Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Material Handling
Uploaded by
NishaThakuriCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Material Handling
Uploaded by
NishaThakuriCopyright:
Available Formats
PRODUCTION
SYSTEM DESIGN
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
Introduction and Definition
Objectives of MH
1. Reduction of Handling Costs
Reduction of labor cost
Reduction of material cost
Reduction of overhead cost
2. Increase of Capacity
Increase of Production
Increase of storage capacity
Improved layout
3. Improvement of working condition
Increase safety
Reduction in fatigue
Strategic location of storage facilities
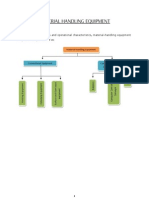
Materials Flow Diagram
MH system in the form of Flow Diagram:
Raw mat. supplier Transportation Receiving at
store
Storing Manufacturing/fabrication units
Flow of parts to
assembly line
Testing and
packaging
shipping
Warehouse
Dealers/consumers
Disposal/
recycling
MATERIAL HANDLING
Functions of MH
1. Minimize the movements
2. Principle of containerization, palletization
3. Minimize the distance moved
4. Employ mechanical aids
5. Minimize back tracking and duplicate movement
6. Safe, standard, efficient, effective, appropriate,
flexible, and proper sized MH equipment
7. No interference with the production line
8. Utilize gravity
9. Design containers, drums, packages
10. MH equipments should be checked up, repaired and
maintained
MATERIAL HANDLING
Principles of MH
Principles related to planning
1. Planning Principles
2. Systems Principles
3. Simplification Principle
4. Material Flow Principle
5. Gravity Principle
6. Use size principle
7. Space Utilization Principle
8. Safety Principle
MATERIAL HANDLING
Principles of MH
Principles related to equipment
1. Mechanization Principles
2. Flexibility Principles
3. Equipment Selection Principle
4. Standardization Principle
5. Light Weight Principle
6. Motion Principle
7. Idle Time Principle
8. Obsolescence Principle
9. Maintenance Principle
10. Control Principle
Factors to be considered in material handling problem
1 Engineering factors 2 Economic factors
Engineering factors to be considered:
Nature of materials and products (solid, gas, etc)
Production process and equipment (sequence of
operation, machine output per unit time)
Building construction (single or multi-storey)
Layout (layout and material handling are not
separable)
Existing material handling equipment
Production planning and control (sequence for
material flow and timing for processing)
Packaging (easy handling of packaged products)
Economic factors to be considered in MH
Initial cost of equipment
Cost of installation
Rearrangement of present equipment
Cost of alternation necessary to the building
Cost of maintenance, repairs, supplies etc
Cost of power, depreciation
Cost of labor to operate
Cost of auxiliary equipment (for example, charging
equipment for truck batteries, etc)
Flexible MH equipment help in reducing operating costs.
Material handling devices
1. Lifting and lowering devices (vertical
movement)
2. Transporting devices (horizontal
movement)
3. Devices with lift and transport (combination
devices)
4. Industrial Robots
5. Automatically guided vehicles
MATERIAL HANDLING
Types of MH Equipments
Characteristics of MH equipment
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
Classification of MH Equipments
1. Industrial Trucks
Manual / Powered Two Wheeled, Three Wheeled,
Four Wheeled Fork lift Truck
2. Cranes
3. Hoists Pneumatic/Electrical
4. Monorail
5. Conveyors Roller, Belt, Bucket, Chain,
Pipeline
6. Slides and Chutes
7. Lifts
8. Tractors and Trailers
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
MATERIAL HANDLING
Industrial Robots
A robot is a reprogrammable multifunctional
manipulator designed to move material, parts,
tools, or specialized devices through variable
programmed motions for the performance of a
variety of tasks
Robots are like human workers
Robot application:
-to pick up hot steel ingots
-handling radioactive rods in nuclear power
plants
-spot welding and arc welding
Automated Guided Vehicle systems (AVGS)
Battery-powered, automatically steered
vehicles designed to follow defined pathways.
Capable of automatically loading and
unloading unit loads
Usually interfaced with other automated
systems to achieve full benefits of integrated
automation.
