Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1st Week (SUN, MON, TUSE
Uploaded by
m0ozOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1st Week (SUN, MON, TUSE
Uploaded by
m0ozCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Radiographic Positioning
(Positioning Terminology )
Lecture 1
2
By the end of this Lecture the student will be able to:
Define sectional anatomy and differentiate between sagittal ,coronal
and transverse plane planes and body sections
Identify and describe terminology related to patient/part positioning.
Distinguish Between radiographic projection, position and view
Identify and describe the four types of body habitus and explain how
they may affect patient centering and positioning.
Learning Objectives
3
References
Positioning in Radiography: By k.C.Clarke.
Text book of radiographic positioning and related anatomy;
by Kenneth L.Bontrager, 5
th
edition
Websites
http://www.e-radiography.net/
http://www.theodora.com/anatomy/surface_anatomy_index.html
Positioning Terminology
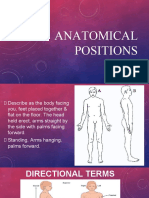
A person in the anatomical position is
standing erect with the head, eyes and
toes pointing forward, feet together with
arms by the side. The palms of the hands
are also point forward.
2
Anatomic Position
A plane is a flat surface passed
through the body or a portion of the
body . Body planes are divided into:-
Longitudinal planes
Coronal
Sagittal
Horizontal plane (Transverse )
Positioning Terminology
Body Planes
3
Body Planes
4
Sagittal Plane (Lateral Plane)
A vertical plane running from front to
back; divides the body or any of its
parts into right and left sides.
Median plane
Sagittal plane through the midline of
the body; divides the body or any of
its parts into right and left halves.
Body Planes
Coronal or (Frontal)
A vertical plane running from side to
side; divides the body or any of its parts
into anterior and posterior portions.
5
Axial Plane (Transverse Plane)
A horizontal plane; divides the body or
any of its parts into upper and lower parts.
Directional Terms
Lateral Vs. Medial
Away from the midline of the body
(On the outer side of) e.g. the arms
are lateral to the chest.
Lateral
Medial
Near to the midline of the body
(On the Inner side of) e.g. the
chest is medial to the arms
Medial
Lateral Lateral
6
Directional Terms
Superior Vs. Inferior
Towards the head end or towards the
upper part of a structure( above)
e.g. The head is superior to the chest.
Superior ( cephalic/ cranial)
Inferior (Caudal)
Away from the head end or towards the
lower part of a structure( Below) e.g.
the abdomen is inferior to the chest.
Inferior
Superior
7
Directional Terms
Anterior Vs. Posterior
Towards or at front of the body ( in front of)
e.g. The sternum is anterior to the spine.
Anterior ( ventral )
Posterior (Dorsal )
Towards or at the back of the body ( Behind)
e.g. The heart is posterior to the sternum.
8
Directional Terms
Proximal Vs. Distal
Close to the origin of the body part or the
point of attachment of a limb to the trunk
e.g. The knee is proximal to the ankle.
Proximal
Distal
Farther or away from the origin of the body
part or the attachment of a limb to the trunk
e.g. The forearm is distal to the arm.
9
Directional Terms
Superficial Vs. Deep
Towards or at the body surface
e.g. The skin is superficial to the skeletal muscles
Superficial
Deep
Away from the body surface ( more internal)
e.g. The skeletal muscles are deep to the skin
10
anterior posterior lateral
p
o
s
t
e
r
i
o
r
cephalic
superior
cranial
inferior
caudal
medial
lateral
proximal
distal
Directional Terms
11
Abduction vs. Adduction
12
Joints movement Terms
Abduction :
movement away from the midline of
the body or body part.
Adduction:
Movement toward the midline of the
body or body part.
Flexion vs. Extension
13
Joints movement Terms
Flexion :
Decrease in the angle of a joint by
bending
Extension:
Increase in the angle of joint or
straightening of a joint
Note : Hyper flexion is over flexion while hyper extension is extension beyond normal limits
Inversion vs. Eversion
14
Joints movement Terms
Inversion :
Turning of foot inward at the ankle joint.
