Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 - Auditing and Assurance Services
Uploaded by
Abdalelah FrarjehOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 - Auditing and Assurance Services
Uploaded by
Abdalelah FrarjehCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 Auditing and
Assurance Services
Presentation Outline
I. The Demand for Reliale Information
II. !nderstanding Assurance Services
III. "anagement Assertions
I#. Saranes$O%le& Act of '(('
#. )ecoming a CPA
I. The Demand for Reliale
Information
A. !nderstanding a Client*s )usiness
). +nvironmental Conditions
C. Information Ris,
A. !nderstanding a Client*s
)usiness
)usiness ris, is the
ris, that an entit& -ill
fail to meet its
o.ectives.
/ailing to reach
o.ectives can
eventuall& result in
temptation to misstate
financial statements
to avoid usiness
failure.
). +nvironmental Conditions
0 Comple%it& Decisions ma,ers
are not trained to collect1 compile1
and summari2e the ,e& operating
information themselves.
0 Remoteness Investors are not
ale to personall& visit locations to
chec, on investments.
0 Time sensitivit& Decisions must
often e made on a moment*s
notice.
0
Conse3uences A drop in
investment value can -ipe out
one*s life savings.
I lost m&
savings in a
ad investment4
C. Information Ris,
Information ris, is the
proailit& that the
information circulated & a
compan& -ill e false or
misleading.
Client management has an
incentive to ma,e the
usiness appear etter than
it actuall& ma& e.
This can create a conflict of
interest et-een client
management and investors.
/inancial
Statements
II. !nderstanding Assurance
Services
A. Definition of Assurance Services
). Definition of Attestation Services
C. Definition of Auditing
D. Overvie- of /inancial Statement Auditing
+. 5raphical Representation of Assurance
Services
A. Assurance Service +lements
Assurance services are 617 independent 6'7
professional services that 687 improve the
quality of information, or its context1 697
for decision makers. Assurance services
include man& areas of information1 including
nonfinancial areas.
6See e%amples on page : of te%t7
). Definition of Attestation Services
Attestation involves an
engagement resulting in
the issuance of a report
on su.ect matter or an
assertion aout the
su.ect matter that is the
responsiilit& of another
part&.
Auditing is a specific t&pe
of attestation.
6See e%amples on p. ; of
te%t7
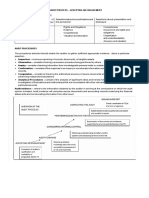
C. Definition of Auditing
6See Auditing Insight on p. < of te%t7
Auditing is a systematic process of
objectively obtaining and
evaluating evidence regarding
assertions about economic actions
and events to ascertain the degree
of correspondence between the
assertions and established criteria
and communicating the results to
interested users.
Financial Statements
(including footnotes)
GAAP
Auditors !eport"
#ther !eports
Persons who rely on
the financial reports
$
%reditors
$
&nvestors
Source: American Accounting Association %ommittee on 'asic
Auditing %oncepts. ()*+. A Statement of Basic Auditing
Concepts, American Accounting Association (Sarasota, F-).
D. Overvie- of /inancial Statement
Auditing
+. 5raphical Representation of Assurance Services
The Relationships Among Auditing1 Attestation1
and Assurance +ngagements
Assurance Services
An& Information
Attestation Services
Primarily Financial &nformation
Auditing
Financial Statements
III. "anagement Assertions
A. Presentation and Disclosure
). +%istence or Occurrence
C. Rights and Oligations
D. Completeness
+. #aluation or Allocation
A. Presentation and Disclosure
/ootnote disclosure of important
accounting policies must e relevant and
reliale.
Transactions must e classified in the
correct accounts.
Information must e transparent 6i.e.1
understandale to a reasonal&
sophisticated person7.
). +%istence or Occurrence
Assets1 liailities1 and e3uities on the
alance sheet actuall& e%ist.
+ach of the revenue and e%pense
transactions actuall& occurred.
C. Rights and Oligations
Amounts reported as assets of the
compan& represent its propert& rights.
Amounts reported as liailities represent
its oligations.
D. Completeness
All transactions1 events1 assets1 liailities1 and e3uities
that should have een recorded have een recorded.
All disclosures that should have een discussed in the
footnotes are there.
Cutoff refers to accounting for revenue1 e%pense1 and
other transactions in the proper period 6neither
postponing some recordings to the ne%t period 6i.e.1
completeness7 nor accelerating ne%t period*s
transactions into the current &ear accounts 6i.e.1
e%istence or occurrence77. The cutoff date refers to
the client*s &ear$end alance sheet date.
+. #aluation or Allocation
Determine -hether proper values have
een assigned to assets1 liailities1 and
e3uities.
+%amples include collectiilit& of
receivales1 recalculating depreciation1
otaining lo-er of cost or mar,et data1 etc.
I#. Saranes$O%le& Act of '(('
6SO=7
A. "a.or Provisions of Saranes$O%le&
). "anagement Responsiilit& !nder SO=
C. Prohiited Services to Audit Clients
A. "a.or Provisions of Saranes$O%le&
Congress passed the Saranes$O%le& Act in an attempt
to address a numer of -ea,nesses found in
corporate financial reporting in the -a,e of the recent
accounting scandals. The Act*s ma.or provisions
include>
Re3uirement of C+O?C/O certification of financial
statements 6Section 8('7
Re3uirement of auditor e%amination of compan& internal
controls
Creation of the Pulic Compan& Accounting Oversight )oard
6PCAO)7 to serve as an auditing profession @-atchdog.A
Prohiition of certain client services & firms conducting a
client*s audit.
). "anagement*s Responsiilit& !nder SO=
One of its most important provisions 6Section 8('7 states that
the ,e& compan& officials must certify the financial
statements. Certification means that the compan& C+O and
C/O must sign a statement indicating>
1. The& have read the financial statements.
'. The& are not a-are of an& false or misleading statements
6or an& ,e& omitted disclosures7.
8. The& elieve that the financial statements present an
accurate picture of the compan&*s financial condition.
Source> !.S. Congress1 Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 20021 Pu. B.
1(:$'(91 11; Stat? :9< 6'(('7.
C. Prohiited Services to Audit Clients
SO= and the PCAO) prohiit professional service firms from
providing an& of the follo-ing services to an audit client>
oo,,eeping and related services
design or implementation of financial information
s&stems
appraisal or valuation services
actuarial services
internal audit outsourcing
management or human resources services
investment or ro,er?dealer services
legal and e%pert services 6unrelated to the audit7
Professional service firms ma& provide client ta% services
6-ith some restrictions7 and other non$prohiited services to
audit clients if the compan&*s audit committee has approved
them in advance.
SO= prohiits professional service firms from performing an&
client services -here auditors ma& find themselves ma,ing
management decisions or auditing their o-n firm*s -or,.
#. )ecoming a
A. +ducation
). +%amination
C. +%perience
Cote that successful candidates actuall& receive a CPA certificate
from their State )oard of Accountanc&. Reciprocal
CPA certificates for other states are also possile.
A. +ducation
"ost states re3uire 1<(
semester hours of college
education to sit for the
e%am.
Continuing professional
education of 1'( contact
hours 6not college semester
or 3uarter hours7 over three
&ear reporting periods -ith
no less than '( hours in an&
one &ear is a common
re3uirement in most states.
). +%amination
The AICPA )oard of +%aminers administers the
!niform CPA +%am as a computer$ased
e%amination in four parts
1. Auditing and attestationD9.< hrs
'. /inancial accounting and reportingD9 hrs
8. RegulationD8 hrs.
9. )usiness environmentD'.< hrs
Consists of multiple$choice testlets 6'9$8( 3uestions
each7 and simulation prolems -here students
electronicall& research a solution to a prolem.
Revealing e%am material can result in certifications
eing revo,ed.
Testing is on demand -ith :<E considered a
passing score.
C. +%perience
Although not a re3uirement
to sit for the CPA e%am1
accounting e%perience
supervised & a competent
accountant is re3uired to
ecome certified.
5enerall& ' &ears for
persons -ith a achelors
degree and 1 &ear for
those -ith a masters.
Some states re3uire the
e%perience to e in pulic
accounting.
Summar&
Audit process considers usiness ris,1
information ris,.
+nvironmental factors result in need for audits.
!nderstanding assurance1 attestation1 and
auditing
The effect of Saranes$O%le& on the audit
process.
CPA re3uirements include education1
e%amination1 and e%perience.
You might also like
- Chapter 1 - Auditing and Assurance ServicesDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Auditing and Assurance ServicesBilal KhalidNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance ServicesDocument27 pagesAuditing and Assurance ServicesLily DaniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Auditing and Assurance ServicesDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Auditing and Assurance ServicesShiMin WongNo ratings yet
- CH1 The Demand For AuditDocument25 pagesCH1 The Demand For Auditsamer1423123No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document16 pagesTutorial 1youssefasaadNo ratings yet
- Auditor Responsibilities After Issuing ReportsDocument45 pagesAuditor Responsibilities After Issuing Reportsathirah jamaludinNo ratings yet
- WK 1 Introduction To Audit ProfessionDocument56 pagesWK 1 Introduction To Audit ProfessionYalliniNo ratings yet
- Assurance, Attestation, AuditDocument14 pagesAssurance, Attestation, AuditNicko AbejeroNo ratings yet
- Audit Practice and Assurance Services - A1.4 PDFDocument94 pagesAudit Practice and Assurance Services - A1.4 PDFFRANCOIS NKUNDIMANANo ratings yet
- Auditing I CH I-3Document64 pagesAuditing I CH I-3mercyteshite5No ratings yet
- 110 Test Bank For Auditing and Assurance Services 5th Edition LouwersDocument28 pages110 Test Bank For Auditing and Assurance Services 5th Edition LouwersEbook freeNo ratings yet
- Acca P6 QuestionDocument8 pagesAcca P6 QuestionChuaJieLingNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument85 pagesPDFlikesNo ratings yet
- AT-03 (Introduction To Auditing)Document4 pagesAT-03 (Introduction To Auditing)Soremn PotatoheadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial Statement AuditDocument63 pagesIntroduction To Financial Statement AuditRica RegorisNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Demand For AuditDocument30 pagesUnit 2 Demand For AuditKaycia HyltonNo ratings yet
- Auditing Teaching MaterialDocument49 pagesAuditing Teaching MaterialGetachew JoriyeNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Audit ExamDocument22 pagesComprehensive Audit ExamADIN IHTISYAMUDDINNo ratings yet
- 1-5 To Do An Audit, There Must Be Information in A Verifiable Form and SomeDocument18 pages1-5 To Do An Audit, There Must Be Information in A Verifiable Form and Somejulivio mewohNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Financial Statement Audit ObjectivesDocument18 pagesIntroduction to Financial Statement Audit ObjectiveskripsNo ratings yet
- Copy1-ACC 421 NOTESDocument18 pagesCopy1-ACC 421 NOTESOkechukwu LovedayNo ratings yet
- Auditing and The Public Accounting ProfessionDocument9 pagesAuditing and The Public Accounting ProfessionIkke Mulyani100% (1)
- Chapter 1-5Document53 pagesChapter 1-5John lordrie HerreraNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory Answer Key 6Document3 pagesAuditing Theory Answer Key 6Jasper GicaNo ratings yet
- Differentiate Assurance From Non-Assurance EngagementsDocument3 pagesDifferentiate Assurance From Non-Assurance EngagementsSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Auditor Interview QuestionsDocument34 pagesAuditor Interview QuestionsZAKA ULLAHNo ratings yet
- Group 4 The Audit ProcessDocument31 pagesGroup 4 The Audit ProcessYonica Salonga De BelenNo ratings yet
- Audit Magical DocumentDocument89 pagesAudit Magical DocumentChip choiNo ratings yet
- 1 AuditDocument9 pages1 Auditahmed sheblNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in AuditingDocument29 pagesBasic Concepts in Auditinganon_672065362100% (1)
- Chapter I-The Nature of Auditing: Information CriteriaDocument10 pagesChapter I-The Nature of Auditing: Information CriteriaAngel TumamaoNo ratings yet
- IM-01 Overview of Audit and Other Assurance ServicesDocument7 pagesIM-01 Overview of Audit and Other Assurance Servicesharley_quinn11No ratings yet
- Auditing and AttestationDocument45 pagesAuditing and Attestationmira01No ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Overview To AuditingDocument43 pagesChapter 1-Overview To Auditingselman AregaNo ratings yet
- Auditing Chapter 1Document7 pagesAuditing Chapter 1Sigei LeonardNo ratings yet
- Activity Worksheet 001Document4 pagesActivity Worksheet 001Pearl Isabelle SudarioNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - The Purpose and Nature of AuditingDocument7 pagesTopic 1 - The Purpose and Nature of AuditingSandile Henry DlaminiNo ratings yet
- Complete Revision Notes Auditing 1Document90 pagesComplete Revision Notes Auditing 1Marwin AceNo ratings yet
- Auditing: Integral To The EconomyDocument32 pagesAuditing: Integral To The Economybaburam100% (2)
- Accepting An EngagementDocument4 pagesAccepting An EngagementRalph Ean BrazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - SOLUTIONSDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - SOLUTIONSGeorge GregoriouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 習題解答Document10 pagesChapter 2 習題解答lo0302No ratings yet
- Roque CPA Reviewer Auditing ch1 Final PDFDocument66 pagesRoque CPA Reviewer Auditing ch1 Final PDFSherene Faith Carampatan100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document27 pagesChapter 1julita08No ratings yet
- Auditing Standards and Client AcceptanceDocument27 pagesAuditing Standards and Client AcceptanceSarim Ahmad100% (1)
- OUM Business School Accounting Information Systems IDocument12 pagesOUM Business School Accounting Information Systems IKen KiongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - The Audit Process - Accepting An EngagementDocument2 pagesChapter 4 - The Audit Process - Accepting An EngagementMichelleNo ratings yet
- IPFM Chapter 1Document20 pagesIPFM Chapter 1Yitera SisayNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Q ADocument5 pagesTutorial 1 Q AKelvin LeongNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument8 pagesIntroductionIsaac MbaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Part I: Introduction To Audit and Assurance ServicesDocument65 pagesLecture 1-Part I: Introduction To Audit and Assurance ServicesShueh Yi LimNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Chapter 1 The Demand For Auditing and Assurance ServicesDocument23 pagesGroup 1 Chapter 1 The Demand For Auditing and Assurance ServicestristahmncdldyNo ratings yet
- Nature, Objective and Scope of Audit (NOSADocument8 pagesNature, Objective and Scope of Audit (NOSAAnkur KunduNo ratings yet
- Audit and Assurance f8.Document96 pagesAudit and Assurance f8.ALEKSBANDANo ratings yet
- AUDITINGDocument20 pagesAUDITINGAngelieNo ratings yet
- General Notes 1Document6 pagesGeneral Notes 1Sherlock HolmesNo ratings yet
- Audit UNIT 1Document9 pagesAudit UNIT 1Nigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- AuditingDocument40 pagesAuditingIrina IordacheNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1THE DEMAND FOR AUDIT AND OTHER ASSURANCE SERVICESDocument46 pagesChapter - 1THE DEMAND FOR AUDIT AND OTHER ASSURANCE SERVICESDina AlfawalNo ratings yet
- Awareness About Cash Less Economy Among Students: K. Girija & M. NandhiniDocument8 pagesAwareness About Cash Less Economy Among Students: K. Girija & M. NandhiniTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Options Open Interest Analysis SimplifiedDocument15 pagesOptions Open Interest Analysis SimplifiedNaveenNo ratings yet
- VATable TransactionsDocument2 pagesVATable TransactionsAngelo D. AventuradoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Money Laundering in KenyaDocument92 pagesChapter 4 - Money Laundering in KenyaFrancis Njihia KaburuNo ratings yet
- Canadian Securities Institute Learning Catalogue: Csi Learning Solutions GuideDocument11 pagesCanadian Securities Institute Learning Catalogue: Csi Learning Solutions Guidemuhammadanasmustafa0% (1)
- TCQTTTDocument32 pagesTCQTTTdohongvinh40No ratings yet
- Accounting-Income Statement MCQDocument19 pagesAccounting-Income Statement MCQHaniyaAngel0% (2)
- Amended 2255 Motion 22-26Document160 pagesAmended 2255 Motion 22-26Samples Ames PLLCNo ratings yet
- Benefit Illustration for HDFC Life Sanchay Fixed Maturity PlanDocument3 pagesBenefit Illustration for HDFC Life Sanchay Fixed Maturity PlanNisha GoyalNo ratings yet
- Deutsche Bank QP1 InternshipsDocument20 pagesDeutsche Bank QP1 Internshipszubezub100% (1)
- Company Profile: PT. Indofood Sukses Makmur TBKDocument7 pagesCompany Profile: PT. Indofood Sukses Makmur TBKAtikaFebriyuliaNo ratings yet
- Wise & Co., Inc. v. Meer (June 30, 1947)Document13 pagesWise & Co., Inc. v. Meer (June 30, 1947)Crizza RondinaNo ratings yet
- Deed of Partition Between Two Co owners-Deeds-Partition-1669Document2 pagesDeed of Partition Between Two Co owners-Deeds-Partition-1669Atoy SantosNo ratings yet
- Securitization Is IllegalDocument34 pagesSecuritization Is IllegalCharlton ButlerNo ratings yet
- AICPADocument5 pagesAICPAMikaela SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Office Russia Off 3q12Document1 pageOffice Russia Off 3q12nikky7771No ratings yet
- CFAB - Accounting - QB - Chapter 10Document14 pagesCFAB - Accounting - QB - Chapter 10Huy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Real Estate Broker License RequirementsDocument42 pagesReal Estate Broker License RequirementsYamada KunNo ratings yet
- Pakistan-Regional Economic Integration Activity (PREIA)Document8 pagesPakistan-Regional Economic Integration Activity (PREIA)Umer MinhasNo ratings yet
- Aftermarket Magazine PDFDocument68 pagesAftermarket Magazine PDFEvgénios SangmorteyNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument8 pagesCost Accountingtushar sundriyalNo ratings yet
- AES Account Listing April 2016Document9 pagesAES Account Listing April 2016Mozam MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Ar2018 EnglishDocument435 pagesAr2018 Englishgl lugaNo ratings yet
- BBA Syllabus (Revised - 2010) - KUDDocument65 pagesBBA Syllabus (Revised - 2010) - KUDMALLIKARJUN100% (2)
- Guinea Mining Code 2011 - Translation - EngDocument44 pagesGuinea Mining Code 2011 - Translation - EngChris JasabeNo ratings yet
- A Study On Difference in Gender Attitude in Investment Decision Making in IndiaDocument17 pagesA Study On Difference in Gender Attitude in Investment Decision Making in IndiaAkit yadavNo ratings yet
- British Airways Report and Accounts For The Period Ending 31 December 2012Document88 pagesBritish Airways Report and Accounts For The Period Ending 31 December 2012A0938746599273927No ratings yet
- US Internal Revenue Service: p1582Document27 pagesUS Internal Revenue Service: p1582IRS100% (9)
- Cyborg FinanceDocument57 pagesCyborg FinancekurtnewmanNo ratings yet
- Upstream - Petroleum Economic AspectsDocument5 pagesUpstream - Petroleum Economic AspectsediwskiNo ratings yet