Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introdu To IC Engines
Uploaded by
SameerAhsan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
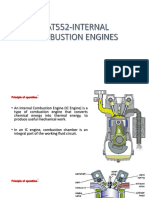
38 views21 pagesInternal Combustion Engines Internal Combustion Engines internal combustion steam engines internal combustion turbines. Internal Combustion Engines are used in: automotive rail transportation power generation ships aviation garden appliances. The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of fuel-oxidizer mixture occurs in a confined space.
Original Description:
Original Title
Introdu to IC Engines
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInternal Combustion Engines Internal Combustion Engines internal combustion steam engines internal combustion turbines. Internal Combustion Engines are used in: automotive rail transportation power generation ships aviation garden appliances. The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of fuel-oxidizer mixture occurs in a confined space.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views21 pagesIntrodu To IC Engines
Uploaded by
SameerAhsanInternal Combustion Engines Internal Combustion Engines internal combustion steam engines internal combustion turbines. Internal Combustion Engines are used in: automotive rail transportation power generation ships aviation garden appliances. The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of fuel-oxidizer mixture occurs in a confined space.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 21
Internal Combustion Engines
Internal Combustion Engines
types of heat engines
external combustion
internal combustion
steam engines
turbines
Stirling engine
Otto engine
Diesel engine
Vankel engine
Internal Combustion Engines
The internal combustion engine is
an engine in which the
combustion of fuel-oxidizer
mixture occurs in a confined space
applied in:
automotive
rail transportation
power generation
ships
aviation
garden appliances
Internal Combustion Engines
Internal Combustion Engines
four stroke-Otto engine -
starting position
a. piston starts moving
down
b. intake valve opens
c. air-fuel mixture
gets in
1. intake
a. piston moves up
b. both valves closed
c. air-fuel mixture
gets compressed
2. compression
Internal Combustion Engines
four stroke -
ignition
a. air-fuel mixture
explodes driving the
piston down
3. power
a. piston moves up
b. exhaust valve opens
c. exhaust leaves the
cylinder
4. exhaust
Internal Combustion Engines
four stroke -
Advantages:
dedicated lubrication system makes to engine
more wear resistant
better efficiency that 2-stroke engine
no oil in the fuel less pollution
Internal Combustion Engines
Diesel -
air intake
compression
fuel injection
combustion
exhaust
exhaust
/intake
Internal Combustion Engines
Diesel -
Advantages:
self ignition (without electrical spark plug)
better efficiency
reliability
higher durability
Drawbacks:
more NO
x
production
more expensive production
more weight
louder
Internal Combustion Engines
Diesel -
fuel injector
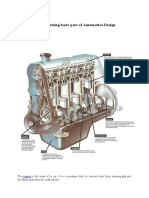
Internal Combustion Engines
multi-cylinder -
Internal Combustion Engines
multi-cylinder -
Cylinder layouts
Internal Combustion Engines
multi-cylinder -
Cylinder layouts
inline
V
flat
V
Internal Combustion Engines
multi-cylinder -
flat
boxer
inline
Internal Combustion Engines
multi-cylinder -
14 cylinder Diesel engine (80 MW)
Internal Combustion Engines
multi-cylinder -
Cylinder layouts
radial
Internal Combustion Engines
Valve operation
Internal Combustion Engines
Wankel rotary engine
Advantages:
higher power output
no reciprocating mass
simpler and lighter construction
Drawbacks:
increased wear of rubbing parts
higher fuel consumption
requirement for better materials
Internal Combustion Engines
two stroke -
Advantages:
lack of valves, which simplifies construction and
lowers weight
fire once every revolution, which gives a
significant power boost
can work in any orientation
good power to weight ratio
Drawbacks:
lack of a dedicated lubrication system makes
the engine to wear faster.
