Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1291
Uploaded by
Waqas JavedCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1291
Uploaded by
Waqas JavedCopyright:
Available Formats
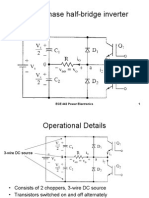
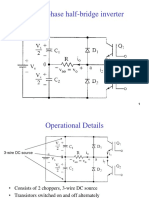
Single-phase half-bridge inverter
Operational Details
Consists of 2 choppers, 3-wire DC source
Transistors switched on and off alternately
Need to isolate the gate signal for Q
1
(upper device)
Each provides opposite polarity of V
s
/2 across the load
3-wire DC source
Q
1
on, Q
2
off, v
o
= V
s
/2
Peak Reverse Voltage of Q
2
= V
s
Q
1
off, Q
2
on, v
o
= -V
s
/2
Waveforms with resistive load
Look at the output voltage
1
2
2 2
0
2
4 2
o
T
s s
o
o
V V
V dt
T
| |
|
= =
|
|
\ .
}
rms value of the output voltage, V
o
Fourier Series of the instantaneous output
voltage
( )
1
0
0
1,3,5,..
cos( ) sin( )
2
, 0
1
sin( ) ( ) sin( ) ( )
2 2
2
1, 3, 5,...
2
sin( )
o
o n n
n
o n
s s
n
s
n
s
o
n
a
v a n t b n t
a a
V V
b n t d t n t d t
V
b n
n
V
v n t
n
t
t
e e
e e e e
t
t
e
t
=
= + +
=
(
= +
(
= =
=
} }
rms value of the fundamental component
1,3,5,..
1
1
2
sin
2 1
2
0.45
s
o
n
s
o
o s
V
v n t
n
V
V
V V
e
t
t
=
=
=
=
When the load is highly inductive
Turn off Q
1
at t = T
o
/2
Current falls to 0 via D
2
, L, V
s
/2 lower
+
V
s
/2
-
+
V
s
/2
-
Turn off Q
2
at t = T
o
Current falls to 0 via D
1
, L, V
s
/2 upper
+
V
s
/2
-
+
V
s
/2
-
Load Current for a highly inductive load
Transistors are only switched on for a quarter-cycle, or 90
Fourier Series of the output current for an
RL load
2 2
1,3,5,...
1
2
sin( )
( )
tan ( )
o o s
o n
n
n
v v V
i n t
Z R jn L
n R n L
n L
R
e u
e
t e
e
u
= = =
+
+
=
Fundamental Output Power
In most cases, the useful power
2
1 1 1 1 1
2
1
2 2
cos
2
2 ( )
o o o o
s
o
P V I I R
V
P R
R L
u
t e
= =
(
= (
+ (
DC Supply Current
If the inverter is lossless, average power
absorbed by the load equals the average
power supplied by the dc source.
For an inductive load, the current is
approximately sinusoidal and the fundamental
component of the output voltage supplies the
power to the load. Also, the dc supply voltage
remains essentially at V
s
.
0 0
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
T T
s s o o
v t i t dt v t i t dt =
} }
1 1
0 0
1
1
1
( ) 2 sin( ) 2 sin( )
cos( )
T T
s o o s
s
o
s o
s
i t dt V t I t dt I
V
V
I I
V
e e u
u
= =
=
} }
DC Supply Current (continued)
Performance Parameters
Harmonic factor of the nth harmonic (HF
n
)
1
on
n
o
V
HF
V
=
for n>1
V
on
= rms value of the nth harmonic component
V
01
= rms value of the fundamental component
Performance Parameters (continued)
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
Measures the closeness in shape between a
waveform and its fundamental component
1
2
2
2,3,...
1
1
( )
on
n
o
THD V
V
=
=
Performance Parameters (continued)
Distortion Factor (DF)
Indicates the amount of HD that remains in a
particular waveform after the harmonics have
been subjected to second-order attenuation.
1
2
2
2
2,3,...
1
2
1
1
on
n
o
on
n
o
V
DF
V n
V
DF
V n
=
(
| |
=
(
|
\ .
(
=
for n>1
Performance Parameters (continued)
Lowest order harmonic (LOH)
The harmonic component whose
frequency is closest to the fundamental,
and its amplitude is greater than or equal
to 3% of the amplitude of the fundamental
component.
