Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FINAL Boeing Case Study (Group 4) 26042014
Uploaded by
Amey Warude0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
169 views29 pagesThis document summarizes a case study presentation about Boeing Commercial Aircraft and its comeback strategy. The presentation agenda covers Boeing's company profile, core competencies, product portfolio, challenges faced, future drivers in the aviation industry, SWOT analysis, corporate and business level strategies, and Boeing's current strategy. The concluding slide summarizes the team's opinion that Boeing can make a comeback by focusing on innovation, fair trade practices, leveraging system integration, improving supply chain management, accepting multiple currencies for orders, and addressing safety concerns.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes a case study presentation about Boeing Commercial Aircraft and its comeback strategy. The presentation agenda covers Boeing's company profile, core competencies, product portfolio, challenges faced, future drivers in the aviation industry, SWOT analysis, corporate and business level strategies, and Boeing's current strategy. The concluding slide summarizes the team's opinion that Boeing can make a comeback by focusing on innovation, fair trade practices, leveraging system integration, improving supply chain management, accepting multiple currencies for orders, and addressing safety concerns.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
169 views29 pagesFINAL Boeing Case Study (Group 4) 26042014
Uploaded by
Amey WarudeThis document summarizes a case study presentation about Boeing Commercial Aircraft and its comeback strategy. The presentation agenda covers Boeing's company profile, core competencies, product portfolio, challenges faced, future drivers in the aviation industry, SWOT analysis, corporate and business level strategies, and Boeing's current strategy. The concluding slide summarizes the team's opinion that Boeing can make a comeback by focusing on innovation, fair trade practices, leveraging system integration, improving supply chain management, accepting multiple currencies for orders, and addressing safety concerns.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 29
Case Study
Boeing Commercial Aircraft: Comeback?
Amey Warude (EAIC)
Ashok Makhijani (Hydrocarbon Upstream)
Dinesh Parmar (Forging)
Girish Mandhene (MMH)
K Ramesh Reddy (Infra, Delhi Metro)
Krishna Bathe (EWAC)
Presented by-
1
26.04.2014
Agenda
Company Profile & Core Competence of Boeing
Product Portfolio
Challenges Faced
Future Drivers for Aviation Industry
SWOT Analysis
Corporate & Business level Strategy
Boeings Comeback Strategy
Teams opinion
2
Company Profile & Core Competence of Boeing
Product Portfolio
Challenges Faced
Future Drivers for Aviation Industry
SWOT Analysis
Corporate & Business level Strategy
Boeings Comeback Strategy
Teams opinion
3
Agenda
Company Profile
Founded in the year 1916 in the Seattle by Mr.
William Boeing.
Boeing acquired Mc Donnell Douglas in 1997,
who was a major and stronger player in Military
business.
Moved its corporate HQ to Chicago in 2000.
Market leader in the industry of military and
commercial aircraft manufacturing.
4
Core Competencies of Boeing
Proactive in meeting customer demand and
needs.
Customization of aircraft and designing.
Product layout for manufacturing.
Contract and agreement with both NASA and
United States Air Force.
The power of vertical integration.
5
Agenda
Company Profile & Core Competence of Boeing
Product Portfolio
Challenges Faced
Future Drivers for Aviation Industry
SWOT Analysis
Corporate & Business level Strategy
Boeings Comeback Strategy
Teams opinion
6
Boeing 737
Seating Capacity 110 to
215
Miles Range 2000 5000
miles
Boeing 747
Seating Capacity 400 to
550
Miles Range 7700 -
8700 miles
Boeing 767
Seating Capacity up to
400
Miles Range up to 9000
miles
Boeing 777
Seating Capacity up to
400
Miles Range up to 9000
miles
Boeing 787
Seating Capacity 200 to
300
Miles Range up to 8500
miles
Company Profile & Core Competence of Boeing
Product Portfolio
Challenges Faced
Future Drivers for Aviation Industry
SWOT Analysis
Corporate & Business level Strategy
Boeings Comeback Strategy
Teams Judgment
8
Agenda
Challenges Faced
Business uncertainty
Synchronizing thousands of designs and deliveries to build an
aero plane
Maintaining supply chains while evolving business processes
and technologies
Cost over-runs
Offshore outsourcing
Tough competition by Airbus
9
Company Profile & Core Competence of Boeing
Product Portfolio
Challenges Faced
Future Drivers for Aviation Industry
SWOT Analysis
Corporate & Business level Strategy
Boeings Comeback Strategy
Teams Opinion
10
Agenda
1. Increase/ decrease in immigration
2. Fuel cost
3. Technology up gradation improving fuel
efficiency
4. Global economic growth
11
Market Drivers for Aviation Industry
Company Profile & Core Competence of Boeing
Product Portfolio
Challenges Faced
Future Drivers for Aviation Industry
SWOT Analysis
Corporate & Business level Strategy
Boeings Comeback Strategy
Teams Opinion
12
Agenda
Market leader in military and commercial
aircraft.
Broad Product Line that covers most major
market niches.
R&D & Innovation.
Strong global network.
Strong supplier network.
13
SWOT Analysis: Strength
A hierarchical, rigid and semi-autocratic management style,
which is a product of its military heritage.
Constrains to reach break even point without reaching the
projected demand.
Dependence on US government and NASA.
Labour problems.
Dependence on supplier.
14
SWOT Analysis: Weakness
Good financial health of aviation industry
and economy.
New aircraft to gain market share.
Airline travel pattern (point to point) changes
supports Boeing Product lines.
Growth of transcontinental traffic.
15
SWOT Analysis: Opportunities
Increase of jet fuel prices.
Terrorist attack effecting the number of travellers
travelling.
Suppliers falling behind schedule designing for
projects.
Changing Govt. politics and business partners.
High volatility.
Aggressive pricing strategy by Airbus.
16
SWOT Analysis: Threats
Company Profile & Core Competence of Boeing
Product Portfolio
Challenges Faced
Future Drivers for Aviation Industry
SWOT Analysis
Corporate & Business level Strategy
Boeings Comeback Strategy
Teams Opinion
17
Agenda
Strategic Decision Value addition and Business
outcome
1. Investments in narrow bodied 757
and wide bodied 767.
1. Investments made from the positive
cash flows attained through breakeven
of their earlier models.
2. Subcontracting in case of Boeing
777 (60% of the work)
2. Resulted in reduction of costs.
3. Merger between Boeing and
McDonnell Douglas
3. Resulting in increase of their
presence in the defense and space side
of aerospace
18
Corporate Level Strategy
Strategic Decision Value addition and Business
outcome
4. Movement of corporate head quarter
from Seattle to Chicago.
4. Signal to the investment community
that Boeing was far more than
commercial business
5. Decision to produce new low cost,
right sized aircrafts
5. Resulting in increase in profit due to
demand for nonstop point to point
flight.
6. Launch of 787 aircraft 6. Stiff competition to Airbus A350 and
A380 aircrafts.
19
Corporate Level Strategy
Strategic Decision Value addition and Business
outcome
1. Adoption of Lean Production and
Six Sigma quality improvement
process.
1. Better Management of warehouses
in terms of inventory, space and time
as well as capital, ultimately improving
the value chain.
2. Introduction of moving assembly
lines.
2. Reduction in time by 50% for
assembly, in addition to reduction of
WIP and stores inventory by 55% and
59% respectively.
20
Operational Strategy
Company Profile & Core Competence of Boeing
Product Portfolio
Challenges Faced
Future Drivers for Aviation Industry
SWOT Analysis
Corporate & Business level Strategy
Boeings Current Strategy
Teams Opinion
21
Agenda
Boeing- Current Strategy
Manufacturing of fuel efficient Airplanes
Complete product mix to meet aviation industry requirements
R&D partnership worldwide in biofuels, manufacturing
processes and robotics
Concurrent and Collaborative Manufacturing
Global Sourcing
Address & Focus Bottom of Pyramid
22
Company Profile & Core Competence of Boeing
Product Portfolio
Challenges Faced
Future Drivers for Aviation Industry
SWOT Analysis
Corporate & Business level Strategy
Boeings Comeback Strategy
Teams Opinion
23
Agenda
Yes, Boeing can comeback*
Become frontrunner in Innovation and New Product
Development
Follow Fair Trade Practices
Leverage System Integration in two ways viz.
Suppliers contribute to the development cost
Subcontractors become risk sharing partners responsible of
aircraft design
Improve Supply Chain and Logistics for improving delivery
of outsourced assemblies/ parts
Acceptance of other currencies (, , ) to book orders
Improve on Time to Market of new aircraft(s)
Address Safety!!
Teams Opinion
24
* Conditions apply
25
26
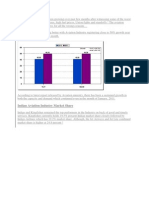
Composition of Launch Funding for Boeing 7e7
Courtesy: Industrial Subsidies and Politics of World Trade. Pritchard & MacPherson
The WTO SCM Agreement contains a definition of the term subsidy. The definition
contains three basic elements: (i) a financial contribution (ii) by a government or
any public body within the territory of a Member (iii) which confers a benefit. All
three of these elements must be satisfied in order for a subsidy to exist (WTO,
2003A).
46% of estimated $ 13.4 bn launch funding consisted
of actionable/ prohibited subsidies under both 1994
WTO-SCM Agreements & 1992 US-EU Agreement on
Trade in Light Commercial Aircraft.
SCM: Subsidies & Countervailing Measures
Launch Cost of Boeing 7e7: $13.4 bn
Launch Cost of A380: $10-12 bn
7e7 launch cost equivalent to A380, though
7e7 was smaller in size
Given that high proportion of the launch cost was
covered by subsidies (illegal?) by its risk-sharing
partners, Boeing might have looked at development
of 7e7 as a profitable venture, provided WTO
litigations did not take place
But Airbus would never sit back and observe
27
The 7e7 launch plan consisted of both
foreign & domestic subsidies
Nearly 50% of the subsidies were slated to
come from sources classified as actionable/
prohibited under WTO-SCM
This implies: Most of the value added on 7e7
would be earned by foreign partners rather
than by Boeing or by US based suppliers
28
Devolution of critical tasks/ part development
& mfg to foreign suppliers raise questions
regarding long term viability of Boeing in
production of Commercial Aircraft category
Boeing should serve its own interest by
subsidizing those aspects of its aerospace
business that operates with higher Boeing &
US content
29
You might also like
- Gamification in Consumer Research A Clear and Concise ReferenceFrom EverandGamification in Consumer Research A Clear and Concise ReferenceNo ratings yet
- Boeing Case StudyDocument7 pagesBoeing Case Studyaakriti aroraNo ratings yet
- Precision Turned Products World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandPrecision Turned Products World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- Airbus A3XX Case QuestionsDocument1 pageAirbus A3XX Case QuestionsPradnya SalveNo ratings yet
- Aviation EconomicsDocument23 pagesAviation EconomicsAniruddh Mukherjee100% (1)
- Future GroupDocument32 pagesFuture GroupFinola FernandesNo ratings yet
- The One-World Airline AllianceDocument4 pagesThe One-World Airline AllianceAthena Hdz GuerraNo ratings yet
- Harsh Bansal Boeing 767Document4 pagesHarsh Bansal Boeing 767Harsh BansalNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument1 pageCase Studyamir755No ratings yet
- Code Sharing in International AirlinesDocument14 pagesCode Sharing in International AirlinesPrashant RampuriaNo ratings yet
- Rolls Royce Mind The GapDocument25 pagesRolls Royce Mind The Gapmarketfolly.comNo ratings yet
- Team 4 Airbus Boeing (Harvard Team Presentation - Background On Companies)Document14 pagesTeam 4 Airbus Boeing (Harvard Team Presentation - Background On Companies)Darragh Martin100% (1)
- Team 14 - Boeing 7E7 - Very GoodDocument10 pagesTeam 14 - Boeing 7E7 - Very GoodXiaoTing HuangNo ratings yet
- Boeing 7E7 Q'sDocument2 pagesBoeing 7E7 Q'smohamedmagdyyy122No ratings yet
- Airbus and BoeingDocument40 pagesAirbus and BoeingPriyank BavishiNo ratings yet
- PrimusDocument11 pagesPrimusClarissa Hapsari100% (1)
- Dmgs Dip 27092 FinalDocument11 pagesDmgs Dip 27092 FinalEsa BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Amy Kakuk, Beth Theriault, and Jessica BourgoinDocument47 pagesAmy Kakuk, Beth Theriault, and Jessica BourgoinmarioNo ratings yet
- Embraer Vs BombardierDocument1 pageEmbraer Vs BombardierJose luis Martinez GarzaNo ratings yet
- Airbus A3XX Developing The World's Largest Commercial Jet - Objetives and QuestionDocument1 pageAirbus A3XX Developing The World's Largest Commercial Jet - Objetives and QuestionJaime Steven Soto ForeroNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis of The Airline IndustryDocument14 pagesEconomic Analysis of The Airline Industrylightknight91No ratings yet
- Airline Industry ReportDocument42 pagesAirline Industry ReportManash Verma67% (3)
- Balance Scorecard For Air IndiaDocument10 pagesBalance Scorecard For Air IndiaRyan HabaNo ratings yet
- PPP in Delhi Gurgaon Expressway - Group 3Document5 pagesPPP in Delhi Gurgaon Expressway - Group 3Nikhil SainiNo ratings yet
- Competition: Airbus and BoeingDocument15 pagesCompetition: Airbus and BoeingHenry DunaNo ratings yet
- QTY8216 Air Arabia-Etihad Case - PESTEL AnalysisDocument6 pagesQTY8216 Air Arabia-Etihad Case - PESTEL AnalysisNouf Bin IshaqNo ratings yet
- Boeing 7E7 Case Questions PDFDocument1 pageBoeing 7E7 Case Questions PDFErick ClarkNo ratings yet
- RFP For Jet Airways v2Document17 pagesRFP For Jet Airways v2rahulalwayzzNo ratings yet
- Boeing Vs AirbusDocument12 pagesBoeing Vs AirbusgoekhankolukisaNo ratings yet
- Management FOCUS: Boeing's Global Production SystemDocument1 pageManagement FOCUS: Boeing's Global Production SystemMinh Trang100% (1)
- Case Study American AirlinesDocument5 pagesCase Study American AirlinessexychameleonNo ratings yet
- Jetblue Strategic Plan ProposalDocument15 pagesJetblue Strategic Plan Proposalapi-280467957No ratings yet
- A Term Paper On Marketing ManagementDocument46 pagesA Term Paper On Marketing ManagementRenesa Haque SarmiNo ratings yet
- M1 - CIMA Masters Gateway Assessment 22 May 2012 - Tuesday Afternoon SessionDocument20 pagesM1 - CIMA Masters Gateway Assessment 22 May 2012 - Tuesday Afternoon Sessionkarunkumar89No ratings yet
- Neil Majumder - Aviation Industry - IndiGo AirlinesDocument19 pagesNeil Majumder - Aviation Industry - IndiGo AirlinesNeil MajumderNo ratings yet
- BoeingDocument18 pagesBoeingGnesh WaraNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Cost of Capital: Case: The Boeing 7E7Document125 pagesEstimation of Cost of Capital: Case: The Boeing 7E7jk kumarNo ratings yet
- Case External Analysis The Us Airline IndustryDocument2 pagesCase External Analysis The Us Airline IndustryPenujakIPJB0% (1)
- A PEST Analysis Is An Analysis of Airline IndustryDocument5 pagesA PEST Analysis Is An Analysis of Airline Industryerohu123456100% (1)
- Air DeccanDocument8 pagesAir Deccanprateekbapna90No ratings yet
- AirAsia - Business StrategyDocument22 pagesAirAsia - Business StrategyAnhbonnieNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Aviation IndustryDocument20 pagesPresentation On Aviation Industryaashna171No ratings yet
- Strengths in The SWOT Analysis of IndigoDocument2 pagesStrengths in The SWOT Analysis of IndigoJyoti joshiNo ratings yet
- Boeing Final ExamDocument25 pagesBoeing Final ExamfouadNo ratings yet
- Boeing Strategy AnalysisDocument16 pagesBoeing Strategy Analysisradkris914100% (1)
- SWOT Analysis of NissanDocument9 pagesSWOT Analysis of NissanArnel BendoNo ratings yet
- SIA B - Case StudyDocument2 pagesSIA B - Case StudyDhanashree GharatNo ratings yet
- Jet AirwaysDocument11 pagesJet AirwaysAnonymous tgYyno0w6No ratings yet
- DuopolyDocument25 pagesDuopolyVishalGuptaNo ratings yet
- Oligopoly in Oil Refinery IndustryDocument5 pagesOligopoly in Oil Refinery IndustryDokania Anish100% (2)
- Indian Aviation IndustryDocument53 pagesIndian Aviation IndustryMandar Chari60% (5)
- Samsung CaseDocument16 pagesSamsung Caseamunhu145No ratings yet
- Structure of The Airline IndustryDocument14 pagesStructure of The Airline IndustryShuvendraNo ratings yet
- Indian Airline Industry - Group1Document58 pagesIndian Airline Industry - Group1Shankho BaghNo ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument47 pagesFinal ProjectKathlyn Kaye SanchezNo ratings yet
- Nike Equity ManagementDocument11 pagesNike Equity ManagementVikrant KumarNo ratings yet
- India AerospaceDocument6 pagesIndia Aerospacevigneshkumar rajanNo ratings yet
- Boeing 7e7Document7 pagesBoeing 7e7kaye100% (2)
- Case Study Analysis Commercial Airline Industry: Airbus & BoeingDocument17 pagesCase Study Analysis Commercial Airline Industry: Airbus & BoeingShone ThattilNo ratings yet
- Umer Daraz (63848) Assignment 4Document3 pagesUmer Daraz (63848) Assignment 4Umer KhanNo ratings yet
- MKT-630 1st QuizDocument34 pagesMKT-630 1st QuizSamina ShamimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Understanding The Nature and Scope of HRM: Topic 1: People Lend Competitive AdvantageDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Understanding The Nature and Scope of HRM: Topic 1: People Lend Competitive AdvantageJigarNo ratings yet
- "A Case Study ON VSP With Reference To: RecruitmentDocument116 pages"A Case Study ON VSP With Reference To: RecruitmentMeghaa DasariNo ratings yet
- Pay Structure DecisionsDocument22 pagesPay Structure Decisionsprasadr_48No ratings yet
- Global Enterprise ExperienceDocument12 pagesGlobal Enterprise ExperienceTLNo ratings yet
- Industry and Competitive AnalysisDocument24 pagesIndustry and Competitive AnalysisAbdelaziz MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Checklists For FranchiseesDocument6 pagesChecklists For Franchiseesmecaunidos7771No ratings yet
- WESCODocument15 pagesWESCOPuneet Arora100% (1)
- MGMT 699 Reusch 201201Document7 pagesMGMT 699 Reusch 201201Siju BoseNo ratings yet
- International Organization Design and Control: After Studying This Chapter, Students Should Be Able ToDocument19 pagesInternational Organization Design and Control: After Studying This Chapter, Students Should Be Able Topratyush parmarNo ratings yet
- HR Skills NeededDocument7 pagesHR Skills NeededambipankajNo ratings yet
- Activity-No-1-My-Personal-Marketing-Quote by Penson RexDocument3 pagesActivity-No-1-My-Personal-Marketing-Quote by Penson RexPenson RexNo ratings yet
- Business Leadership SkillsDocument3 pagesBusiness Leadership SkillsM ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Safety Climate Assessment Toolkit PDFDocument60 pagesSafety Climate Assessment Toolkit PDFHermawan Agus100% (2)
- Technology Workshop Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesTechnology Workshop Lesson Planapi-290468840No ratings yet
- D MBA+Brochure+-+PartnerDocument8 pagesD MBA+Brochure+-+PartnerWorld CitizenNo ratings yet
- IIML Casebook 2014-15Document135 pagesIIML Casebook 2014-15hetvi9100% (3)
- Competitive Intelligence: Concept, Context and A Case of Its ApplicationDocument15 pagesCompetitive Intelligence: Concept, Context and A Case of Its Applicationghanshyam sidhdhapuraNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On: Asian Paints LimitedDocument50 pagesA Project Report On: Asian Paints Limitedutpa8080100% (4)
- Chapter 1 - 7 Discussion Question Jay - Heizer - Barry - Render - Chuck - Munson - Operation Operation Management 12th EditionDocument37 pagesChapter 1 - 7 Discussion Question Jay - Heizer - Barry - Render - Chuck - Munson - Operation Operation Management 12th EditionJeannete MeliianaNo ratings yet
- HP Swot & Space MatrixDocument5 pagesHP Swot & Space MatrixTeacherSOSNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Marketing Social Responsibility and EthicsDocument50 pagesSustainable Marketing Social Responsibility and EthicsanonlukeNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy and Competitive PostioningDocument35 pagesMarketing Strategy and Competitive PostioningfaniNo ratings yet
- Lessons From The Art of War As Building Blocks For Business StrategyDocument23 pagesLessons From The Art of War As Building Blocks For Business StrategyDr Rahul Mirchandani100% (1)
- Mamaru Final Paper FinalDocument72 pagesMamaru Final Paper FinalBaby BayisaNo ratings yet
- Product Brand Management (PBM)Document230 pagesProduct Brand Management (PBM)Adeland Solafide MasihoroeNo ratings yet
- IKEADocument133 pagesIKEAkhaofaang100% (1)
- The Changing Role of HR ProfessionalsDocument8 pagesThe Changing Role of HR Professionalsarmughan050% (1)
- Hal Post Superannuation Group Health Insurance Schemes: HR VisionDocument2 pagesHal Post Superannuation Group Health Insurance Schemes: HR VisionArunkumarNo ratings yet
- Baron95 Non Market Strategy Ocr 2Document13 pagesBaron95 Non Market Strategy Ocr 2Hung CuongNo ratings yet