Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Economics - ppt1
Uploaded by
Akshay HemanthOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Economics - ppt1
Uploaded by
Akshay HemanthCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS
AIMS & OBJECTIVES
After studying this lesson you should be able to understand
What is economics? Concepts like scarcity & efficiency microeconomics Vs macroeconomics
Basic problems of an economic organization
Economic systems Societys technological possibilities Economics & managerial decision making
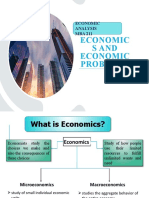
WHAT IS ECONOMICS?
It is the study of how societies use scarce resources to produce valuable goods and services and distributes them among different individuals
SCARCITY & EFFICIENCY
Two key ideas that run through all of economics: that goods are scarce & that society must use its resources efficiently.
Scarcity of goods refer to a situation in which goods are limited relative to desires Efficiency denotes the most effective use of a societys resources in satisfying peoples wants & needs. Economic efficiency requires that an economy produce the highest combination of quantity & quality of goods & services given its technology & scarce resources
MICROECONOMICS & MACROECONOMICS
Economics is divided into two major subfields
Microeconomics concerned with the behaviour of individual entities such as households, firms & markets. Adam Smith (The Wealth of Nations, 1776) is considered the founder Macroeconomics concerned with the overall performance of the economy. John Maynard Keynes (General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money, 1936) is considered the founder of modern macroeconomics.
Note: the present course discusses microeconomics with focus on Firms, Markets & their behaviour
THE THREE PROBLEMS OF ECONOMIC
ORGANIZATION
Three fundamental economic problems of an economy are:
What commodities are produced and in what quantities? How are goods produced? For whom goods are produced? The answers to these questions vary according to the type of economic system that is in place in a given country.
ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
Economic systems: Different societies are organized through different economic systems and that organization determines the ways the three fundamentals questions are answered. The two fundamentally different economic systems are: Market economy one in which individuals & private firms make the major decisions about production and consumption. A system of prices, of markets, of profits and losses, of incentives & rewards determine the answer to the 3 fundamental questions Command economy one in which the government makes all important decisions about production & distribution
Note:
Extreme form of market economy is laissez-faire economy Most economics of the world are mixed economies
7
SOCIETYS TECHNOLOGICAL POSSIBILITIES
Problem facing a society is: given a stock of limited resources (labour, technical knowledge, tools & machinery, land etc), the society has to decide how to allocate these limited resources among thousands of different possible commodities & services To summarize: given resources are scarce relative to wants, an economy must choose among different potential bundle of goods (the what), select from different techniques of production (the how) and decide in the end who will consume the goods ( the for whom) Given this problem facing the economy two concepts are very important: Inputs commodities or services used to produce goods & services. Also called factors of production Outputs various useful goods or services that result from the production process & are either consumed or used for further production
THE PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY FRONTIER (PPF)
PPF shows the maximum quantity of goods that can be efficiently produced by an economy, given its technological knowledge and quantity of available inputs. Economic growth shifts the PPF outward
PPF & OPPORTUNITY COST
In a world of scarcity, choosing one thing means giving up something else. The opportunity cost of a decision is the value of the good or service foregone. This is a very important concept in economics As we move up the PPF, good X is given up to have additional quantities of Y. The opportunity cost of producing additional Y is the amount of X foregone.
10
HOW IS ECONOMICS USEFUL IN MANAGERIAL DECISION MAKING?
Evaluating Choice Alternatives Identify ways to efficiently achieve goals. Specify pricing and production strategies. Provide production and marketing rules to help maximize net profits.
Making the Best Decision
Economics, in particular managerial economics, can be used to efficiently meet management objectives. Economics, in particular managerial economics, can be used to understand logic of company, consumer, and government decisions.