Eversion:
Turning of the foot outward at the ankle
joint.
Pronation vs. Supination
15
Joints movement Terms
Pronation :
Turning the hand so that the palm is
down or onto one's stomach
Supination:
Turning the hand so the palm is facing
upward or turning onto one's back.
Body Position Terms
Describe the overall placement of the body in the desired
position.
Erect "upright"
Position when the Sagittal and coronal planes of the
body are perpendicular to the horizon
Recumbent "lying down"
Position when the transverse plane of the body is perpendicular to the horizon
16
Recumbent Positions
Supine
(posterior recumbent position)
Lying down on the back
Prone
(anterior recumbent position)
Lying face down
xx lateral recumbent
lying down on the xx side
Body Position Terms
17
Decubitus vs. Recumbent
general meanings are the same "LYING DOWN"
but in radiography, decubitus has a special meaning
DECUBITUS
patient is lying down & the x-ray beam is parallel to the horizon
Body Position Terms
18
Oblique (Erect or Recumbent)
Position when the body is rotated so that
the MS plane is neither nor to the film
but at an angle
Exact position is indicated by the surface
closest to the film and the angle of rotation
May be erect or recumbent
abbreviations:
RPO, LPO, RAO, LAO
45 RPO
Body Position Terms
^
19
Decubitus Positions
Ventral decubitus
patient is prone ,Cassette (IR) is vertical & a
horizontal beam is used
Dorsal decubitus
patient is supine ,Cassette (IR) is vertical & a
horizontal beam is used
Lateral decubitus ( Right or Left)
patient lying on the left lateral side ,Cassette
(IR) is vertical & a horizontal beam is used
Body Position Terms
20
Erect Positions
Surface of body closest to the film used to give
a more specific description
Examples:
Posterior erect -- patient is standing with
the posterior surface of the body next to the
cassette
Left lateral erect -- patient is standing with
the left side of the body next to the cassette
Unit III
Left lateral
erect position
Body Position Terms
21
Fowler's Position
A person in the Fowler's position is
sitting leaning slightly back 45
o
-
90
o
.legs may either be straight or bent.
Trendelenburg Position
A person in the Trendelenburg position
is lying supine with head slightly lower
than their feet.
Unit III
Body Position Terms
22
Sim's Position
A near lateral Left anterior oblique ( Left Sim's ) OR right anterior oblique with the top
leg in front the lower leg.
Unit III
Body Position Terms
23
Projection
Refers to the path the x-ray beam takes
through part
Anteroposterior projection (AP)
Beam enters the front surface and
exits the back surface of the part
Posteroanterior projection (PA)
Beam enters the back and exits the
front of the part
AP projection in supine position
Positioning Terms
24
Lateral Projections
Torso (Trunk) and head
Right to left lateral projection
Left to right lateral projection
Extremities (Limbs)
Mediolateral projection
Lateromedial projection
Note:
Normally the positioning terminology is
used rather than projection.
Left lateral erect position
R to L lateral projection
Positioning Terms
X-ray
25
Special Projections
Axial Projection
Right to left lateral projection
Left to right lateral projection
Tangential projection
Mediolateral projection
Lateromedial projection
Note:
Normally the positioning terminology is
used rather than projection.
Positioning Terms
X-ray beam
AP axial with 40 caudal angle
X-ray beam
X-ray beam
26
Classification of Body Habitus
Hypersthenic
Deep broad thorax
Short thoracic cavity
Short wide heart
Elevated diaphragm
Stomach and GB very high
Colon high and wide
Unit III
Sthenic
Lightly longer and shallow thorax
Ribs more vertical
Heart narrow and longer
Thoracic cavity longer
Diaphragm is not as high
Colon slightly lower and more
centrally located.
27
Classification of Body Habitus
Hyposthenic
Thorax longer
Diaphragm lower
Stomach and GB lower and
close to midline.
Colon lower and close to
midline of abdomen
Unit III
Asthenic
Exaggeration of Hyposthenic type
Thorax narrow and shallow
Heart longer and narrow
Thoracic cavity longer
Diaphragm is very low
Stomach and GB very lower
,vertical and near midline.
