Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7.alkil Halida (SN Dan E)
Uploaded by
akbar_rozaaqOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7.alkil Halida (SN Dan E)
Uploaded by
akbar_rozaaqCopyright:
Available Formats
REAKSI ALKIL HALIDA :
SUBSTITUSI NUKLEOFILIK
DAN ELIMINASI
Oleh : Alvan Febrian Shalas, S.
Farm., Apt
TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN
Mahasiswa dapat memahami Mekanisme dan
Karakteristik reaksi :
1. SN1
2. SN2
3. E1
4. E2
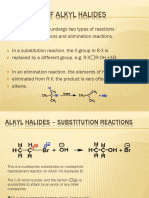
Alkyl halides do one of two things when they
react with a nucleophile/base, such as hydroxide
ion: either they undergo substitution of the X
group by the nucleophile, or they undergo
elimination of HX to yield an alkene
REAKSI SN2
SUBSTITUSI
NUKLEOFILIK
BIMOLEKULAR
INVERSI KONFIGURASI
REAKSI ORDE KEDUA
SINGLE STEP
REAKSI SN2
REAKSI SN2
REAKSI ORDE KEDUA
The rate of reaction is linearly dependent on the
concentrations of two species
Alkil halida
Nukleofil
REAKSI SN2
SUBSTRAT
NUKLEOFIL
LEAVING GROUP
SOLVENT
REAKSI SN2
SUBSTRAT
STERIC HINDRANCE
REACTION RATE
REAKSI SN2
REAKSI SN2
NUKLEOFIL
NUKLEOFILISITAS
REACTION RATE
REAKSI SN2
REAKSI SN2
Nucleophilicity roughly parallels basicity when
comparing nucleophiles that have the same reacting atom.
Thus, OH
-
is both more basic and more nucleophilic than
acetate ion, CH3CO2
-
, which in turn is more basic and more
nucleophilic than H2O
Nucleophilicity usually increases going down a column
of the periodic table. Thus, HS
-
is more nucleophilic than
HO
-
, and the halide reactivity order is I
-
> Br
-
> Cl
Negatively charged nucleophiles are usually more
reactive than neutral ones
REAKSI SN2
LEAVING GROUP
STABILISASI MUATAN (-)
pd TRANSITION
STATE
REACTION RATE
REAKSI SN2
SOLVENT
GROUND STATE
ENERGY OF NU
POLAR PROTIC SOLVENT
(CONTAIN OH; NH)
REACTION RATE
POLAR APROTIC SOLVENT
REAKSI SN2
SOLVENT
DMSO : Dimetilsulfoksida
DMF : Dimetilformamida
HMPA : Heksametilfosforamida
REAKSI SN2
SN1
SUBSTITUSI
NUKLEOFILIK
UNIMOLEKULAR
REAKSI ORDE PERTAMA
PRODUK CAMPURAN RASEMAT
TWO STEPS
SN1
TWO STEPS
SN1
SN1
the SN1 reaction has a rate that depends only on the
alkyl halide concentration and is independent of the
nucleophil concentration. In other words, the
reaction is a first-order process; the concentration of
the nucleophile does not appear in the rate
equation.
REAKSI ORDE PERTAMA
SN1
SUBSTRAT
NUKLEOFIL
LEAVING GROUP
SOLVENT
SN1
SUBSTRAT
STABILITAS
KARBOKATION
REACTION RATE
SN1
LEAVING GROUP
Good leaving groups increase the reaction
rate by lowering the energy level of the
transition state for carbocation formation.