necessity of oil addition into the fuel
low efficiency
produce a lot of pollution
Internal Combustion Engines
two stroke -
1. Power / Exhaust
2. Intake / Compression
a. ignition
b. piston moves downward
compressing fuel-air mixture
in the crankcase
c. exhaust port opens
a. inlet port opens
b. compressed fuel-air mixture
rushes into the cylinder
c. piston upward movement
provides further compression
Internal Combustion Engines
You might also like
- Cantilever Calculation ToolDocument10 pagesCantilever Calculation ToolEnoch Twumasi50% (2)
- TurbochargerDocument10 pagesTurbochargernavle krushnaNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument25 pagesInternal Combustion EnginesPradeep Kumar MehtaNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument27 pagesInternal Combustion EnginesSri RNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument27 pagesInternal Combustion EnginesSRINIVAS TNo ratings yet
- Ic EngineDocument27 pagesIc EngineAnil MishraNo ratings yet
- Lesson One: Understanding Principles of Operation of Internal Combustion EnginesDocument45 pagesLesson One: Understanding Principles of Operation of Internal Combustion Engineswaleed yehiaNo ratings yet
- IcenginesDocument27 pagesIcenginessaravanan l mechNo ratings yet
- Combustion Ass 1Document6 pagesCombustion Ass 1Shane Michael BacalsoNo ratings yet
- Heat Engine & IC EnginesDocument26 pagesHeat Engine & IC EnginesVeeresh Kumar G BNo ratings yet
- MARPOWERDocument4 pagesMARPOWERREY SELWYN MANALANGNo ratings yet
- Different Types of IC Engine: - Rated by Their Maximum Horsepower - Three TypesDocument14 pagesDifferent Types of IC Engine: - Rated by Their Maximum Horsepower - Three TypesmharitmsNo ratings yet
- Diesel PPDocument58 pagesDiesel PPManvendra Pratap Singh Bisht100% (1)
- LEC# 14. I.C EngineDocument43 pagesLEC# 14. I.C EngineAhmer KhanNo ratings yet
- LEC# 14. I.C EngineDocument43 pagesLEC# 14. I.C EngineAli Murad JokhioNo ratings yet
- Thermal 1unit3Document178 pagesThermal 1unit3NAGU2009No ratings yet
- Of Operation of Internal Combustion EnginesDocument31 pagesOf Operation of Internal Combustion EnginesNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document30 pagesUnit 1RakeshkumarcegNo ratings yet
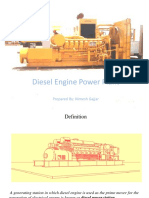
- Diesel Engine Power PlantsDocument58 pagesDiesel Engine Power PlantsVadiraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Two Stroke Internal Combustion Engines: How A Two Stroke Engine Works Advantages/DisadvantagesDocument13 pagesTwo Stroke Internal Combustion Engines: How A Two Stroke Engine Works Advantages/DisadvantagesrajfacebookNo ratings yet
- Two Stroke Internal Combustion Engines: How A Two Stroke Engine Works Advantages/DisadvantagesDocument13 pagesTwo Stroke Internal Combustion Engines: How A Two Stroke Engine Works Advantages/Disadvantagessherifkazem2010No ratings yet
- Fuel Properties and Use of Hydrogen I.C.enginesDocument95 pagesFuel Properties and Use of Hydrogen I.C.enginesSiemensNo ratings yet
- Otto CyclePowePointDocument27 pagesOtto CyclePowePointVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Advantages of 4 Stroke EngineDocument6 pagesAdvantages of 4 Stroke EngineJILLIEN KAITH ARELLANONo ratings yet
- Advantages of 4 Stroke Engine:-: DifferencesDocument3 pagesAdvantages of 4 Stroke Engine:-: DifferencescidracNo ratings yet
- IC Engines Amar1Document73 pagesIC Engines Amar1amarparimiNo ratings yet
- Ic Engines-Bme Ae&iDocument53 pagesIc Engines-Bme Ae&iAshitaNo ratings yet
- Welcome: BY, Anoopkrishna K S6-Mechanical NO-19 Carmel PolyDocument20 pagesWelcome: BY, Anoopkrishna K S6-Mechanical NO-19 Carmel PolyANOOPNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine: Aguinaldo, Cellan, Gregorio, MedranoDocument33 pagesDiesel Engine: Aguinaldo, Cellan, Gregorio, MedranoHannah AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Engines: Reciprocating EngineDocument46 pagesAircraft Engines: Reciprocating EngineBadal Machchhar100% (1)