28
Assignment.1
Positioning Terminology Interactive quiz At
http://faculty.ksu.edu.sa/74344/default.aspx
Results must be submitted before the next lecture
Note
Unit III 32
You might also like
- Rad. Positioning 2Document553 pagesRad. Positioning 2Lalaine De JesusNo ratings yet
- Anatomical-Positions-Directional-Terms PE 2 ACTIVITY - FLORES, RENNETH READocument9 pagesAnatomical-Positions-Directional-Terms PE 2 ACTIVITY - FLORES, RENNETH REARenneth Rea FloresNo ratings yet
- Decriptive Anatomical Terminology Body PlanesDocument2 pagesDecriptive Anatomical Terminology Body Planesskyler andrada100% (1)
- Radiology Terminology Print Basic Medical TerminologyDocument3 pagesRadiology Terminology Print Basic Medical TerminologyyeenfeiNo ratings yet
- Anatomical terms-WPS OfficeDocument14 pagesAnatomical terms-WPS Officeibm.zakariyaNo ratings yet
- 1 An&phssssDocument57 pages1 An&phssssabelashe2No ratings yet
- PC1 - AnatomyDocument102 pagesPC1 - Anatomysinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MedicinesDocument35 pagesIntroduction To MedicinesARUNROCKZNo ratings yet
- Handbook of General AnatomyDocument7 pagesHandbook of General AnatomyXyzNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy Lec1Document38 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy Lec1Ahmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature and Descriptive TerminologiesDocument28 pagesNomenclature and Descriptive TerminologiesEzri ChilengweNo ratings yet
- AP Positions and PlanesDocument20 pagesAP Positions and PlanesBrunero Meozzi100% (1)
- 1st Practical LabDocument17 pages1st Practical LabSheel GuptaNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomical TermsDocument12 pagesBasic Anatomical Termsoluebuben02No ratings yet
- GA&E 2 - Intro To AnatomyDocument62 pagesGA&E 2 - Intro To AnatomySu ZikaiNo ratings yet
- Saqib KhanDocument8 pagesSaqib Khanmskhan5445No ratings yet
- UNIT 3 - Planes and Directional TermsDocument35 pagesUNIT 3 - Planes and Directional Termsyohandra cabreraNo ratings yet
- MCT Chapter 2Document8 pagesMCT Chapter 2Kenneth BocterNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminology: Assoc Prof DR Mohamad Aris Mohd Moklas (PHD) Department of Human Anatomy FMHS, UpmDocument62 pagesAnatomical Terminology: Assoc Prof DR Mohamad Aris Mohd Moklas (PHD) Department of Human Anatomy FMHS, UpmYasif AbbasNo ratings yet
- Module 2 THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMYDocument10 pagesModule 2 THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMYMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminology 2022Document24 pagesAnatomical Terminology 2022Arm UdomratNo ratings yet
- Overview of Anatomical PositionsDocument8 pagesOverview of Anatomical Positionsmarcus colgrove0% (1)
- Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and MovementsDocument36 pagesAnatomical Position, Directional Terms and MovementsPaul Nichol De VeraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy For Nutrition and Dietetics: BY Enye, Linus AndersonDocument53 pagesAnatomy For Nutrition and Dietetics: BY Enye, Linus AndersonscholasticaNo ratings yet
- محاضره 1Document7 pagesمحاضره 1zsnsj0No ratings yet
- 1 A. Introduction To IntroductionDocument30 pages1 A. Introduction To IntroductionafaqgoharNo ratings yet
- Lec1 Introduction To Anatomy MyDocument12 pagesLec1 Introduction To Anatomy Mysaifh9762No ratings yet
- REHA2171 - Osteopathy Theory and Practice 1: Anatomical PlanesDocument3 pagesREHA2171 - Osteopathy Theory and Practice 1: Anatomical PlanesHammad -ullahNo ratings yet
- PosicionesDocument12 pagesPosicioneshumberto paco jachoNo ratings yet
- Anatomical TermsDocument31 pagesAnatomical Termsedgar largoNo ratings yet