Single-phase full-bridge inverter
Operational Details
Consists of 4 choppers and a 3-wire DC source
Q
1
-Q
2
and Q
3
-Q
4
switched on and off alternately
Need to isolate the gate signal for Q
1
and Q
3
(upper)
Each pair provide opposite polarity of V
s
across the load
Q
1
-Q
2
on, Q
3
-Q
4
off, v
o
= V
s
+ V
s
-
Q
3
-Q
4
on, Q
1
-Q
2
off, v
o
= -V
s
- V
s
+
When the load is highly inductive
Turn Q
1
-Q
2
off Q
3
-Q
4
off
Turn Q
3
-Q
4
off Q
1
-Q
2
off
Load current for a highly inductive load
Example 6.3 MultiSim7
Q1
1 V 0 V
Q2
1 V 0 V
Q3
1 V 0 V
Q4
1 V 0 V
D1
DIODE_VIRTUAL
D2
DIODE_VIRTUAL
D3
DIODE_VIRTUAL
D4
DIODE_VIRTUAL
R
10 Ohm
L
31.5mH
C
112uF
XFG1
C1
1000uF
C2
1000uF
Example 6.3 using the scope
Vs
220 V
Q1
1 V 0 V
Q2
1 V 0 V
Q3
1 V 0 V
Q4
1 V 0 V
D1
DIODE_VIRTUAL
D2
DIODE_VIRTUAL
D3
DIODE_VIRTUAL
D4
DIODE_VIRTUAL
R
9 Ohm
L
31.5mH
C
112uF
XFG1
C1
1000uF
C2
1000uF
XSC1
A B
G
T
Rs
1 Ohm
You might also like
- Single-phase half-bridge inverter overviewDocument29 pagesSingle-phase half-bridge inverter overviewSwati MishraNo ratings yet
- Single-phase half-bridge inverter analysisDocument29 pagesSingle-phase half-bridge inverter analysisSyed Ejaz Hussain AbidiNo ratings yet
- CH4Document55 pagesCH4Mohamad SyazwanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 InvertersDocument86 pagesUnit 4 InvertersHaritha RkNo ratings yet
- BooksDocument30 pagesBooksHabib IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document23 pagesUnit 3Prema ElizabethNo ratings yet
- L3. Single Phase Ac Voltage ControllersDocument68 pagesL3. Single Phase Ac Voltage ControllersSourabh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Line or Naturally Commutated ConvertersDocument32 pagesLine or Naturally Commutated ConvertersMichael Adu-boahenNo ratings yet
- Chopper Basic PDFDocument12 pagesChopper Basic PDFSoumya DuttaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Converters (Half Controlled)Document52 pagesUnit 2 Converters (Half Controlled)Tenzin JamtshoNo ratings yet
- Lec 9Document27 pagesLec 9ahmed ragabNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2012-13 CP0991 03-Aug-2012 RM01Document4 pagesFALLSEM2012-13 CP0991 03-Aug-2012 RM01Ankit BhattNo ratings yet
- AC Voltage Controller Classification and Control StrategiesDocument6 pagesAC Voltage Controller Classification and Control StrategiesTuhin ShahNo ratings yet
- Hafta1.compressedDocument28 pagesHafta1.compressedSersio BordiosNo ratings yet
- Single Phase InverterDocument29 pagesSingle Phase InverterEla ResearchNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 1-2015bjrDocument80 pagesPower Electronics 1-2015bjrNurAdiFirawanNo ratings yet
- Dual ConverterDocument16 pagesDual ConverterUdayakumar VengatesanNo ratings yet
- 5 - AC-AC Converters (Compatibility Mode)Document32 pages5 - AC-AC Converters (Compatibility Mode)OmkarNo ratings yet
- AC to AC Converter Chapter on Thyristors and Control MethodsDocument25 pagesAC to AC Converter Chapter on Thyristors and Control Methodst1m0thyNo ratings yet
- Single Phase C LLDR Ifi Controlled RectifierDocument21 pagesSingle Phase C LLDR Ifi Controlled RectifierTuhin ShahNo ratings yet
- POWER ELECTRONICS FORMULA SHEETDocument11 pagesPOWER ELECTRONICS FORMULA SHEETAzfar UmarNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Full Wave Ac Voltage ControllerDocument20 pagesSingle Phase Full Wave Ac Voltage ControllerNurindah Atika86% (22)
- 3 Phase Full Wave Bridge ConverterDocument55 pages3 Phase Full Wave Bridge ConvertersubhasishpodderNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy Generation Electrical Energy GenerationDocument10 pagesElectrical Energy Generation Electrical Energy GenerationKadhane NavnathNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document21 pagesModule 2Anandu DipukumarNo ratings yet
- CH.4 Full-wave and Three-phase Rectifiers for AC to DC ConversionDocument55 pagesCH.4 Full-wave and Three-phase Rectifiers for AC to DC ConversionImran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - AC TO DC CONVERTER (Student Updated)Document60 pagesCHAPTER 2 - AC TO DC CONVERTER (Student Updated)Ct KhatijahNo ratings yet
- AC-AC Controllers: EE307 - Power Electronics Spring 2019Document22 pagesAC-AC Controllers: EE307 - Power Electronics Spring 2019Abdullah NasirNo ratings yet
- CukonverterDocument30 pagesCukonverterPowersavvyNo ratings yet
- 10 InvertersDocument136 pages10 InverterszapzahtNo ratings yet
- MSC Rectifier CorrectedDocument53 pagesMSC Rectifier CorrectedashammoudaNo ratings yet
