Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Control of Processes
Uploaded by
maheshboobalan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views15 pagesPPT file for introduction
Original Title
Computer control of processes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPPT file for introduction
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views15 pagesComputer Control of Processes
Uploaded by
maheshboobalanPPT file for introduction
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
To identify the information flow, and to
manipulate the material and energy flow of
the given process in a desired optimal way.
Response time, computing power, flexibility
and fault tolerance-crucial ON LINE
Requirements
Objective of CCP
Digital computer control
in Process Industries
Active Applications
Manipulation of
process and
Optimisation
Passive Applications
Acquisition and
manipulation of
process data.
Monitoring ,alarming
Smart sensors, smart transmitters and smart
actuators(final control elements) has inbuilt
microcomputer.
To get real time process measurement information
and automatic transmission in required form.
To ensure that the actuator ,transmitter or sensor
function according to the design.
Smart Instruments
Video display terminals to supervise the
whole plant from control room.
A few keyboards and screens replace large
panel of instruments, switches and knobs.
Control rooms are much smaller and few
people are required to monitor the plant.
Sophisticated mathematical models can be
implemented.
Modernisation
Modernisation
Plant managers and engineers can be provided
with comprehensive information concerning the
status of plant operations to aid effective
operation.
Automatic tuning of controller parameters for the
best performance.
Model based Predictive technique-optimisation
of process operation
PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY-
CONTROL ROOM
NATURAL GAS INDUSTRY-
CONTROL ROOM
BASIC FUNCTIONS OF COMPUTER AIDED
PROCESS
Measurements and data acquisition
Data conversion with scaling and checking
Data accumulation and formatting
Visual display
Comparing with limits and alarm raising
Recording and monitoring of events,
sequences and trends
Data logging
Control Actions
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM OF COMPUTER
AIDED PROCESS CONTROL
The control strategy is repeated at some
predetermined frequency to achieve closed loop
computer control system.
Computer Controlled Process-
Mode of Operations
Batch or Sequential control
Continuous Control
Supervisory Control
Direct digital control
BATCH PROCESS
CONTINUOUS PROCESS
Supervisory Control
Comprehensive picture of the status of the
plant operations.
To optimize the plant operations by
maximizing the plant yield, production
rates,minimising energy consumption, etc.
Computing set points-reorganise the control
algorithm
Review the operating conditions periodically.
Direct digital control
Computer directly controlled the process.
Loop control-Functions of Comparator,
controller, safe guarding operations
Large computer-to implement hundreds of
control loops
Control equation is chosen to suit dynamic
characteristic of the process.
Not only limited to the 3 term PID control
action.
Drawback One processor used.
A single failure affect a large no.of controlled
variables and disable the entire process
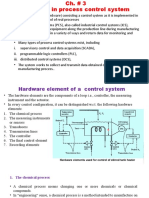
Architecture of Computer Aided Process
Control
Centralized controlled system-Large
computer system both Supervisory
and DDC
Distributed controlled system (DCS)
-Total work is divided and spread
across several computers.
