Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Uploaded by
ldw627Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Uploaded by
ldw627Copyright:
Available Formats
S
Obstructive Sleep
Apnea
Overview
S Epidemiology
S Definitions
S Anatomy
S Conditions associated w/ OSA
S Pathophysiology
S Pathophysiologic Risk Factors
S Signs and Symptoms
S Differential Diagnosis
S Workup
S Case Presentation
Epidemiology
S Risk
S 25% of adults worldwide
S Prevalence
S 2-5% of children
S 2-9% of adults
S Age
S Prevalence increases from
18-45 yo
S Plateau at 55-65 yo
S Race
S More prevalent in African-
Americans (craniofacial
structure)
Definitions
S Apnea = breathing pause >10 seconds + >90% drop in airflow
S Hypopnea
S 3% drop in O
2
sat + >10 seconds of >50% reduction in airflow
S 4% drop in O
2
sat + > 10 seconds of >30% reduction in airflow
S Apnea Hypopnea Index (AHI) = # of apneas and hypopneas / hour of sleep
Conditions associated w/ OSA
S Obesity
S Atrial fibrillation
S Acute coronary syndrome
S Congestive heart failure
S Type 2 diabetes
S Stroke
S Nocturnal dysrhythmias
S Pulmonary hypertension
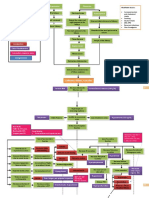
Pathophysiology
S Reduced upper airway size due to excess surrounding
soft tissue or a highly compliant airway
S Diminished neural input to the upper airway muscles
during sleep and at apnea onset
Theory: Loop Gain
Apnea
Increased respiratory
drive
Inspiration/ventilation
Decrease CO
2
Decreased respiratory
drive
Risk Factors
S Obesity
S Smoking
S Upper airway soft tissue
abnormalities
S Enlarged tonsils
S Nasal polyps
S Thyroid enlargement
S Acromegaly
S Supine
S REM Sleep
S Craniofacial abnormalities
S Micrognathia (small mandible)
S Retrognathia (posteriorly
displaced mandible)
Signs and Symptoms
S Daytime symptoms attributed to disrupted sleep
S Sleepiness, fatigue, poor concentration
S Signs of disturbed sleep
S Snoring, restlessness, resuscitative snorts
Differential Diagnosis
S Central sleep apnea
S Narcolepsy
S Alcohol or sedative abuse
S Depression
S Hypothyroidism
S Obesity-hypoventilation syndrome
S PCO
2
> 45 mmHg
Workup
S Comprehensive sleep evaluation
S Sleep-related history
S Snoring
S Choking or gasping during sleep
S Sleep amount
S Nocturia
S Morning headache
S Insomnia
S Frequent awakenings
S Concentration and memory
S Falling asleep at the wheel
S Epworth Sleepiness Scale, Stanford
Sleepiness Scale, Fatigue Severity
Scale
S Physical examination
S Evaluate for risk factors (ie. BMI,
macroglossia, micrognathia, etc.)
S If OSA suggested by history and
physical:
S Polysomnogram
S Confirm Dx
S AHI or RDI > 15/hour w/ or
w/out symptoms
S AHI or RDI > 5/hour w/
symptoms
S Determine severity
S Mild: 5-15 RDI
S Moderate: 15-30 RDI
S Severe: >30 RDI
Epworth Sleepiness Scale
S How likely are you to doze off or fall asleep in the following situations, in contrast to feeling just tired?
