Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power System Contingencies
Uploaded by
Sal ExcelCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Power System Contingencies
Uploaded by
Sal ExcelCopyright:
Available Formats
Seminar On
Power System
Contingencies
Power System
Power System voltage control has a hierarchy structure with three
levels: the primary, secondary, and the tertiary voltage control.
Over the past 20 yrs, one of the most successful measures
proposed to improve Power System voltage regulation has been
the application of secondary voltage control, initiated by the
French Electricity Company.
Important Of Features
Power System
Flickers
Harmonics
Interruption
Long Lines
Long Cables
Loop Flow
Reactive Power
Sags & Swells
Unbalanced Load
Voltage Instability
Flickers
A fluctuation in system voltage that can
lead to noticeable changes in light
output.
Voltage Flicker can either be a periodic
or non-periodic fluctuation in voltage
magnitude i.e. the fluctuation may
occur continuously at regular intervals
or only on occasions.
How To Reduce Flickers
Installation of a MiniCap to reduce flicker during large motor
starting .
Minicap is nothing but the Installation of a series capacitor in
the feeder strengthens the network .
Benefits
Reduced voltage fluctuations (flicker)
Improved voltage profile along the line
Easier starting of large motors
Self-regulation
Harmonics
Harmonics are associated with steady-state
waveform distortion of currents and voltages.
Harmonics are components that make up a
waveform where each component has a
frequency that is an integral multiple of the
fundamental frequency. The term Harmonic is
normally applied to waveform components that
have frequencies other than the fundamental
frequency. For a 50 Hz or 60Hz system the
fundamental frequency is 50HZ or 60Hz. A
waveform that contains any components other
than the fundamental frequency is non-
sinusoidal and considered to be distorted.
How To Reduce Harmonics
Installing filters near the harmonic
sources can effectively reduce
harmonics.
Benefits
Eliminates harmonics.
Improved Power Factor.
Reduced Transmission Losses.
Increased Transmission Capability.
Improved Voltage Control.
Improved Power Quality.
Interruptions
Occur when the supply voltage drops below 10% of the nominal
value.
An interruption is usually caused by downstream faults that are
cleared by breakers or fuses. A sustained interruption is caused
by upstream breaker or fuse operation. Upstream breakers may
operate due to short-circuits, overloads, and loss of stability on
the bulk power system.
Long Lines
Long lines need special consideration in the
planning of a power system.
For long AC lines one must consider i.e. the
reactive power compensation, the transient
stability and switching over voltages and how
many intermediate substations one needs.
Area of application:-Expressway
for power
A HVDC transmission line costs less than
an AC line for the same transmission
capacity.
Benefits
Lower investment cost
Lower losses
Lower right-of-way requirement for DC lines than for AC lines
HVDC does not contribute to the short circuit current
Long cables
Basically Long cables are of two types
Submarine Cables
Under Ground Cables
Submarine Cables
Application
Submarine Cables are used for long distance water crossing.
Benefits
Lower investment cost
Lower losses
Loop flow
Unscheduled power flow on a given transmission path in an
interconnected electrical system.
Unscheduled power flows on transmission lines or facilities may
result in a violation of reliability criteria and decrease available
transfer capability between neighbouring control areas or utility
systems.
Area of application:
Interconnected power systems
Benefits
HVDC can be controlled to transmit contracted
amounts of power and alleviate unwanted loop
flows.
An HVDC link can alternatively be controlled to
minimize total network losses
An HVDC link can never be overloaded
Reactive Power Factor
Reactive power is defined as the product of the r.m.s. voltage,
current, and the sine of the difference in phase angle between the
two.
To maintain efficient transmission and distribution, it is necessary
to improve the reactive power factor.
How to Improve power factor
The use of the MiniCap on a distribution
feeder provides self-regulated reactive power
for improved power factor at the utility
source.
Benefits
Increased power factor at the utility source.
Easier starting of large motors .
Improved voltage regulation and reactive power
balance.
Self-regulation Improved power factor, Reduced
transmission losses, Increased transmission
capability.
Improved voltage control, Improved power quality,
Eliminates harmonics S.
Sags & Swells
Short duration decrease/increase (sag/swell) in
supply voltage.
Voltage sags are one of the most commonly
occurring power quality problems. They are
usually generated inside a facility but may also
be a result of a momentary voltage drop in the
distribution supply.