You might also like
- MODULE V.PPTXDocument170 pagesMODULE V.PPTXRijo MathewNo ratings yet
- Industrial Control SystemsDocument34 pagesIndustrial Control SystemsAmmar OwesNo ratings yet
- Practical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneFrom EverandPractical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneNo ratings yet
- Define? - Purpose of Using DCS?Document30 pagesDefine? - Purpose of Using DCS?deep_the_creepNo ratings yet
- Automation Systems ArchitectureDocument159 pagesAutomation Systems ArchitectureTeenaNo ratings yet
- Distributed Computer ControlDocument124 pagesDistributed Computer ControlManjula SutagundarNo ratings yet
- Cit Eee Ecs DDC DCSDocument19 pagesCit Eee Ecs DDC DCSchandiraNo ratings yet
- DCS LectureDocument80 pagesDCS LectureShashankRajoria100% (3)
- CT 03 (PLC)Document23 pagesCT 03 (PLC)Nazmul AhsanNo ratings yet
- PC-Hardware of A Process Control SystemDocument22 pagesPC-Hardware of A Process Control SystemSafyan Manzoor0% (1)
- Monitoring and Controling of Remote Industrial PlantDocument15 pagesMonitoring and Controling of Remote Industrial PlantraghuNo ratings yet
- Psoc Notes Vtu Unit 1Document17 pagesPsoc Notes Vtu Unit 1Rohit SarafNo ratings yet
- Digital Factory1Document39 pagesDigital Factory1Tushar AnandNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - What Is Automation (Printed)Document12 pagesLecture 1 - What Is Automation (Printed)Aung Naing OoNo ratings yet
- MM UNIT 3b 2021Document78 pagesMM UNIT 3b 2021Mr. S. Paul JoshuaNo ratings yet
- MachineAutomationANDProcessControl Part 1Document244 pagesMachineAutomationANDProcessControl Part 1rotcdublinNo ratings yet
- Application of Scada For Water Treatment Plant: - by Shraddha Malve MT19ENV017Document34 pagesApplication of Scada For Water Treatment Plant: - by Shraddha Malve MT19ENV017Shraddha Malve100% (1)
- Honeywell Sugar PresentationDocument31 pagesHoneywell Sugar Presentationaharnisha100% (1)
- Cs Unit 3Document19 pagesCs Unit 3gchinnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - What Is AutomationDocument14 pagesLecture 1 - What Is AutomationAung Naing OoNo ratings yet
- InternDocument11 pagesInternSrajay SsNo ratings yet
- SCADA and Central Applications: An IntroductionDocument53 pagesSCADA and Central Applications: An IntroductionBADRI VENKATESH100% (1)
- SCADA - Unit VI & VIIDocument65 pagesSCADA - Unit VI & VIIAswinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document19 pagesLecture 6Philani XabaNo ratings yet
- SCADA of The Future: Kelly DoranDocument32 pagesSCADA of The Future: Kelly DoranYM6BNo ratings yet
- Power Plants InspectionDocument2 pagesPower Plants InspectionRamkumar KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document16 pagesUnit 1CHETAN SETIYANo ratings yet
- AutomationDocument15 pagesAutomationmoney_kandan2004No ratings yet
- Chapter-3 InstrumentationDocument14 pagesChapter-3 InstrumentationIrtiza RasulNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Automation, PLC and Scada: By, Saikat Rahut Instrumentation and Control EngineeringDocument15 pagesPresentation On Automation, PLC and Scada: By, Saikat Rahut Instrumentation and Control EngineeringShivani SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- What Is SCADA SystemDocument10 pagesWhat Is SCADA SystemDhaval TailorNo ratings yet
- Process Control AutomationDocument244 pagesProcess Control AutomationGanesh GholapNo ratings yet
- MES; SCADA; PLCDocument11 pagesMES; SCADA; PLCashish2718No ratings yet
- SCADA Systems: Zhu Kun 2012-4-17Document28 pagesSCADA Systems: Zhu Kun 2012-4-17gabriel galvez figueroaNo ratings yet
- Algorithms: Performance Assessment of Predictive Control - A SurveyDocument22 pagesAlgorithms: Performance Assessment of Predictive Control - A Surveyali coNo ratings yet
- Operations Management 2Document13 pagesOperations Management 2Shame BopeNo ratings yet
- Implementation Expert ControlDocument23 pagesImplementation Expert Controljcaceresn8949No ratings yet
- Distributed Control System: Submitted By: Roll No:35 To 59Document35 pagesDistributed Control System: Submitted By: Roll No:35 To 59sningleNo ratings yet
- Transmission Automation and SCADA Systems ExplainedDocument21 pagesTransmission Automation and SCADA Systems ExplainedDishika PoddarNo ratings yet
- SCADADocument10 pagesSCADAMOUSIN PASHANo ratings yet