S Sitting and reading
S Watching TV
S Sitting inactive in a public place (ie. Theater or meeting)
S As a passenger in a car for an hour w/out a break
S Lying down to rest in the afternoon when circumstances permit
S Sitting and talking to someone
S Sitting quietly after a lunch w/out alcohol
S In a car, while stopped for a few minutes in traffic
S 0 = no chance of dozing, 1 = slight chance of dozing, 2 = moderate chance of dozing, 3 = high chance
of dozing
S 1-6 = good, 7-8 = average, >9 = seek sleep specialist w/out delay
Polysomnogram
Multi parametric Test
EEG
Airflow
Heart rate
Rhythm
Leg movements
Eye movements
Chin muscle muscle tone
Oxygen saturation
Chest wall movement
Treatment
S Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
S Treatment of choice for OSA of all severities
S Supine position, 5 cm H
2
0 20 cm H
2
0
S Pt. education on behavioral changes
S Weight loss
S Avoidance of alcohol and sedating medications
S Modifying risk factors
S Driving precautions
S Tennis ball for supine sleeping
Treatment contd
S Oral Appliances
S Mandibular repositioning appliances (MRA)
S Tongue retaining devices (TRD)
S Surgical therapy
S Tracheostomy
S Bariatric surgery
S Pharmacologic therapy
S Treat underlying cause (ie. Hypothyroidism)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Bipolar Depression/Mania: SKINNY ReasoningDocument9 pagesBipolar Depression/Mania: SKINNY ReasoningSharon TanveerNo ratings yet
- Executive Order No. 003-ADocument2 pagesExecutive Order No. 003-AAndrew Murray D. DuranoNo ratings yet
- CortisolDocument2 pagesCortisolkitu_alagappan4720No ratings yet
- Narendra Kumar NayakDocument3 pagesNarendra Kumar NayakSankar PattnaikNo ratings yet
- High-Risk Prenatal ClientDocument8 pagesHigh-Risk Prenatal ClientLRDR UCMEDNo ratings yet
- ATLS Chapter Review QuestionsDocument36 pagesATLS Chapter Review QuestionsKen Evans89% (57)
- Paediatrics Ii (A)Document1 pagePaediatrics Ii (A)AlolikaNo ratings yet
- Voluntary Self-Identification of Disability Form CC-305Document1 pageVoluntary Self-Identification of Disability Form CC-305kNo ratings yet
- MCQ NelsonDocument433 pagesMCQ NelsonShashank MisraNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Diseases: Dr. Ansar Uddin Ahmed Asst. Prof and Head Dept. of Periodontology and Oral PathologyDocument13 pagesAutoimmune Diseases: Dr. Ansar Uddin Ahmed Asst. Prof and Head Dept. of Periodontology and Oral PathologyTas DidNo ratings yet
- Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument41 pagesClick To Edit Master Subtitle StyleMahar NaveedNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands: Ms TeamDocument36 pagesDisorders of The Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands: Ms TeamShy Dela PuertaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- Mnlkaxi QH: Manisha M.Sc. NursingDocument57 pagesMnlkaxi QH: Manisha M.Sc. NursingManisha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Vector Borne Disease Malaria Dengue Kalazar Chikungunya Filiarisis Indian Council Medical ResearchDocument44 pagesVector Borne Disease Malaria Dengue Kalazar Chikungunya Filiarisis Indian Council Medical Researchanupsingh775No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Practice - MidtermDocument24 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Practice - MidtermShene Claire VigillaNo ratings yet
- Virus & Antiviral Drugs: Prof. Dr. Ishrat ImranDocument57 pagesVirus & Antiviral Drugs: Prof. Dr. Ishrat Imransomi shaikh100% (1)
- Laporan GiziDocument11 pagesLaporan GiziEfrata MadridistaNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology in Psychopharmacology in Psychiatry PsychiatryDocument16 pagesPsychopharmacology in Psychopharmacology in Psychiatry PsychiatryHasnain HyderNo ratings yet
- NCP For UDHDocument3 pagesNCP For UDHTomohiro HorieNo ratings yet
- NARCISISSMDocument23 pagesNARCISISSMjordanmcmillan04No ratings yet
- OPD Rot Exam StudentDocument3 pagesOPD Rot Exam StudentFerdinand TerceroNo ratings yet
- 2004 NEJM Photosensitivity NEJ 2004Document7 pages2004 NEJM Photosensitivity NEJ 2004Alma EscobarNo ratings yet
- Ancylostoma DuodenaleDocument2 pagesAncylostoma DuodenaleBlessy BreganzaNo ratings yet
- Capillary Fragility/ Resistance Test: Tourniquet or Rumpel-Leede or Hess TestDocument4 pagesCapillary Fragility/ Resistance Test: Tourniquet or Rumpel-Leede or Hess TestGerly MaglangitNo ratings yet
- NCM 101-GenogramDocument1 pageNCM 101-GenogramCarolyn Moquerio-serniculaNo ratings yet
- Common Sleep Problems in Children - Pediatrics in Review - 2011Document11 pagesCommon Sleep Problems in Children - Pediatrics in Review - 2011JanelleNo ratings yet
- Herbal MedicinesDocument8 pagesHerbal MedicinesKrishna BalsarzaNo ratings yet
- Takayasu S Arter It IsDocument5 pagesTakayasu S Arter It IsButarbutar MelvaNo ratings yet
- Alcoholism ShresthaDocument9 pagesAlcoholism ShresthaTapas PaulNo ratings yet