SN1
NUKLEOFIL
the nucleophile does not affect an SN1
reaction
SN1
SOLVENT
Solvent molecules orient around the carbocation so that the
electron rich ends of the solvent dipoles face the positive charge,
thereby lowering the energy of the ion and favoring its formation
SN vs E
Designed by TheTemplateMart.com
You might also like
- Sayre Materia Medica-2Document89 pagesSayre Materia Medica-2ven_bams5840100% (3)
- PGHU-EH-CSPDS-000103 Rev 0 - Design Loads For StructuresDocument10 pagesPGHU-EH-CSPDS-000103 Rev 0 - Design Loads For StructuresGiovanni AlfieriNo ratings yet
- Sayre Materia Medica-1Document108 pagesSayre Materia Medica-1ven_bams584075% (4)
- Build Your Own Garden Pond PDFDocument10 pagesBuild Your Own Garden Pond PDFMwagaVumbiNo ratings yet
- Sayre Materia Medica-6Document79 pagesSayre Materia Medica-6ven_bams5840100% (2)
- Sayre Materia Medica-3Document87 pagesSayre Materia Medica-3ven_bams5840No ratings yet
- An Overview of Sn1 and Sn2 ReactionsDocument35 pagesAn Overview of Sn1 and Sn2 ReactionsPedro Suyu100% (1)
- Chemistry Equilibrium WorksheetDocument5 pagesChemistry Equilibrium WorksheetMarkNo ratings yet
- Aib ZT ZR55 75 90Document138 pagesAib ZT ZR55 75 90nidnitrkl05129650% (2)
- 131 - 1.9.1.2-95MXC - UltraHardDocument4 pages131 - 1.9.1.2-95MXC - UltraHardJSH100No ratings yet
- Reaction Mechanism DDocument36 pagesReaction Mechanism Dprajaktac506No ratings yet
- 10hl.20.1 Types of Organic ReactionsDocument74 pages10hl.20.1 Types of Organic ReactionsKatarina VleugelsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10. Substitution Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocument49 pagesChapter 10. Substitution Reactions of Alkyl HalidesThanh NguyênNo ratings yet
- Organic Lecture Notes: TTTTT: TTTTTTTT TTTTTTTTTDocument13 pagesOrganic Lecture Notes: TTTTT: TTTTTTTT TTTTTTTTTSesha Sai Kumar0% (2)
- Chapter Four 221212Document24 pagesChapter Four 221212Barnabas YohannesNo ratings yet
- Concrete Society - Concrete Advice No 26 - RC Bund StructuresDocument3 pagesConcrete Society - Concrete Advice No 26 - RC Bund StructuresKarishma JuttunNo ratings yet
- Reaksi SN-1, SN-2, E-1, Dan E-2.Document64 pagesReaksi SN-1, SN-2, E-1, Dan E-2.Annik QurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halide PDFDocument29 pagesAlkyl Halide PDFSantosh Potdar100% (2)
- Introduction To Antibiotics: Mrs Natasha MahajanDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Antibiotics: Mrs Natasha Mahajannatasha jadhavNo ratings yet
- Deligate ExcelFormatDocument60 pagesDeligate ExcelFormatrashidnyou0% (2)
- W3 - Air Pollutants Emission MeasurementDocument35 pagesW3 - Air Pollutants Emission Measurementevolution95No ratings yet
- Preparation of Alkyl Halides by Nucleophilic Aliphatic Substitution NewDocument9 pagesPreparation of Alkyl Halides by Nucleophilic Aliphatic Substitution NewMunna Patel0% (1)
- Sewing ThreadsDocument27 pagesSewing ThreadsRikhil NagpalNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocument49 pagesReactions of Alkyl Halidesgsy2023-9150-52879No ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides SN1,2 and E1,2,1cbDocument45 pagesAlkyl Halides SN1,2 and E1,2,1cblorrainebarandonNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic SubstitutionDocument18 pagesNucleophilic SubstitutionShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document56 pagesChapter 3Hazimah BasriNo ratings yet
- S 1 & S 2 Reaction: Integral UniversityDocument18 pagesS 1 & S 2 Reaction: Integral UniversityAbuzar Mohammad ShaibanNo ratings yet
- Organic Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions sn1 and sn2 ReactioDocument13 pagesOrganic Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions sn1 and sn2 ReactioDebarjan DattaNo ratings yet
- WK 2-2 Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Jan 18Document54 pagesWK 2-2 Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Jan 18cerelia.dkuNo ratings yet
- Kof 2a SubstitutionDocument43 pagesKof 2a Substitutionkaharanian 17No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Alkyl Halides 2022Document66 pagesChapter 7 - Alkyl Halides 2022Hoài Nguyễn Phan VũNo ratings yet
- Year 2 - : Organic ChemistryDocument33 pagesYear 2 - : Organic ChemistryManWol JangNo ratings yet
- Hasham Anas PresentationDocument14 pagesHasham Anas PresentationirfansaeedNo ratings yet
- SN Reactions Lecture3Document21 pagesSN Reactions Lecture3Kalpa DihingiaNo ratings yet
- 10 Ak Part 3Document4 pages10 Ak Part 3Shamanth MNo ratings yet
- SN ReactionsDocument60 pagesSN Reactionsnur ainiNo ratings yet
- Organic RXN MechanismDocument24 pagesOrganic RXN MechanismNabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions: Lecture by Kalpajyoti Dihingia Department of Chemistry DHSK CollegeDocument21 pagesChemical Reactions: Lecture by Kalpajyoti Dihingia Department of Chemistry DHSK CollegeKalpa DihingiaNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides - pdf234Document37 pagesAlkyl Halides - pdf234Fakhri ElabbarNo ratings yet
- SubstitionDocument36 pagesSubstitionExcellent KhozaNo ratings yet
- Class Slides Jan 2023Document105 pagesClass Slides Jan 2023Prarabdha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and EliminationsDocument70 pagesReactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and EliminationsIrfan ShahNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 Alkylhalide-Sn eDocument59 pagesLec 4 Alkylhalide-Sn eNida Nur FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Alkylhalide ReactionsDocument36 pagesAlkylhalide ReactionsTobenna100% (1)
- Substitution & Elimination Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocument71 pagesSubstitution & Elimination Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDaniel McDermottNo ratings yet
- Chem Bio 4Document47 pagesChem Bio 4leafyNo ratings yet
- Sn2 and Sn1 Reactions: Sethuranga Skanthan.P.TDocument12 pagesSn2 and Sn1 Reactions: Sethuranga Skanthan.P.TSethuNo ratings yet
- Substitution Reactions - PMDocument64 pagesSubstitution Reactions - PMprasoon jhaNo ratings yet
- 11-Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocument56 pages11-Reactions of Alkyl HalidesnursenaNo ratings yet
- Senyawa Halogen OrganikDocument54 pagesSenyawa Halogen OrganikKarina Nurcahyani ArifahNo ratings yet
- GssDocument26 pagesGssvnikhar123100% (1)
- Chapter 7Document37 pagesChapter 7민규강No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Major Organic ReactionDocument55 pagesChapter 4 Major Organic ReactionTolera TadesseNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Major Organic ReactionsDocument63 pagesChapter Four Major Organic ReactionsdagmawiNo ratings yet
- KOF-mekanisme ReaksiDocument64 pagesKOF-mekanisme ReaksiAudry YuniarNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument112 pagesChapter Fourbahru demekeNo ratings yet
- REACTION-MECHANISM HandoutDocument3 pagesREACTION-MECHANISM HandoutAlthea Jones S. SaysayNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions PDFDocument13 pagesNucleophilic Substitution Reactions PDFBhushan Dravyakar100% (6)
- Ankyl Halogenua Phan Ung The Nucleophil Va Tach LoaiDocument103 pagesAnkyl Halogenua Phan Ung The Nucleophil Va Tach LoaiQuang Cường HoàngNo ratings yet
- KNC1063 Organic Chemistry: DR Md. Rezaur RahmanDocument19 pagesKNC1063 Organic Chemistry: DR Md. Rezaur RahmanKunashiny RamashNo ratings yet
- Art Integrated Learning Project (Ritik Kumar)Document49 pagesArt Integrated Learning Project (Ritik Kumar)abhiabhishek6073No ratings yet
- Nuceleophilic Substitution ReactionDocument7 pagesNuceleophilic Substitution ReactiondayhunterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Substitution ReactionDocument43 pagesChapter 4 Substitution ReactionNahom AmanuelNo ratings yet
- Lec 11,12 Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocument20 pagesLec 11,12 Reactions of Alkyl Halidesinushanth inuNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions (SN1, SN2) AND Elimination Reactions (E1, E2)Document11 pagesNucleophilic Substitution Reactions (SN1, SN2) AND Elimination Reactions (E1, E2)Makhdoom JahaniaNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction - Nur Aisyah ImranDocument3 pagesNucleophilic Substitution Reaction - Nur Aisyah ImranNur ImranNo ratings yet