- Diode Rectifier Performance ParametersDocument30 pagesDiode Rectifier Performance ParametersنورالغامديNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Differential AmplifiersDocument21 pagesLecture 4 Differential Amplifierstranhieu_hcmutNo ratings yet
- AC to AC Converters Classification Includes Voltage Controllers Power CircuitsDocument26 pagesAC to AC Converters Classification Includes Voltage Controllers Power Circuitsherokaboss1987No ratings yet
- UNIT II - PE - Control - 1PFWRectifiers PDFDocument24 pagesUNIT II - PE - Control - 1PFWRectifiers PDFramaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Rectifier DiodesDocument31 pagesApplications of Rectifier DiodesBeatriz Fernández NicolásNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Half Bridge InverterDocument29 pagesSingle Phase Half Bridge InverterGnanaseharan Arunachalam100% (1)
- Power Electronics 1: ENEL371S2Document30 pagesPower Electronics 1: ENEL371S2bpd21No ratings yet
- BEE Small Signl ModelDocument13 pagesBEE Small Signl ModelalysonmicheaalaNo ratings yet
- Single-phase half-bridge inverter operational details and analysisDocument31 pagesSingle-phase half-bridge inverter operational details and analysistintuvrNo ratings yet
- PE Lecture 9Document24 pagesPE Lecture 9ahmed el-sayedNo ratings yet
- PE Lecture 9 TotDocument43 pagesPE Lecture 9 Totahmed el-sayedNo ratings yet
- EEE 447 Power Electronics Chapter on InvertersDocument45 pagesEEE 447 Power Electronics Chapter on InvertersMd. Anisur RahmanNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1: Linear Wave ShapingDocument24 pagesUNIT-1: Linear Wave Shapingmahender1987No ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Halfwave and Fullwave RectifiersDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 1: Halfwave and Fullwave RectifiersTonmoy RafiNo ratings yet
- DC AC ConverterDocument16 pagesDC AC ConverterPaikoNo ratings yet
- EEE424 InverterV2Document82 pagesEEE424 InverterV2M.Feridun HızNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers and Switched Mode Power Supply UnitDocument85 pagesRectifiers and Switched Mode Power Supply UnitVignesh MeyyappanNo ratings yet
- AC Voltage Controllers for Inductive LoadsDocument15 pagesAC Voltage Controllers for Inductive LoadsSumukha KumarNo ratings yet
- Week03 Diode CircuitDocument29 pagesWeek03 Diode CircuitEstika Vriscilla GintingNo ratings yet
- Concordia University Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument17 pagesConcordia University Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringghaffarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document41 pagesChapter 4Anil ParmarNo ratings yet
- AC Voltage Controller CircuitsDocument211 pagesAC Voltage Controller CircuitsTran Binh DuongNo ratings yet
- A Unified Model For The ZVS DC-DC Converters With Active ClampDocument31 pagesA Unified Model For The ZVS DC-DC Converters With Active ClampTirthankar MohantyNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- CFP Ceit15 PDFDocument2 pagesCFP Ceit15 PDFNoureddine BounaslaNo ratings yet
- موقع تحميل الكتابDocument1 pageموقع تحميل الكتابNoureddine BounaslaNo ratings yet
- Article CERE 2013 PDFDocument6 pagesArticle CERE 2013 PDFNoureddine BounaslaNo ratings yet
- 6374 14655 1 PB PDFDocument11 pages6374 14655 1 PB PDFNoureddine BounaslaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning A Ten-Step GuideDocument14 pagesStrategic Planning A Ten-Step Guideearl58100% (1)
- 13 PisanoDocument124 pages13 PisanoNoureddine BounaslaNo ratings yet
- An Improved Efficiency of Fuzzy Sliding Mode Cont PDFDocument5 pagesAn Improved Efficiency of Fuzzy Sliding Mode Cont PDFNoureddine BounaslaNo ratings yet
- IATS'11 Sliding Mode Control of DC-DC Buck-Boost ConverterDocument6 pagesIATS'11 Sliding Mode Control of DC-DC Buck-Boost Converterrkp369No ratings yet
- Algerian passport and ID card application formDocument2 pagesAlgerian passport and ID card application formNoureddine BounaslaNo ratings yet
- (FLUX2D76) FLUX2D To Simulink Technology Technical PaperDocument54 pages(FLUX2D76) FLUX2D To Simulink Technology Technical PaperovidiudabijaNo ratings yet
- 111111111111111Document6 pages111111111111111Noureddine BounaslaNo ratings yet
- Flux 2D TutorialDocument42 pagesFlux 2D Tutorialboldogsz88No ratings yet
- 123 Paper V MihovDocument6 pages123 Paper V MihovNoureddine BounaslaNo ratings yet
- Flux enDocument2 pagesFlux enNoureddine BounaslaNo ratings yet
- Level-2 MATLAB S-FunctionsDocument21 pagesLevel-2 MATLAB S-FunctionsaryamasNo ratings yet
- 1WCE2009 pp435-440Document6 pages1WCE2009 pp435-440Noureddine BounaslaNo ratings yet