Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap 002
Uploaded by
Lucas Freire MartinsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chap 002
Uploaded by
Lucas Freire MartinsCopyright:
Available Formats
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
Copyright 2011 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, I nc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/I rwin
CHAPTER 2
Asset Classes and Financial
Instruments
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-2
Asset Classes
Money market instruments
Capital market instruments
Bonds
Equity Securities
Derivative Securities
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-3
The Money Market
Subsector of the fixed-income market:
Securities are short-term, liquid, low
risk, and often have large
denominations
Money market mutual funds allow
individuals to access the money
market.
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-4
Table 2.1 Major Components of
the Money Market
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-5
Money Market Securities
Treasury bills: Short-term debt of U.S.
government
Bid and asked price
Bank discount method
Certificates of Deposit: Time deposit with a
bank
Commercial Paper: Short-term, unsecured
debt of a company
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-6
Money Market Securities
Bankers Acceptances: An order to a bank
by a banks customer to pay a sum of
money on a future date
Eurodollars: dollar-denominated time
deposits in banks outside the U.S.
Repos and Reverses: Short-term loan
backed by government securities.
Fed Funds: Very short-term loans between
banks
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-7
Yields on Money Market Instruments
Except for Treasury bills, money market
securities are not free of default risk
Both the premium on bank CDs and the
TED spread have often become greater
during periods of financial crisis
During the credit crisis of 2008, the federal
government offered insurance to money
market mutual funds after some funds
experienced losses
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-8
The Bond Market
Treasury Notes and Bonds
Inflation-Protected Treasury
Bonds
Federal Agency Debt
International Bonds
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-9
The Bond Market
Municipal Bonds
Corporate Bonds
Mortgages and Mortgage-Backed
Securities
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-10
Treasury Notes and Bonds
Maturities
Notes maturities up to 10 years
Bonds maturities from 10 to 30
years
Par Value - $1,000
Interest paid semiannually
Quotes percentage of par
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-11
The Bond Market
Inflation-Protected Treasury Bonds
TIPS: Provide inflation protection
Federal Agency Debt
Debt of mortgage-related agencies such as
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac
International Bonds
Eurobonds and Yankee bonds
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-12
Municipal Bonds
Issued by state and local governments
Interest is exempt from federal income
tax and sometimes from state and local
tax
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-13
Municipal Bonds
Types
General obligation bonds: Backed by taxing
power of issuer
Revenue bonds: backed by projects
revenues or by the municipal agency
operating the project.
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-14
Figure 2.4 Tax-exempt Debt
Outstanding
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-15
Municipal Bond Yields
To choose between taxable and tax-exempt
bonds, compare after-tax returns on each
bond.
Let t equal the investors marginal tax
bracket
Let r equal the before-tax return on the
taxable bond and r
m
denote the municipal
bond rate.
If r (1 - t ) > r
m
then the taxable bond gives
a higher return; otherwise, the municipal
bond is preferred.
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-16
Table 2.2 Tax-Exempt Yield Table
The equivalent taxable yield is simply the tax-free
rate, r
m
, divided by (1-t).
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-17
Corporate Bonds
Issued by private firms
Semi-annual interest payments
Subject to larger default risk than
government securities
Options in corporate bonds
Callable
Convertible
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-18
Proportional ownership of a mortgage
pool or a specified obligation secured by
a pool
Produced by securitizing mortgages
Mortgage-backed securities are called
pass-throughs because the cash flows
produced by homeowners paying off their
mortgages are passed through to
investors.
Mortgage-Backed Securities
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-19
Mortgage-Backed Securities
Most mortgage-backed securities were
issued by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
Traditionally, pass-throughs were
comprised of conforming mortgages,
which met standards of credit worthiness.
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-20
Mortgage-Backed Securities
Eventually, Private-label issuers
securitized large amounts of subprime
mortgages, made to financially weak
borrowers.
Finally, Fannie and Freddie were allowed
and even encouraged to buy subprime
mortgage pools.
September, 2008: Fannie and Freddie got
taken over by the federal government.
