Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vitamin-A: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.D
Uploaded by
Dr. M. Prasad NaiduOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vitamin-A: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.D
Uploaded by
Dr. M. Prasad NaiduCopyright:
Available Formats
VITAMIN- A
M.Prasad Naidu
MSc Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D,.
VITAMIN- A
Structure
6C beta-ionine ring with 11C polyprenoid side chain with
alternate double bonds.
Provitaminbeta carotene [Retinal+Retinal]
Active forms 1.Retinol
2.Retinal
3.Retinoic acid
CH
3
CH
3 H
3
C
CH
3
CH
2
OH
CH
3
VITAMIN A (RETINOL)
RDA: 0.7 mg
Poly isoprenoid side chain
VITAMIN A
Retinol Retinal retinoicacid All-trans Retinal A
1
common in circulation.
11cis- Retinal form is present in rhodopsin.
Active forms are heat stable and light sensitive.
VITAMIN A
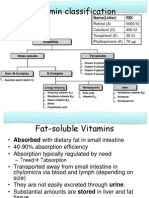
Sources
Animal marine fish liver oils
Plant - mango\papaya\carrot
RDA 1000 ug \ day
1 RE = 1ug of retinol = 0.6 ug of betacarotene
VITAMIN A
.
FUNTIONS
1. Retinal and Retinol vision
2. Retinoic acid
cell differentiation
glycoprotein synthesis
reproduction.
3.Beta-carotene- Anti-oxidant
WALDS VISUAL CYCLE
The Cyclic events that occur in the process
of vision is visual cycle. .
Rhodopsin is a photoreceptor present in
retinal rod cells.
Rhodopsin is a conjugated protein with 11-cis
retinal and protein opsin.
FUNCTIONS OF VIT A
WALDS
VISUAL CYCLE
DEFECIENCY
primary causes [dietary]
secondarycauses[malabsorption]
Results in
Night blindness
Conjunctival xerosis
Bitots spots
Corneal xerosis
keratomalasia
Blindness
.
Toxicity of vit-A is either due to
1. over-dosage of vit-A supplements
2. excess dietary intake [
As vitamin A is not excreted from the body it
isccumulated in liver producing toxic
effects
Toxicity produces headache , nausea , vomitings
, liver damage alterations in the skin and mucous
membranes etc.
.
Vit-A can be used to treat diseases where
epithelial surface is damaged.
Retinoic acid acts on cell differentiation and
growth therefore used as a drug.
It is used to treat diseases like Measles,
Acne, Psoriasis , Leukemia etc.
VISUAL CYCLE
meta-rhodopsin
Transducin Transducin [A]
PDE PDE [A]
CGMP GMP
VISUAL CYCLE
Decreased CGMP
closes Na
+
channels in rod cell membrane
hyper polarization of rod cell membrane
generation of nerve impulse to visual cortex
VITAMIN D
Structure
plants - Ergosterol Ergocalciferol [D
2
]
Active form in animals is calcitriol
UV
VITAMIN D
Sources
1. sunlight
2. animal sources; fish liver oils \ eggs
3. plant sources
4. food fortification ; milk\ butter
RDA
200-400 IU \ day
VITAMIN D
Digestion \ absorption \ transport
Digested and absorbed in small intestine
using bile salts .
Vit-D is transported from intestine to
circulation by chylomicrons and stored in the
liver.
VITAMIN D
Synthesis of vit-D
Regulation of synthesis by Ca and PO
4
.
Low calcium stimulates PTH secretion which
activates 1- hydroxylase
FUNCTIONS
Vit-D plays a major role in regulation of calcium
and phosphate levels by mainly acting on 3
different organs.
Intestine ; increases absorption of Ca and PO
4
Bone ; increases deposition of CaPO
4
thus
increasing mineralization of bones .
Kidneys ; reabsorbs Ca and decreases Ca
excretion.
VITAMIN D
Deficiency
Children ---Rickets
Adults ------ Osteomalacia
VITAMIN D
Toxicity
hyper-vitaminosis D causes toxic effects
like de-mineralization , hyper-calcemia ,
renal calculi etc.
ABSORPTION AND TRANSPORT
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
Laboratory findings
Hypochromic microcytic
anemia
ferritin ( 30 to 300
Nanogm/ml)
serum iron (50 to175 gm/dl)
TIBC (300 to 350 gm/dl)
transferrin (200 to 400 mg/dl)
Spoon-shaped nails (koilonychia)
Dental fluorosis
THANK Q
You might also like
- Bioche VitaminsDocument7 pagesBioche Vitaminsharips motupalliNo ratings yet
- Vitamina2023Document26 pagesVitamina2023NiᝨHiLᗅN NlghNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients, VitaminsDocument32 pagesMicronutrients, VitaminsEsdras DountioNo ratings yet
- Vitamin: Nurina TyagitaDocument42 pagesVitamin: Nurina TyagitaJessica Green100% (1)
- VitaminsDocument77 pagesVitaminsEsosa OdighizuwaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Vit KDocument6 pagesJurnal Vit KTisenda TimiselaNo ratings yet
- Calories, Vitamins and Minerals: Nutrition - Finals Lesson 12Document12 pagesCalories, Vitamins and Minerals: Nutrition - Finals Lesson 12yoonie catNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D: Gandham. RajeevDocument66 pagesVitamin D: Gandham. Rajeevguna sundariNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D: Gandham. RajeevDocument63 pagesVitamin D: Gandham. Rajeevguna sundari100% (2)
- Fats and Water Soluble VitaminsDocument31 pagesFats and Water Soluble VitaminshafizahhoshniNo ratings yet
- VITAMINSDocument6 pagesVITAMINSJohn Rick OrineNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument32 pagesVitaminsdivya100% (5)
- Nutritional Biochemistry: Vitamins Dr. Bidhan Chandra KonerDocument50 pagesNutritional Biochemistry: Vitamins Dr. Bidhan Chandra KonerElenanana100% (1)
- VitaminsDocument24 pagesVitaminsRachit VyasNo ratings yet
- Vitamins - Fat SolubleDocument45 pagesVitamins - Fat SolubleJasmine sindhooNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12 Vitamin C Vitamin E Vitamin D Vitamin KDocument28 pagesVitamin A Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12 Vitamin C Vitamin E Vitamin D Vitamin KSajanMaharjanNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A - BDSDocument34 pagesVitamin A - BDSIsaiah JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble Vitamin-1Document74 pagesFat Soluble Vitamin-1Himank RanaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of VitaminsDocument64 pagesBiochemistry of VitaminsConrado CatimbangNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Source Vitamin A Occurs in Nature in Several Forms. RetinolDocument6 pagesChemistry and Source Vitamin A Occurs in Nature in Several Forms. RetinolElly NurlaelyNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Final YrDocument37 pagesVitamins Final YrPooja ReddyNo ratings yet
- VADD - StudentsDocument38 pagesVADD - Studentsonline masterNo ratings yet
- K4. Aspek Biokimia MataDocument74 pagesK4. Aspek Biokimia MataSarahGustiaWoromboniNo ratings yet
- 1 Relationship of VItamins FinalDocument9 pages1 Relationship of VItamins FinalRajkumar YadavNo ratings yet
- 1 Relationship of VItamins FinalDocument9 pages1 Relationship of VItamins FinalRajkumar YadavNo ratings yet
- New Vitamin ADocument24 pagesNew Vitamin ANurul NajibNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and VitaminDocument70 pagesNutrition and VitaminTob JurNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A & D: Chemistry, Biochemical Role, RDA & Deficiency DiseasesDocument20 pagesVitamin A & D: Chemistry, Biochemical Role, RDA & Deficiency DiseasesSELVI ANo ratings yet
- A Presentation On: Presented byDocument67 pagesA Presentation On: Presented byOlufemi KolawoleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 53 2015 LeaDocument33 pagesLecture 53 2015 LeaYehundinokibaathai FcNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A & D: Chemistry, Biochemical Role, RDA & Deficiency DiseasesDocument20 pagesVitamin A & D: Chemistry, Biochemical Role, RDA & Deficiency DiseasesSELVI ANo ratings yet
- Vitamin Deficiency in FishesDocument40 pagesVitamin Deficiency in FishesDuong Vu TungNo ratings yet
- Define VitaminsDocument22 pagesDefine Vitaminsantesar reheemNo ratings yet
- 10 Nutrients Involved in Energy Metabolism and Blood HealthDocument8 pages10 Nutrients Involved in Energy Metabolism and Blood HealthKavisa GhoshNo ratings yet
- Vitamin I & II - Noor WaseemDocument49 pagesVitamin I & II - Noor Waseemqueenmasa191No ratings yet
- Vitamin ADocument19 pagesVitamin AIram AnwarNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Chart 2009Document1 pageVitamin Chart 2009Surpreet AroraNo ratings yet
- VitaminDocument79 pagesVitaminhana rizkiaNo ratings yet
- VITAMINSDocument10 pagesVITAMINSkerynne dyNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A - BIOT 203Document21 pagesVitamin A - BIOT 203Soniya BastolaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Metabolism Intro - BC I 2565-SheetDocument43 pagesVitamin and Metabolism Intro - BC I 2565-SheetWirawit SIWONGTRAKULNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble Vitamins - 0Document7 pagesFat Soluble Vitamins - 0joyasafiullah466No ratings yet
- Classification of VitaminsDocument26 pagesClassification of VitaminsRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Deficiency DisordersDocument23 pagesVitamin Deficiency DisordersKibromWeldegiyorgisNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A FinalDocument64 pagesVitamin A FinalLiaqat HussainNo ratings yet
- 4 - Metabolisme Vit A DDocument51 pages4 - Metabolisme Vit A DPaulinNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Larut Lemak 2016Document30 pagesVitamin Larut Lemak 2016Arum KunarniNo ratings yet
- FAT Soluble VitaminsDocument53 pagesFAT Soluble VitaminsFaria LatifNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument20 pagesFat Soluble VitaminsWati WindayaniNo ratings yet
- 2-Vitamin ADocument31 pages2-Vitamin ARutvik DhoriyaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Nutrition: Bruno SopkoDocument64 pagesBiochemistry of Nutrition: Bruno SopkoMamtaNo ratings yet
- The Eldoret National Polytechnic, Diploma in Pharmaceutical TechnologyDocument20 pagesThe Eldoret National Polytechnic, Diploma in Pharmaceutical TechnologyGerald Limo Arap ChebiiNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument77 pagesVitaminsLoredana100% (1)
- Vitamins N MSC 2019Document105 pagesVitamins N MSC 2019Shasha Reverse AgingNo ratings yet
- Vitamin For Final MCQDocument14 pagesVitamin For Final MCQSajia Abedin 1821432649No ratings yet
- PresentationDocument52 pagesPresentationsahilarrain0011No ratings yet
- Vitamins & NutritionDocument56 pagesVitamins & Nutritionahmed abd elazizNo ratings yet
- Lecture Vitamins 2020Document99 pagesLecture Vitamins 2020Lawal Bello DanchadiNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & MineralsDocument89 pagesVitamins & MineralsSoffa ShmuelNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble VitaminsDocument55 pagesWater Soluble VitaminsDr. M. Prasad Naidu100% (1)
- Signal TransductionDocument77 pagesSignal TransductionM.PRASAD NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormonesDocument63 pagesThyroid HormonesDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Translation: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDocument33 pagesTranslation: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Non-Parametric Tests: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDocument15 pagesNon-Parametric Tests: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDocument23 pagesM.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Transcription: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemisty, Ph.D.Research ScholarDocument33 pagesTranscription: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemisty, Ph.D.Research ScholarDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- STUDENT T-TestDocument20 pagesSTUDENT T-TestDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Urea CycleDocument8 pagesUrea CycleDr. M. Prasad Naidu100% (1)
- M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDocument17 pagesM.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Rna Processing: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDocument33 pagesRna Processing: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Serum Ferritin and Diabetes Mellitus Type LLDocument21 pagesSerum Ferritin and Diabetes Mellitus Type LLM.PRASAD NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Thin Layer ChromatographyDocument16 pagesThin Layer ChromatographyDr. M. Prasad Naidu100% (1)
- TGF-β Signalling From CellDocument14 pagesTGF-β Signalling From CellDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Sex HormonesDocument10 pagesSex HormonesM.PRASAD NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Serum Protein Electrophoresis & Their Clinical ImportanceDocument44 pagesSerum Protein Electrophoresis & Their Clinical ImportanceDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Peptides and Proteins: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDocument30 pagesPeptides and Proteins: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Sequence DatabaseDocument36 pagesSequence DatabaseDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Renal CalculiDocument49 pagesRenal CalculiDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument34 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologyDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDocument12 pagesProtein Synthesis: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- MikroekonomiDocument1 pageMikroekonomiYudhaPrakosoIINo ratings yet
- Pursanova IXC ManualDocument16 pagesPursanova IXC ManualHector Serrano MagañaNo ratings yet
- Play Tennis Manual PDFDocument52 pagesPlay Tennis Manual PDFAnonymous GJuRvp9A5T100% (2)
- Symbolic Interaction Theory: Nilgun Aksan, Buket Kısac, Mufit Aydın, Sumeyra DemirbukenDocument3 pagesSymbolic Interaction Theory: Nilgun Aksan, Buket Kısac, Mufit Aydın, Sumeyra DemirbukenIgor Dutra BaptistaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Improvement SYMPOSIUM SCRIPTDocument3 pagesContinuous Improvement SYMPOSIUM SCRIPTChanda Marie AsedillaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Logistics XI - 2023Document45 pagesFundamentals of Logistics XI - 2023saiyaNo ratings yet
- University Physics With Modern Physics 2nd Edition Bauer Test BankDocument24 pagesUniversity Physics With Modern Physics 2nd Edition Bauer Test BankJustinTaylorepga100% (42)
- (1908) Mack's Barbers' Guide: A Practical Hand-BookDocument124 pages(1908) Mack's Barbers' Guide: A Practical Hand-BookHerbert Hillary Booker 2nd100% (1)
- New Admission Form Short CourseDocument4 pagesNew Admission Form Short CourseSyed badshahNo ratings yet
- WB-Mech 120 Ch05 ModalDocument16 pagesWB-Mech 120 Ch05 ModalhebiyongNo ratings yet
- Business ProposalDocument35 pagesBusiness ProposalMJ MacapagalNo ratings yet
- Power - of - Suffering 2Document21 pagesPower - of - Suffering 2jojiNo ratings yet
- Networking With OrganizationsDocument23 pagesNetworking With OrganizationsClaudette Lui Cabanos- Mercado-ReyesNo ratings yet
- List of Marketing Metrics and KpisDocument5 pagesList of Marketing Metrics and KpisThe KPI Examples ReviewNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics MaterialDocument86 pagesMechatronics MaterialKota Tarun ReddyNo ratings yet
- Defining Who Is A Volunteer ConceptualDocument21 pagesDefining Who Is A Volunteer ConceptualYosep Trisaputro WahyuNo ratings yet
- The Goldfish and Its Culture. Mulertt PDFDocument190 pagesThe Goldfish and Its Culture. Mulertt PDFjr2010peruNo ratings yet
- English Idioms and PhrasesDocument384 pagesEnglish Idioms and Phrasesthwe thweNo ratings yet
- ĐÁP ÁN ĐỀ THI THỬ SỐ 03 (2019-2020)Document8 pagesĐÁP ÁN ĐỀ THI THỬ SỐ 03 (2019-2020)Đào VânNo ratings yet
- Dawn of The DhammaDocument65 pagesDawn of The Dhammaarkaprava paulNo ratings yet
- REF615 PG 756379 ENs PDFDocument96 pagesREF615 PG 756379 ENs PDFandi mulyanaNo ratings yet
- GE Elec 7 UNIT-3 NoDocument22 pagesGE Elec 7 UNIT-3 NoLyleNo ratings yet
- Rabbit Book PDFDocument20 pagesRabbit Book PDFMatumelo Rebecca DaemaneNo ratings yet
- DR Cast Iron Fittings CharlotteDocument124 pagesDR Cast Iron Fittings CharlotteMohamad NohayliNo ratings yet
- AADE Review of Lost Circulation Materials and Treatments With An Updated ClassificationDocument9 pagesAADE Review of Lost Circulation Materials and Treatments With An Updated ClassificationMuhamad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Sponsor and Principal Investigator: Responsibilities of The SponsorDocument10 pagesSponsor and Principal Investigator: Responsibilities of The SponsorNoriNo ratings yet
- Pre-Qin Philosophers and ThinkersDocument22 pagesPre-Qin Philosophers and ThinkersHelder JorgeNo ratings yet
- Secondary Scheme of Work Form 2Document163 pagesSecondary Scheme of Work Form 2Fariha RismanNo ratings yet
- Year 10 English Unit Plan AdvertisingDocument5 pagesYear 10 English Unit Plan Advertisingapi-333849174No ratings yet
- Delay Codes1 3Document10 pagesDelay Codes1 3AhmedNo ratings yet