Electronic equipment is usually the main victim
of sags, as they do not contain sufficient internal
energy to ride through the disturbance.
Voltage Instability
Post-disturbance excursions of voltages at some buses in the
power system out of the steady operation region.
Voltage instability is basically caused by an unavailability of
reactive power support in an area of the network, where the
voltage drops uncontrollably.
Unbalanced Load
A load which does not draw balanced current from a balanced
three-phases supply.
A single-phase load, since it does not draw a balanced three-
phase current, will create unequal voltage drops across the
series impedances of the delivery system.
Area of application:-Railway
Feeder connected to the Public
Grid
Modern electric rail system is a major source
of unbalanced loads.
STATCOM can elegantly be used to restore
voltage and current balance in the grid, and
to mitigate voltage fluctuations generated by
the traction loads.
Benefits
Voltage Balancing
Harmonic Filtering
Power Factor Correction
Other applications:
Power Quality Improvement, Flicker Mitigation
Grid Voltage Support
Summary
The new electricity supply industry presents increasing
challenges for stable and secure operation of power systems.
State-of-the-art methods and tools have advanced our
capabilities significantly facing the challenges-
comprehensive stability analysis tools
coordinated design of robust stability controls
on-line dynamic security assessment
Industry yet to take full advantage of these developments!
Need to review and improve
The reliability criteria.
Thank You ..!
You might also like
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsFrom EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo ratings yet
- SRMDocument60 pagesSRMKrupa KaranNo ratings yet
- Paper Battery ReportDocument17 pagesPaper Battery ReportIshuNo ratings yet
- Automatic Railway Gate ControlDocument22 pagesAutomatic Railway Gate ControlsriramNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Fault MonitoringDocument16 pagesTransmission Line Fault MonitoringVikash Vicky KumarNo ratings yet
- Advancements in Inverter TechnologyDocument9 pagesAdvancements in Inverter TechnologyAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Surge Current Protection Using Super ConductorsDocument23 pagesSurge Current Protection Using Super ConductorsPratik KumarNo ratings yet
- Home Appliance Control Using TV Remote - Report PDFDocument23 pagesHome Appliance Control Using TV Remote - Report PDFEngineers SolutionNo ratings yet
- S124-Solar Based Mobile Charger For Rural AreasDocument4 pagesS124-Solar Based Mobile Charger For Rural AreasYellaturi Siva Kishore ReddyNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter To Step Up Input VoltageDocument3 pagesDC-DC Converter To Step Up Input VoltageFawwaaz HoseinNo ratings yet
- Solar Power Charge Controller Seminar PresentationDocument16 pagesSolar Power Charge Controller Seminar PresentationPravat SatpathyNo ratings yet
- 1.protection of Busbar Distribution From Over LoadDocument4 pages1.protection of Busbar Distribution From Over LoadPooja BanNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project ReportDocument40 pagesFinal Year Project ReportNAKUL KANARNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous ChipsDocument25 pagesAsynchronous ChipsAbin Varkey Varghese100% (1)
- Distribution Line Fault Detection and Intimation Using GSM PDFDocument5 pagesDistribution Line Fault Detection and Intimation Using GSM PDFanon_674602089No ratings yet
- (REPORT) - Automatic Sun Tracking SystemDocument14 pages(REPORT) - Automatic Sun Tracking SystemPrashant Kumar100% (1)
- Speed Control of DC Motor Using PWMDocument8 pagesSpeed Control of DC Motor Using PWMsunny kumarNo ratings yet
- Power TheftDocument16 pagesPower TheftSreenu vasuNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Based Solar Charger: A Project Report OnDocument51 pagesMicrocontroller Based Solar Charger: A Project Report Oniwantinthatve67% (3)
- Condition Based Maintenance of Underground Cable Systems: A Seminar Report OnDocument20 pagesCondition Based Maintenance of Underground Cable Systems: A Seminar Report OnChethan PintoNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument6 pagesMini Projectirene0% (1)