Examples: driverless trains, pallet trucks, unit
load carriers
Relation between plant layout and MH
Close relation
MH methods influence the layout and factory building
Integral part of plant layout to design low cost handling
system
Good MH is resulted based on the arrangement of
production equipment, location of departments, logical
sequence of operations, location of stores, tools
MH system/equipment can be selected only after the
appropriate floor plan
Plant layout considers the points for material receiving
and shipping of products
Careful arrangement of work centers and storage areas
Consider horizontal or vertical material transportation
Process layout and MH system
Need of flexibility-flexibility of path, and flexibility of size,
weight and shape of load
Mobile trucks, tractor trains, cranes, and forklift trucks, etc.
Loading and unloading time is very important for efficient
MH system
Quick pick up systems have developed around skids and
pallets
Material is loaded directly on skid or pallet by worker as
S/he completes his operation on the part
Heavy parts/loads are handled by overhead cranes
How much MH equipment is needed? Difficult question
because of random variations on demand for transporting
capacity in process layouts.
Line layout and MH
Nature of line layout requires direct means of transportation
between operations
Arrange the material flow so that each operator places the
unit down in such a position that it can be picked up by the
succeeding worker
Where possible gravity chutes can be used
Chutes are common in railway and air line terminal for
handling baggage.
Conveyers to lift all types of parts are available
Conveyers require a considerable amount of special design
to fit them into an effective overall design of a line layout
Task for self study
Review the literatures on material handling
equipment. Understand the basic physical
construction and application of major
material handling equipment used in
manufacturing and construction sector.
Participate actively in class room discussion
and demonstrate your knowledge and
understanding ability on material handling
equipment.
MATERIAL HANDLING
References:
Industrial Engineering and Management Dr.
O. P. Khanna Dhanpat Rai Publications
Industrial Engineering A. P. Verma S. K.
Kataria and Sons
Industrial Engineering and Production
Management M. Mahajan Dhanpat Rai and
Co.
QUESTIONS ?
THANK YOU!
You might also like
- Organisational Structure of NetflixDocument2 pagesOrganisational Structure of NetflixAnkita Das57% (7)
- WoodCarving Illustrated 044 (Fall 2008)Document100 pagesWoodCarving Illustrated 044 (Fall 2008)Victor Sanhueza100% (7)
- The Van Conversion Bible - The Ultimate Guide To Converting A CampervanDocument170 pagesThe Van Conversion Bible - The Ultimate Guide To Converting A CampervanPil100% (3)
- Summary Studying Public Policy Michael Howlett CompleteDocument28 pagesSummary Studying Public Policy Michael Howlett CompletefadwaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Material Handling AssignmentDocument27 pagesPrinciples of Material Handling AssignmentMuriithi MichaelsNo ratings yet
- Purchase and Material Management PDFDocument137 pagesPurchase and Material Management PDFMohamed ShareefNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes During 1st Stage of LaborDocument18 pagesPhysiological Changes During 1st Stage of LaborNishaThakuri90% (39)
- Timken Bearing Damage PosterDocument1 pageTimken Bearing Damage Postera04205100% (5)
- Material Handling 2009Document45 pagesMaterial Handling 2009FarhinNo ratings yet
- Material HandlingDocument64 pagesMaterial HandlingDaniel Espina100% (1)
- 7-Principles of Material Handling-170811Document5 pages7-Principles of Material Handling-170811pammy313No ratings yet
- Material HandlingDocument26 pagesMaterial HandlingRohit AroraNo ratings yet
- Materials HandlingDocument6 pagesMaterials HandlingRose LopezNo ratings yet
- Material HandlingDocument17 pagesMaterial HandlingJessica SaballeroNo ratings yet