- ATEN 202 LecturesDocument19 pagesATEN 202 LecturesEngrKaisanMuhammadUsmanNo ratings yet
- Engine Classification, Parts Identification: To .. Head:yousef Alkhattam V.H: Ahmed Ashraf By:saad Yasser SaadDocument49 pagesEngine Classification, Parts Identification: To .. Head:yousef Alkhattam V.H: Ahmed Ashraf By:saad Yasser SaadSaad YasserNo ratings yet
- Technical PresentationDocument15 pagesTechnical Presentationdiliph.21.bemeNo ratings yet
- Difference Between 4 Stroke & 2 Stroke - EngineDocument6 pagesDifference Between 4 Stroke & 2 Stroke - EngineMOAZNo ratings yet
- PP1 PresentationDocument22 pagesPP1 Presentationmhawan104No ratings yet
- Engine and TransmissionDocument26 pagesEngine and TransmissionWFilmy STARNo ratings yet
- Engine and Motor (4 Stroke Engine and 2 Stroke Engine)Document27 pagesEngine and Motor (4 Stroke Engine and 2 Stroke Engine)Bias PanduNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument33 pagesInternal Combustion EnginesDeepikaNo ratings yet
- 2003 ExhaustDocument47 pages2003 ExhaustThip ZazaNo ratings yet
- Natural Heat Flow Increases Entropy - Converting Heat To Work Decreases EntropyDocument5 pagesNatural Heat Flow Increases Entropy - Converting Heat To Work Decreases EntropyDuraimurugannNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine Chapter 1Document31 pagesInternal Combustion Engine Chapter 1norazwanizaNo ratings yet
- Operating PDFDocument31 pagesOperating PDFResearch DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Internal CombussionDocument80 pagesLecture 2 - Internal Combussionchoongwenkang100% (1)
- C.S.I Institute of Technology, Thovalai: Department of Mechanical Engineering Semester: 5Document32 pagesC.S.I Institute of Technology, Thovalai: Department of Mechanical Engineering Semester: 5samuelben87No ratings yet
- Mini Project PresentationDocument24 pagesMini Project PresentationHarshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Engine Construction & Principles of OperationDocument22 pagesEngine Construction & Principles of OperationShanmuga RajNo ratings yet
- Test Engine - Arman ShaikhDocument4 pagesTest Engine - Arman ShaikhArmanNo ratings yet
- EnE 250 Air Quality Management and Pollution Control Lecture 02 - 3 APC Mobile Sources Aug 2015 v2Document117 pagesEnE 250 Air Quality Management and Pollution Control Lecture 02 - 3 APC Mobile Sources Aug 2015 v2Alexis Bryan RiveraNo ratings yet
- Dual Fuel Engine & TechnologyDocument10 pagesDual Fuel Engine & Technologyjameela chandranNo ratings yet
- Negative Pressure SuperchargingDocument38 pagesNegative Pressure SuperchargingPrakash Chandrasekaran100% (1)
- CLSU ABE Review 2022 APE Chap 04 Internal Combustion EngineDocument55 pagesCLSU ABE Review 2022 APE Chap 04 Internal Combustion EngineBilly AgustinNo ratings yet
- Turbo Charger PresentationDocument22 pagesTurbo Charger PresentationPragyan Kumar0% (1)
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument37 pagesInternal Combustion EnginesFake IdentityNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Communication SkillsDocument32 pagesPresentation of Communication SkillsShakeel MohmandNo ratings yet
- ET Answer KeyDocument9 pagesET Answer KeyGodwinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Diesel Engine Power PlantDocument60 pagesLecture 1 - Diesel Engine Power PlantbarryNo ratings yet
- Different Configurations of EnginesDocument25 pagesDifferent Configurations of EnginesPrajwal JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesFrom EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Unit - 2: Cutting Tool MaterialsDocument16 pagesUnit - 2: Cutting Tool MaterialsSameerAhsanNo ratings yet
- CADDocument21 pagesCADajit1130No ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument18 pagesInternal Combustion EnginesSameerAhsanNo ratings yet
- Lubrication SystemDocument8 pagesLubrication SystemSameerAhsanNo ratings yet
- Vtu - Ac.in PDF Scheme2014 WorkshopDocument1 pageVtu - Ac.in PDF Scheme2014 WorkshopMurugesan KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Caed 14Document5 pagesCaed 14SameerAhsanNo ratings yet
- Eme 14Document3 pagesEme 14SameerAhsanNo ratings yet
- Finite Element MethodDocument24 pagesFinite Element Methodshivam choudhary0% (1)
- PPC Master MarchDocument148 pagesPPC Master MarchSandip JadhavNo ratings yet
- ReddyheaterDocument268 pagesReddyheaterstraffer1No ratings yet
- Design of Partition PlateDocument5 pagesDesign of Partition Platepippo2378793No ratings yet
- Dream Residences - Water Supply & Fire Protection BOMDocument1 pageDream Residences - Water Supply & Fire Protection BOMPatrick LlenaresNo ratings yet
- MOS COUPLER FOR TcsDocument25 pagesMOS COUPLER FOR TcsRituraj RNo ratings yet
- MagnaflocDocument3 pagesMagnaflocfrancsanchezNo ratings yet
- NEXTSTATION Turbo Color Capacitor ReplacementDocument8 pagesNEXTSTATION Turbo Color Capacitor ReplacementPiotr TwareckiNo ratings yet
- NSC 200-250/D271DC4-ADV: Technical DataDocument3 pagesNSC 200-250/D271DC4-ADV: Technical DatajtorerocNo ratings yet
- GemDocument9 pagesGemRam Prasidh AnaswaraNo ratings yet
- Science Scavenger HuntDocument2 pagesScience Scavenger HuntJosie StewartNo ratings yet
- Naphtha Catalytic Cracking For Propylene ProudctionDocument5 pagesNaphtha Catalytic Cracking For Propylene ProudctionWong Yee SunNo ratings yet
- PC-Bedienungsanleitung Heater enDocument33 pagesPC-Bedienungsanleitung Heater enZoran Tanja JarakovićNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document36 pagesLecture 6keiNo ratings yet
- How Do You Make LiquidDocument2 pagesHow Do You Make LiquidjukortaNo ratings yet
- Dge 169Document6 pagesDge 169Krittika ChandranNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual Activity 1 Separation TechniquesDocument6 pagesLaboratory Manual Activity 1 Separation TechniquesMhartin SortonisNo ratings yet
- Arch. DictionaryDocument68 pagesArch. DictionaryVinay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Few Aspects in Deep Drawing Process: D Swapna, Ch. Srinivasa Rao, S RadhikaDocument5 pagesFew Aspects in Deep Drawing Process: D Swapna, Ch. Srinivasa Rao, S RadhikaBoby Madesen100% (1)
- 6 - Geomembrane Lifetime Prediction PDFDocument27 pages6 - Geomembrane Lifetime Prediction PDF齐左No ratings yet
- Xylazine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageXylazine HydrochlorideKasidit SornchaiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Gear Manufacturing and FinishingDocument1 pageAdvanced Gear Manufacturing and FinishingImad LamNo ratings yet
- Om The Laboratory To Ton Scale in Continuous FlowDocument3 pagesOm The Laboratory To Ton Scale in Continuous FlowAaron Troy SmallNo ratings yet
- Tin ADocument3 pagesTin ANishit TrivediNo ratings yet
- Buna EP LanxessDocument51 pagesBuna EP LanxessANHVUDRCNo ratings yet
- Oryx Postmansburg Mixes 11-5-2021Document2 pagesOryx Postmansburg Mixes 11-5-2021MantshaNo ratings yet
- Automotive Connectors: BAB Connector SISC ConnectorDocument13 pagesAutomotive Connectors: BAB Connector SISC ConnectorPrabhansh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Install ManualDocument190 pagesInstall ManualMarios KaridisNo ratings yet
- Legrand Cable Lighting & Data Trunking Technical PDFDocument35 pagesLegrand Cable Lighting & Data Trunking Technical PDFHarshith KunjathurNo ratings yet
- Shaper Planer and SlotterDocument21 pagesShaper Planer and SlotterBharathiraja MoorthyNo ratings yet