- Major Project 2 (Faults in Transmission Line)Document31 pagesMajor Project 2 (Faults in Transmission Line)Khaja SameeduddinNo ratings yet
- Multilevel Inverter 3-Level Topologies D PDFDocument39 pagesMultilevel Inverter 3-Level Topologies D PDFSUNIL MANJHINo ratings yet
- Solar Power Wireless Battery ChargerDocument18 pagesSolar Power Wireless Battery ChargerClassic PrintersNo ratings yet
- Wireless Mobile Charger Using Inductive Coupling: October 2017Document17 pagesWireless Mobile Charger Using Inductive Coupling: October 2017Jerin TasnimNo ratings yet
- Multi Level Inverter DocumentationDocument25 pagesMulti Level Inverter Documentationn anushaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Power Supply Control From Four Different SourcesDocument21 pagesAutomatic Power Supply Control From Four Different SourcesJishnu Ps100% (1)
- Underground Cable Fault Detection Using ZigbeeDocument36 pagesUnderground Cable Fault Detection Using ZigbeeRana AbrarNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting CircuitDocument29 pagesAdaptive Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting Circuitgangad_1No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Power Quality Management in Smart Grid Emc - Electromagnetic CompatibilityDocument18 pagesUnit 4 Power Quality Management in Smart Grid Emc - Electromagnetic CompatibilityMathumathi TNo ratings yet
- Underwater Communication Using LI-FI Technology: Names of The Students 2. Aviraj Shejawal 3. Dharyashil WaghchaureDocument19 pagesUnderwater Communication Using LI-FI Technology: Names of The Students 2. Aviraj Shejawal 3. Dharyashil WaghchaureSudarshan RautNo ratings yet
- 048.wireless Water Level ControllerDocument3 pages048.wireless Water Level Controllerpwdsaravanan50% (2)
- Title: Automatic Load Sharing of Transformer: A Synopsis Report OnDocument5 pagesTitle: Automatic Load Sharing of Transformer: A Synopsis Report OnAshish Ghadoje100% (1)
- Protection and Monitoring of Three Phase Induction Motor From Over Voltage, Under Voltage, Single Phasing, Phase Reversal, and Overheating ReviewDocument4 pagesProtection and Monitoring of Three Phase Induction Motor From Over Voltage, Under Voltage, Single Phasing, Phase Reversal, and Overheating ReviewAnonymous CUPykm6DZNo ratings yet
- Solar Charge ControllerDocument11 pagesSolar Charge Controllerayirp89No ratings yet
- Underground Cable Fault Detection and LocationDocument77 pagesUnderground Cable Fault Detection and LocationZerihun PaulosNo ratings yet
- Solar Mobile ChargerDocument16 pagesSolar Mobile ChargerDivyanshu nagarNo ratings yet
- Arduino Based Underground and Overhead Cable Fault DetectionDocument7 pagesArduino Based Underground and Overhead Cable Fault DetectionUmair Mansoor100% (1)
- Pce Mini Project Report: "RF Transmitter and Receiver"Document9 pagesPce Mini Project Report: "RF Transmitter and Receiver"sumit sanchetiNo ratings yet
- Seminar Topics Eee 7thDocument2 pagesSeminar Topics Eee 7thRama Krishna Samireddy100% (1)
- Automatic Railway Gate Controller DocumentationDocument53 pagesAutomatic Railway Gate Controller Documentationmnair201167% (3)
- Smart Energy MeterDocument16 pagesSmart Energy Meterjhansi gouravarapuNo ratings yet
- Batch13 FinalYearProject SynopsisDocument10 pagesBatch13 FinalYearProject SynopsisAdithya KsNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Report On: Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor NetworksDocument9 pagesA Seminar Report On: Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor NetworksNecon ElectricalNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Power Generation by Solar - WindDocument27 pagesHybrid Power Generation by Solar - WindUday Wankar100% (1)
- Water Level Indicator Using Iot Blynk App With Sms NotificationDocument7 pagesWater Level Indicator Using Iot Blynk App With Sms NotificationHassan AliNo ratings yet
- Phase Change Materials For Photovoltaic Thermal ManagementDocument25 pagesPhase Change Materials For Photovoltaic Thermal ManagementSubharanjan Panigrahi100% (1)
- Gogte Institute of Technology: Dr.V.N.SatwikDocument16 pagesGogte Institute of Technology: Dr.V.N.Satwikaditya thakkarNo ratings yet