- Batch ControlDocument18 pagesBatch ControlGanesh Kumar VNo ratings yet
- Jahid 1Document24 pagesJahid 1Nazmul AhsanNo ratings yet
- Air Miser System Benefits MS129Document4 pagesAir Miser System Benefits MS129Diego PareschiNo ratings yet
- Optimize Energy Use With SCADA AutomationDocument25 pagesOptimize Energy Use With SCADA Automationkazi ahadNo ratings yet
- Scada (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) : PgdiaeDocument49 pagesScada (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) : PgdiaeAdrian ReyesNo ratings yet
- PCT23MkII _ Process Plant Trainer (Process Control Trainer)Document10 pagesPCT23MkII _ Process Plant Trainer (Process Control Trainer)veronicaNo ratings yet
- INFO409 Operations Management ControlsDocument13 pagesINFO409 Operations Management ControlsMusariri TalentNo ratings yet
- Manvir Singh Gill 123613 M Tech (I&CDocument20 pagesManvir Singh Gill 123613 M Tech (I&CManvir Singh GillNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle Stages and Economies of Scale & ScopeDocument52 pagesProduct Life Cycle Stages and Economies of Scale & ScopeMrityunjay JhaNo ratings yet
- Process Expert 1544294431Document4 pagesProcess Expert 1544294431Ahmed Mohamed KassemNo ratings yet
- Cc&a - 4Document51 pagesCc&a - 4Gauri SinghNo ratings yet
- 1 CAM Intro DocsDocument41 pages1 CAM Intro DocsVaibhav KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit - V: Computer Control of Power SystemsDocument18 pagesUnit - V: Computer Control of Power Systemsjagan gnitNo ratings yet
- Industrial Control SystemsDocument52 pagesIndustrial Control SystemsDeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- CH 4 PLC LecureDocument30 pagesCH 4 PLC LecurekvaijnathNo ratings yet
- DDE 3443 Industrial Automation Introduction To AutomationDocument74 pagesDDE 3443 Industrial Automation Introduction To AutomationAmar Banerjee100% (1)
- Automated Manufacturing Systems - HSC IPT NotesDocument13 pagesAutomated Manufacturing Systems - HSC IPT Notesquynhanh.dang1029No ratings yet
- Lecture 2a Automation Scope 2023 KSBDocument21 pagesLecture 2a Automation Scope 2023 KSBDaniel JonesNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Additive Manufacturing TechnologiesDocument11 pagesHybrid Additive Manufacturing TechnologiesmaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Controllers and Microcontrollers ExamDocument1 pageProgrammable Logic Controllers and Microcontrollers ExammaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- 9Document6 pages9maheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- WISE IOT WG 2017.08.15 v3Document22 pagesWISE IOT WG 2017.08.15 v3maheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Lab Cosumable 2015-18Document2 pagesLab Cosumable 2015-18maheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- IotDocument3 pagesIotmaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- M.E PED Model Lab QuestionDocument1 pageM.E PED Model Lab QuestionmaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Scheme For Young Scientists and TechnologistsDocument15 pagesScheme For Young Scientists and TechnologistsmaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Presented by S.Keerthi Vasan G.Dinakaran 3rd YEAR - MCT 'A'Document16 pagesPresented by S.Keerthi Vasan G.Dinakaran 3rd YEAR - MCT 'A'maheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Application Sizing GuideDocument19 pagesApplication Sizing GuideOmar Eladel MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Counter PBMDocument4 pagesCounter PBMmaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Piezoelectric RoadsDocument17 pagesPiezoelectric RoadsSoma Giri86% (7)
- Internet of Things TutorialDocument53 pagesInternet of Things Tutorialboka987100% (1)