11
12
13
You might also like
- Lesson 01 Principles of Economics Handout 1Document42 pagesLesson 01 Principles of Economics Handout 1seyon sithamparanathanNo ratings yet
- Economics: The Study of How Scarce, or Limited, Resources Are Used To Satisfy People's Unlimited Material Wants and NeedsDocument15 pagesEconomics: The Study of How Scarce, or Limited, Resources Are Used To Satisfy People's Unlimited Material Wants and NeedsNIKNISHNo ratings yet
- What Is Economics?: Unit - I 2 MarksDocument4 pagesWhat Is Economics?: Unit - I 2 MarkssaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Basic Economics 1Document6 pagesLecture Notes - Basic Economics 1lei_sangabrielNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics 1Document36 pagesPrinciples of Economics 1reda gadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1& 2Document24 pagesChapter 1& 2Michael GezahegnNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 DhdeecdgdvDocument6 pagesChapter-2 DhdeecdgdvVipin SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Scrib EconomyDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 Scrib EconomysuccessseakerNo ratings yet
- A. A. The Twin Themes of Economics: Scarcity and EfficiencyDocument19 pagesA. A. The Twin Themes of Economics: Scarcity and EfficiencyIrenej Krayewsky100% (1)
- Lesson 2 - Applied EconomicsDocument5 pagesLesson 2 - Applied EconomicsShanna Cielo Jean BerondoNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument36 pagesEconomicsAbdataNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics: Module No. 2: Week 2: First QuarterDocument8 pagesApplied Economics: Module No. 2: Week 2: First QuarterGellegani, JuliusNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Ppt. Chapter 1Document21 pagesMicroeconomics Ppt. Chapter 1Kim Gomez100% (5)
- Central Concepts of EconomicsDocument21 pagesCentral Concepts of EconomicsREHANRAJNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info CXC Economics Study Guide PRDocument31 pagesToaz - Info CXC Economics Study Guide PRRickoy Playz100% (1)
- Introduction To Economics,: A Class Note On Complied by Bindu Raj KhanalDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Economics,: A Class Note On Complied by Bindu Raj KhanalkashishNo ratings yet
- Econ 1-Lesson 1 ModuleDocument9 pagesEcon 1-Lesson 1 ModuleArnie Jovinille Sablay RemullaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics: Prof. Swaha ShomeDocument33 pagesManagerial Economics: Prof. Swaha ShomeGaurav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- The Economic Problem: Industrial RevolutionDocument16 pagesThe Economic Problem: Industrial RevolutionhenniekNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Utility and Application of Applied EconomicsDocument23 pagesWeek 2 - Utility and Application of Applied EconomicsChristopher DacatimbanNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis and Policies: AssignmentDocument8 pagesEconomic Analysis and Policies: AssignmentMuhammad Shahzad IjazNo ratings yet
- Economics Grade 11 Lesson Note 2Document10 pagesEconomics Grade 11 Lesson Note 2Eyerusalem solomonNo ratings yet
- 1.intro Engg EcoDocument26 pages1.intro Engg EcoadroitdexterNo ratings yet
- Productivity 1 2Document74 pagesProductivity 1 2sasi tsk 24No ratings yet
- Basic MicroeconomicsDocument219 pagesBasic Microeconomicsloc dinhNo ratings yet
- Micro 111 C1 by NayemDocument10 pagesMicro 111 C1 by NayemHasibul Hasan NayemNo ratings yet
- Economics&Economic ProblemsDocument22 pagesEconomics&Economic ProblemsRhocel TolenadaNo ratings yet
- Material No. 1Document18 pagesMaterial No. 1rhbqztqbzyNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Review QuestionDocument2 pagesModule 1 - Review QuestionJC AbelloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Economic Issues and ConceptsDocument87 pagesLecture 1 - Economic Issues and ConceptsB-ton LimbeNo ratings yet
- Eco Term PaperDocument27 pagesEco Term PaperKalyaniNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument182 pagesManagerial Economicsmurali_aNo ratings yet