- An 1.1 - Introduction Anatomical Terminology DR - GosaiDocument46 pagesAn 1.1 - Introduction Anatomical Terminology DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 01terminology Human Anatomy 1 YearDocument7 pages01terminology Human Anatomy 1 Yearderasadeth deadNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - 1.6Document7 pagesModule 2 - 1.6TH TNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionsDocument32 pagesAnatomical PositionsPearl Lee MetiamNo ratings yet
- It Is A Greek Word (Ana-Tome) : Meaning Cutting Up.: AnatomyDocument34 pagesIt Is A Greek Word (Ana-Tome) : Meaning Cutting Up.: AnatomyHamzaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Position Direction and TermsDocument6 pagesAnatomical Position Direction and TermsB Palaruan Christian NoelNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology: Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and MovementsDocument28 pagesMedical Terminology: Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and MovementsSALMANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 General Orientation To Human Body and Basic Anatomical TerminologyDocument41 pagesChapter 2 General Orientation To Human Body and Basic Anatomical TerminologymintsaoraNo ratings yet
- Directional Terms and Body TermsDocument26 pagesDirectional Terms and Body TermsMartinArciniegaNo ratings yet
- 1P - Medical Terminology of Anatomical PositionsDocument29 pages1P - Medical Terminology of Anatomical PositionsMission AidNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionsDocument39 pagesAnatomical PositionsWaqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument34 pagesIntroductionYousef El bannaNo ratings yet
- LEC1Document49 pagesLEC1youssef.yma999No ratings yet
- BIO+108+Terms+and+Orientation - AnnotatedDocument4 pagesBIO+108+Terms+and+Orientation - Annotatedzrpkfhp9gwNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Positioning 2Document76 pagesRadiographic Positioning 2Gernalyn Ann MagayagaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy-1-1Document46 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy-1-1Vinod SharmaNo ratings yet
- Manual in Radiographic Positioning.Document116 pagesManual in Radiographic Positioning.Jestia Lyn EngracialNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Positioning TermsDocument4 pagesRadiographic Positioning TermsEngielyn Valencia AldeaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy: DR: IleeyeDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy: DR: IleeyeĎŕ Àbdìĺàhì MùśțàphèNo ratings yet
- Basic Rad PosDocument14 pagesBasic Rad PosJayson EsplanaNo ratings yet
- Intro JemalDocument89 pagesIntro Jemalyigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- Anatomical TerminologyDocument5 pagesAnatomical TerminologyShereen AlobinayNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Positions & Body MovementsDocument29 pagesAnatomical Positions & Body MovementsWilbert Antonino Cabanban100% (1)
- Anatomcial PositonDocument18 pagesAnatomcial PositonAicelle GayapNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminology - Anatomy and Physiology IDocument11 pagesAnatomical Terminology - Anatomy and Physiology Ikick leejohNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionsDocument31 pagesAnatomical PositionsShravani NajanNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionsDocument18 pagesAnatomical PositionsAnji JoguilonNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionsDocument20 pagesAnatomical PositionskimberlynNo ratings yet
- Tips for Everyday Life and Sports With an Artificial Joint: Expert guidebook for dealing with a prosthesis for patients with a new hip or knee jointFrom EverandTips for Everyday Life and Sports With an Artificial Joint: Expert guidebook for dealing with a prosthesis for patients with a new hip or knee jointNo ratings yet
- Transient Thermal Conduction ExampleDocument14 pagesTransient Thermal Conduction ExampleDevendra BangarNo ratings yet
- M 02 0001Document3 pagesM 02 0001Miguel ruizNo ratings yet
- Sample CBAP Elicitation Scenario Based Questions Set 01Document31 pagesSample CBAP Elicitation Scenario Based Questions Set 01Rubab Javaid100% (1)
- Student Report: Social Studies Class TestDocument4 pagesStudent Report: Social Studies Class Testila thakurNo ratings yet
- AKIM Mühendislik - Primavera Türkiye - Earned Value Analysis - v2Document1 pageAKIM Mühendislik - Primavera Türkiye - Earned Value Analysis - v2Ece GürtekinNo ratings yet
- Product Matrix: Network Security Platform - Top Selling Models MatrixDocument6 pagesProduct Matrix: Network Security Platform - Top Selling Models MatrixWashington CárdenasNo ratings yet
- Ens Air To Water Operation ManualDocument8 pagesEns Air To Water Operation ManualcomborNo ratings yet
- Lock Maiolo Savonarola MachiavelliDocument22 pagesLock Maiolo Savonarola MachiavelliHeliogabolusNo ratings yet
- Michael S. Lewis-Beck-Data Analysis - An Introduction, Issue 103-SAGE (1995)Document119 pagesMichael S. Lewis-Beck-Data Analysis - An Introduction, Issue 103-SAGE (1995)ArletPR100% (1)
- 3949-Article Text-8633-1-10-20180712Document10 pages3949-Article Text-8633-1-10-20180712Volodymyr TarnavskyyNo ratings yet
- DPL MDDocument3 pagesDPL MDCoy IngramNo ratings yet
- 107 01 Covers and Side Doors A SideDocument38 pages107 01 Covers and Side Doors A Sideben vervuurtNo ratings yet
- (Dust of Snow) & 2 (Fire and Ice) - NotesDocument3 pages(Dust of Snow) & 2 (Fire and Ice) - NotesdakshNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Is The Backbone of ResearchDocument7 pagesLiterature Review Is The Backbone of Researchafmzweybsyajeq100% (1)
- Comparison of Plate Count Agar and R2A Medium For Enumeration of Heterotrophic Bacteria in Natural Mineral WaterDocument4 pagesComparison of Plate Count Agar and R2A Medium For Enumeration of Heterotrophic Bacteria in Natural Mineral WaterSurendar KesavanNo ratings yet
- Almugea or Proper FaceDocument5 pagesAlmugea or Proper FaceValentin BadeaNo ratings yet
- Perkins - General Ti BulletinDocument65 pagesPerkins - General Ti BulletinUTEL CARTERNo ratings yet
- Green ICT: A Study of Awareness, Attitude and Adoption Among IT/Computer Engineering Students of LDRP-ITR, GandhinagarDocument13 pagesGreen ICT: A Study of Awareness, Attitude and Adoption Among IT/Computer Engineering Students of LDRP-ITR, GandhinagarAHMAD ARESYADNo ratings yet
- Civil & Structural Designer'S Data Pack: Section 7: MasonryDocument5 pagesCivil & Structural Designer'S Data Pack: Section 7: MasonryMirea Florentin0% (1)
- Gravitational Fields 1Document18 pagesGravitational Fields 1Smart linkNo ratings yet
- API RP 1102 SpreadsheetDocument5 pagesAPI RP 1102 Spreadsheetdrramsay100% (4)
- Detail Project Report: (Heidelberg Cement Group)Document42 pagesDetail Project Report: (Heidelberg Cement Group)saravananNo ratings yet
- Strain GaugeDocument7 pagesStrain GaugefahadarizkiNo ratings yet
- RH 120eDocument8 pagesRH 120eSawadogo Gustave NapinguebsonNo ratings yet
- Intro To Geometric Design and Vertical AlignmentDocument25 pagesIntro To Geometric Design and Vertical AlignmentAhsan ArfanNo ratings yet
- Metascope An/Pas-6 (5855-790-6197) : Technical ManualDocument38 pagesMetascope An/Pas-6 (5855-790-6197) : Technical ManualDens VillaNo ratings yet
- ZEOS-AS ManualDocument2 pagesZEOS-AS Manualrss1311No ratings yet
- MoveInSync Native Android Mobile AppDocument12 pagesMoveInSync Native Android Mobile AppRismaNo ratings yet
- Catalog ITEM - Pdf4a3667894b315Document552 pagesCatalog ITEM - Pdf4a3667894b315Domokos LeventeNo ratings yet
- Headworks & Barrage: Chapter # 09 Santosh Kumar GargDocument29 pagesHeadworks & Barrage: Chapter # 09 Santosh Kumar GargUmer WaheedNo ratings yet