- LISTnet SharonyDocument100 pagesLISTnet SharonymaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Design For Sustainable Virtual Power Plant FormationDocument6 pagesMechanism Design For Sustainable Virtual Power Plant FormationmaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Ghavidel 2016Document6 pagesGhavidel 2016maheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Control and Bidding Strategy For VPPDocument14 pagesControl and Bidding Strategy For VPPmaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Technical Club ActivityDocument1 pageTechnical Club ActivitymaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Design For Sustainable Virtual Power Plant FormationDocument6 pagesMechanism Design For Sustainable Virtual Power Plant FormationmaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Measurements and InstrumentationsDocument2 pagesMeasurements and InstrumentationsmaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- R 2016 Be EeeDocument6 pagesR 2016 Be EeemaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- 3 Monthly Test (20 Marks), Laboratory Rubrics (40 Marks)Document2 pages3 Monthly Test (20 Marks), Laboratory Rubrics (40 Marks)maheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- DC Machines and Transformers GuideDocument12 pagesDC Machines and Transformers GuidemaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- 3 Monthly Test (20 Marks), Laboratory Rubrics (40 Marks)Document2 pages3 Monthly Test (20 Marks), Laboratory Rubrics (40 Marks)maheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Annual Recruitment Planner - 2017Document1 pageAnnual Recruitment Planner - 2017IsmailBugareeNo ratings yet
- QQ2 LBVDH 2 I XZ NWTRDocument2 pagesQQ2 LBVDH 2 I XZ NWTRmaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Bionic LegDocument2 pagesBionic LegmaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Staff Recruit 12x8 2Document1 pageStaff Recruit 12x8 2maheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Atal Pension Yojana-SchemeDocument9 pagesAtal Pension Yojana-SchemeSaurabhNo ratings yet
- Discover Your True Self: A Tibetan Personality Test in 4 QuestionsDocument24 pagesDiscover Your True Self: A Tibetan Personality Test in 4 QuestionsmaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Group 4 HR201 Last Case StudyDocument3 pagesGroup 4 HR201 Last Case StudyMatt Tejada100% (2)
- ContactsDocument10 pagesContactsSana Pewekar0% (1)
- 2022 Product Catalog WebDocument100 pages2022 Product Catalog WebEdinson Reyes ValderramaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Investment Unit 5Document8 pagesFundamental of Investment Unit 5commers bengali ajNo ratings yet
- Account STMT XX0226 19122023Document13 pagesAccount STMT XX0226 19122023rdineshyNo ratings yet
- Econometrics Chapter 1 7 2d AgEc 1Document89 pagesEconometrics Chapter 1 7 2d AgEc 1Neway AlemNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Networks - Networks Affect Our LivesDocument2 pages1.1 Introduction To Networks - Networks Affect Our LivesCristian MoralesNo ratings yet
- 2CG ELTT2 KS TitanMagazine Anazelle-Shan PromoDocument12 pages2CG ELTT2 KS TitanMagazine Anazelle-Shan PromoJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Diana's Innermost House: MagazineDocument42 pagesDiana's Innermost House: MagazinealexgoagaNo ratings yet
- E2 PTAct 9 7 1 DirectionsDocument4 pagesE2 PTAct 9 7 1 DirectionsEmzy SorianoNo ratings yet
- Difference Between OS1 and OS2 Single Mode Fiber Cable - Fiber Optic Cabling SolutionsDocument2 pagesDifference Between OS1 and OS2 Single Mode Fiber Cable - Fiber Optic Cabling SolutionsDharma Teja TanetiNo ratings yet
- Dell 1000W UPS Spec SheetDocument1 pageDell 1000W UPS Spec SheetbobNo ratings yet
- Chill - Lease NotesDocument19 pagesChill - Lease Notesbellinabarrow100% (4)
- Fundamentals of Corporate Finance Canadian Canadian 8th Edition Ross Test Bank 1Document36 pagesFundamentals of Corporate Finance Canadian Canadian 8th Edition Ross Test Bank 1jillhernandezqortfpmndz100% (22)
- Multiple Choice Question (MCQ) of Alternator and Synchronous Motors PageDocument29 pagesMultiple Choice Question (MCQ) of Alternator and Synchronous Motors Pagekibrom atsbha0% (1)
- Comparing Time Series Models to Predict Future COVID-19 CasesDocument31 pagesComparing Time Series Models to Predict Future COVID-19 CasesManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- FEM Lecture Notes-2Document18 pagesFEM Lecture Notes-2macynthia26No ratings yet
- Super Flexible, Super Fast, Super Value: Gigabit PTMP Client and PTP With Modular AntennasDocument5 pagesSuper Flexible, Super Fast, Super Value: Gigabit PTMP Client and PTP With Modular AntennasAbdallaNo ratings yet
- MN AG v. SANOFI - 3:18-cv-14999 - Defendants' Joint Motion To Dismiss - 2019-08-12Document124 pagesMN AG v. SANOFI - 3:18-cv-14999 - Defendants' Joint Motion To Dismiss - 2019-08-12The Type 1 Diabetes Defense FoundationNo ratings yet