- Password Based Circuit BreakerDocument8 pagesPassword Based Circuit BreakerRakshitha kNo ratings yet
- Automatic Street Light Using Solar and Piezoelectric SensorDocument4 pagesAutomatic Street Light Using Solar and Piezoelectric SensorIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Integration of Green and Renewable Energy in Electric Power SystemsFrom EverandIntegration of Green and Renewable Energy in Electric Power SystemsNo ratings yet
- Research and Development in Non-Mechanical Electrical Power Sources: Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium Held at Brighton, September 1968From EverandResearch and Development in Non-Mechanical Electrical Power Sources: Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium Held at Brighton, September 1968No ratings yet
- UDAYDocument52 pagesUDAYShravan KumarNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Lab Manual (EE-801)Document12 pagesPower Quality Lab Manual (EE-801)ASHU KNo ratings yet
- Quote CT PT Isolator VCB AB Switch Drop Out Fuse Set TPMO SMC LT Distribution Box HT PanelDocument11 pagesQuote CT PT Isolator VCB AB Switch Drop Out Fuse Set TPMO SMC LT Distribution Box HT PanelSharafatNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power CompensationDocument50 pagesReactive Power CompensationGanja mnNo ratings yet
- Power Sharing MethodDocument9 pagesPower Sharing Methodnavidelec0% (1)
- Notification WaterDocument25 pagesNotification WaterSurender NNo ratings yet
- Wrist Pulse OximeterDocument6 pagesWrist Pulse OximeterSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power and Voltage Stabilization: David F. TaggartDocument32 pagesReactive Power and Voltage Stabilization: David F. TaggartSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- M.tech II Sem R13Document13 pagesM.tech II Sem R13R Straw Hatz RNo ratings yet
- Power Sharing MethodDocument9 pagesPower Sharing Methodnavidelec0% (1)
- Lab 36Document3 pagesLab 36Kiran KumarNo ratings yet
- LFQ in Two Area Interconnected SystemDocument6 pagesLFQ in Two Area Interconnected SystemSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- IJEITDocument7 pagesIJEITSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- Gate Previous PaperDocument3 pagesGate Previous PaperSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- EIL Placement SampleDocument3 pagesEIL Placement SampleSumit DhallNo ratings yet
- Linearized Model of SMIBDocument8 pagesLinearized Model of SMIBSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- EIL Sample PaperDocument2 pagesEIL Sample PaperSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- Gate EE 01/03/14 EveningDocument30 pagesGate EE 01/03/14 EveningSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- Facts Previous PapersDocument1 pageFacts Previous PapersSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- Load Flow Analysis: Modeling of Power System ComponentsDocument8 pagesLoad Flow Analysis: Modeling of Power System ComponentsSai SivaNo ratings yet
- Damping Low Frequency Oscillations in PsDocument4 pagesDamping Low Frequency Oscillations in PsSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- Neural NetworksDocument10 pagesNeural NetworksSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- Application of Particle Swarm Optimization For Economic Load Dispatch and Loss ReductionDocument5 pagesApplication of Particle Swarm Optimization For Economic Load Dispatch and Loss ReductionSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- HVDC - ConverterDocument14 pagesHVDC - ConverterSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- Ee Gate'13Document16 pagesEe Gate'13menilanjan89nLNo ratings yet
- Gate EeDocument4 pagesGate EeSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Pattern For PG R13Document1 pageQuestion Paper Pattern For PG R13Sal ExcelNo ratings yet
- HVDC Padiyar Sample CpyDocument15 pagesHVDC Padiyar Sample CpySal Excel60% (5)
- Question Paper Pattern For PG R13Document1 pageQuestion Paper Pattern For PG R13Sal ExcelNo ratings yet
- Design Transmission LineDocument7 pagesDesign Transmission LineAnonymous ufMAGXcskMNo ratings yet
