completion PlinthDocument1 pageBLDG Notice of Completion PlinthLucasNo ratings yet
- Project Administration ManualDocument31 pagesProject Administration ManualZeuss MohamedNo ratings yet
- 1302134458-k10.SPP DA E.Service - Agree-1Document11 pages1302134458-k10.SPP DA E.Service - Agree-1Jeanine ClarkNo ratings yet
- The Essentials of Construction ContractsDocument29 pagesThe Essentials of Construction ContractsSajjad AminNo ratings yet
- THRU: Payroll Department PersonnelDocument1 pageTHRU: Payroll Department PersonnelNadj MclightNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument103 pagesProject ManagementUmutoni ornellaNo ratings yet
- Department Order No.2021-007Document60 pagesDepartment Order No.2021-007EDH100% (1)
- 04 A Model RFP For Selection of Financial Consultant and Transaction Adviser Word PDFDocument154 pages04 A Model RFP For Selection of Financial Consultant and Transaction Adviser Word PDFNityaMurthyNo ratings yet
- AgraDocument10 pagesAgraMichaelCalzadoNo ratings yet
- Logical Reasoning: Understanding Valid and Invalid ArgumentsDocument42 pagesLogical Reasoning: Understanding Valid and Invalid ArgumentsHector100% (1)
- Delivery Receipt TemplateDocument1 pageDelivery Receipt Templatejaguirre_03No ratings yet
- Procedure For Land AcquisitionDocument25 pagesProcedure For Land AcquisitionRob ClosasNo ratings yet
- PCAB List of Licensed Contractors For CFY 2018-2019 As of 24 Sep 2018 - WebDocument69 pagesPCAB List of Licensed Contractors For CFY 2018-2019 As of 24 Sep 2018 - WebedisonNo ratings yet
- Repatriation and Replacement of Contractor PersonnelDocument9 pagesRepatriation and Replacement of Contractor Personnelankit jainNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive CSHP - Cover.quilatDocument3 pagesComprehensive CSHP - Cover.quilatRobert R. Tiin100% (1)
- Assignment 3Document14 pagesAssignment 3prmmgsaNo ratings yet
- The PARC StoryDocument59 pagesThe PARC StoryRio AlmenaNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Policy On Public Private Partnership PDFDocument17 pagesPakistan Policy On Public Private Partnership PDFAli BaigNo ratings yet
- Pub AdDocument76 pagesPub AdDarshan KannurNo ratings yet
- Central Luzon Link Expressway Phase IIDocument13 pagesCentral Luzon Link Expressway Phase IIAngel YuNo ratings yet
- PPP for Infrastructure DeliveryDocument43 pagesPPP for Infrastructure DeliveryMarvin CabantacNo ratings yet
- PPPC Pub Brochure Feb 2018Document36 pagesPPPC Pub Brochure Feb 2018Rheneir MoraNo ratings yet
- Public-Private Partnership in The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesPublic-Private Partnership in The PhilippinesCarlos RabagoNo ratings yet
- Procurement and Supply Chain Management: Emerging Concepts, Strategies and ChallengesFrom EverandProcurement and Supply Chain Management: Emerging Concepts, Strategies and ChallengesNo ratings yet
- After 2017Document2 pagesAfter 2017NonoyTaclino100% (1)
- Drafting and Design DefinitionsDocument20 pagesDrafting and Design DefinitionsJared Aaron CruzNo ratings yet
- Drawings 7 11 2019 PDFDocument7 pagesDrawings 7 11 2019 PDFJared Aaron CruzNo ratings yet
- TOA QuizDocument35 pagesTOA QuizJared Aaron CruzNo ratings yet
- Thesis Formatting ManualDocument27 pagesThesis Formatting ManualManish ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Shades and Shadows in Orthographic ViewsDocument26 pagesShades and Shadows in Orthographic ViewsAshwin PrakashNo ratings yet
- Guidelines on Tree Cutting for Power Transmission ProjectsDocument7 pagesGuidelines on Tree Cutting for Power Transmission ProjectsSheery Mariz FernandezNo ratings yet
- SPP 203 SpecializedarchlservicesDocument52 pagesSPP 203 SpecializedarchlservicesJared Aaron CruzNo ratings yet
- SPP 201 Pre DesignservicesDocument17 pagesSPP 201 Pre DesignservicesJared Aaron CruzNo ratings yet
- Cascade CatalogDocument23 pagesCascade CatalogJared Aaron CruzNo ratings yet
- SCG Decorative Wall Panel ModeenaDocument2 pagesSCG Decorative Wall Panel ModeenaJared Aaron CruzNo ratings yet
- Building Technology/Utilities Sample QuestionsDocument35 pagesBuilding Technology/Utilities Sample QuestionsJared Aaron CruzNo ratings yet
- Irr PD 957Document2 pagesIrr PD 957Jared Aaron CruzNo ratings yet
- Revised IRR PD 957 2009Document66 pagesRevised IRR PD 957 2009Kaye ReguladoNo ratings yet
- Condominium Unit Sample RenovationDocument6 pagesCondominium Unit Sample RenovationJared Aaron CruzNo ratings yet
- CHICKEN BACOLOD (Admin Punch-List)Document2 pagesCHICKEN BACOLOD (Admin Punch-List)Jared Aaron CruzNo ratings yet