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-21
Figure 2.6 Mortgage-backed securities
outstanding
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-22
Equity Securities
Common stock: Ownership
Residual claim
Limited liability
Preferred stock: Perpetuity
Fixed dividends
Priority over common
Tax treatment
American Depository Receipts
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-23
Stock Market Indexes
Dow Jones Industrial Average
Includes 30 large blue-chip
corporations
Computed since 1896
Price-weighted average
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-24
Example 2.2 Price-Weighted Average
Portfolio: Initial value $25 + $100 = $125
Final value $30 + $ 90 = $120
Percentage change in portfolio value
= 5/125 = -.04 = -4%
Index: Initial index value (25+100)/2 = 62.5
Final index value (30 + 90)/2 = 60
Percentage change in index -2.5/62.5
= -.04 = -4%
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-25
S&P 500
Broadly based index of 500 firms
Market-value-weighted index
Investors can base their portfolios
on an index:
Buy an index mutual fund
Buy exchange traded funds (ETFs)
Standard & Poors Indexes
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-26
Other Indexes
U.S. Indexes
NYSE Composite
NASDAQ Composite
Wilshire 5000
Foreign Indexes
Nikkei (Japan)
FTSE (U.K.; pronounced
footsie)
DAX (Germany),
Hang Seng (Hong Kong)
TSX (Canada)
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-27
Derivatives Markets
Options and futures provide payoffs that
depend on the values of other assets such
as commodity prices, bond and stock
prices, or market index values.
A derivative is a security that gets its value
from the values of another asset.
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-28
Options
Call: Right to buy underlying asset at the
strike or exercise price.
Value of calls decrease as strike price
increases
Put: Right to sell underlying asset at the
strike or exercise price.
Value of puts increase with strike price
Value of both calls and puts increase with
time until expiration.
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-29
Futures Contracts
A futures contract calls for delivery of an
asset (or in some cases, its cash value) at
a specified delivery or maturity date for an
agreed-upon price, called the futures
price, to be paid at contract maturity.
Long position: Take delivery at maturity
Short position: Make delivery at maturity
INVESTMENTS | BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
2-30
Comparison
Option
Right, but not obligation,
to buy or sell; option is
exercised only when it is
profitable
Options must be
purchased
The premium is the price
of the option itself.
Futures Contract
Obliged to make or take
delivery. Long position
must buy at the futures
price, short position must
sell at futures price
Futures contracts are
entered into without cost
You might also like
- Study Plan - CFADocument19 pagesStudy Plan - CFALucas Freire MartinsNo ratings yet
- Hedge funds capitalize on distressed securitiesDocument25 pagesHedge funds capitalize on distressed securitiesAlexandre DeneuvilleNo ratings yet
- Understanding J Curve PDFDocument16 pagesUnderstanding J Curve PDFLucas Freire MartinsNo ratings yet
- Final Initial Initial Final Initial InitialDocument3 pagesFinal Initial Initial Final Initial InitialLucas Freire MartinsNo ratings yet
- 316 TA Section 2Document5 pages316 TA Section 2Lucas Freire MartinsNo ratings yet
- Hedge funds capitalize on distressed securitiesDocument25 pagesHedge funds capitalize on distressed securitiesAlexandre DeneuvilleNo ratings yet
- Understanding J Curve PDFDocument16 pagesUnderstanding J Curve PDFLucas Freire MartinsNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 316 Fall 2013Document2 pagesSyllabus 316 Fall 2013stofangerNo ratings yet
- Einstein biography reveals genius and innovationDocument18 pagesEinstein biography reveals genius and innovationDoru MardariNo ratings yet
- 316 TA Section 1Document5 pages316 TA Section 1Lucas Freire MartinsNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement ModelingDocument1 pageFinancial Statement ModelingLucas Freire MartinsNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 316 Fall 2013Document2 pagesSyllabus 316 Fall 2013stofangerNo ratings yet
- Chap 001Document31 pagesChap 001Lucas Freire MartinsNo ratings yet
- Chap 005Document44 pagesChap 005Lucas Freire MartinsNo ratings yet
- Man - Invest Chap 006Document34 pagesMan - Invest Chap 006yolaNo ratings yet
- Arellano BondDocument22 pagesArellano BondVu Thi Duong BaNo ratings yet
- Chap 004Document24 pagesChap 004Lucas Freire MartinsNo ratings yet
- Chap 003Document39 pagesChap 003Lucas Freire MartinsNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractLucas Freire MartinsNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- General Quarter 2 - Week 1: ZZZZZZDocument14 pagesGeneral Quarter 2 - Week 1: ZZZZZZJakim Lopez0% (1)
- ECGC Export Credit Guarantee Corp of India Summer TrainingDocument24 pagesECGC Export Credit Guarantee Corp of India Summer TrainingPhxx619No ratings yet
- Financial Statements PreparationDocument6 pagesFinancial Statements Preparationana lopezNo ratings yet
- Section "A" Very Short Answer Questions) (Attempt All Questions)Document5 pagesSection "A" Very Short Answer Questions) (Attempt All Questions)Ayusha TimalsinaNo ratings yet
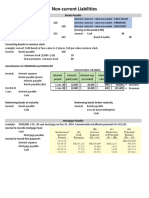
- Non-Current Liabilities Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNon-Current Liabilities Cheat SheetSarah SafiraNo ratings yet
- Financial Management PPT PresentationDocument52 pagesFinancial Management PPT PresentationJadez Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Admission of A New PartnerDocument36 pagesAdmission of A New PartnerSreekanth DogiparthiNo ratings yet
- Control of The Money SupplyDocument2 pagesControl of The Money SupplyMario SarayarNo ratings yet
- Private Credit Solutions:: A Closer Look at The Opportunity in Emerging MarketsDocument48 pagesPrivate Credit Solutions:: A Closer Look at The Opportunity in Emerging MarketsAljon Del Rosario100% (1)
- Omtex Classes: "The Home of Success"Document4 pagesOmtex Classes: "The Home of Success"AMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADERNo ratings yet
- Torrent Electricity BillDocument2 pagesTorrent Electricity BillSaiyad MoinmiyaNo ratings yet
- Basis Trading BasicsDocument51 pagesBasis Trading BasicsTajinder SinghNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument42 pagesFinalumshzzNo ratings yet
- NLU Jodhpur SyllabusDocument87 pagesNLU Jodhpur SyllabusDiya PandeNo ratings yet
- Sample Loan Mod Package W ProposalDocument12 pagesSample Loan Mod Package W ProposalJules Caesar VallezNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal of Gold ETFS in India: Finance ManagementDocument4 pagesPerformance Appraisal of Gold ETFS in India: Finance ManagementpatelaxayNo ratings yet
- Prelim ExamDocument5 pagesPrelim Examdasha limNo ratings yet
- 2021 Annual Financial Report For The National Government Volume IDocument506 pages2021 Annual Financial Report For The National Government Volume IAliah MagumparaNo ratings yet
- Barclays Shiller White PaperDocument36 pagesBarclays Shiller White PaperRyan LeggioNo ratings yet
- Bank Statement: Bizdirect Contact Centre: 0860 109 075Document6 pagesBank Statement: Bizdirect Contact Centre: 0860 109 075GabrielNo ratings yet
- GulfDocument17 pagesGulfmastermind_2848154No ratings yet
- Icici Bank and Bank of MaduraDocument2 pagesIcici Bank and Bank of MaduraKrupa ShahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Corporate FinanceDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Corporate FinanceYee Mon AungNo ratings yet
- ALEKSANDRADocument1 pageALEKSANDRARODRIGUE ACCIARONo ratings yet
- International Corporate FinanceDocument380 pagesInternational Corporate FinanceBiju GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Alexander Del Mar, The Science of MoneyDocument152 pagesAlexander Del Mar, The Science of Moneyquintus14100% (2)
- 31 Excel Powerful FormulaDocument15 pages31 Excel Powerful FormulaGanesh Tiwari0% (1)
- Corporate Financial Management IntroDocument17 pagesCorporate Financial Management IntroADEYANJU AKEEMNo ratings yet
- Deloitte Au Tax Insight Deconstructing Chevron Transfer Pricing Case 041115 PDFDocument8 pagesDeloitte Au Tax Insight Deconstructing Chevron Transfer Pricing Case 041115 PDFCA.Srikant Parthasarathy ParthasarathyNo ratings yet