Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Decision Making: The Elements of Decision
Uploaded by
sidrabatool0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views11 pagesThe document discusses the key elements of decision making:
1. The decision body - the individual or group responsible for making the decision. This includes what options and information they consider, and how each option is evaluated.
2. The decision options - the possible courses of action being considered. Decisions usually involve at least two options: taking an action or doing nothing.
3. The uncontrollable factors - aspects that can influence the outcome but cannot be controlled, like demand or costs. These should be identified and their possible levels predicted to help evaluate consequences.
4. The consequences of each option - the expected operational results, how outcomes are measured or interpreted, and how worthwhile the different outcomes may be
Original Description:
Original Title
DM - Presentation.pptx
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the key elements of decision making:
1. The decision body - the individual or group responsible for making the decision. This includes what options and information they consider, and how each option is evaluated.
2. The decision options - the possible courses of action being considered. Decisions usually involve at least two options: taking an action or doing nothing.
3. The uncontrollable factors - aspects that can influence the outcome but cannot be controlled, like demand or costs. These should be identified and their possible levels predicted to help evaluate consequences.
4. The consequences of each option - the expected operational results, how outcomes are measured or interpreted, and how worthwhile the different outcomes may be
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views11 pagesDecision Making: The Elements of Decision
Uploaded by
sidrabatoolThe document discusses the key elements of decision making:
1. The decision body - the individual or group responsible for making the decision. This includes what options and information they consider, and how each option is evaluated.
2. The decision options - the possible courses of action being considered. Decisions usually involve at least two options: taking an action or doing nothing.
3. The uncontrollable factors - aspects that can influence the outcome but cannot be controlled, like demand or costs. These should be identified and their possible levels predicted to help evaluate consequences.
4. The consequences of each option - the expected operational results, how outcomes are measured or interpreted, and how worthwhile the different outcomes may be
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Decision Making
Presentation By: Kashif Ahmad
The Elements of Decision
To Understand Fully Decision of Management Four Key elements in a decision are: 1. 2. 3. 4. The Decision Body The Decision Options The Uncontrollable Factors The Consequences of Each Options
"Advice to Youth," by Mark Twain (1882): "Always obey your parents, when they are present. This is the best policy in the long run, because if you dont, they will make you. Most parents think they know better than you do, and you can generally make more by humoring that superstition than you can by acting on your own better judgment."
1. The Decision Body
Individual/ Individuals who make decision Single Decision Maker or Multiple Decision Makers-Decision Body Important point Very few individual Decision Makers (Owners) In other scenario the Decision Body is most important element in decision Decision Body can control 1. 2. 3. What Options that are to be considered? Which Information that is relevant? How each option is evaluated?
2. The Decision Options
Alternate courses of actions for decision body to select Single Option-No choice therefore no decision Multiple Options- from two to infinity Decision has two courses 1. Take a course of Action 2. Do Nothing-Yes or No Example from Book How much grit should we buy this winters road gritting? Sensible upper limit or Sensible lower limit Some decisions have options which are obvious when the decision is defined Should we subscribe to market information service? Mintzberg classify decision options in following ways. A-Given-Fully developed at the start of the decision B-Found Ready Made-Fully developed in the environment of the decision and discovered during the decision process C-Custom Made-developed especially for the decision in question D-Modified-ready made options with some customized features
3. The Uncontrollable Factors
Parts of decision that can influence final outcome but cannot be controlled by decision body Example: Based on the product demand We cannot control the level of demand for a product directly How much production capacity be allocated to a new product 1. 2. One uncontrollable Factor Multiple uncontrollable Factors
What is the total demand of raw material cost?