- The Essence of EconomicsDocument16 pagesThe Essence of EconomicsPatNo ratings yet
- Scarce ResourcesDocument6 pagesScarce ResourcesAta U SAmadNo ratings yet
- Introd To Econ CH 1 Lecture 2Document53 pagesIntrod To Econ CH 1 Lecture 2Heni GirmaNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics: Module No. 2: Week 2: First QuarterDocument7 pagesApplied Economics: Module No. 2: Week 2: First QuarterhiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document9 pagesAssignment 2vaibhavi mirajkarNo ratings yet
- Economic System (Assignment 1)Document8 pagesEconomic System (Assignment 1)tasfia12100% (1)
- Applied Economics Senior High SchoolDocument7 pagesApplied Economics Senior High SchoolNicolette SaangNo ratings yet
- Principles of Microeconomics: ECO 101: The Central Concepts of EconomicsDocument20 pagesPrinciples of Microeconomics: ECO 101: The Central Concepts of EconomicsCyber Hunter GamersNo ratings yet
- Allocation of Resources: 1) What To Produce?Document4 pagesAllocation of Resources: 1) What To Produce?mohamed sobahNo ratings yet
- Exm 12975Document17 pagesExm 12975Pavan Jp100% (3)
- Unit-1 Economics For EngineersDocument21 pagesUnit-1 Economics For EngineersShubham JhaNo ratings yet
- Principles of EconomicsDocument13 pagesPrinciples of EconomicsTaher KagalwalaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Economics Class 12 NotesDocument73 pagesNCERT Economics Class 12 NotesPrachi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Economic System - ECONOMICSDocument24 pagesChapter 2 - Economic System - ECONOMICSJUAN PAULO ICAWATNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics: Introduction-For ABM-12 Rembrandt 10:30-11:30 - Oct 2020Document21 pagesApplied Economics: Introduction-For ABM-12 Rembrandt 10:30-11:30 - Oct 2020Arjae Dantes100% (2)
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1tiffada86No ratings yet
- An Inquiry Into The Nature and Causes of The Wealth of NationsDocument16 pagesAn Inquiry Into The Nature and Causes of The Wealth of NationsNahrozNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Roadmap For EconomicsDocument17 pagesChapter One: Roadmap For EconomicsManjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument0 pagesIntroductionramanagpalNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To EconomicsDocument24 pages1 Introduction To Economicsrommel legaspiNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Notes:: Week 1 - Introduction To EconomicsDocument42 pagesMicroeconomics Notes:: Week 1 - Introduction To EconomicsGeleta TuluNo ratings yet
- Economics NotesDocument60 pagesEconomics Notesyigermalamanuel32100% (1)
- EconomicsDocument24 pagesEconomicsshahidNo ratings yet
- 3566 Micro EconomicsDocument60 pages3566 Micro EconomicsPirya HussainNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "Economics, Principles And Applications" By Mochón & Becker: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "Economics, Principles And Applications" By Mochón & Becker: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Roduction Usiness OrganizationDocument24 pagesRoduction Usiness OrganizationAkshay HemanthNo ratings yet
- Demand & Supply - ppt2Document59 pagesDemand & Supply - ppt2Akshay Hemanth100% (1)
- Keac 108Document52 pagesKeac 108Ias Aspirant AbhiNo ratings yet
- Trial BalanceDocument46 pagesTrial BalanceChetan MetkarNo ratings yet
- Ncert Fm-Ac-xi Chapter 7Document52 pagesNcert Fm-Ac-xi Chapter 7shaannivasNo ratings yet
- Keac 103Document50 pagesKeac 103Akshay Hemanth0% (1)
- Ncert Fm-Ac-xi Chapter 4Document59 pagesNcert Fm-Ac-xi Chapter 4shaannivasNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts of Finance: Understanding RiskDocument2 pagesKey Concepts of Finance: Understanding RiskAkshay HemanthNo ratings yet
- SDDDDDDocument106 pagesSDDDDDAkshay HemanthNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts of Finance: Understanding MoneyDocument4 pagesKey Concepts of Finance: Understanding MoneyAkshay HemanthNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Management at Icici Bank: Akshay Hemanth A023Document30 pagesKnowledge Management at Icici Bank: Akshay Hemanth A023Akshay HemanthNo ratings yet