- Material Handling LeturerDocument42 pagesMaterial Handling LeturerMohammad Anwar AliNo ratings yet
- 1 Material Handling and Identification TechnologiesDocument75 pages1 Material Handling and Identification TechnologiesPavan Teja100% (1)
- Lecture 6 Overview of Material Handling and Management (Part I)Document20 pagesLecture 6 Overview of Material Handling and Management (Part I)sharifah atiqahNo ratings yet
- Material Handling Equipment...Document41 pagesMaterial Handling Equipment...Shubhan Singh100% (2)
- Types of Material Handling EquipmentDocument7 pagesTypes of Material Handling EquipmentWilly K. Ng'etichNo ratings yet
- Material Handling & Storage SystemsDocument22 pagesMaterial Handling & Storage SystemsShikha KathuriaNo ratings yet
- Material Handling SystemsDocument30 pagesMaterial Handling SystemsSaadShees100% (1)
- Material HandlingDocument26 pagesMaterial HandlingSahil KhuntetaNo ratings yet
- Material Handling NewDocument70 pagesMaterial Handling Newphilo minaNo ratings yet
- Facilities Layout and Materials HandlingDocument22 pagesFacilities Layout and Materials HandlingHarish PadmanabanNo ratings yet
- Material HandlingDocument4 pagesMaterial HandlingVaidehiranaNo ratings yet
- Material Handling Notes 2013Document198 pagesMaterial Handling Notes 2013taridan100% (1)
- Case Study-Material Handling SystemDocument22 pagesCase Study-Material Handling Systemmsquire4100% (2)
- Chapter 6 Storage SystemsDocument53 pagesChapter 6 Storage SystemsTú QuyênNo ratings yet
- Material Handling EquipmentDocument7 pagesMaterial Handling EquipmentT ShanmugavelNo ratings yet
- Types of Material Handling EquipmentDocument17 pagesTypes of Material Handling EquipmentAdhanom G.100% (1)
- Manufacturing Material Handling Equipment: Profile No.: 225 NIC Code: 28162Document11 pagesManufacturing Material Handling Equipment: Profile No.: 225 NIC Code: 28162Vikram PhalakNo ratings yet
- Material Handling Equipment Is Equipment That Relate To The MovementDocument4 pagesMaterial Handling Equipment Is Equipment That Relate To The MovementResh MaNo ratings yet
- Material Handling: Material Handling Involves Short-Distance Movement Within The Confines of A Building orDocument7 pagesMaterial Handling: Material Handling Involves Short-Distance Movement Within The Confines of A Building orNidhi EnterprisesNo ratings yet
- 5.material Handling System Design and DecisionDocument19 pages5.material Handling System Design and DecisionSaranya SathiyamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Material HandlingDocument31 pagesMaterial HandlingcataninoNo ratings yet
- Just in TimeDocument4 pagesJust in TimeMariano RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Material Handling EquipmentsDocument12 pagesMaterial Handling EquipmentsHaresh Pawar100% (1)
- ConveyorsDocument17 pagesConveyorsmissy forlajeNo ratings yet
- Material Handling EquipmentsDocument35 pagesMaterial Handling EquipmentsKailas Sree Chandran100% (4)
- 11.0 Material HandlingDocument4 pages11.0 Material HandlingNol BarandonNo ratings yet
- Design and Control of Warehouse Order Picking A Literature ReviewDocument33 pagesDesign and Control of Warehouse Order Picking A Literature ReviewPatcharapon SukjumratNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Material Handling SystemDocument16 pagesMechanical Material Handling SystemsarabjeetjoharNo ratings yet
- Material Handling (Full Notes)Document320 pagesMaterial Handling (Full Notes)Kailas Sree Chandran90% (52)
- Material Handling PRD 430Document94 pagesMaterial Handling PRD 430Dr_M_Soliman75% (4)
- Logistics Driven PackagingDocument20 pagesLogistics Driven PackagingnixamaniNo ratings yet
- Warehouse OperationsDocument9 pagesWarehouse Operationssanzit100% (1)
- Design Optimization For Modification of Trough Belt Conveyor To Reduce Material Spillage Used in Clinker Transport in Cement PlantDocument11 pagesDesign Optimization For Modification of Trough Belt Conveyor To Reduce Material Spillage Used in Clinker Transport in Cement PlantBob AntunesNo ratings yet
- Materials HandlingDocument34 pagesMaterials HandlingPrachi SinghNo ratings yet
- Material HandlingDocument30 pagesMaterial HandlingGeeta Rani100% (1)
- Unit 3.2 - Material HandlingDocument23 pagesUnit 3.2 - Material Handlinglamao123No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - MATERIAL HANDLING PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 3 - MATERIAL HANDLING PDFShiverrania 29080% (1)
- Material HandlingDocument20 pagesMaterial HandlingmehariiNo ratings yet
- Plant LayoutDocument66 pagesPlant LayoutSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Warehouse OverviewDocument18 pagesWarehouse OverviewpremNo ratings yet
- Material Handling & Identification TechnologiesDocument66 pagesMaterial Handling & Identification TechnologiesFiroz Khan100% (1)
- Stores Management and Materials HandlingDocument21 pagesStores Management and Materials HandlingMr. Umang PanchalNo ratings yet
- 04.material HandlingDocument88 pages04.material HandlingPurav Riat67% (3)
- Unit Load ConceptsDocument5 pagesUnit Load ConceptsProf C.S.Purushothaman100% (1)
- Design of Material Handling EquipmentsDocument1 pageDesign of Material Handling Equipmentsviswa375No ratings yet
- Supply Chain & LogisticsDocument44 pagesSupply Chain & LogisticsashwinsudaNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2021-22 MEE1018 TH VL2021220503069 Reference Material I 11-04-2022 Module6Document57 pagesWINSEM2021-22 MEE1018 TH VL2021220503069 Reference Material I 11-04-2022 Module6Harsh VermaNo ratings yet
- Material Handling Systems: For Exploiting Productivity Potential in LogisticsDocument25 pagesMaterial Handling Systems: For Exploiting Productivity Potential in LogisticsSwapnil MalpathakNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 - Introduction To Material Handling EquipmentsDocument20 pagesUNIT 1 - Introduction To Material Handling EquipmentsAdugna GosaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Basics of MHEsDocument48 pages1 - Basics of MHEsMengie ManNo ratings yet
- Material HandlingDocument19 pagesMaterial Handlingcooljudgesingh0% (1)
- Chapter 6Document36 pagesChapter 6Gaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Appendix B: The Work Plan of The Research StudyDocument1 pageAppendix B: The Work Plan of The Research StudyNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Regarding Oxytocin Administration Among Nurses in Phect NepalDocument1 pageKnowledge Regarding Oxytocin Administration Among Nurses in Phect NepalNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal o NishaDocument14 pagesResearch Proposal o NishaNishaThakuri100% (1)
- Physiological Changes During 2nd Stage of LaborDocument5 pagesPhysiological Changes During 2nd Stage of LaborNishaThakuri100% (4)
- Normal Labor Unit 2.1Document19 pagesNormal Labor Unit 2.1NishaThakuri100% (1)
- Breeech PresentationDocument3 pagesBreeech PresentationNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument4 pagesFetal CirculationNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Normal LaborDocument8 pagesNormal LaborNishaThakuri100% (2)
- Forcep DeliveryDocument26 pagesForcep DeliveryNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Newborn ResuscitationDocument34 pagesNewborn ResuscitationNishaThakuri100% (2)
- Report of PPHDocument58 pagesReport of PPHNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Failure To Initiate and Sustain Breathing at Birth Is Called Birth AsphyxiaDocument21 pagesFailure To Initiate and Sustain Breathing at Birth Is Called Birth AsphyxiaNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- The UK All Party Parliamentary Group On Population, Development and Reproductive Health Parliamentary Hearings Into Maternal MorbidityDocument2 pagesThe UK All Party Parliamentary Group On Population, Development and Reproductive Health Parliamentary Hearings Into Maternal MorbidityNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- PERINATAL PATIENT SAFETY: Management of Oxytocin For Labor Induction and Augmentation MCN, The American Journal of Maternal/Child NursingDocument2 pagesPERINATAL PATIENT SAFETY: Management of Oxytocin For Labor Induction and Augmentation MCN, The American Journal of Maternal/Child NursingNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Mid BDocument11 pagesCurriculum Mid BNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin (: ActionsDocument8 pagesOxytocin (: ActionsNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Entrance Preparation Model Questions FinalDocument33 pagesEntrance Preparation Model Questions FinalNishaThakuri100% (1)
- Mental Case StudyDocument38 pagesMental Case StudyNishaThakuri80% (5)
- The Behaviour of Ductile and Brittle Material On Different Loading Conditions (Recovered)Document7 pagesThe Behaviour of Ductile and Brittle Material On Different Loading Conditions (Recovered)NishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- IMO Publication Catalogue List (June 2022)Document17 pagesIMO Publication Catalogue List (June 2022)Seinn NuNo ratings yet
- FinTech RegTech and SupTech - What They Mean For Financial Supervision FINALDocument19 pagesFinTech RegTech and SupTech - What They Mean For Financial Supervision FINALirvandi syahputraNo ratings yet
- Form Ticketing Latihan ContohDocument29 pagesForm Ticketing Latihan ContohASPIN SURYONONo ratings yet
- Attachment 05 - BFD, ELD and P&I Diagrams-PearlDocument77 pagesAttachment 05 - BFD, ELD and P&I Diagrams-Pearlum er100% (1)
- Valery 1178Document22 pagesValery 1178valerybikobo588No ratings yet
- Output Vat Zero-Rated Sales ch8Document3 pagesOutput Vat Zero-Rated Sales ch8Marionne GNo ratings yet
- Heirs of Tancoco v. CADocument28 pagesHeirs of Tancoco v. CAChris YapNo ratings yet
- Pivacare Preventive-ServiceDocument1 pagePivacare Preventive-ServiceSadeq NeiroukhNo ratings yet
- Philippine Disaster Risk Reducation and ManagementDocument10 pagesPhilippine Disaster Risk Reducation and ManagementDareNo ratings yet
- COST v. MMWD Complaint 8.20.19Document64 pagesCOST v. MMWD Complaint 8.20.19Will HoustonNo ratings yet
- Octopus 900 Instructions For UseDocument18 pagesOctopus 900 Instructions For UseAli FadhilNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management - Introduction - A Revision Article - A Knol by Narayana RaoDocument7 pagesHuman Resource Management - Introduction - A Revision Article - A Knol by Narayana RaoHimanshu ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Art 3 Sec 2Document157 pagesArt 3 Sec 2KELVINNo ratings yet
- Management by ObjectivesDocument30 pagesManagement by ObjectivesJasmandeep brar100% (4)
- Data Loss PreventionDocument20 pagesData Loss Preventiondeepak4315No ratings yet
- Class B Digital Device Part 15 of The FCC RulesDocument7 pagesClass B Digital Device Part 15 of The FCC RulesHemantkumarNo ratings yet
- Definition of Sustainable Packaging PDFDocument10 pagesDefinition of Sustainable Packaging PDFProf C.S.PurushothamanNo ratings yet
- Invidis Yearbook 2019Document51 pagesInvidis Yearbook 2019Luis SanchezNo ratings yet
- Magicolor2400 2430 2450FieldSvcDocument262 pagesMagicolor2400 2430 2450FieldSvcKlema HanisNo ratings yet
- Shareholder Agreement 06Document19 pagesShareholder Agreement 06Josmar TelloNo ratings yet
- Eletrical InstallationDocument14 pagesEletrical InstallationRenato C. LorillaNo ratings yet
- ABES Engineering College, Ghaziabad Classroom Photograph: (Ramanujan Block, First Floor)Document21 pagesABES Engineering College, Ghaziabad Classroom Photograph: (Ramanujan Block, First Floor)Avdhesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Nfjpia Mockboard 2011 BLTDocument12 pagesNfjpia Mockboard 2011 BLTVon Wilson AjocNo ratings yet
- MushroomDocument8 pagesMushroomAkshay AhlawatNo ratings yet
- Aml Questionnaire For Smes: CheduleDocument5 pagesAml Questionnaire For Smes: CheduleHannah CokerNo ratings yet