3. The Uncontrollable Factors
When dealing with uncontrollable factors within a decision it is useful to follow three steps: 1. Identify the factors that influence final consequences of a decision Example: The major uncontrollable factors are How much is the demand there for a product and raw material cost? 2. Identify levels which each uncontrollable factors could take Example The level of demand will be between 5000 and 7000 units a year or between 7000 and 9000 units a year. The raw material cost is between $25 and $30 per unit 3. Attempt to predict the likelihood of these levels occurring for each of the uncontrollable factors Example: Probability of demand being between 5000 and 7000 unit is 50%. In Production capacity decision sequence might Identify the factors. For example: The major uncontrollable factors are 1) The level of the demand for the product 2) The raw material cost of the product
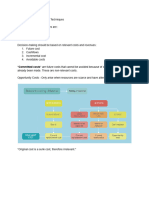
3. The Consequences of Each Option
For each combination of a decision option and the state of nature there is a consequence. Three types of Consequences a) Primary Consequence Straight forward statements of the operational results of an event Example: Annual demand: 8000 Units, Plant capacity: 7000 Raw material Cost &24 b) Surrogate-substitute or Replacement Interpretation of the event expressed in whatever measure we are using to describe the outcomes Example: Profit & 50,000 backlog order is high and increasing c) Evaluated Consequences Which are a measure of the worth or utility of a the outcome Example: Company is getting revenue needed badly worried about the increasing backlog what are our possible trade offs to reduce backlog.
Managers and Decision Making
3. The Decision Tree
You might also like
- Achieving a Safe and Reliable Product: A Guide to Liability PreventionFrom EverandAchieving a Safe and Reliable Product: A Guide to Liability PreventionNo ratings yet
- Cost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsFrom EverandCost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Decision Making EnvironmentDocument8 pagesDecision Making EnvironmentJessie Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- RelevantCosts F07Document16 pagesRelevantCosts F07aymanaym0% (1)
- Unit 3 Decision MakingDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Decision MakingShellian CunninghamNo ratings yet
- Assignment Econ EntrepDocument3 pagesAssignment Econ EntrepEJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Module 7 Decision MakingDocument18 pagesUnit 4 Module 7 Decision MakingJem100% (1)
- Chapter Two Relevant Information and Decision Making: 5.1 The Role of Accounting in Special DecisionsDocument11 pagesChapter Two Relevant Information and Decision Making: 5.1 The Role of Accounting in Special DecisionsshimelisNo ratings yet
- Decision Theory RevisedDocument41 pagesDecision Theory RevisedBryan AguilarNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Basics of Managerial Ecnomics LESSON 5-Tools and Technique of Decision MakingDocument5 pagesUnit - 1 Basics of Managerial Ecnomics LESSON 5-Tools and Technique of Decision Makingumeshk1No ratings yet
- Risk Based Decision MakingDocument5 pagesRisk Based Decision MakingAhmed ShahNo ratings yet
- Decision Making .PPT 4th Sem McomDocument16 pagesDecision Making .PPT 4th Sem Mcomnousheen rehmanNo ratings yet
- Sample Decision Analysis 1Document18 pagesSample Decision Analysis 1rajeshviswaNo ratings yet
- Decision TheoryDocument34 pagesDecision Theoryhsrinivas_7No ratings yet
- Be ImpDocument54 pagesBe ImpMridula NairNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document13 pagesChapter 2MarvinNo ratings yet
- Decision Making: By: Lloyd, Klynt, Arjun, and LemDocument32 pagesDecision Making: By: Lloyd, Klynt, Arjun, and LemgeorgeNo ratings yet
- Criteria For Decision AnalysisDocument27 pagesCriteria For Decision AnalysisPhilemoni AngaliNo ratings yet
- Management For Engineers - 3Document33 pagesManagement For Engineers - 3alant k josephNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SupplementshortDocument9 pagesChapter 2 SupplementshortSaloni ThakurNo ratings yet
- MISChapter 2Document33 pagesMISChapter 2pallaviingaleNo ratings yet
- Paul Schneiderman, PH.D., Professor of Finance & Economics, Southern New Hampshire University ©2008 South-WesternDocument33 pagesPaul Schneiderman, PH.D., Professor of Finance & Economics, Southern New Hampshire University ©2008 South-WesternEmily TanNo ratings yet
- CH - 5 and 6 Relevant Information and Decision MakingDocument9 pagesCH - 5 and 6 Relevant Information and Decision Makingtamirat tadeseNo ratings yet
- 4 Book Managerial EconomicsDocument44 pages4 Book Managerial EconomicsFilomena AndjambaNo ratings yet
- Cost Ii Chapter 5Document13 pagesCost Ii Chapter 5Biniyam TsegayeNo ratings yet
- 2122 2 C2 MGT PPT Week 3Document50 pages2122 2 C2 MGT PPT Week 3Dessa GuditoNo ratings yet
- Demand Forecasting Demand ForecastingDocument21 pagesDemand Forecasting Demand Forecastingsheel_shaliniNo ratings yet
- Decision AnalysisDocument13 pagesDecision AnalysisRenan RaquipoNo ratings yet
- Decide ModelDocument15 pagesDecide ModelAman BhalotiaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet For Evaluating Alternatives: Use This Tool To Help You Think Through Your AlternativesDocument2 pagesWorksheet For Evaluating Alternatives: Use This Tool To Help You Think Through Your AlternativesrameelNo ratings yet
- 1) Comparison Between MIS and DSSDocument3 pages1) Comparison Between MIS and DSSAbhisek SarkarNo ratings yet
- SBL NotesDocument8 pagesSBL NotesAdnan MalikNo ratings yet
- Appendix A Decision TreeDocument17 pagesAppendix A Decision TreefundeepNo ratings yet
- Decision Making - BlablaDocument46 pagesDecision Making - BlablaNortom SilencerNo ratings yet
- Section B, C AND E NotesDocument29 pagesSection B, C AND E NotesCorrinaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making ProcessDocument11 pagesDecision Making ProcessLakshayNo ratings yet
- Managerial EcnomiccsDocument7 pagesManagerial EcnomiccsEzam ShahNo ratings yet
- Make or BuyDocument3 pagesMake or BuyShreyashi PalNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Market ForcesDocument73 pagesModule 3 - Market ForcesShamanth GowdaNo ratings yet
- Computerized Decision SupportDocument15 pagesComputerized Decision SupportSangamesh balakundiNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Making DecisionsDocument46 pagesCH 2 Making Decisionsdawood zaheerNo ratings yet
- BBA SEM-V Herbert Simon Model of Decision Makeing Process by Dr. Rakesh RanjanDocument7 pagesBBA SEM-V Herbert Simon Model of Decision Makeing Process by Dr. Rakesh RanjanSunny AnandNo ratings yet
- Decision Theory and TreeDocument50 pagesDecision Theory and TreeKrislyn Ann Austria AldeNo ratings yet
- Chapter V: Relevant Information and Decision MakingDocument37 pagesChapter V: Relevant Information and Decision MakingBereket DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Unit III FinalDocument37 pagesUnit III FinalAccurate Health Care CenterNo ratings yet
- 3decision MakingDocument18 pages3decision MakingJade Carlo AntonioNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 (Managerial Decision Making)Document22 pagesUnit - 3 (Managerial Decision Making)Mangesh DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument49 pagesStrategic ManagementSameh_Abd_AzizNo ratings yet
- IMPROVED Chapter 5 ModuleDocument16 pagesIMPROVED Chapter 5 ModuleAbdu MohammedNo ratings yet
- AMA Lecture 5Document81 pagesAMA Lecture 5Mohammed FouadNo ratings yet
- BAC 201 - MGT ACC Select TopicsDocument43 pagesBAC 201 - MGT ACC Select TopicsRebeccah NdungiNo ratings yet
- Simons 3 Stage ModelDocument6 pagesSimons 3 Stage Modelatulshhh100% (4)
- Arambala Decision MakingDocument28 pagesArambala Decision MakingKathleen Tatierra ArambalaNo ratings yet
- Lecturer-16 - Assessment of Economic Viability, Decision Making, Expected CostsDocument26 pagesLecturer-16 - Assessment of Economic Viability, Decision Making, Expected Costsaakash srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Short-Run Decision Making: Relevant CostingDocument17 pagesShort-Run Decision Making: Relevant CostingManan SuchakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Decision MakingDocument41 pagesChapter 3 Decision Makingarooj100% (1)
- UNIT 2 Decision AnalysisDocument66 pagesUNIT 2 Decision AnalysisBrennan BarnettNo ratings yet
- IIBM Case Study AnswersDocument98 pagesIIBM Case Study AnswersAravind 9901366442 - 990278722422% (9)
- Socsci2 Lesson 3 (Akmad)Document5 pagesSocsci2 Lesson 3 (Akmad)Alimansor M. DarpingNo ratings yet
- Book On AutismDocument1 pageBook On AutismAbd ALRahmanNo ratings yet
- Focus SystemDocument10 pagesFocus SystemHarthwell CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Most Significant Change (MSC) : Tools For Knowledge and LearningDocument3 pagesMost Significant Change (MSC) : Tools For Knowledge and Learninginayat1No ratings yet
- Table of Specification For Applied Social ScienceDocument3 pagesTable of Specification For Applied Social ScienceMark Nel Venus67% (3)
- Ten Commandments For Good Language LearningDocument4 pagesTen Commandments For Good Language Learningapi-25885984No ratings yet
- Parent Effectiveness Session: Virtual Meeting Via Google MeetDocument17 pagesParent Effectiveness Session: Virtual Meeting Via Google MeetCatherine SanchezNo ratings yet
- 5e Lesson Plan Ideas 2Document2 pages5e Lesson Plan Ideas 2api-328238549100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan V LunaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan V LunaAnya MayNo ratings yet
- Q1. What Should Sunita Advise Anuj's Boss On How To Counsel Him ?Document4 pagesQ1. What Should Sunita Advise Anuj's Boss On How To Counsel Him ?zoeb_eisa2002No ratings yet
- Tool 7-Fundamentals of Monitoring and EvaluationDocument12 pagesTool 7-Fundamentals of Monitoring and EvaluationRo BinNo ratings yet
- HUMA1000-L3 Lecture+1 Week+1Document30 pagesHUMA1000-L3 Lecture+1 Week+1c19911116No ratings yet
- Revision Test IME I PREZIMEDocument2 pagesRevision Test IME I PREZIMESanja DžaltoNo ratings yet
- MORRNAHDocument5 pagesMORRNAHvictorphh8567% (3)
- Experiment No: 6 Date: 09/10/2021 Experiment Name: Comprehensive Interest ScheduleDocument12 pagesExperiment No: 6 Date: 09/10/2021 Experiment Name: Comprehensive Interest ScheduleAiswarya Venkataramanan100% (2)
- OCS FrameworkDocument23 pagesOCS FrameworkmreuanwilsonNo ratings yet
- Focus & Concentration: Accomplish More in Less Time With ThinkingDocument20 pagesFocus & Concentration: Accomplish More in Less Time With ThinkingJim McLaughlinNo ratings yet
- Xie, Et Al (2016) - Linking Calling and Engagement, Role of Career AdaptabilityDocument9 pagesXie, Et Al (2016) - Linking Calling and Engagement, Role of Career AdaptabilitywidyaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Online LET ReviewerDocument8 pages2017 Online LET ReviewerJules Marco100% (1)
- Practical Research 2 Unit 1: Nature of Inquiry and Research: Pre-Test QuestionsDocument3 pagesPractical Research 2 Unit 1: Nature of Inquiry and Research: Pre-Test QuestionsChampii Pups100% (2)
- October 24 - Gestalt PsychologyDocument23 pagesOctober 24 - Gestalt PsychologyEdgar Miralles Inales ManriquezNo ratings yet
- Course Guide Introduction To Psychology: Rizal Technological UniversityDocument5 pagesCourse Guide Introduction To Psychology: Rizal Technological UniversityJonathan PoloNo ratings yet
- JA of Janice Psychologist DraftDocument11 pagesJA of Janice Psychologist DraftcaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Stage 6: Postgroup Issues-Evaluation and Follow-UpDocument4 pagesStage 6: Postgroup Issues-Evaluation and Follow-Upadi mawaridzNo ratings yet
- Desicion Making SkillsDocument4 pagesDesicion Making SkillskurutalaNo ratings yet
- 8807 - H1GP - Analysis of Compre Passages and AQ by SchoolDocument2 pages8807 - H1GP - Analysis of Compre Passages and AQ by SchoolYap Way Shen RussellNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - CommunicationDocument58 pagesModule 3 - CommunicationMishal UbaidullahNo ratings yet
- HistoryofreadingDocument10 pagesHistoryofreadingapi-305248498No ratings yet
- Tetralemma - A 3,000-Year-Old Method For 21st Century Decisions - LinkedInDocument6 pagesTetralemma - A 3,000-Year-Old Method For 21st Century Decisions - LinkedInmona_mi8202No ratings yet
- Foundations of Problem-Based Learning: The Society For Research Into Higher EducationDocument214 pagesFoundations of Problem-Based Learning: The Society For Research Into Higher EducationsuhailNo ratings yet