- ACYFMG1 Unit IV Formula (2022.04.04)Document5 pagesACYFMG1 Unit IV Formula (2022.04.04)KRABBYPATTY PHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: International Financial Markets Book: Madura, Jeff. International Financial Management, India Edition, 2008 South-WesternDocument2 pagesChapter 3: International Financial Markets Book: Madura, Jeff. International Financial Management, India Edition, 2008 South-WesternChristian PiguerraNo ratings yet
- Egypt Country Risk: Executive SummaryDocument6 pagesEgypt Country Risk: Executive SummarySawa SportNo ratings yet
- Church FellowshipDocument2 pagesChurch FellowshipBalachandran. DNo ratings yet
- Your Insurance Firm ProcessesDocument1 pageYour Insurance Firm ProcessesrogealynNo ratings yet
- A. Jackie Chan Leasing Signs An Equipment Lease Contract With Chris Tucker On January 1Document2 pagesA. Jackie Chan Leasing Signs An Equipment Lease Contract With Chris Tucker On January 1Avox EverdeenNo ratings yet
- Sub Order LabelsDocument26 pagesSub Order LabelsfonemNo ratings yet
- Khin Kyawt Kyawt Phyu (Final) PDFDocument18 pagesKhin Kyawt Kyawt Phyu (Final) PDFKyaw Thu KoNo ratings yet
- Hamachandru S Infosys Technologies Limited, Hyderabad: Name CompanyDocument6 pagesHamachandru S Infosys Technologies Limited, Hyderabad: Name CompanyreenajoseNo ratings yet
- Role of Government in Economic PolicyDocument22 pagesRole of Government in Economic PolicyMiss PauNo ratings yet
- Sr. No Subject NoDocument5 pagesSr. No Subject NoKailash Chandra Pradhan0% (1)
- IT77 Registration As A Taxpayer 2013Document5 pagesIT77 Registration As A Taxpayer 2013BunnyCoder1No ratings yet
- Battle of StakesDocument22 pagesBattle of StakesNandini ChandraNo ratings yet
- The Times They Are Not Changin': Days and Hours of Work in Old and New Worlds, 1870-2000Document30 pagesThe Times They Are Not Changin': Days and Hours of Work in Old and New Worlds, 1870-2000StefanoNo ratings yet
- MMT of Foreign ExchangeDocument15 pagesMMT of Foreign ExchangeParul AsthanaNo ratings yet
- Site Report Check ListDocument4 pagesSite Report Check ListShureendran Muniandy RajanNo ratings yet
- Desig A Fabricatio of Rice DehullerDocument4 pagesDesig A Fabricatio of Rice DehullerNAJJEMBA WINNIFREDNo ratings yet
- Transforming Nigerian Informal Settlementsinto Liveable CommunitiesDocument43 pagesTransforming Nigerian Informal Settlementsinto Liveable CommunitiesAngelo NgoveneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chapter 7Document22 pagesChapter 1 Chapter 7Nica MontevirgenNo ratings yet
- Janosch Sbeih (2014) - New Economic Cultures in Spain and GreeceDocument73 pagesJanosch Sbeih (2014) - New Economic Cultures in Spain and GreeceJanosch Kamal100% (1)
- Week 1 Introduction (Ses 23 - 24)Document18 pagesWeek 1 Introduction (Ses 23 - 24)23004245No ratings yet
- IB Economics IA SampleDocument26 pagesIB Economics IA SampleYeşim Eylül ÇimenciNo ratings yet
- CIRPASS PresentationDocument9 pagesCIRPASS PresentationGustavo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Committee/Commission Head ObjectiveDocument5 pagesCommittee/Commission Head ObjectiveadmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 PPT - Holthausen & Zmijewski 2019Document96 pagesChapter 13 PPT - Holthausen & Zmijewski 2019royNo ratings yet
- SLD BulukandangDocument1 pageSLD BulukandangirfanNo ratings yet
- Lét S N 6: Effective Effective Qualified Smoothly Quietly FastDocument6 pagesLét S N 6: Effective Effective Qualified Smoothly Quietly FastTrịnh Bảo MinhNo ratings yet
- IB Economics: International Economics CommentaryDocument8 pagesIB Economics: International Economics CommentaryMomina Amjad94% (16)
- Company Stats EuropeDocument375 pagesCompany Stats Europesourabh6chakrabort-1No ratings yet
- Ek 1999 53-4-01 PDFDocument29 pagesEk 1999 53-4-01 PDFCansel CakinNo ratings yet