- 7th Kannada Science 01Document160 pages7th Kannada Science 01Edit O Pics StatusNo ratings yet
- AE383LectureNotes PDFDocument105 pagesAE383LectureNotes PDFPoyraz BulutNo ratings yet
- Qatar Airways E-ticket Receipt for Travel from Baghdad to AthensDocument1 pageQatar Airways E-ticket Receipt for Travel from Baghdad to Athensمحمد الشريفي mohammed alshareefiNo ratings yet
- Gerhard Budin PublicationsDocument11 pagesGerhard Budin Publicationshnbc010No ratings yet
- POS CAL SF No4 B2 BCF H300x300 7mmweld R0 PDFDocument23 pagesPOS CAL SF No4 B2 BCF H300x300 7mmweld R0 PDFNguyễn Duy QuangNo ratings yet
- 9 QP - SSC - MOCK EXAMDocument5 pages9 QP - SSC - MOCK EXAMramNo ratings yet
- Short Term Training Curriculum Handbook: General Duty AssistantDocument49 pagesShort Term Training Curriculum Handbook: General Duty AssistantASHISH BARAWALNo ratings yet
- Chaman Lal Setia Exports Ltd fundamentals remain intactDocument18 pagesChaman Lal Setia Exports Ltd fundamentals remain intactbharat005No ratings yet
- 3DS MAX SYLLABUSDocument8 pages3DS MAX SYLLABUSKannan RajaNo ratings yet
- Geneva IntrotoBankDebt172Document66 pagesGeneva IntrotoBankDebt172satishlad1288No ratings yet
- MCDO of Diesel Shed, AndalDocument12 pagesMCDO of Diesel Shed, AndalUpendra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Defensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityFrom EverandDefensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Dealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeFrom EverandDealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (88)
- Scary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldFrom EverandScary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsFrom EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (722)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveFrom EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNo ratings yet
- Digital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyFrom EverandDigital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessFrom EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessNo ratings yet
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumFrom EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (12)
- 8-Bit Apocalypse: The Untold Story of Atari's Missile CommandFrom Everand8-Bit Apocalypse: The Untold Story of Atari's Missile CommandRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- AI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderFrom EverandAI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (398)
- CompTIA Security+ Get Certified Get Ahead: SY0-701 Study GuideFrom EverandCompTIA Security+ Get Certified Get Ahead: SY0-701 Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (227)
- The Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldFrom EverandThe Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (107)
- Blood, Sweat, and Pixels: The Triumphant, Turbulent Stories Behind How Video Games Are MadeFrom EverandBlood, Sweat, and Pixels: The Triumphant, Turbulent Stories Behind How Video Games Are MadeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (335)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldFrom EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- So You Want to Start a Podcast: Finding Your Voice, Telling Your Story, and Building a Community that Will ListenFrom EverandSo You Want to Start a Podcast: Finding Your Voice, Telling Your Story, and Building a Community that Will ListenRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (35)
- The Corporate Startup: How established companies can develop successful innovation ecosystemsFrom EverandThe Corporate Startup: How established companies can develop successful innovation ecosystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Artificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking HumansFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking HumansRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- Data-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseFrom EverandData-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (12)
- Who's Afraid of AI?: Fear and Promise in the Age of Thinking MachinesFrom EverandWho's Afraid of AI?: Fear and Promise in the Age of Thinking MachinesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet