Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Financial System Structure Importance
Uploaded by
harmeet_7000 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views27 pagesThe Financial System is the process by which money flows from savers to users. Primary Market - firms and governments issue securities and sell them initially to the public. Secondary Market - collection of financial markets in which previously issued securities are traded among investors.
Original Description:
Original Title
financial system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Financial System is the process by which money flows from savers to users. Primary Market - firms and governments issue securities and sell them initially to the public. Secondary Market - collection of financial markets in which previously issued securities are traded among investors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views27 pagesFinancial System Structure Importance
Uploaded by
harmeet_700The Financial System is the process by which money flows from savers to users. Primary Market - firms and governments issue securities and sell them initially to the public. Secondary Market - collection of financial markets in which previously issued securities are traded among investors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
> > > > > > > >
The Financial System
Outline the structure and
importance of the financial
system.
List the various types of
securities.
Define financial market, and
distinguish between primary and
secondary financial markets.
Describe the characteristics of the
major stock exchanges.
Discuss the organization and
functioning of financial institutions.
Explain the functions of the Federal
Reserve System and the tools it
uses to control the supply of money
and credit.
Evaluate the major features of
regulations and laws affecting the
financial system.
Describe the global financial
system.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
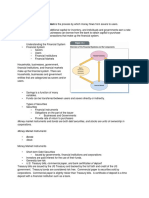
The financial system is the
process by which money
flows from savers to users.
Financial System
Savers
Users
Financial Institutions
Financial Markets
Savings is a function of many variables.
Funds can be transferred between users and
savers directly or indirectly.
Securities
Financial instruments
Obligations on the part of the issuer
Businesses and Governments
Provide rate of return to purchasers
Money Market Instruments
Bonds
Stock
Short-term Debt Securities
Issued by governments, financial institutions
and corporations
Investors are paid interest for the use of
their funds.
Generally low-risk
U.S. Treasury bills, commercial paper, and
bank certificates of deposit
Government Bonds
Bonds sold by the U.S. Department of the
Treasury.
Municipal Bonds
Bonds issued by state or local governments
Revenue bonds are used toward a project that will
produce revenue, General Obligation Bonds are
not.
Price is determined by risk and interest
rate.
Several firms rate bonds
Standard & Poors (S&P)
Moodys
Investment-grade
Speculative/Junk
Common stock ownership claims in
corporations.
Vote on major company decisions
Cash dividends
Price appreciation
Preferred stock stockholders with
preference in the payment of dividends.
Stockholder has the
right to exchange the
bond or preferred
stock for a fixed
number of shares of
common stock.
Primary Market firms and governments
issue securities and sell them initially to
the public.
When a firm offers a stock for sale to the
general public for the first time.
Secondary Market collection of financial
markets in which previously issued
securities are traded among investors.
Stock market (exchange)
market in which common
stocks are traded, such as the
New York Stock Exchange.
The New York Stock Exchange the Big Board is the
most famous and one of the oldest stock markets in the
world. More than 3,000 stocks are listed on NYSE.
The Nasdaq Stock Market the second largest stock
market. Over 5,000 companies have their stocks listed
on Nasdaq but many are smaller firms.
Other U.S. Stock Markets
The American Stock Exchange/AMEX
Regional Stock Exchanges
Foreign Markets
ECNs electronic communication
networks
The 4
th
Market
Buyers and sellers meet in a virtual market
and exchange with one another
Take place on INET or Archipelago
INET and Archipelago have been
purchased by Nasdaq and NYSE
Investors use brokerage firms, they:
1) Establish an account
2) Enter orders
3) Trade stock
The brokerage firm executes the trade
on behalf of the investor, charging a fee
for the order
Market Order
Limit Order
Commercial Banks
Savings Banks and Credit Unions
Non-depository Institutions
An increasing amount of funds move through electronic
funds transfer (EFTs).
Millions of businesses and consumers now pay bills and
receive payments electronically.
Most employees directly deposit employee paychecks.
Social security and other federal payments are made
each year electronically.
Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) continue to grow in
popularity.
More than 1/3 of American households use some online
banking.
Enacted by the Banking Act of 1933
Restore public confidence in the banking system
Before deposit insurance, runs were common as
people rushed to withdraw their money from the
bank
Deposit insurance shifts the risk of bank failures
from individuals to the FDIC
Offer a variety of consumer services
85% of their loans are real estate loans
Credit unions are cooperative financial
institutions that are owned by
depositors/members.
Credit unions are created to serve consumers.
Insured by National Credit Union Administration
(NCUA) which functions the same as the FDIC
Insurance Companies
Pension Funds
Finance Companies
Created In 1913
Central bank of the United States
Regulate commercial banks
Perform banking-related activities for the
U.S. Department of Treasury
Providing services for banks
Setting monetary policy
12 Federal reserve districts
Own federal reserve bank
District banks are run by a nine-member board
of directors.
The board of governors is the governing body.
Politically independent
Federal Open Markets Committee (FOMC)
sets most policies concerning monetary policy
and interest rates.
Americans still write billions of paper checks.
The process by which funds are transferred from
the check writer to receiver
The multiple-step process is managed and
cleared by the FED.
The Check Clearing for the 21
st
Century Act is
making this process more electronic.
Supply of money and credit
Measures of the money supply: M1 & M2
The FED requires banks to maintain
reserves.
Set the discount rate
Open Market Operations
Bank Regulation
Government Regulation of the Financial
Markets
Industry Self-Regulation
Rules of conduct by professional
organizations like National Association of
Securities Dealers
Market Surveillance
The financial system is
more connected.
Financial institutions are
more global.
Only 3 of the 30 largest
banks in the world are US
institutions.
Most nations have a
central bank.
You might also like
- Role of Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument30 pagesRole of Financial Markets and InstitutionsĒsrar BalócNo ratings yet
- International Working Capital Management TechniquesDocument16 pagesInternational Working Capital Management TechniquesNancy DsouzaNo ratings yet
- MNC TNCDocument1 pageMNC TNCshakiraNo ratings yet
- Emerging trends in global marketsDocument54 pagesEmerging trends in global marketsChandan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Is the WTO Dispute Settlement System EffectiveDocument20 pagesIs the WTO Dispute Settlement System EffectiveSumitkumar SumanNo ratings yet
- Capital MarketDocument15 pagesCapital Marketरजनीश कुमारNo ratings yet
- What is the WTO? Understanding the World Trade OrganizationDocument7 pagesWhat is the WTO? Understanding the World Trade OrganizationJaya Krishna100% (1)
- DR Stanisław Kubielas: International FinanceDocument4 pagesDR Stanisław Kubielas: International FinanceGorana Goga RadisicNo ratings yet
- Euro Bond Market & TypesDocument2 pagesEuro Bond Market & TypesVikram Kaintura100% (1)
- Money Market and Capital MarketDocument36 pagesMoney Market and Capital Marketmisakisakura1102No ratings yet
- Asset Backed SecuritiesDocument179 pagesAsset Backed SecuritiesShivani NidhiNo ratings yet
- The Global Market Investment Decision: Chapter 3Document35 pagesThe Global Market Investment Decision: Chapter 3Esraa AhmedNo ratings yet
- CH 1 - Scope of International FinanceDocument7 pagesCH 1 - Scope of International Financepritesh_baidya269100% (3)
- International Capital MarketsDocument16 pagesInternational Capital Marketsshah_ashikaNo ratings yet
- Strikes, Picketing and LockoutsDocument43 pagesStrikes, Picketing and LockoutsnorzeNo ratings yet
- Shareholders' PresentationDocument29 pagesShareholders' PresentationBernard Tagoe100% (1)
- INR-YEN CURRENCY SWAP AGREEMENTDocument19 pagesINR-YEN CURRENCY SWAP AGREEMENTneha sharma100% (1)
- Financial Market PDFDocument19 pagesFinancial Market PDFAditya ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Central Bank (BNM)Document56 pagesTopic 4 Central Bank (BNM)Ing HongNo ratings yet
- International Financial InstitutionsDocument34 pagesInternational Financial InstitutionsMelvin Jan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Financial Services.Document127 pagesFinancial Services.srn@1234No ratings yet
- Global Capital Market & Their EffectsDocument22 pagesGlobal Capital Market & Their EffectsJay KoliNo ratings yet
- 3.3.6 Multinational CorporationsDocument32 pages3.3.6 Multinational CorporationsAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- The International Bond MarketDocument23 pagesThe International Bond Market2005raviNo ratings yet
- DAIBB Foreign Exchange-2Document15 pagesDAIBB Foreign Exchange-2arman_2772762710% (1)
- Monetary POLICYDocument21 pagesMonetary POLICYSrishti VasdevNo ratings yet
- Sources of international financing and analysisDocument6 pagesSources of international financing and analysisSabha Pathy100% (2)
- Function of Financial MarketsDocument11 pagesFunction of Financial MarketsYepuru ChaithanyaNo ratings yet
- HSE Saint Petersburg Financial Markets SyllabusDocument50 pagesHSE Saint Petersburg Financial Markets SyllabusSam PskovskiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Ethical Theories of Business EthicsDocument32 pagesLecture 2 - Ethical Theories of Business EthicsAishviniNo ratings yet
- Financial DerivativesDocument54 pagesFinancial Derivativesgaurav2616146No ratings yet
- The Shareholders: DR Safdar A ButtDocument23 pagesThe Shareholders: DR Safdar A ButtAhsanNo ratings yet
- Financial SystemDocument26 pagesFinancial Systemsheena guptaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Futures MarketsDocument20 pagesMechanics of Futures Marketsuuuuufffff0% (1)
- What Is A "Derivative" ?Document4 pagesWhat Is A "Derivative" ?RAHULNo ratings yet
- International Capital MarketsDocument11 pagesInternational Capital MarketsAmbika JaiswalNo ratings yet
- A Critical Analysis of IMFDocument31 pagesA Critical Analysis of IMFvssm123No ratings yet
- 2839 Financial Globalization Chapter May30Document45 pages2839 Financial Globalization Chapter May30indiaholicNo ratings yet
- M07 MishkinEakins3427056 08 FMI C07Document58 pagesM07 MishkinEakins3427056 08 FMI C07Declan ShuitNo ratings yet
- What Is A Financial MarketDocument1 pageWhat Is A Financial Marketamitrao1983No ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Mutual FundsDocument7 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Mutual FundsNeha GoyalNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Financial SystemDocument12 pagesEvolution of Financial SystemGautam JayasuryaNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Cost ofDocument17 pagesMCQ On Cost ofbarbie dollNo ratings yet
- The Bond Market in GhanaDocument12 pagesThe Bond Market in GhanaJohn Kennedy Akotia100% (3)
- Currency Exposure ManagementDocument52 pagesCurrency Exposure ManagementBernardCharo100% (1)
- Functions of the Money Market: Financing, Central Bank Policies, Industry Growth, Bank LiquidityDocument2 pagesFunctions of the Money Market: Financing, Central Bank Policies, Industry Growth, Bank LiquidityDiyaNo ratings yet
- Factor Endowment Theory FialDocument38 pagesFactor Endowment Theory FialKarthik SivaNo ratings yet
- Import Finance MethodsDocument6 pagesImport Finance MethodsSammir Malhotra0% (1)
- International Banking Functions GuideDocument22 pagesInternational Banking Functions GuideMayankTayalNo ratings yet
- Mergeracquisitionwithcasestudy PPTPDFDocument45 pagesMergeracquisitionwithcasestudy PPTPDFMandip LuitelNo ratings yet
- Chapter16 by Group CDocument33 pagesChapter16 by Group CMohamedAli AbdulleNo ratings yet
- AAOIFI Standards For Istisna'ADocument19 pagesAAOIFI Standards For Istisna'AAshraf FarhadNo ratings yet
- Institutional Reform of The WTODocument27 pagesInstitutional Reform of The WTOOxfamNo ratings yet
- CH12 Mish11 EMBFMDocument40 pagesCH12 Mish11 EMBFMBradley Ray100% (1)
- What is a euro bondDocument5 pagesWhat is a euro bondpranoti_shinde8167No ratings yet
- Understanding the Financial System and its Key ComponentsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding the Financial System and its Key ComponentsKen TuazonNo ratings yet
- The Financial SystemDocument31 pagesThe Financial SystemFarjad AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-2Document40 pagesChapter 1-2jakeNo ratings yet
- 1201 CCP Literature ReviewDocument5 pages1201 CCP Literature Reviewapi-548148057No ratings yet
- Native Immersion #2 - Shopping in A Nutshell PDFDocument43 pagesNative Immersion #2 - Shopping in A Nutshell PDFmeenaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Customer Loyalty to Indosat OoredooDocument13 pagesFactors Affecting Customer Loyalty to Indosat OoredooDede BhubaraNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 2019-20Document33 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 2019-20omvrat singhNo ratings yet
- File 1599385749210Document21 pagesFile 1599385749210adel madanyNo ratings yet
- Enuma Elish LitChartDocument20 pagesEnuma Elish LitChartsugarntea24No ratings yet
- Chisholm - Referring To Things That No Longer ExistDocument13 pagesChisholm - Referring To Things That No Longer ExistMichele Paolini PaolettiNo ratings yet
- Narrative Techniques To Kill A MockingbirdDocument4 pagesNarrative Techniques To Kill A MockingbirdJoshua LawrenceNo ratings yet
- College Resume TemplateDocument7 pagesCollege Resume Templatevofysyv1z1v3100% (1)
- Phronesis Volume 7 Issue 1 1962 (Doi 10.2307/4181698) John Malcolm - The Line and The CaveDocument9 pagesPhronesis Volume 7 Issue 1 1962 (Doi 10.2307/4181698) John Malcolm - The Line and The CaveNițceValiNo ratings yet
- Antenna & Wave Propagation - Course OutlineDocument2 pagesAntenna & Wave Propagation - Course OutlineSabuj AhmedNo ratings yet
- Disirders of Synaptic Plasticity and Schizophrenia - J.smythiesDocument559 pagesDisirders of Synaptic Plasticity and Schizophrenia - J.smythiesBrett CromptonNo ratings yet
- A Summer's Reading - Sample Questions With AnswersDocument11 pagesA Summer's Reading - Sample Questions With AnswersRoy SchwartzNo ratings yet
- Mars - Andrew D. Basiago - Letter To The Ngs - 12 12 08Document4 pagesMars - Andrew D. Basiago - Letter To The Ngs - 12 12 08Gavin SimmonsNo ratings yet
- Assessing Learning Methods and TestsDocument2 pagesAssessing Learning Methods and TestsZarah Joyce SegoviaNo ratings yet
- (PC) Brian Barlow v. California Dept. of Corrections Et Al - Document No. 4Document2 pages(PC) Brian Barlow v. California Dept. of Corrections Et Al - Document No. 4Justia.comNo ratings yet
- José Rizal: The Life of The National HeroDocument9 pagesJosé Rizal: The Life of The National HeroMark Harry Olivier P. VanguardiaNo ratings yet
- Epd-Lca Meranti Plywood-Final ReportDocument29 pagesEpd-Lca Meranti Plywood-Final ReporttangNo ratings yet
- MCD2040 T2 2019 Exam Content and StructureDocument18 pagesMCD2040 T2 2019 Exam Content and StructureheyitsmemuahNo ratings yet
- Living Water by David FeddesDocument44 pagesLiving Water by David FeddesBenjaminFigueroaNo ratings yet
- Court Document SummaryDocument15 pagesCourt Document SummaryAkAsh prAkhAr vErmA100% (1)
- The Loner-Staying Clean in IsolationDocument4 pagesThe Loner-Staying Clean in Isolationgemgirl6686No ratings yet
- Laertes' Temper: Definition of DiacopeDocument27 pagesLaertes' Temper: Definition of DiacopeAhmad Abdellah ElsheemiNo ratings yet
- Nokia CaseDocument28 pagesNokia CaseErykah Faith PerezNo ratings yet
- HI6025 Assignment T3, 2016Document3 pagesHI6025 Assignment T3, 2016Abeer ArifNo ratings yet
- Ansys Geotechnical Geology - Finite Element ModelingDocument25 pagesAnsys Geotechnical Geology - Finite Element ModelingvishnuNo ratings yet
- NIH Strategic Plan For Data ScienceDocument26 pagesNIH Strategic Plan For Data ScienceAristide AhonzoNo ratings yet
- Pope Francis' Call to Protect Human Dignity and the EnvironmentDocument5 pagesPope Francis' Call to Protect Human Dignity and the EnvironmentJulie Ann BorneoNo ratings yet
- Ageli Software DevelopmentDocument112 pagesAgeli Software DevelopmentRyan Adrian100% (2)
- Biology-A Complete Solution For - V. Educational ServicesDocument2,088 pagesBiology-A Complete Solution For - V. Educational Servicesteamindian gamersNo ratings yet