- Dissertationguide PDFDocument33 pagesDissertationguide PDFAlvin John Benavidez SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Ground Floor Plan: Entertainment Room T&B BAR Garden BED RoomDocument1 pageGround Floor Plan: Entertainment Room T&B BAR Garden BED RoomJared Aaron CruzNo ratings yet
- Office Schematic Study PresentationDocument10 pagesOffice Schematic Study PresentationJared Aaron CruzNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Contract LawDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Contract LawTsholofeloNo ratings yet
- Memorandum: United States Department of EducationDocument3 pagesMemorandum: United States Department of EducationKevinOhlandtNo ratings yet
- Sutan Sjahrir and The Failure of Indonesian SocialismDocument23 pagesSutan Sjahrir and The Failure of Indonesian SocialismGEMSOS_ID100% (2)
- Bedan Scholars' Guild: Bringing Smiles To The Dumagat TribeDocument3 pagesBedan Scholars' Guild: Bringing Smiles To The Dumagat TribeShelumiel EmuslanNo ratings yet
- The Problem With Separate Toys For Girls and BoysDocument7 pagesThe Problem With Separate Toys For Girls and BoysNico DavidNo ratings yet
- Ict Slac MatrixDocument3 pagesIct Slac Matrixarmand resquir jrNo ratings yet
- Castro vs. Gregorio (2014)Document1 pageCastro vs. Gregorio (2014)Xavier BataanNo ratings yet
- B.A (Prog) History 4th Semester 2019Document22 pagesB.A (Prog) History 4th Semester 2019lakshyadeep2232004No ratings yet
- Rizal's works promote nationalism and patriotismDocument5 pagesRizal's works promote nationalism and patriotismEleanor RamosNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Consent and Intellectual Cloning at Leicester University - Letter To Dr. RofeDocument57 pagesManufacturing Consent and Intellectual Cloning at Leicester University - Letter To Dr. RofeEyemanProphetNo ratings yet
- (LEGMETH) PAFLU vs. Bureau of Labor RelationsDocument2 pages(LEGMETH) PAFLU vs. Bureau of Labor RelationsMarc Virtucio0% (1)
- 80-Madeleine HandajiDocument85 pages80-Madeleine Handajimohamed hamdanNo ratings yet
- League of Minnesota Cities - Data Practices - Analyze Classify RespondDocument84 pagesLeague of Minnesota Cities - Data Practices - Analyze Classify RespondghostgripNo ratings yet
- THE INDEPENDENT Issue 541Document44 pagesTHE INDEPENDENT Issue 541The Independent MagazineNo ratings yet
- (Advances in Political Science) David M. Olson, Michael L. Mezey - Legislatures in The Policy Process - The Dilemmas of Economic Policy - Cambridge University Press (1991)Document244 pages(Advances in Political Science) David M. Olson, Michael L. Mezey - Legislatures in The Policy Process - The Dilemmas of Economic Policy - Cambridge University Press (1991)Hendix GorrixeNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Board - Accountable Leadership ModelDocument5 pagesThe Role of The Board - Accountable Leadership Modelsagugu20004394No ratings yet
- A Post-Washington ConsensusDocument6 pagesA Post-Washington ConsensuszakariamazumderNo ratings yet
- 18 Barreto-Gonzales v. Gonzales, 58 Phil. 67, March 7, 1933Document5 pages18 Barreto-Gonzales v. Gonzales, 58 Phil. 67, March 7, 1933randelrocks2No ratings yet
- Philippine Collegian Tomo 90 Issue 19Document12 pagesPhilippine Collegian Tomo 90 Issue 19Philippine CollegianNo ratings yet
- Predicaments of An Exile in Rawi Hage's CockroachDocument5 pagesPredicaments of An Exile in Rawi Hage's CockroachIJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Tribes in India Terms of DiscourseDocument7 pagesTransformation of Tribes in India Terms of DiscourseJYOTI JYOTINo ratings yet
- Persuasive EssayDocument4 pagesPersuasive Essayapi-462774675No ratings yet
- Jerome PPT Revamp MabiniDocument48 pagesJerome PPT Revamp Mabinijeromealteche07No ratings yet
- Indian Engagement With Taliban-Led Afghanistan and Implications For PakistanDocument10 pagesIndian Engagement With Taliban-Led Afghanistan and Implications For Pakistanhamza132065No ratings yet
- Styhre, Alexander - Precarious Professional Work - Entrepreneurialism, Risk and Economic Compensation in The Knowledge Economy (2017, Springer International Publishing)Document263 pagesStyhre, Alexander - Precarious Professional Work - Entrepreneurialism, Risk and Economic Compensation in The Knowledge Economy (2017, Springer International Publishing)miguelip01100% (1)
- America Counts On... : Scholarship Scam Spreads To Bihar, Ropes in School From Punjab TooDocument16 pagesAmerica Counts On... : Scholarship Scam Spreads To Bihar, Ropes in School From Punjab TooAnshu kumarNo ratings yet
- Grand Forks BallotDocument3 pagesGrand Forks BallotinforumdocsNo ratings yet
- PIL NotesDocument19 pagesPIL NotesGoldie-goldAyomaNo ratings yet