- 01-01-2021 GOC2 English ADocument39 pages01-01-2021 GOC2 English APrabhakar BandaruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Substituion RXNDocument35 pagesChapter 4 Substituion RXNmichot feleguNo ratings yet
- SN1 and SN2 ReactionDocument10 pagesSN1 and SN2 Reactionarizza_mendozaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 9,10Document28 pagesLecture - 9,10Amierson TilendoNo ratings yet
- BijuDocument8 pagesBijuBijay SahuNo ratings yet
- Module 2.3 NGPDocument3 pagesModule 2.3 NGPIshaan ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- 1000Document1 page1000akbar_rozaaqNo ratings yet
- Abstract NKI KnoopsDocument1 pageAbstract NKI Knoopsakbar_rozaaqNo ratings yet
- 100Document1 page100akbar_rozaaqNo ratings yet
- Suharjono Farmakokinetik Metabolisme Obat-Revisi Mei 2008Document50 pagesSuharjono Farmakokinetik Metabolisme Obat-Revisi Mei 2008akbar_rozaaqNo ratings yet
- Struktur Atom Dan Ikatan - Kimor 1Document30 pagesStruktur Atom Dan Ikatan - Kimor 1akbar_rozaaqNo ratings yet
- Alkohol: Oleh: Alvan Febrian Shalas, S. Farm., AptDocument45 pagesAlkohol: Oleh: Alvan Febrian Shalas, S. Farm., Aptakbar_rozaaqNo ratings yet
- Reaksi Organik - Kimia Organik 4Document21 pagesReaksi Organik - Kimia Organik 4akbar_rozaaqNo ratings yet
- Ikatan Kovalen Polar Dan Asam Basa - Kimor 2Document29 pagesIkatan Kovalen Polar Dan Asam Basa - Kimor 2akbar_rozaaqNo ratings yet
- Sayre's Materia Medica FreeDocument84 pagesSayre's Materia Medica Freeakbar_rozaaqNo ratings yet
- Sayre's Materia Medica-5Document87 pagesSayre's Materia Medica-5Dr Rushen SinghNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatik Application PDFDocument27 pagesBioinformatik Application PDFakbar_rozaaqNo ratings yet
- Crude Distillation Unit: Atmospheric and Vacuum Crude TowersDocument5 pagesCrude Distillation Unit: Atmospheric and Vacuum Crude TowersLuz Angela Jaramillo CiprianNo ratings yet
- Certificate: Internal Teacher's SignDocument8 pagesCertificate: Internal Teacher's SignVyomNo ratings yet
- The Public's Love Affair With Geodes: Rock MineralDocument3 pagesThe Public's Love Affair With Geodes: Rock MineralSerkan KocapinarNo ratings yet
- Japan Engine CatalgoDocument40 pagesJapan Engine CatalgoKarim Sowley DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Vacuum Pump LubricantsDocument21 pagesUnderstanding Vacuum Pump LubricantsengrsurifNo ratings yet
- Dna ExtractionDocument2 pagesDna Extractionapi-358984084No ratings yet
- Landing NippleDocument4 pagesLanding NippleMohamed Abd El-MoniemNo ratings yet
- Automotive Gray Iron Castings: Standard Specification ForDocument5 pagesAutomotive Gray Iron Castings: Standard Specification ForSaravanan MNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding DPPDocument24 pagesChemical Bonding DPPKalyan ReddtNo ratings yet
- Using Reverse Osmosis For Boiler PretreatmentDocument3 pagesUsing Reverse Osmosis For Boiler Pretreatmentنيرمين احمدNo ratings yet
- Aubf ReviewerDocument8 pagesAubf ReviewerAngel Cris Alegado AguirreNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment-6 (Practice Problem) Chapter-7Document2 pagesHome Assignment-6 (Practice Problem) Chapter-7Rounak MajumdarNo ratings yet
- 0620 m23 QP 22-MinDocument14 pages0620 m23 QP 22-Minjelani17fNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes: N 2n+2 27 56 N 2n+2 42 86Document18 pagesChapter 3-Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes: N 2n+2 27 56 N 2n+2 42 86張湧浩No ratings yet
- Tappi Extrution Coating and LaminatingDocument26 pagesTappi Extrution Coating and LaminatingKhương HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument6 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersrajeshwariNo ratings yet
- Essential Molecular BiologyDocument19 pagesEssential Molecular BiologySandra JelynNo ratings yet
- Honda BayDocument16 pagesHonda BayVicente Jr. BallonoNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument19 pagesReviewerCarlos Miguel Dacaimat100% (1)
- 120131-Perforated Sheet Metal - IPRF - CD PDFDocument239 pages120131-Perforated Sheet Metal - IPRF - CD PDFMisagh100% (1)