- Electrical Considerations For HVDC Transmission LinesDocument45 pagesElectrical Considerations For HVDC Transmission LinesNunna Baskar50% (2)
- Linear Quadratic RegulatorDocument52 pagesLinear Quadratic RegulatorSal Excel0% (1)
- Revised M Tech r13 RegulationsDocument9 pagesRevised M Tech r13 RegulationsSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- Pogon Lifta MRL PDFDocument128 pagesPogon Lifta MRL PDFMašinsko ProjektovanjeNo ratings yet
- Pyromet Examples Self StudyDocument2 pagesPyromet Examples Self StudyTessa BeeNo ratings yet
- Canon I-SENSYS MF411dw Parts CatalogDocument79 pagesCanon I-SENSYS MF411dw Parts Catalogmarian100% (1)
- An Analysis of Students' Error in Using Possesive Adjective in Their Online Writing TasksDocument19 pagesAn Analysis of Students' Error in Using Possesive Adjective in Their Online Writing TasksKartika Dwi NurandaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Principle of Marketing UpdateDocument58 pagesChapter 5 - Principle of Marketing UpdateKhaing HtooNo ratings yet
- Rdramirez Aota 2018 Poster For PortfolioDocument1 pageRdramirez Aota 2018 Poster For Portfolioapi-437843157No ratings yet
- Economics Exam Technique GuideDocument21 pagesEconomics Exam Technique Guidemalcewan100% (5)
- The Intel 8086 / 8088/ 80186 / 80286 / 80386 / 80486 Jump InstructionsDocument3 pagesThe Intel 8086 / 8088/ 80186 / 80286 / 80386 / 80486 Jump InstructionsalexiouconNo ratings yet
- Assessing Apical PulseDocument5 pagesAssessing Apical PulseMatthew Ryan100% (1)
- Rapp 2011 TEREOS GBDocument58 pagesRapp 2011 TEREOS GBNeda PazaninNo ratings yet
- Current Harmonics: Electric Power System Power QualityDocument3 pagesCurrent Harmonics: Electric Power System Power QualityAlliver SapitulaNo ratings yet
- BSNL BillDocument3 pagesBSNL BillKaushik GurunathanNo ratings yet
- Standard BMW PDFDocument19 pagesStandard BMW PDFIna IoanaNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Storage Tank Systems: Codes, Regulations, and DesignsDocument4 pagesHandbook of Storage Tank Systems: Codes, Regulations, and DesignsAndi RachmanNo ratings yet
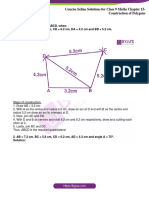
- Concise Selina Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 15 Construction of PolygonsDocument31 pagesConcise Selina Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 15 Construction of Polygonsbhaskar51178No ratings yet
- Institutions and StrategyDocument28 pagesInstitutions and StrategyFatin Fatin Atiqah100% (1)
- Capgemini - 2012-06-13 - 2012 Analyst Day - 3 - Michelin - A Better Way ForwardDocument12 pagesCapgemini - 2012-06-13 - 2012 Analyst Day - 3 - Michelin - A Better Way ForwardAvanish VermaNo ratings yet
- Driver Drowsiness Detection System Using Raspberry PiDocument7 pagesDriver Drowsiness Detection System Using Raspberry PiIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Raiseplus Weekly Plan For Blended LearningDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Raiseplus Weekly Plan For Blended LearningMARILYN CONSIGNANo ratings yet
- Not CE 2015 Version R Series 1t-3.5t Operating Manua 2015-08Document151 pagesNot CE 2015 Version R Series 1t-3.5t Operating Manua 2015-08hocine gherbiNo ratings yet
- Worked Solution Paper5 A LevelDocument8 pagesWorked Solution Paper5 A LevelBhoosan AncharazNo ratings yet
- 02 CT311 Site WorksDocument26 pages02 CT311 Site Worksshaweeeng 101No ratings yet
- 1KHW001492de Tuning of ETL600 TX RF Filter E5TXDocument7 pages1KHW001492de Tuning of ETL600 TX RF Filter E5TXSalvador FayssalNo ratings yet
- OBOE GougerDocument2 pagesOBOE GougerCarlos GaldámezNo ratings yet
- Kallatam of Kallatar (In Tamil Script Tscii Format)Document78 pagesKallatam of Kallatar (In Tamil Script Tscii Format)rprabhuNo ratings yet
- Flipkart Labels 06 Jul 2022 09 52Document37 pagesFlipkart Labels 06 Jul 2022 09 52Dharmesh ManiyaNo ratings yet
- Ode To The West WindDocument4 pagesOde To The West WindCharis Mae DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- Tata NanoDocument25 pagesTata Nanop01p100% (1)
- Formato MultimodalDocument1 pageFormato MultimodalcelsoNo ratings yet
- EPMS System Guide For Subcontractor - V1 2Document13 pagesEPMS System Guide For Subcontractor - V1 2AdouaneNassim100% (2)